The smallest sugars are
aldoses or ketose
Monosaccharides cyclize to form
alpha or beta anomers
The derivatives of monosaccharides include
aldonic acids, uronic acids, alditols, deoxy sugars, and amino acids
What links monosaccharides to other molecules?
glycosidic bonds
Monosaccharides are ______ from smaller precursors that are derived from _______ by photosynthesis
synthesized, CO2 and H2O
Carbohydrates are classified into three groups:
Monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides
Monosaccharides are not broken down into
simple sugars under mild conditions
Oligosaccharides usually have
2 to 10 simple sugar residues
Polysaccharides are
polymers of simple sugars
What functional groups do Aldose and ketone have in common?
An aldehyde and ketone functional group
Examples of chiral monosaccharides:
-Aldose with 3 or more carbon atoms
- Ketone with 4 or more carbon atoms
How do you know if it has a D or L configuration?
look at the highest-numbered chiral center
what structure does Gram-negative have?
two membranes with a thin peptidoglycan shell
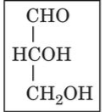
D-glyceraldehyde

D-ribose
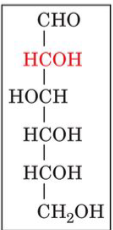
D-glucose
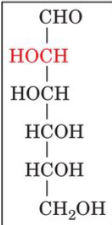
D-mannose
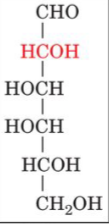
D-galactose
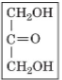
dihydroxyacetone
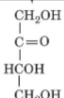
D-Erythrulose
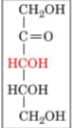
D-ribulose
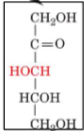
D-Xylulose
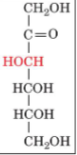
D-fructose
What configuration predominates in nature?
D-sugars
Starch and glycogen are (homopolysaccharides) and their job is
storage of molecules
Isomers that have opposite configuration at one or more chiral centers but not mirror images are
diastereomers
Sugars that differ only by one chiral center are
epimers
Pyranose (6-membered ring)
cyclic form of glucose
Furanose (5-membered ring)
cyclic form of fructose
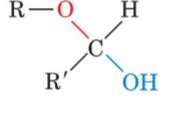
Glucose(an aldose) can cyclize for form a
cyclic hemiacetal
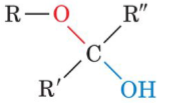
Fructose (a ketone) can cyclize to form
cyclic hemiketal
When hemiacetals and hemiketals are formed, the carbonyl atoms becomes a
new asymmetric center
When OH bond on carbon 1 if down it's
alpha
When OH bond on carbon 1 if up it's
beta
Isomers of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration in the asymmetric carbon are called
anomers
Sugar alcohols are formed by
mild reduction of sugars
Sugar esters phosphate esters are important for
energy like ATP
Disaccharides are the simplest oligosaccharides with
2 monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bond
Each unit in an oligosaccharide is termed as a
residue
reducing sugar can open to
linear form and undergo reduction
Sucrose is not a reducing sugar because
it doesn't have a free anomeric carbon
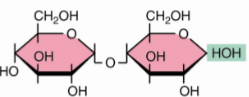
Maltose α(1→4)
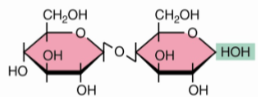
Cellobiose β(1→4)
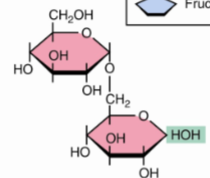
Isomaltoseα(1→6)
Are composed of the vitreous humor of the eye and is the lubricant fluid for joints
Hyaluronates
A polysaccharide made up of different monosaccharides
heteropolysaccharide
Starch and glycogen are (homopolysaccharides) and their job is
storage molecules
Chitin and cellulose are (homopolysaccharides) and they are
structural molecules
cell surface polysaccharides' job is
recognition of molecules (hetero)
Starch has 2 forms
amylose and amylopectin
Amylose has a _____links, no branches and____reducing end
α(1→4), one
Amylopectin branches are______ every 12-30 residues, ____reducing end
α(1→6), one
Amylose has poor solubility in water and has a
helical and hollow shape
Iodine can fit into the hydrophobic middle of
amylose
the more branches, the more sites for
phosphorylase to release glucose 1-P
glycogen is the glucose (energy) storage device in
animals
Glycogen has____ backbone, ____branches every 8-12 branches
α(1→4), α(1→6)
When iodine is added to glycogen,
it becomes a red-violet color
Dextrans formed by bacteria are components of
dental plaque
Amylose prefers a____ conformation due to its bent α(1→4) linkages
helical
Cellulose with beta(1→4) linkages can adopt an ____ conformation
extended
Is a structural polysaccharide, most abundant polymer, and found in plant cell walls
Cellulose
Cellulose has
Interchain and Intra chain H-bonds
Is found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans, insects, spiders, and fungi walls
chitin
Cellulose strand are
parallel
Chitin has both
antiparallel and parallel strands
Has repeating disacchairde with amino sugars and negative charge
glycosaminoglycans
Heparin has a very high negative charge and is a natural
anticogulant
Are found in tendons, cartilage, and connective tissues
chondroitin and keratan
Proteoglycans are large
glycosaminoglycan-containing proteins
Bacterial cell walls consists of glycan chains cross-linked by peptides
peptidoglycans
The oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to eukaryotic proteins play a role in protein structure and recognition
glycoproteins
N-linked carbohydrates are attached to side-chain amide nitrogen of
asparagine residues on glycoproteins
O-linked carbohydrates are attached to side chain hydroxyl groups of
serine residues on glycoproteins and proteoglycans
How do proteoglycans and glycoproteins differ?
proteoglycans have O-linked glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins have N-linked olgiosaccharides
Proteoglycans are components of
animal cells, membranes and glycocalyx
Proteoglycans are soluble protein components of the
extracellular matrix outside the cell membrane
Functions of proteoglycan
1. Modulation of cell growth
2. Cushioning in joints
Gram-positive has
one membrane with a thick peptidoglycan outer shell
Gram-negative has
two membranes with a thin peptidoglycan shell
Gram-negative cells have "hairy"
lipopolysaccharide
lipopolysaccharide consists of
lipid group joined to polysaccharide and create monosaccharide chain
The three types of N-linked glycoproteins:
high mannose, complex, and hybrid
Can alter chemical and physical properties of proteins, stabilize protein conformation, and cleave monosaccharide units from N-linked glycoproteins
oligosaccharides