What is cell turnover
the process of shedding/ replacing old cells with new ones, happens in the skin and bone marrow
What is ischemia
a less-than-normal amount of blood flow to part of your body
What are the functions of epithelium
- Regulate diffusion, absorption and secretions
- Cover the innner and outer layer of the organs
What are the bases we classify epithelial cells on
Based on:
- How many layers
- Cell shape
Where you can find simple squamous epithelial
Lungs, blood vessels and body cavities
Where can you find simple cuboidal cells
In kidney tubules
Where can you find simple columnar cells
In the stomach and gallbladder
Where can you find stratified squamous epithelial cells
Skin, esophagus
Where can you find stratified cuboidal epithelial cells
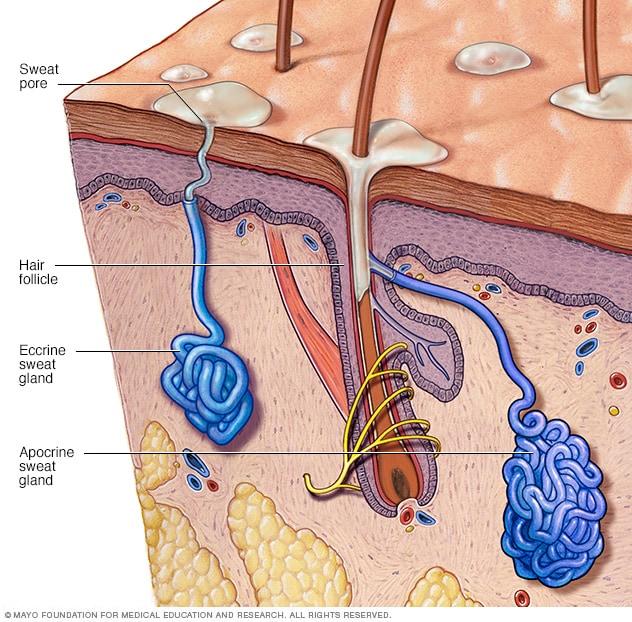
Sweat glands
Where can you find pseudostratified epithelial cells
Respiratory tracts
Where can you find transitional epithelial cells
Bladder
What are the specialisation of epithelium
- Microvilli
- Cilia
- Goblet cells
- Keratin
What are the types of connections in the epithelium
- Tight
- Adherens
- Desmosomes
- Gap
- Hemidesmosomes
What are tight junctions good for?
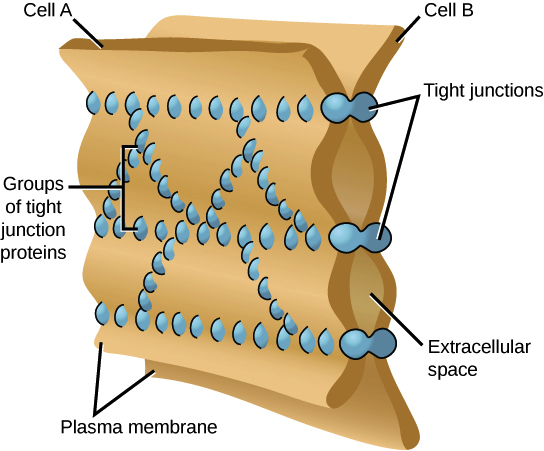
They're in the apical(surface level) and they're good to not allow leakage
What are adherent junctions made from
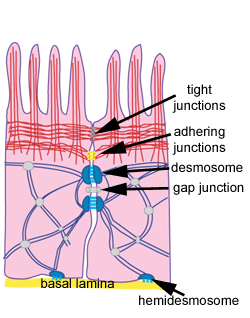
Actin filament
What are desmosomes made from
Intermediate filament
What are gap junctions used for
To transmit ions and soluble in water stuff for communication between cells
What are hemidesmosomes good for
Connection between the epithelial cell and basal membrane
What are the bases we categories epithelial glands on
Based on:
- If it secrets to tubes or blood vessels directly
- The shape of secretary regions
- Secretion mechanism
- Secretion type
What are the types of exocrine glands
- Simple
- Compound: branched ducts
Name examples of tubular secretory region epithelial glands

Sweat glands
Name examples of acinar(grape shaped) secretory region epithelial glands
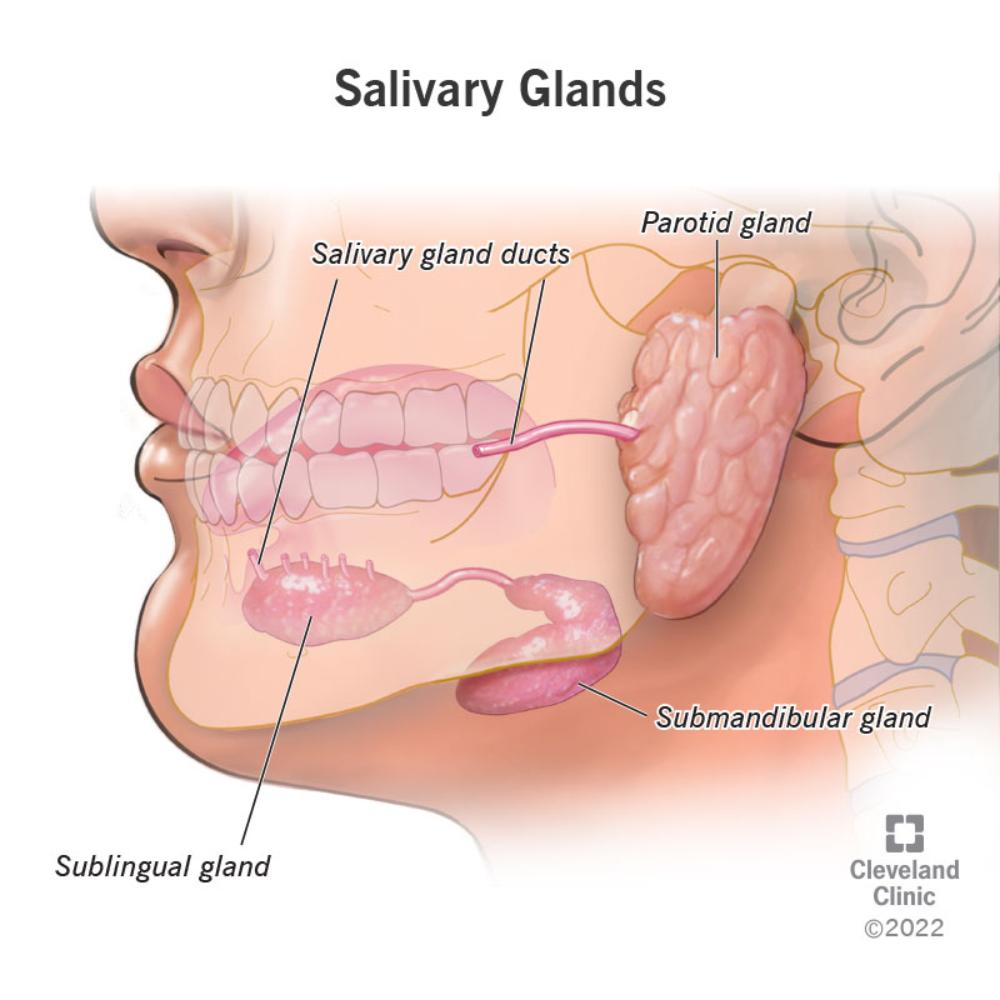
Salivary glands
Name the types of epithelial glands based on secretion mechanism
- Mecrocrine: by exocytosis(sending vesicles to outside the cell)
- Holocrine: the stuff are made in the cytoplasm, then the cell explodes causing the stuff to spill all over the place
- Apcrine: mix of both, which is rare
What are epithelial glands secretion types
- Serous
- Mucous
- Mixed
What are the biggest cells in the human body based on size
Skeletal muscle cells
Whats the job of the sino-atrial node
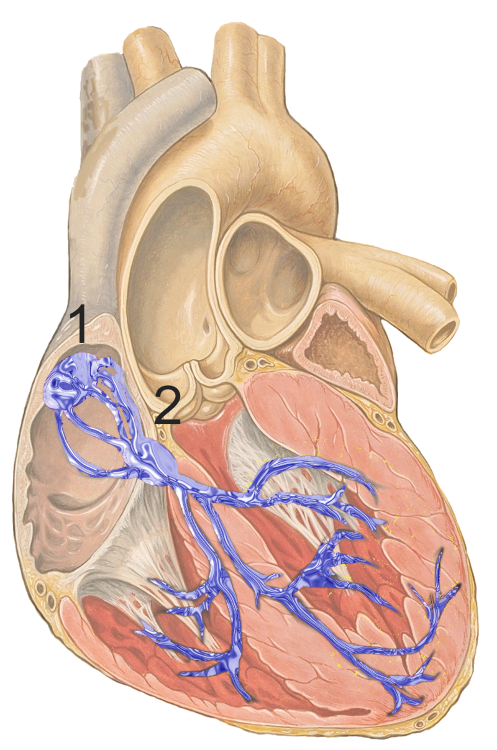
Its what controls the heart beating, signaling it to beat and regulates it like a peacmaker device would which is a device that balances the heart that beats too fast or too slow
How many nucleus does the cardiomyocytes have
One or two centrally located nucleus
How many junctions are in intercalated discs
Adherens, desmoses and gap junctions
Why do cardiac muscle seem straited
Because of how sarcomers are arranged
How long are cardiomyocytes
80-100 microns
How much is the diameter of cardiomyocytes
15 microns
Whats hypertrophy
Increasing in cardiac muscle size
Whats hypotrophy
Decreasing in cardiac muscle size
Whats the shape of smooth muscle cells
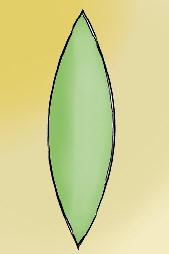
Spindle-shaped
What are the junctions in smooth muscle cells
Desmosomes and gap junctions
How are smooth muscles not strained but cardiac and skeletal are
Because smooth muscles lack sarcomers
Amongst muscle cells which one of them has an undeveloped sarcoplasmatic reticulum SR
Smooth muscle cells
Whats smooth muscle cells function in blood vessels
They contract to ecpel content
How is duration of smooth muscle contraction
Long, takes a long time
Which one of the muscles have the greatest generative capacity
Smooth muscles
Whats hyperplasia
Enlargement of an organ or a tissue by proliferation(quick increasing of number) of cells
How do smooth muscles regenerate
By Pericytes that are present in them that devide causing making new muscle cells