Why is protein degradation important?
It allows the cell to have a constant supply of amino acids and prevents the accumulation of abnormal proteins.
Short-lived proteins with a half-life with seconds and minutes are degraded by what pathway?
Cytosolic ATP dependent pathway
Cytosolic ATP dependent pathway is mediated by-
the proteosome
What is the function of the proteosome?
carries out hydrolytic cleavage
What degrades proteins with long half lives?
Lysosomes
What pathways can degrade proteins?
Cytosolic ATP dependent and Lysosomal
What is a lysosome?
membrane-enclosed organelle that contain the digestive enzymes: lipases, nucleases and proteases.
What is the function of a lysosome?
the digestive system of the cell, breaks down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign particles in the cell using digestive enzymes
What is the term for the cellular process that breaks down and recycles olf, damaged, or abnormal cell parts?
Autophagy
What is the process of autophagy?
a process where vesicles called autophagosomes engulf small amounts of cytoplasm or specific organelles using the endoplasmic reticulum
what occurs when vesicles fuse with lysosomes?
the release of the lysosomal hydrolytic enzymes causing degradation of macromolecules
LC3-I and LC3-II does what for autophagosomes
decides and regulates
When you have more LC3-II you will have more
autophagosomes
What is a autolysosome?
a compartment that is created when an autophagosome fuses with a lysosome
Lysosomes can selectivley degrade-
cytosolic proteins
The target proteins of lysosomes are usallly proteins with
long half lives
The function of dispensible proteins is -
to be sacrifies to make amino acids and energy to support basic metabolic reactions
The ATP dependent pathway involves the protein ______________
ubiquitin (highly conserved protein containing 76 amino acids)
What is the function of ubiquitin in the ATP dependent pathway?
it tags proteins that are destined for destruction via. a covalent attatchment
What are the mechanisms for recognition?
Half-life of proteins, recogition of phsophorylated substrates, recogition of ancillary porteins bound to the substrate, recogition of mutated abnormal protein.
The half-life of proteins correlates with what?
amino-terminal residue
Proteins with N-terminal Met, Ser, Ala, Thr, Val, or Gly have half lives greater than?
20 hours
Proteins with the N-terminal Phe, Leu, Asp, Lys, or Arg have half-lives of ?
3 mins or less.
Proteins rich in Pro (P), Glu (E), Ser (S), and Thr (T) are more ____________ degraded than other proteins
rapidly
Ubiquitin is ____________ linked to proteins through the ATP dependent pathway involving enzymes ___ , ____ , ____.
covalently, E1, E2, E3
Ubiquitination of proteins results in what?
the linking the carboxy-terminal glycine residue in ubiquitin to a lysine residue in the protein to be degraded
What is the function of the E1 enzyme?
acitivates ubiquitin, to bind to it
What is the function of the E2 enzyme?
conjugates ubiquitin
The function of E3 enzyme?
ubitquitin ligase, promotes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to the lysine residue of the protein recognized by the E3 as being slated for degradation.
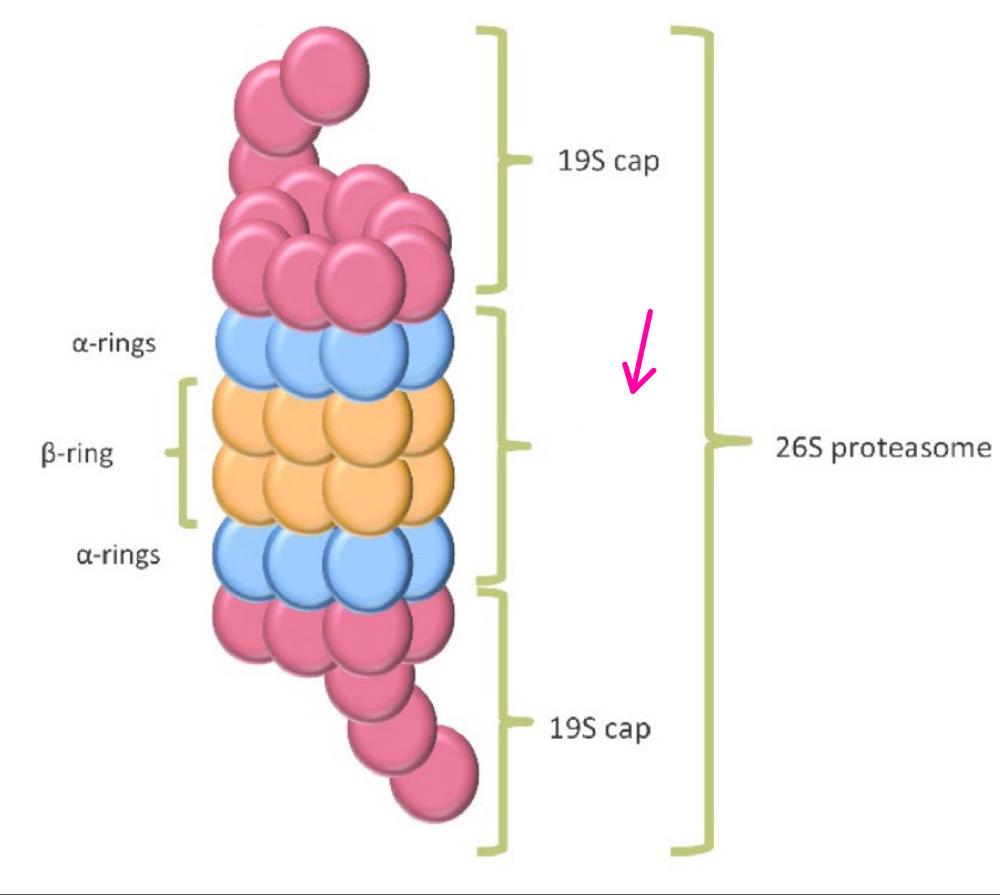
What is the 26S proteosome?
a large complex of proteins that structurally resembles a large cylinder that is covered on both ends.
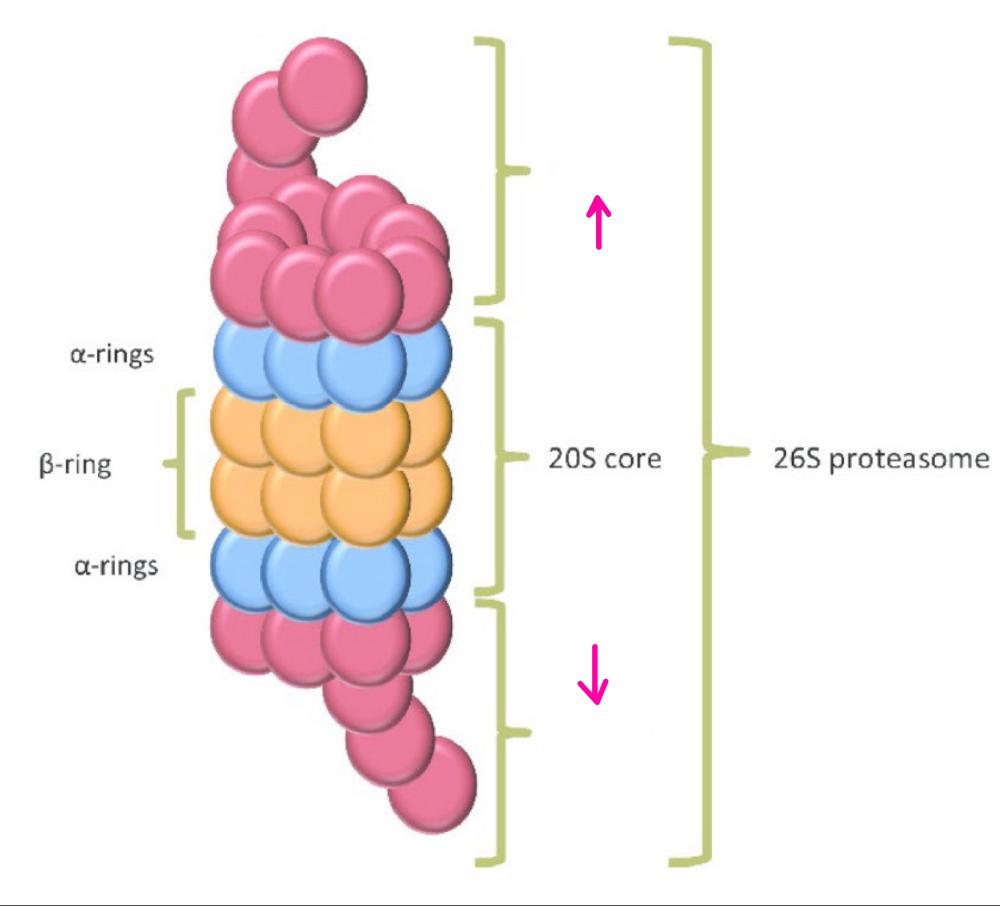
What is the central 20S core particle?
is a barrel shaped formed of 4 rings, outer rings formed of 7 alpha rings and inner rings formed of 7 beta rings
What part of the proteosome is this?
The central 20S core particle
What part(s) of the proteosome is this?
The 19S regulatory particle caps
Why are the 19S regulatory caps important?
they are important for recogition and binding of polyubiquinated proteins, removal of ubiquitin, unfolding of protein substrate, and translocation into the central core
How many ubiquitin are needed to be recoginzed by proteosome?
a minimum of 4
Degradation of proteins in the proteosomes are faciliated by ________ and hydrolyzed by ________
19S particles, central 20S core
What is bortezomib?
the 1st therapeutic proteosome inhibitor to be tested in humans.
What is the function of bortezomib?
a peptide that binds in the catalytic site of the 26S proteosome and inhibits the degradtionof proteins