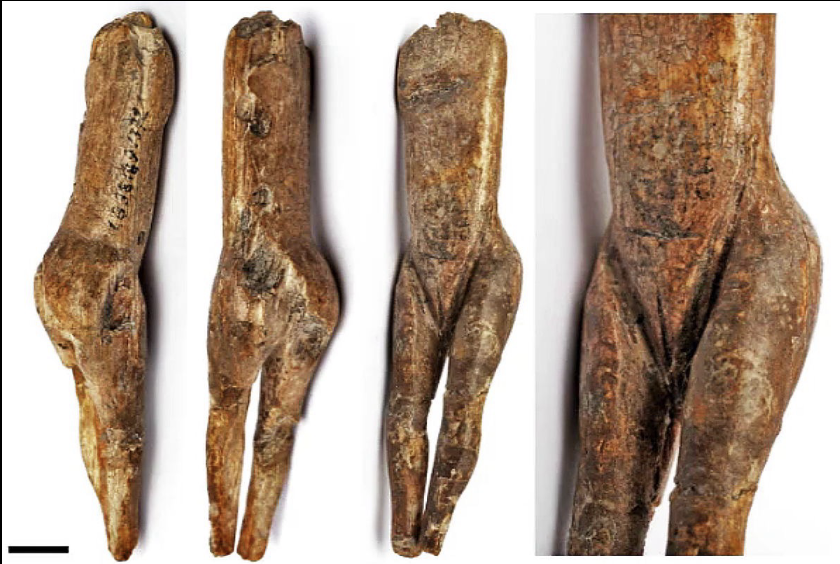

Vénus impudique
Paleolithic, ivory, 8 cm
first Venus figurine to be discovered (1834), impudique = immodest --> immodest venus
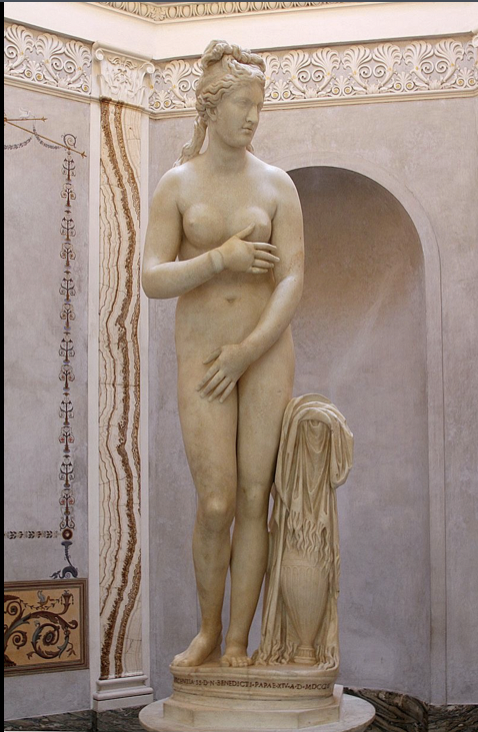

Capitoline Venus
Roman, marble, 193 cm
modest venus

Woman of Willendorf
Paleolithic (32,000 BCE), limestone and ochre, 11.1 cm
found in 1908
small so easily portable since art needed to move with the nomadic people
red (ochre) in pubic area = menstrual blood
emphasis on breasts and hips = figure of motherhood and ideal for abundance
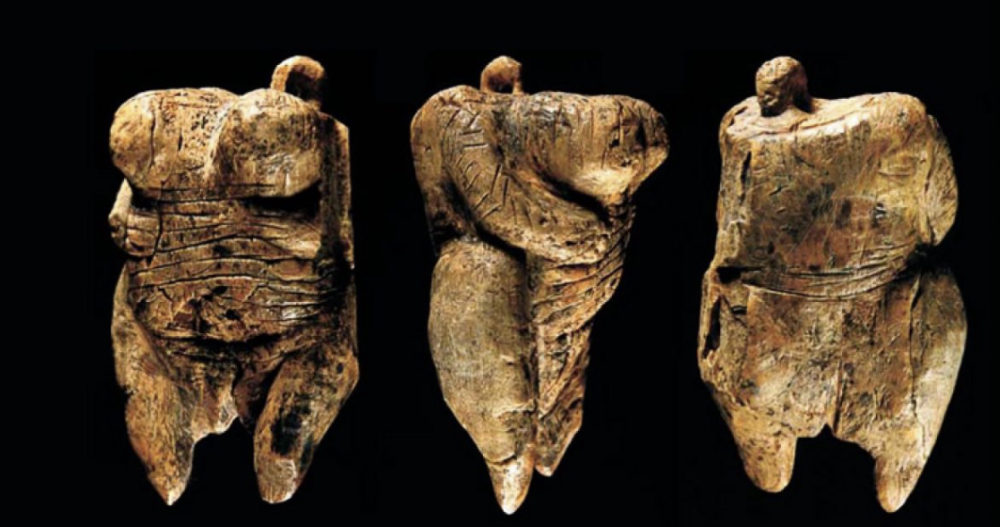

Venus of Hohle Fels
Paleolithic (40,000 - 35,000 BCE), ivory, 6.6 cm
no head, worn as a pendant so you become the head
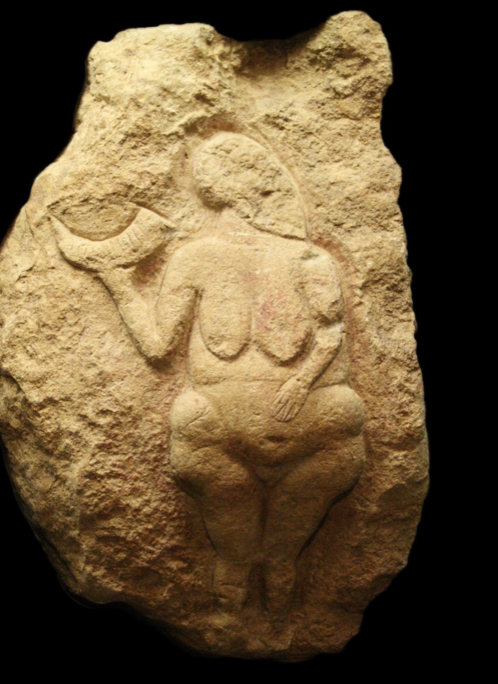

Venus of Laussel
Paleolithic (25,000 BCE), limestone bas-relief, 46 cm
right hand holding horn = crescent moon shape, left hand towards belly = fertility symbol
made to represent women being able to bear children AND keep them
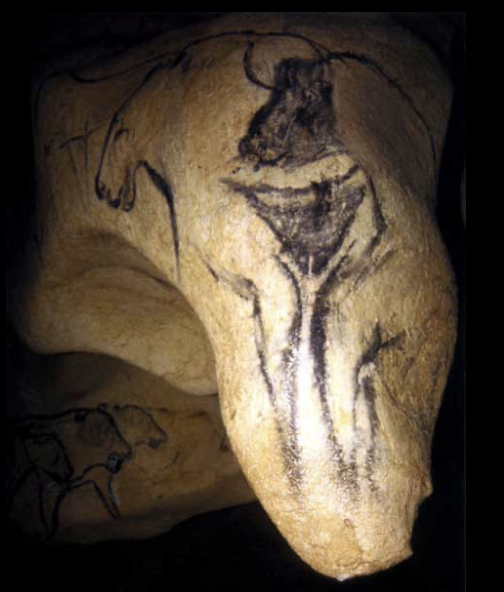
Partial Venus
Paleolithic (30,000 - 20,000 BCE), charcoal on limestone, Chauvet Cave
pubic region hybrodized creature (female)
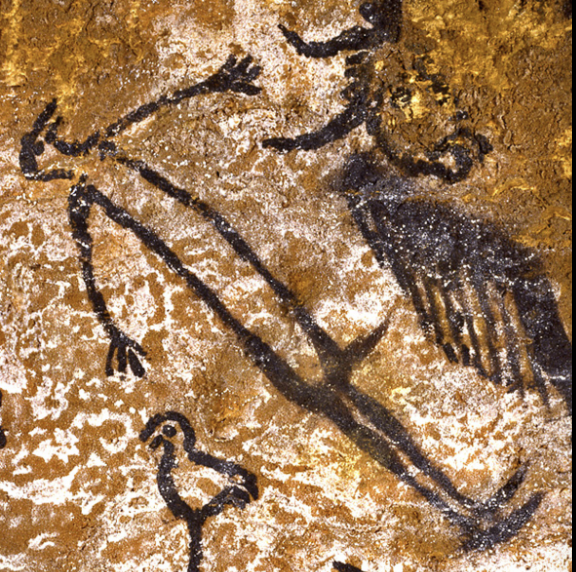

Birdman
Paleolithic (15,000 BCE), charcoal on limestone, Lascaux Cave
pubic region hybridized creature (male)
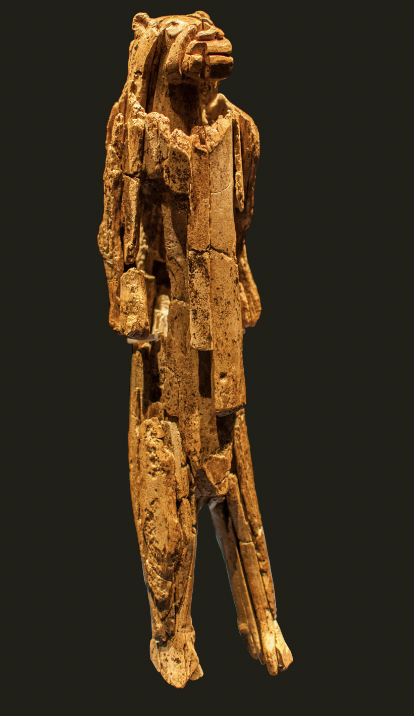

Lion-man of Hohlenstein-Stadel
Prehistoric (40,000 - 35,000 BCE), ivory, 31.1 cm
370 hours of labor, made from tusks like material, leans back more (in shape of tusk)
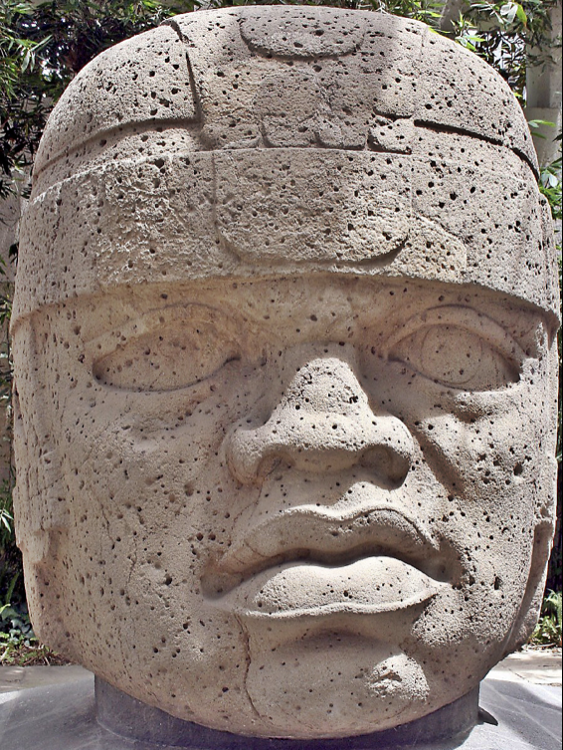

San Lorenzo Colossal Head 1
Olmec (neolithic), (1200 - 900 BCE), basalt, 25 tons
basalt 80 km away --> protocheifdome (able to make someone get the basalt from so far away and bring it back)
only heads, not bodies
stern / focused
broad noses --> jaguar like = apex predator
wear helmet for represent leaders / playing the ball game
if they were defaced, it was intentional
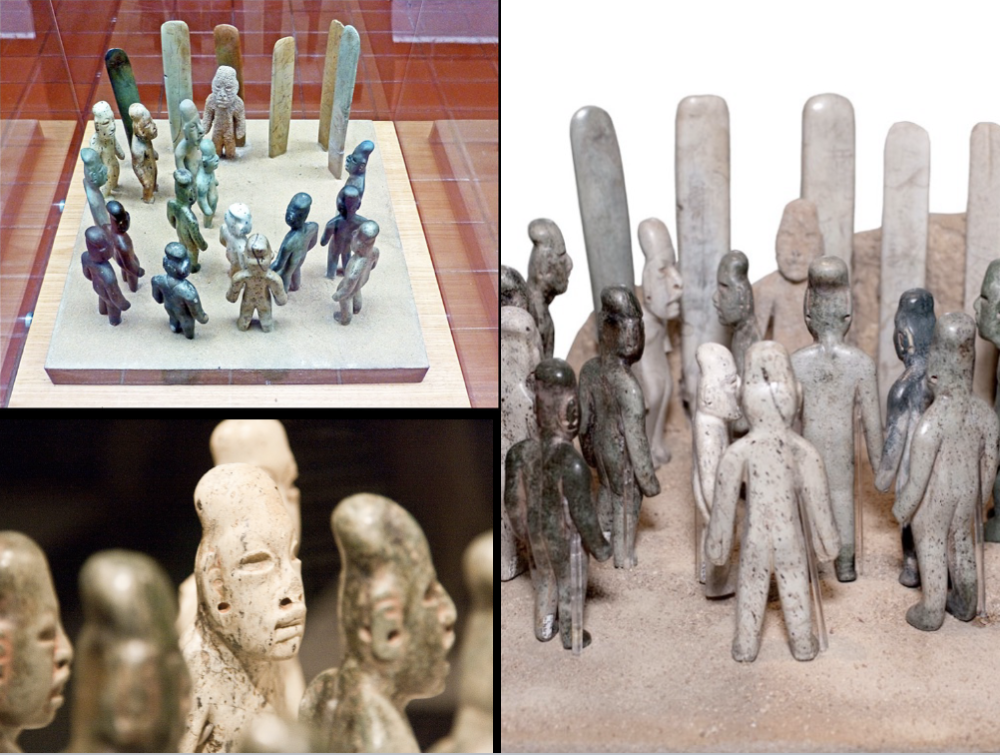

La Venta
Olmec (neolithic), (1200 - 400 BCE)
little figurines facing each other --> look like they are in a meeting (found like that)
elongated man / long man --> elongated heads and ear holds big
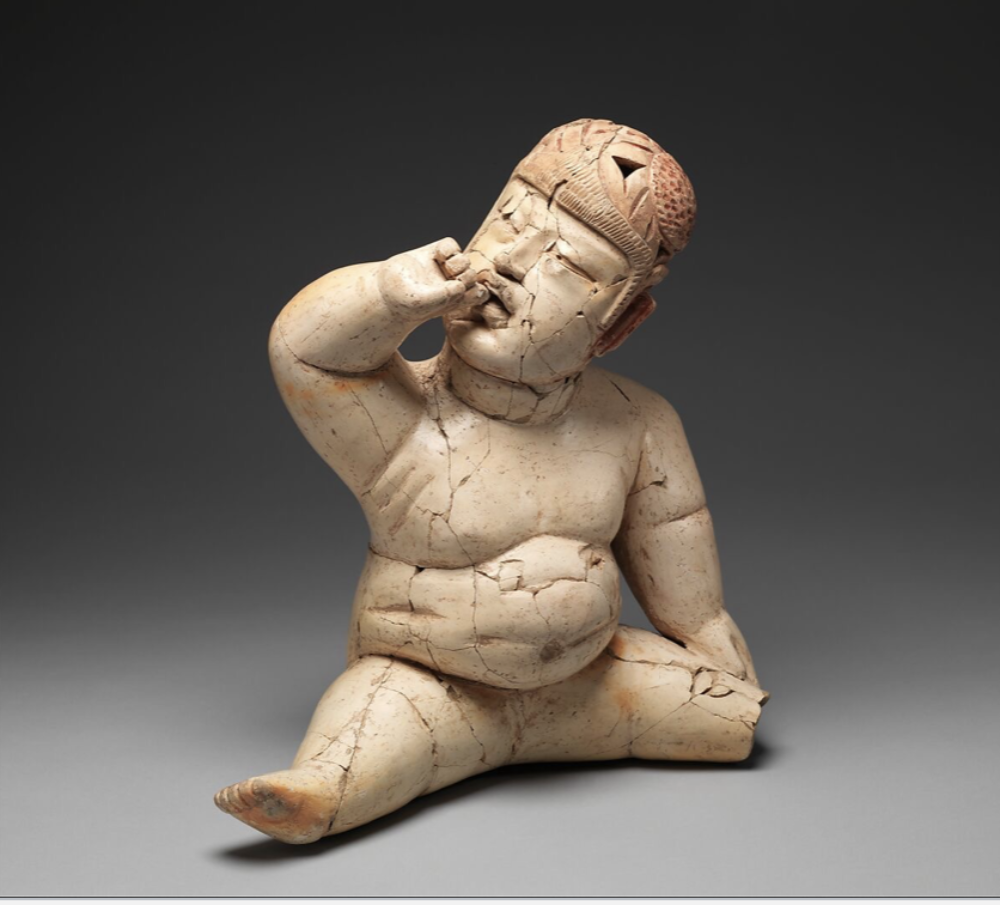

Seated Figure
olmec, (12th-9th cent. BCE), ceramic, cinnabar and red ochre
handbuilt
cinnabar has funerary symbolism
dressed for ball game --> will become a leader
helmet protect head
flat head in the back
wish for an ideal well-fed, healthy, wealthy, alive baby

El Manatí Wooden Busts
Olmec, (1200 BCE), wooden
long heads, flat noses, downturned mouth
newborn bones found within them
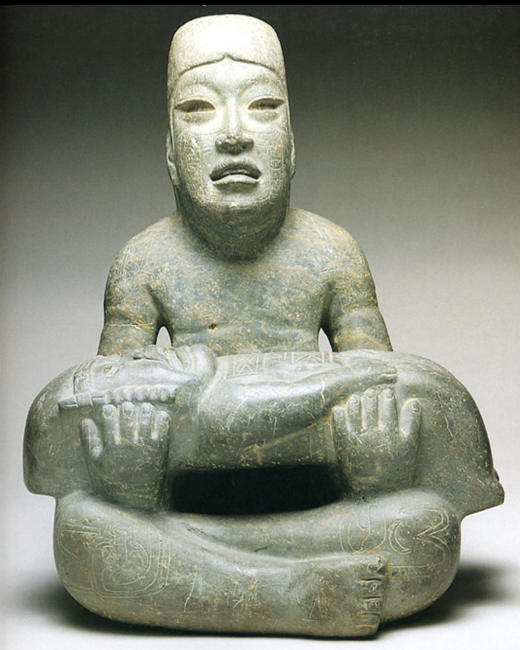

Seńor de Las Limas
Olmec, (1200 - 400 BCE), serpentine and pyrite
holding baby
represent olmec supernaturals
baby looks like jaguar or frog
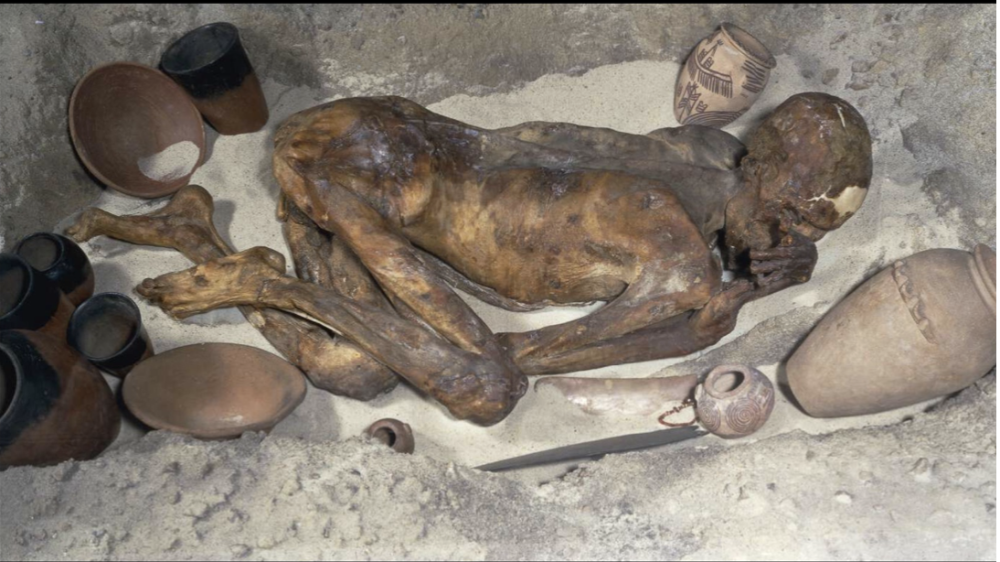
Human mummy
Egyptian, (3400 BCE), Gebelein cemetery
left shoulder facing west --> rest = realm of dead
fetal position = symbolically reborn
put into sand --> sand desecrates (dries out) body
body with pots, bowls, bracelet, cosmetic pallets so he can take this stuff into he after life with him
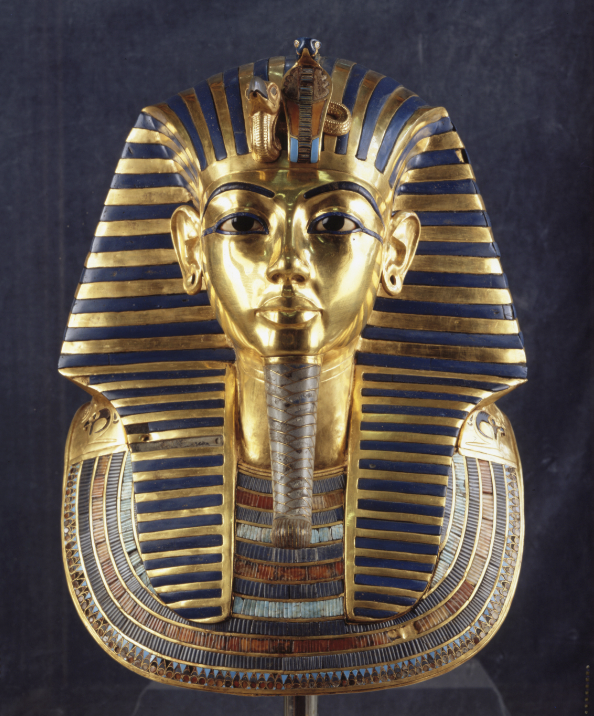

The Gold Mask of Tutankhamen
Egyptian, (1327 BCE), gold, lapis lazuli, carnelian, quartz, obsidian, turquoise, and colored glass, 28 lbs.
Egyptian museum, Cairo
most intact tomb there is
arms crossed = royalty
discovered on Nov 4, 1922
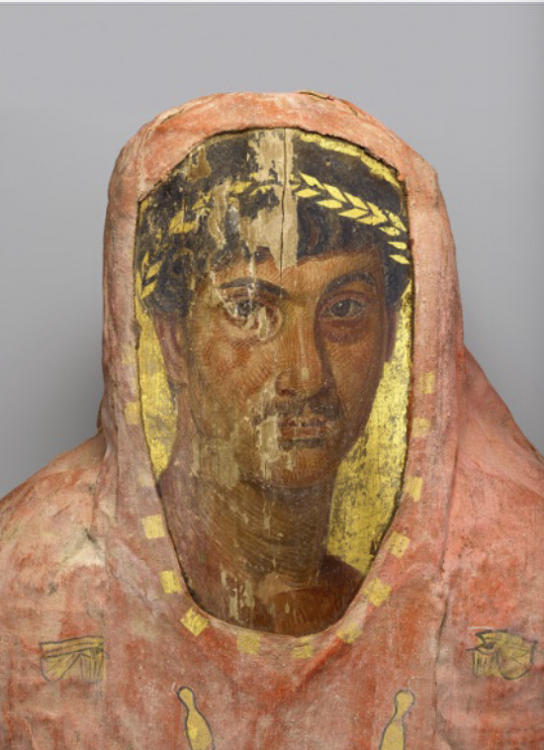

Mummy portrait
Egyptian, (80-100 CE), encaustic on limewood
painted on wood --> faces are curved
encaustic is hot wax ink, mimics human skin well, keeps woods and beeswax warm, looks 3-dimesional
tempura can be used but it is dries fast, hard to blend, difficult to work with and looks like a two-dimensional cartoon
portraits placed on tomb --> specifically for funerary not domesticity!!
realism --> emphasis on eyes, not happy nor sad, gold n hair, jewelry, looking at you
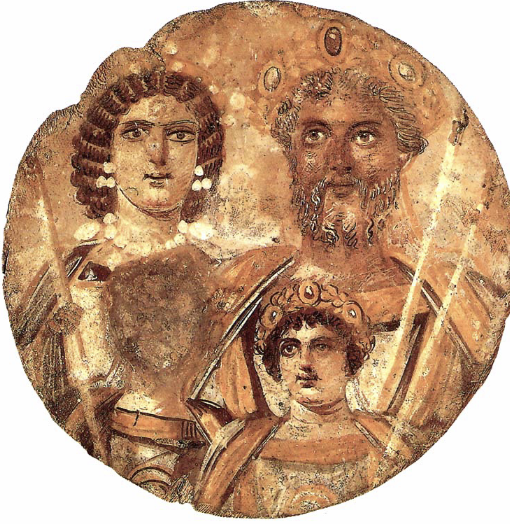

Several Tondo
Egyptian, (200 CE), tempura on wood, 12 inches
egg and pigment
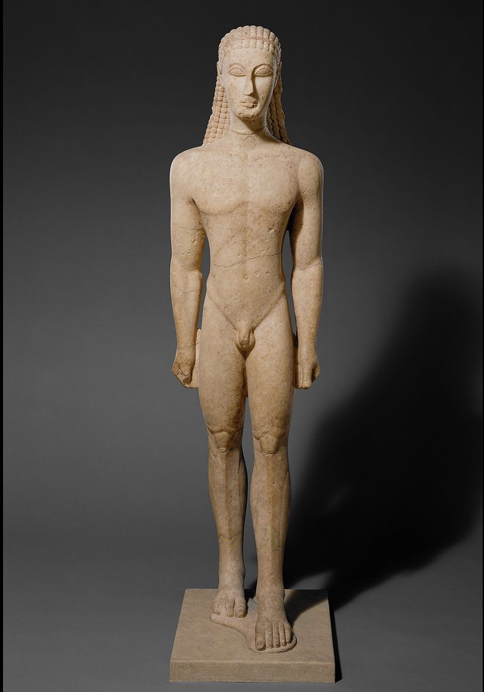

New York Kouros
Archaic (Greek), (590 - 580 BCE), marble
stiff, naked besides choker
braid-like hair and eyes bulge%
abstract --> reads as a human, not anatomically accurate
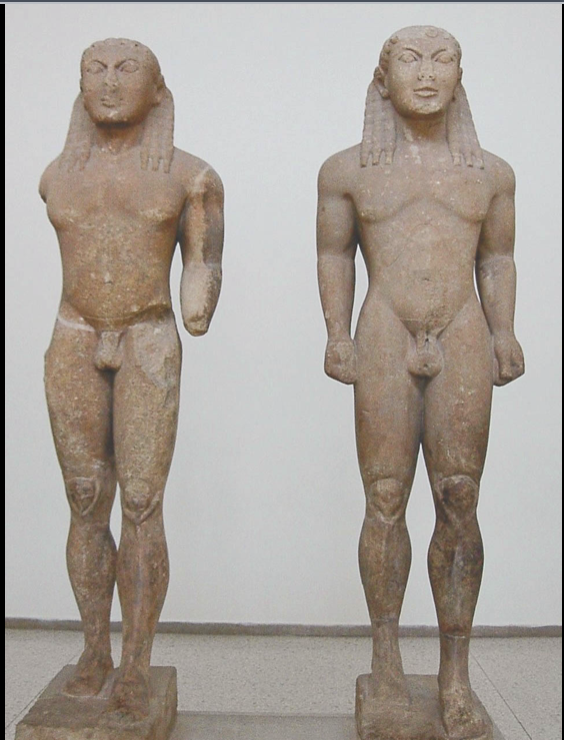

Kleobis and Biton
Archaic (Greek), (580 BCE), marble, found in Delphi
heroically nude --> expresses arete (living up to ones potential / bestness)
thicker, more realistic looking than New York Kouros

Kroisos (Anavysos Kouros)
Archaic (Greek), (540 - 525 BCE), marble, in National Museum in Athens
more naturalistic --> s-shaped spine
soldier --> god of war took him down
funerary / at grave of soldier
heroic nudity
archaic smile
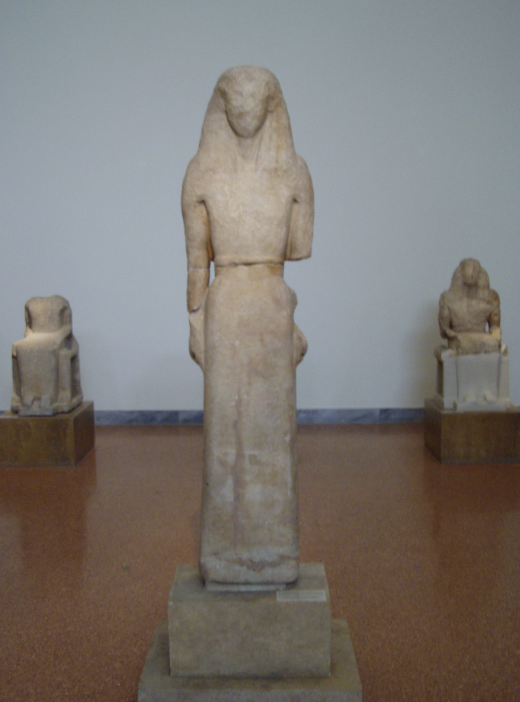

Nikandre Kore
Archaic, (650 BCE), marble, 1.7 m tall
dedicated to artemus --> twin to Apollo
small frame that is completely covered
hands long and open

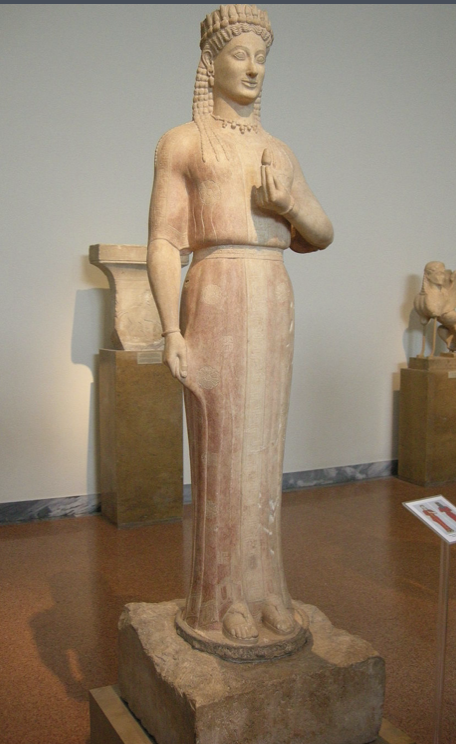
Lady of Auxerre
Archaic, (650 - 625 BCE), limestone, 65 cm tall
would've been painted in polychrome (various colors) and bright colors

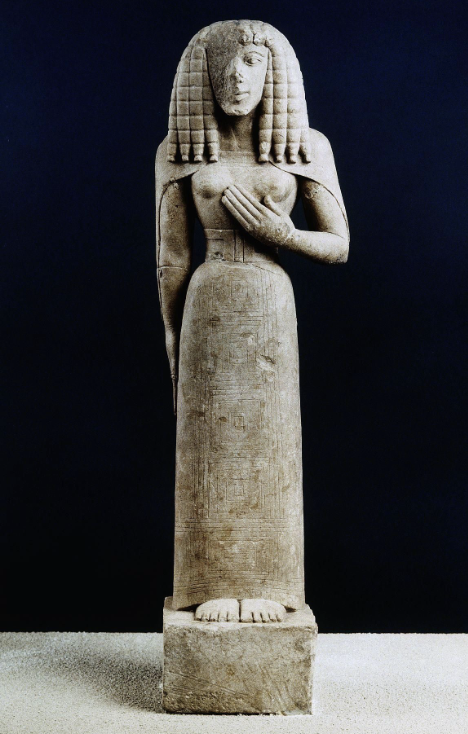
Phrasikleia Kore
Archaic, (550 - 540 BCE), marble, 1.79 m tall
hold sunken flower bud and pomegranate on necklace --> fertility
died before she was married --> before period
could not live to her best potential (arete) before she died

Peplos Kore
Archaic (Greek), (530 BCE), marble, 118 cm tall
more modest
soft face, comforting
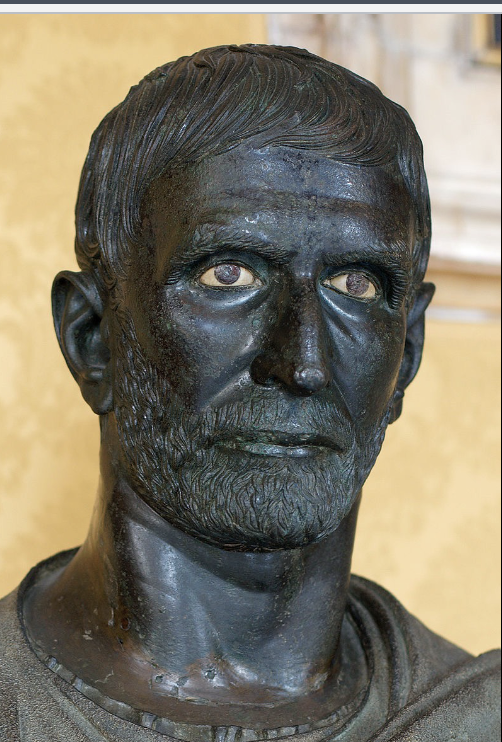

Capitoline Brutus
Roman, (late 4th - early 1st cent BCE), bronze
has smile lines and wrinkles
old = idealistic since it shows wisdom and it was a privilege being able to live to being old
age come with experience, wisdom and luck
upper-class people were old and you had to be old in order to be in the government
the cursus honorum takes years to work yourself up to the top
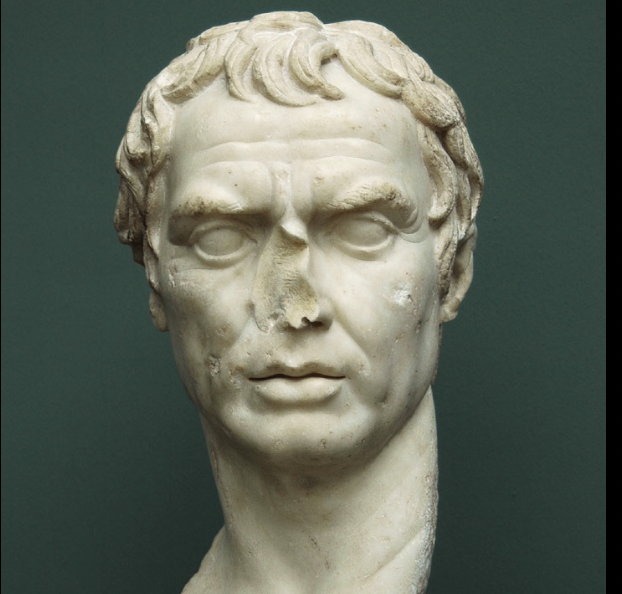

Bust of Scipio Africanus
Republican Roman, marble
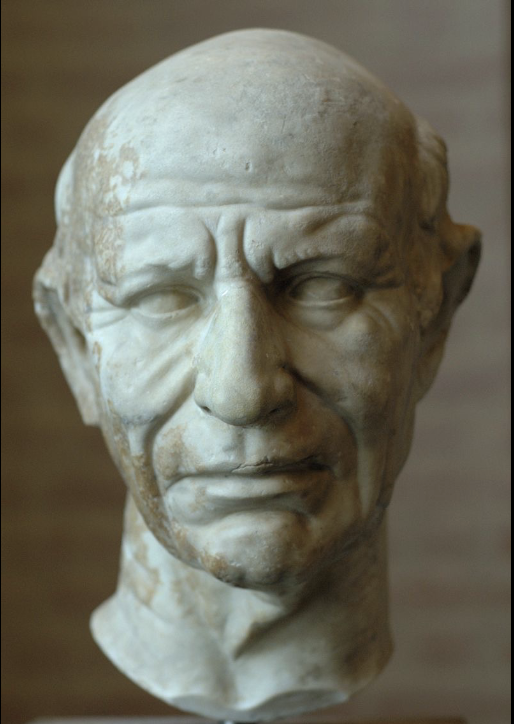

Portrait bust of a Man
Late Republican Roman, (60 BCE), marcle
bald and lots of wrinkles
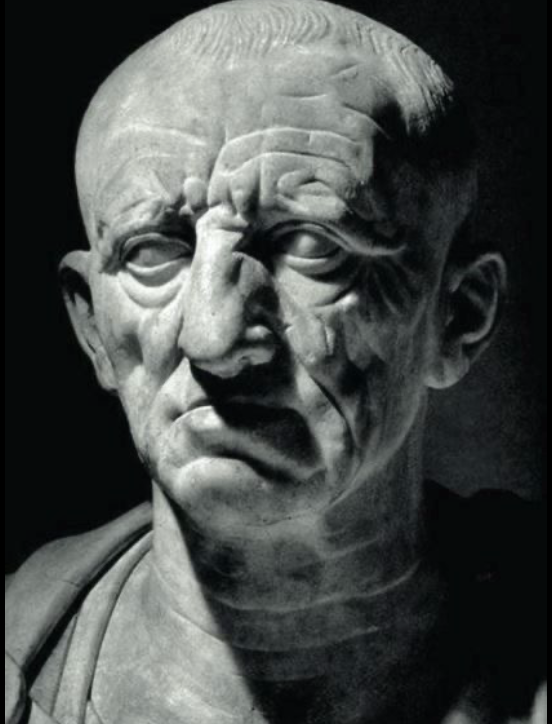

Patrician Torlonia
Roman, (1st century BCE), marble
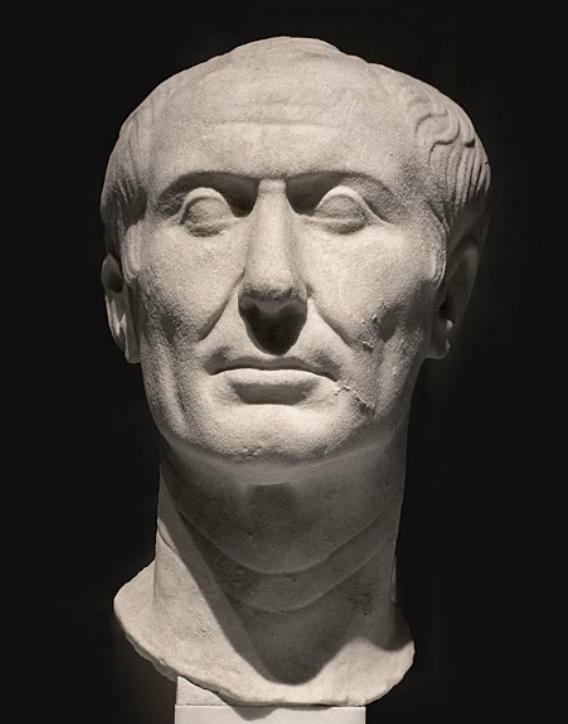

Tusculum Portrait of Julius Caesar
Roman, (50 - 40 BCE), marble
folds in neck and cheeks
male pattern baldness
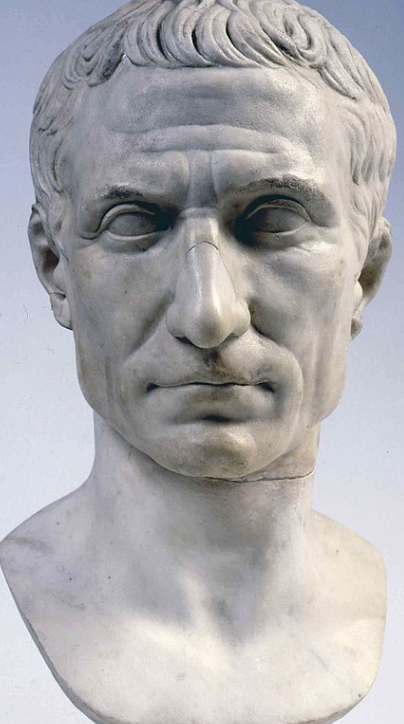

Chiaramonti Caesae
Roman, (44 - 30 BCE), marble
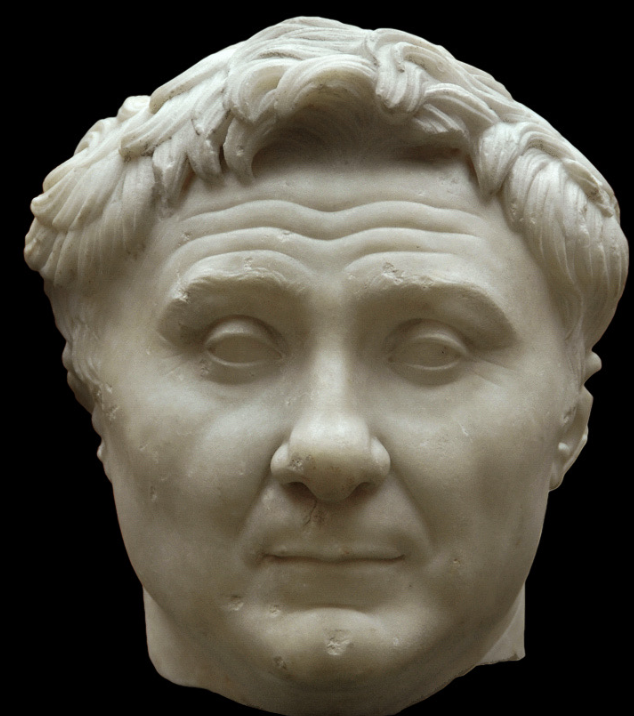

Pompey the Great
Roman, (50 - 30 BCE), marble, located in Port Pia, Rome
deep wrinkles in forehead
puffy --> makes him look younger
long hair
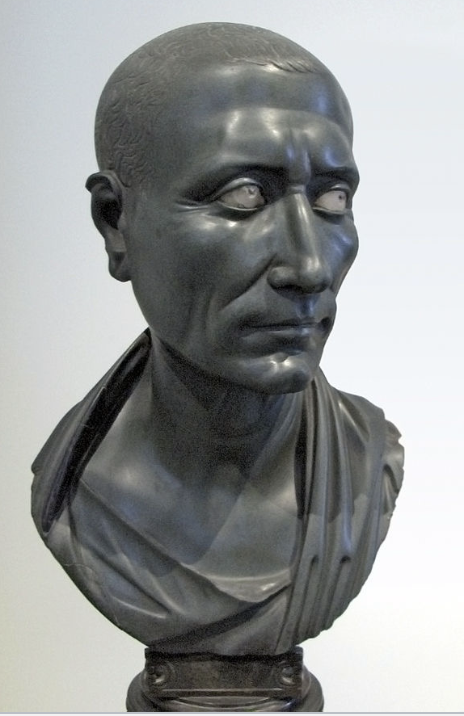

Green Caesar
Roman, (1st century CE), slate
posthumous portrait --> after death
frail and has crowfeet
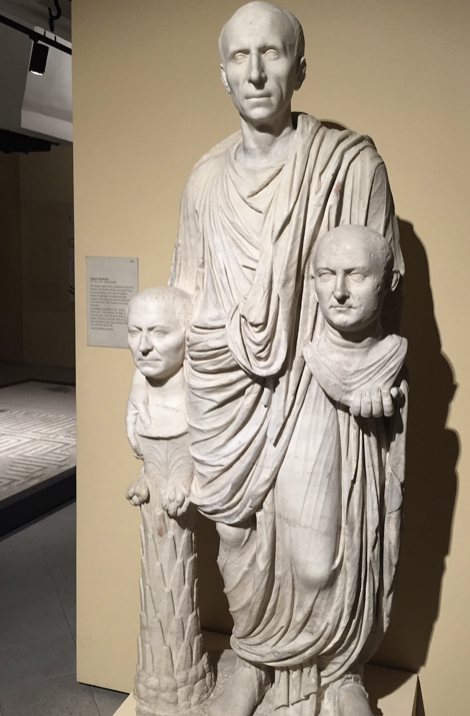

Patrician carrying two portraits heads
Roman, (1st century CE), marble
lararium --> where you celebrate ancestors
fides = good faith
virtues = virtue / manliness --> not manly to love your wife
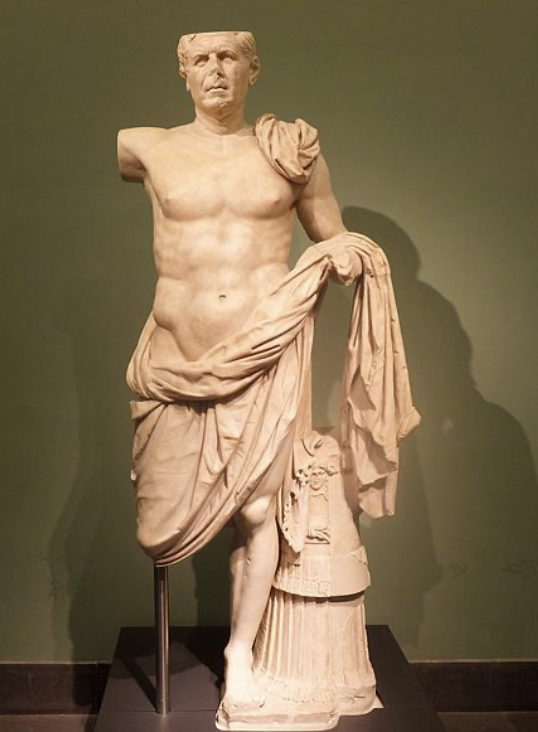

Tivoli General
Late Republican Roman, (80 - 60 BCE), marble
no limbs
idealized general --> ripped body but idealized old age

Christ Pantocreator icon
(6th cent CE), encaustic
encaustic has pigment suspended in wax
cruciform halo for Jesus
holding a codex, benediction gesture, eyes in different directions (two different people)
Christian icons are domestic icons --> meant to be touched and kissed

Christ Enthroned
(6th or 7th cent), Sinai in Monastery of St. Catherine
white hair and whimsical --> clothes na rainbow stars
full body, not just head like mummy portraits%
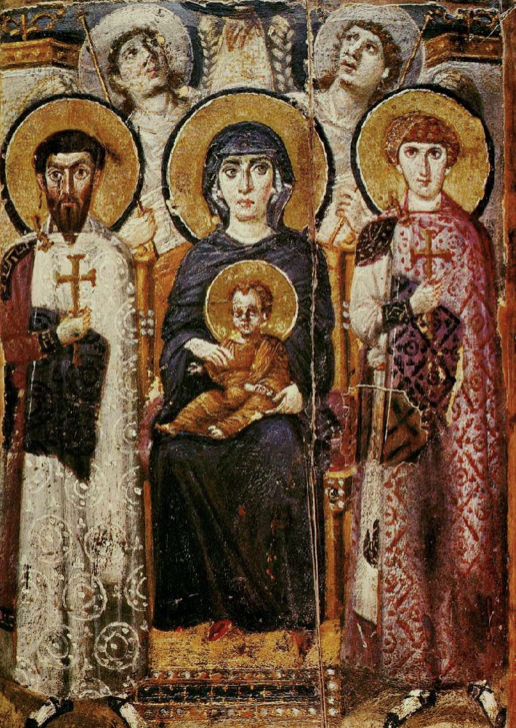

Virgin an Child Enthroned (Theotokos)
(6th cent CE), encaustic on Wood Panel, in Monastery of St. Catherine in Egypt
curved because it is so big
Mary is in throne of God
Angels (most 3 dimensional) are looking at hands of God --> anaiconic representation (also seen in synagogue)
icons go against 2 commandment
orthodox to use icons --> not worshipped!
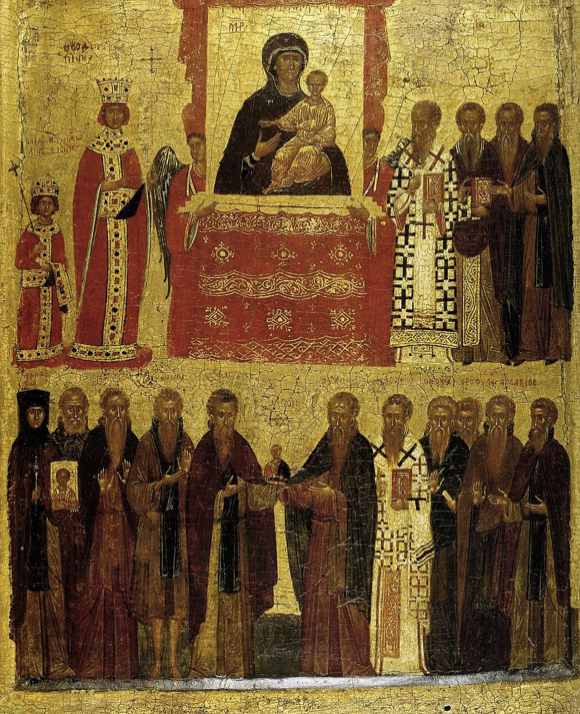

Icon of the Triumph of Orthodoxy
(late 14th century CE), egg tempura and gold leaf on wooden panel
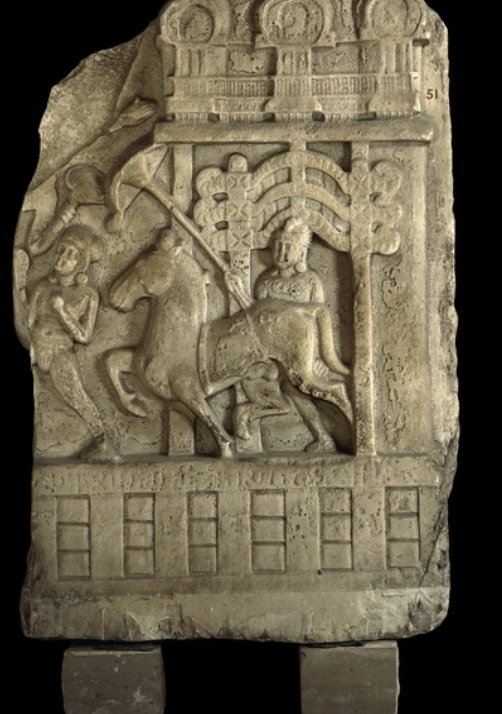

Great Departure of Prince Siddhartha
(2nd cent CE), limestone
cannot actually show Siddartha as Buddha
riding white horse = special
riders horse with parasol = anionic representation of Buddha
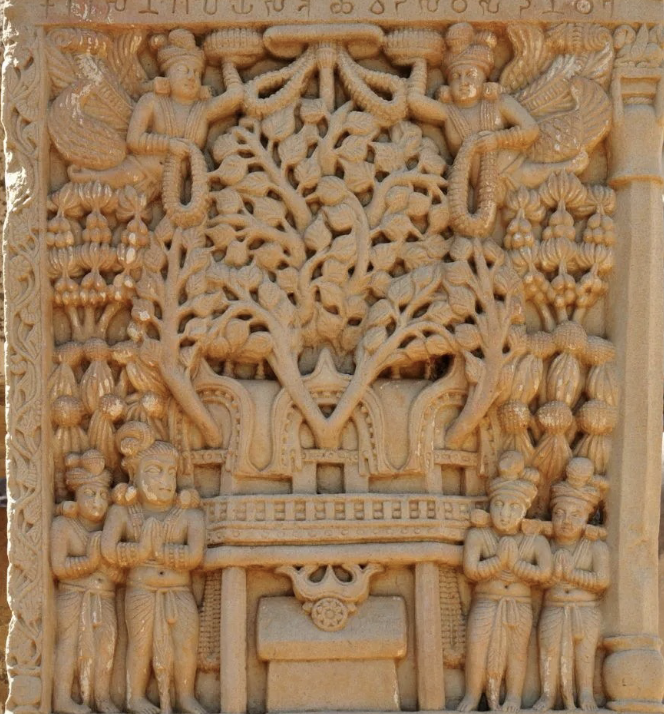

Bodhi tree with shrine
(2nd - 1st cent BCE), in Sanchi at eastern gateway
no buddha
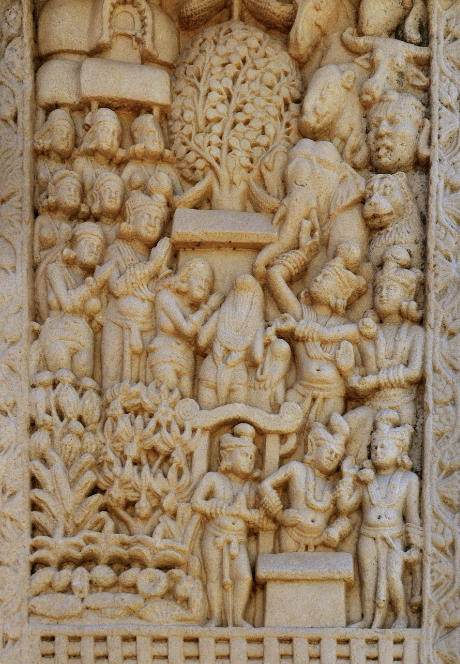

Temptation and Enlightenment
west gateway in Sanchi
footprints, but no person --> aniconic
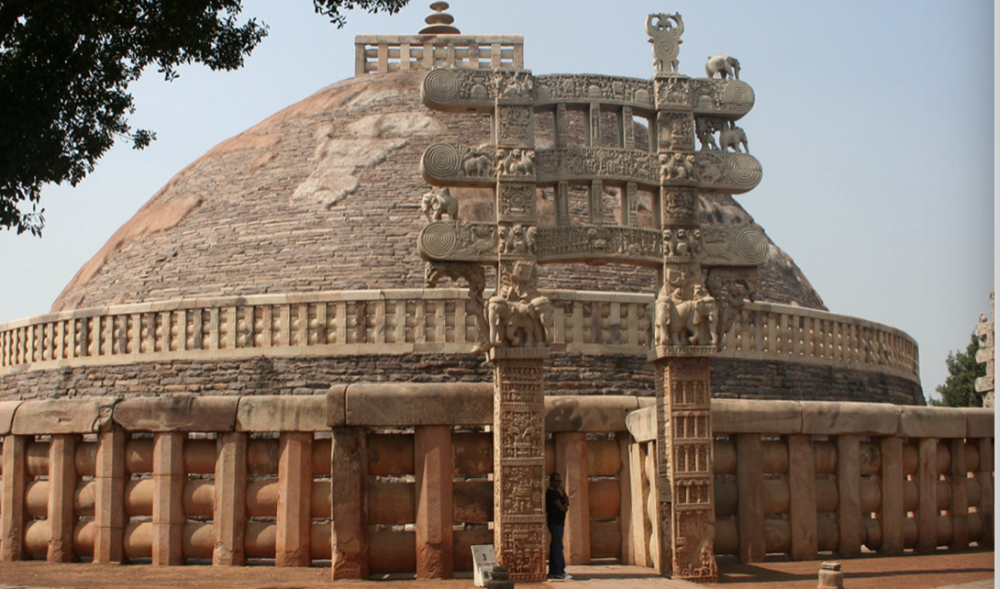

Great Stupa
(3rd - 1st cent BCE), Sanchi
people cannot go in
holds relics (physical reminders) of Buddha
small scale model of the universe
Ashoka showed his power
go around in clockwise circle to represent the constant cycle of life --> can be meditative
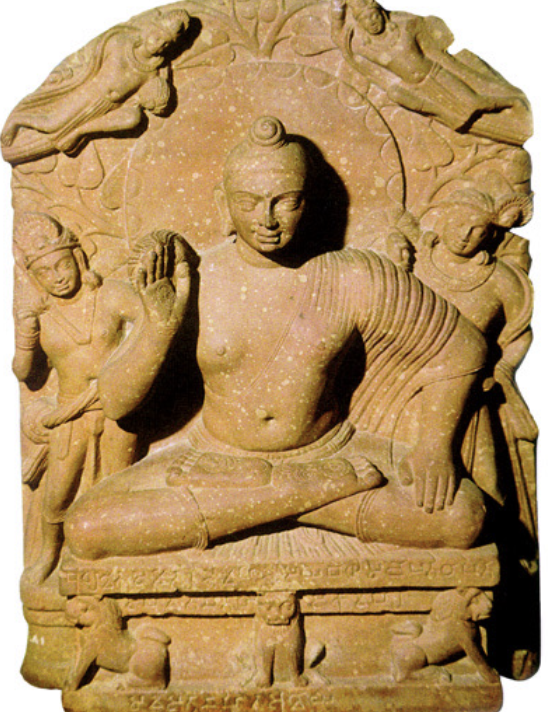

Buddha and Attendant
(early 2nd cent CE), red sandstone
iconic representation
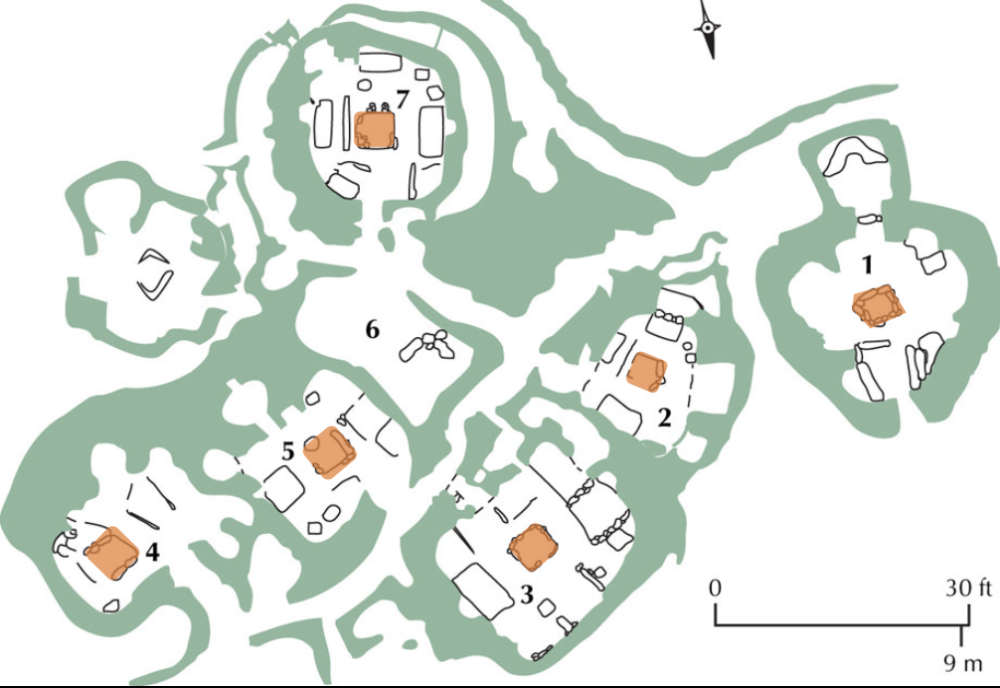
Skara Brae
Neolithic, (3200 - 2500 BCE)
goes with hills
hearth in middle of sectors
house made of flatstone --> all connected by covered pathways (corbel vaults)
rely on neighbors = easy access
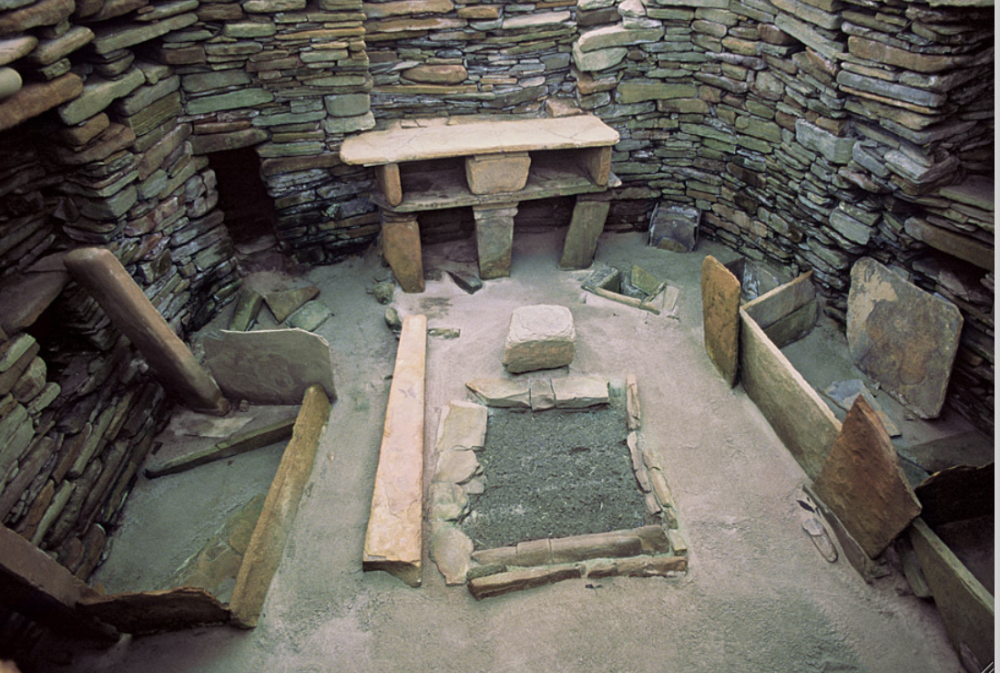

House 7
lots of shelves
fire in the middle --> warmth (hearth)
beds around fire
shelf across from doors --> understand who lives there
pits in floor that connect to ocean for poopy time%
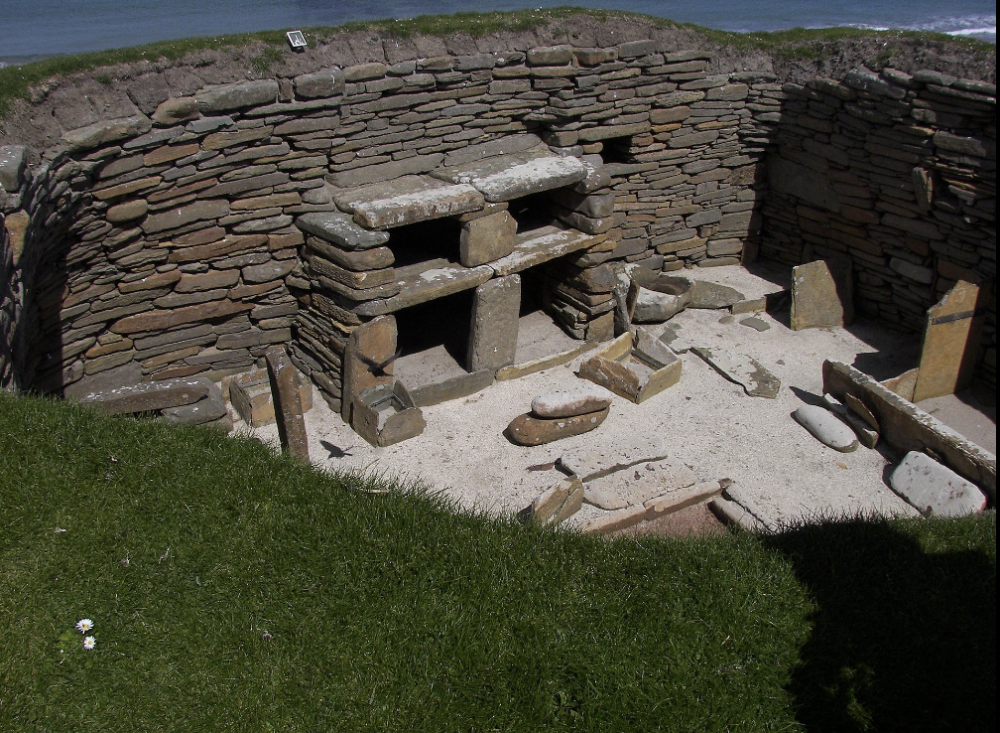

house 1
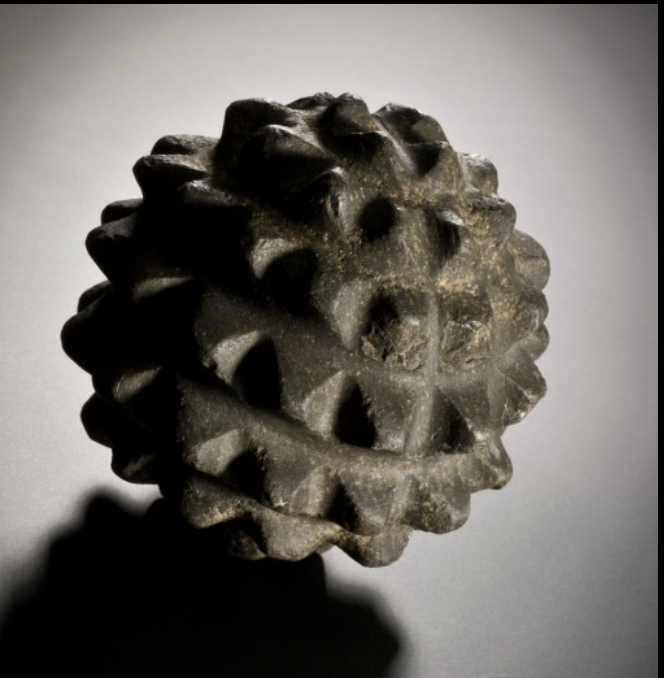

stone objects
measuring tools most likely
megaliths --> big stone
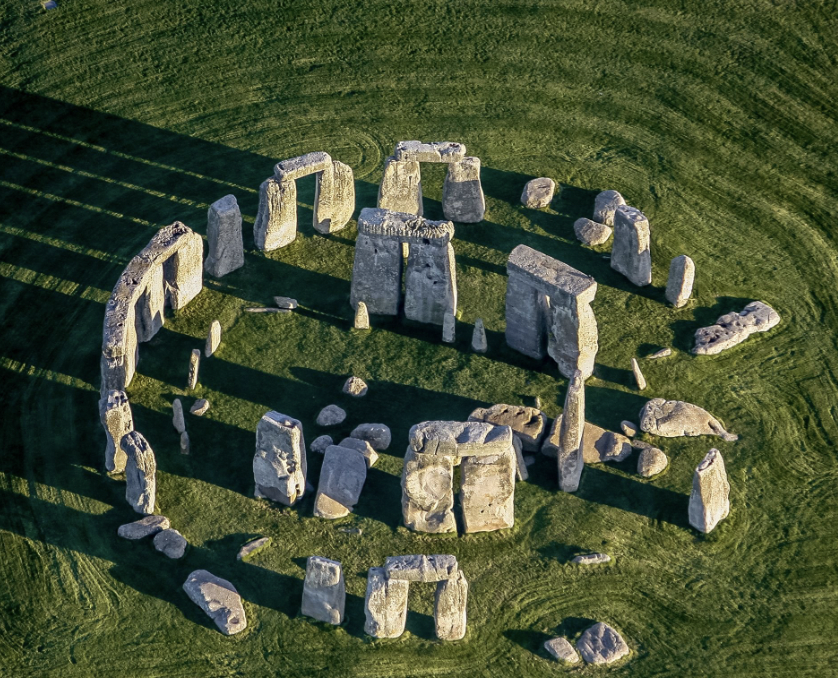

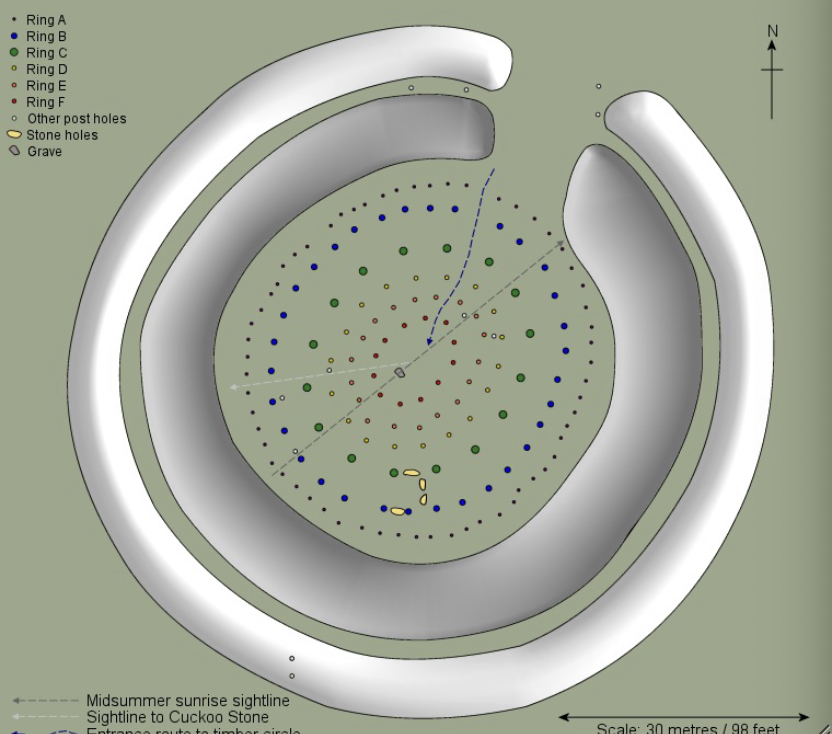
Stonehenge
Neolithic, (3000-1500 BCE), sarsen and bluestones
sarsen stone = local, bluestone = 150 miles away --> trading or someone in charge to control people to get the stone and bring back (governmental effect)
built in 3 stages --> 1) Aubrey holes that have blue stone (some with human remains), no stones in middle 2) ? 3) cromlech which is inhumation in Stonehenge
burial / graveyard / non-domestic --> ceremonial
also seen as an astronomical calendar --> farmers look at stars for seasons
trilithons = 3 stones
woodhenge
neolithic, (2600 BCE)
aligns with summer solstice
domestically area, unlike Stonehenge --> has trees (living)
during ton walls = domesticated village near Stonehenge
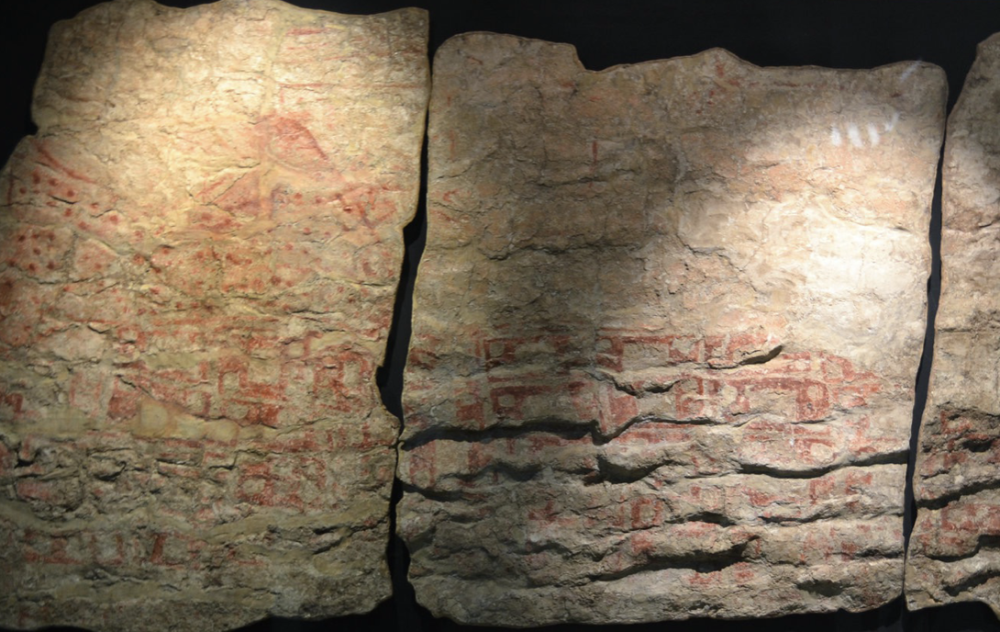

Mural, Catal Huyuk
Neolithic, (6000 BCE)
geometric linear pattern
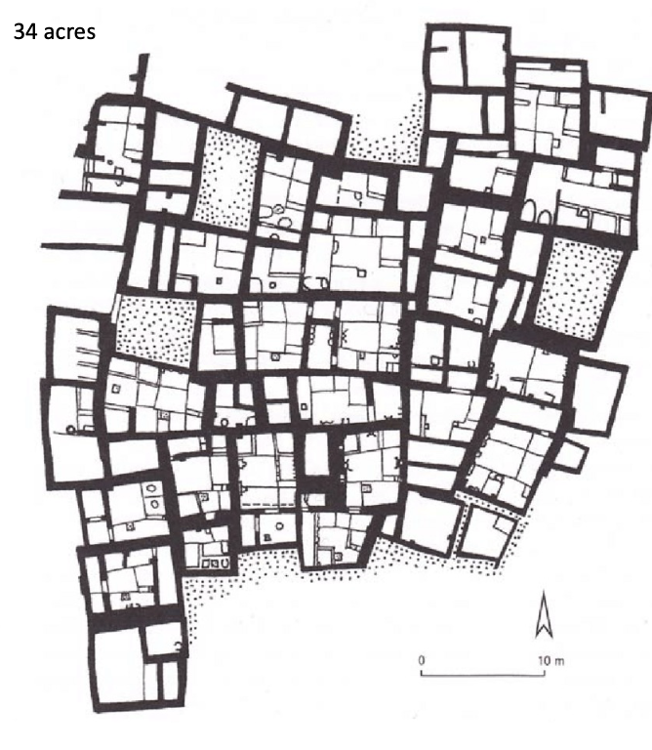
Catalhuyuk
Neolithic, houses made of mud brick
houses in bird's eye view --> share walls, no streets = depend and rely on each other, no room stands out
18 levels of time
only lived in houses for 50 years but house lifespan is 2000
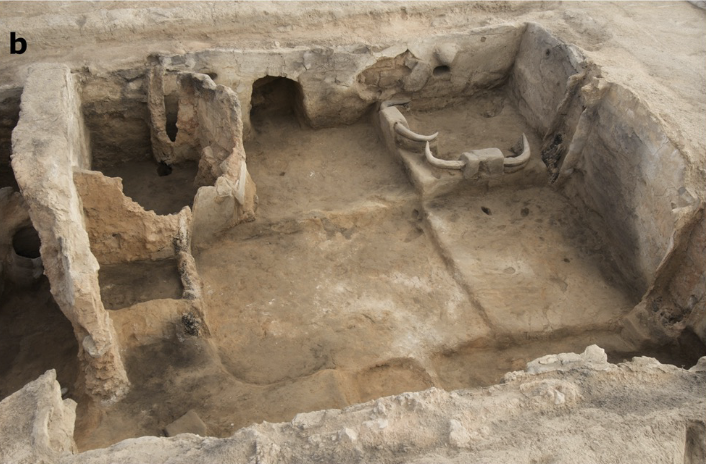

Building 77
bull horns in corner --> platforms, bulls represent abundance and harshness
aurox = wild bull --> had to hunt, not domesticated
domestic space seem as funerary space --> feel close to deceased, babies in baskets when died (treated different from adults)
oven on south side
entrance above oven
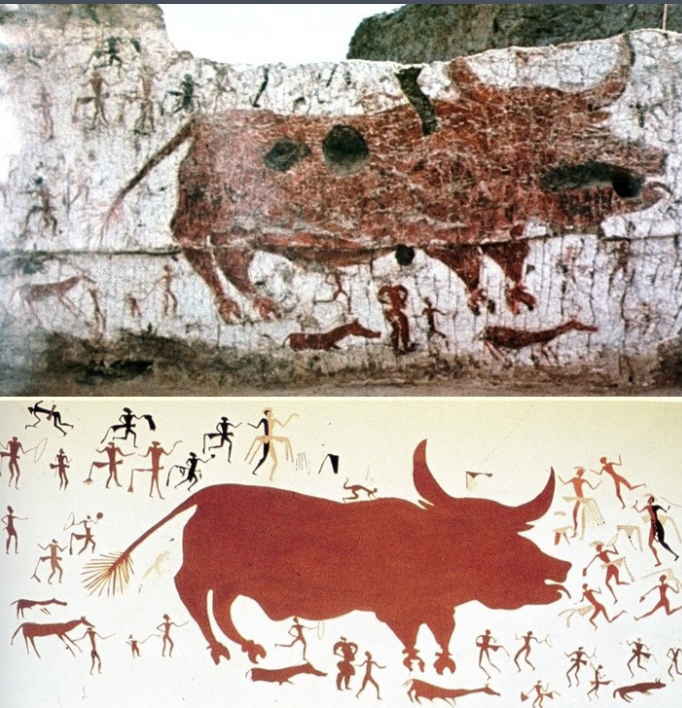

village gathering around bull
work spread out, no specialization -->shared labor
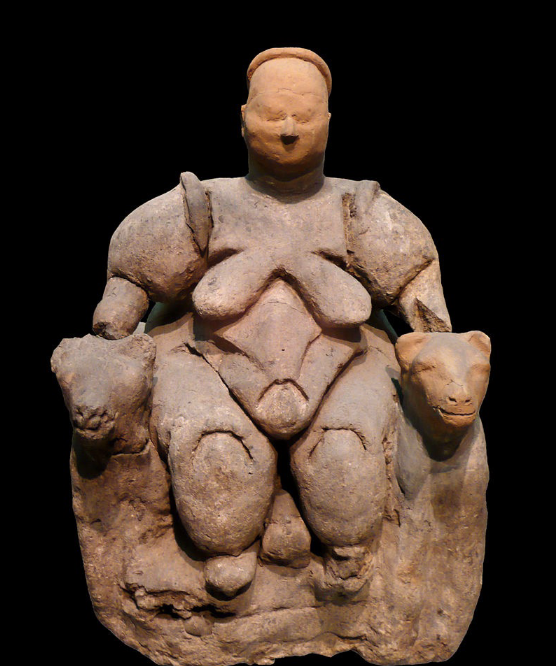

Seated Woman
Neolithic (Catal Huyuk), (6000 BCE), clay
5-10% of statues in canal huyuk are women
demonstrates the ideal fro abundance and good health
arms and legs small = not important
voluptuous = fertility
she's giving birth
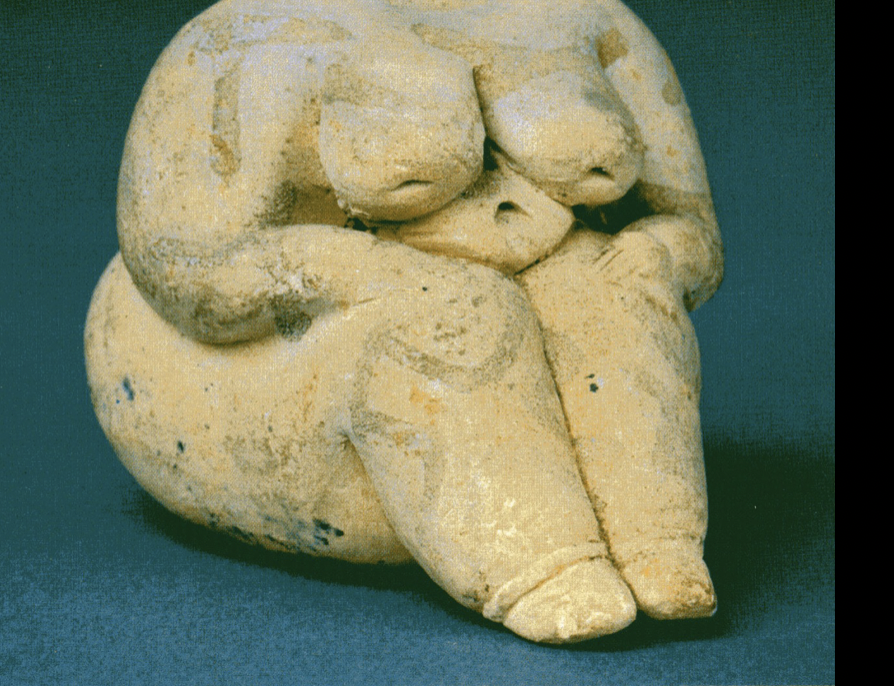

Painted Female Figurine
Neolithic (Catal Huyuk), (6000 BCE)
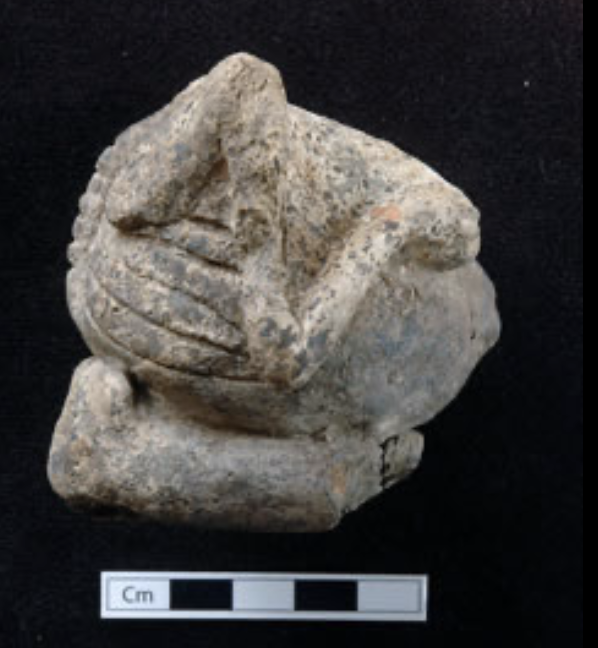

Clay Figurine
neolithic
skeletal except for pregnant belly
life and death
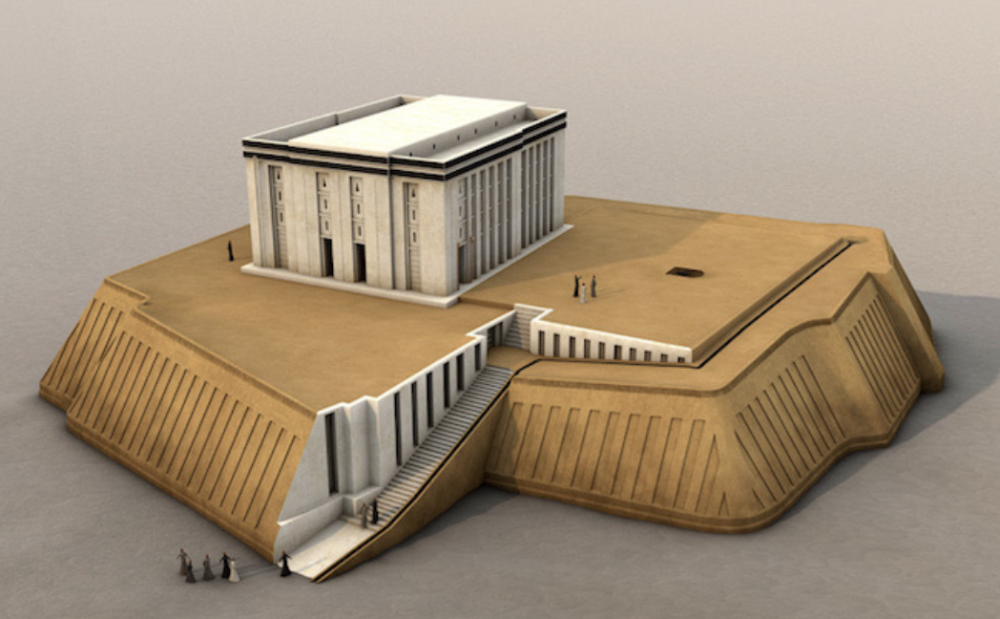
Ziggurat
Uruk / Sumerian, (4000 BCE), mud brick
visible for miles --> artificial mountain --> ziggurat elevates temple
believed gods lived in white temples
priestly class and higher can go up to ziggurat
circumambulate around temple to get in --> thing in the middle is VERY important
gypsum based plater = visually striking
sense experience different things (dark / incense) --> feel apart of the deity / spirit manifest in physical
bathe, feed, kiss, take care of cult image in ziggurat --> treat cult image like real person
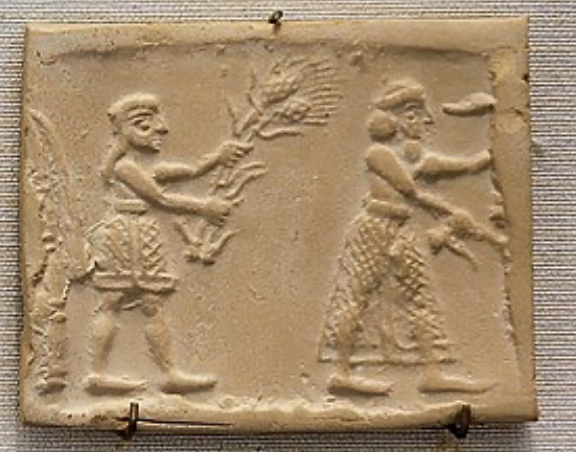

Cylinder Seal
Uruk / Sumerian, (3200 BCE),
one picture that rolls to get. clear image
preist = king (ensi), gods overall ruler
king takes care of fertility (pp)
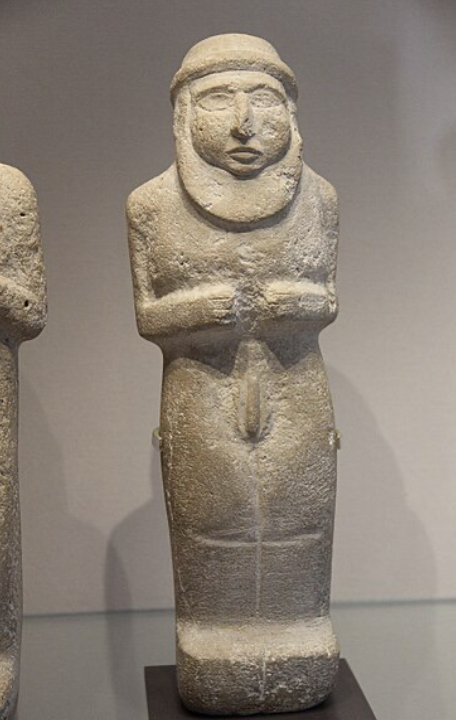

Limestone Statuette of bearded man
Uruk / Sumerian, (3300 BCE), limestone
possibly a priest-king --> ensi
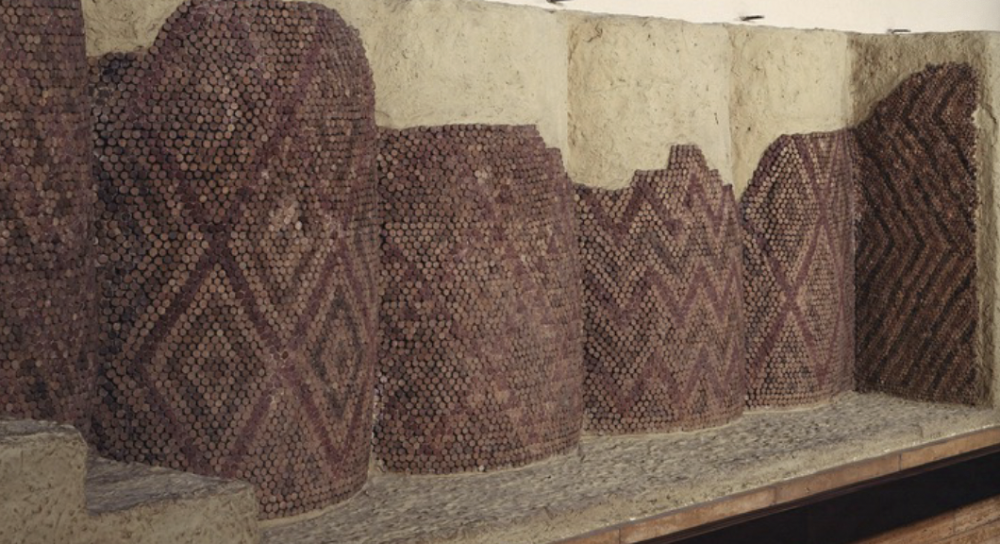

Cone Mosaic
Uruk / Sumerian, (3500 - 3000 BCE), limestone, Cone Mosaic Cortyard in Eanna District
triangle / zigzags separate our world form underworld
visual interest
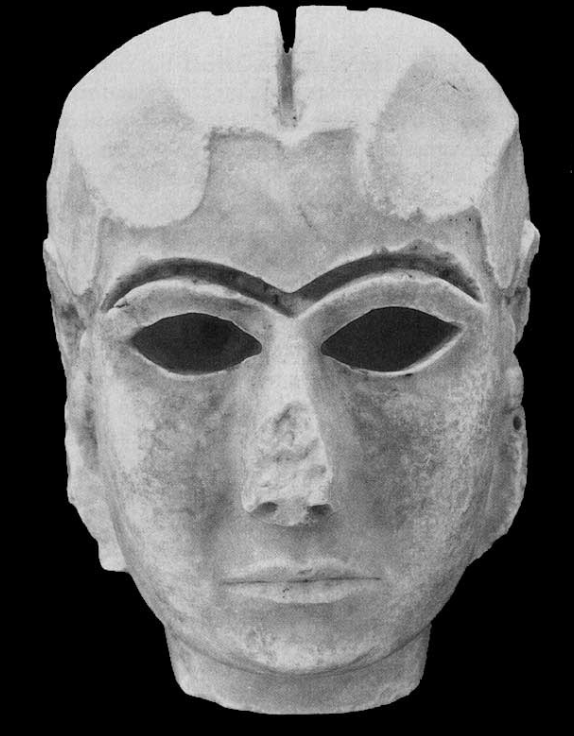

Mask of Warka / Lady of Uruk
Uruk / Sumerian, (3200-3000 BCE), marble
cult image of inanna --> taken care of and dressed
unibrow made of lapis lazuli --> comes from Afghanistan (hundreds of miles away = active trading)
very stern and intimidating
not 3 dimensional
taped to a board that looks like a body

Uruk Vase (Warka Vase)
Uruk / Sumerian, (3200 BCE), alabaster
multiple ground lines in a single object = register
ancient repaired = important to society
poles = anionic representation of inanna
top = offerings form nude people --> vulnerable cannot hide anything from inanna
middle = naked offerings again
bottom = sheep and barely --> that's what they used to survive
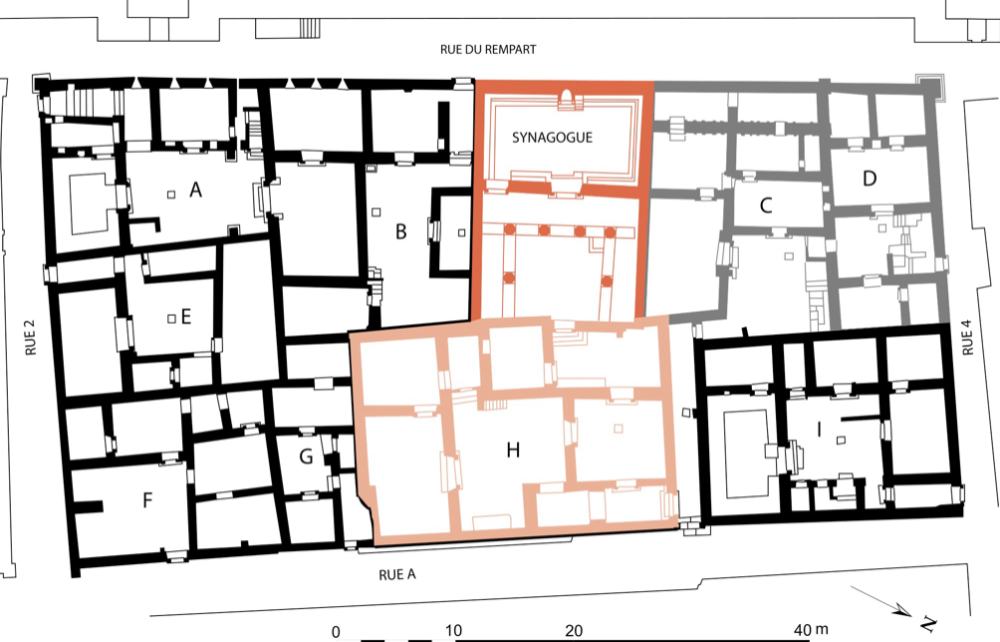
Synagogue
Dura Europos, (245 CE)
controlled access --> no entrance form street (not everyone is allowed in)
ISIS destroyed lots of Dura Europos because of lots of looting

West Wall
Dura Europos Synagogue
cut and removed because they would have been destroyed by ISIS
tempura plaster
now in Yale University
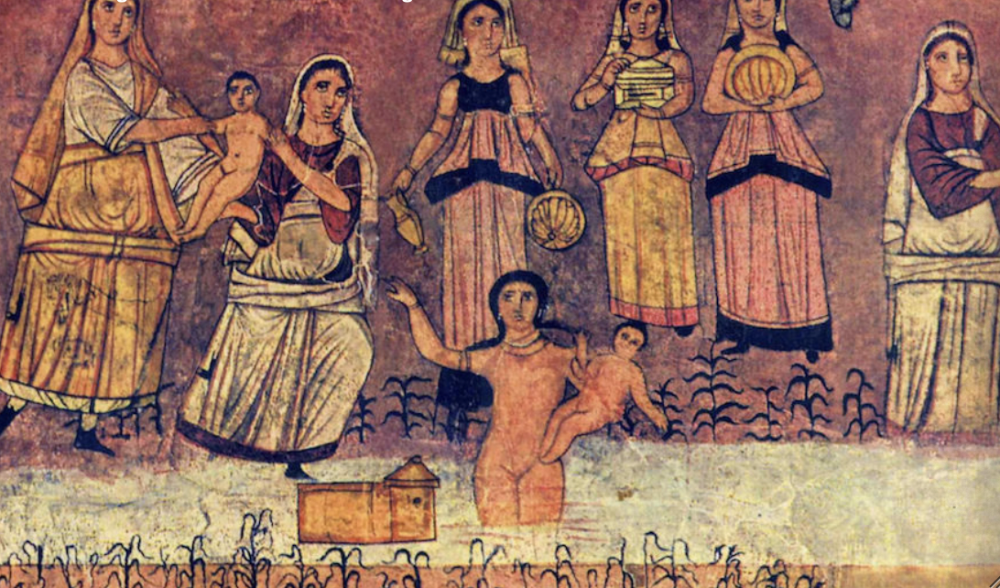

Moses Scene from West Wall of Synagogue
both babies in the pictures are Moses
continuous narrative in one painting --> dingle picture with mulit[le narratives
use dominate visual to get point across
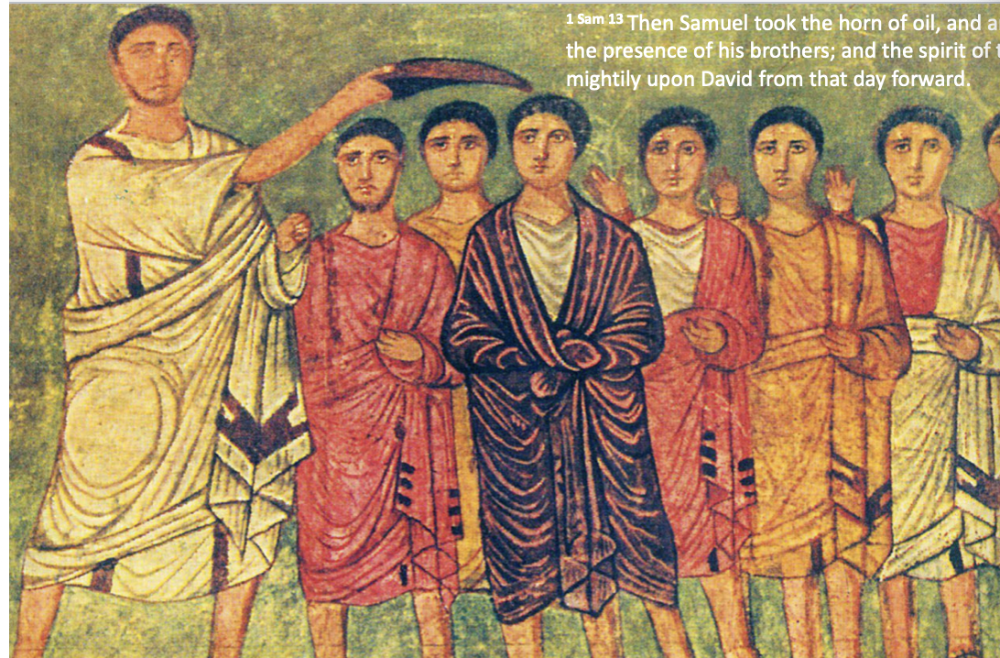

David on the West Wall of the Synagogue
David both of the boys in yellow
purple = royalty --> David in purple
Samuel annoying David --> religiously symbolic with oil
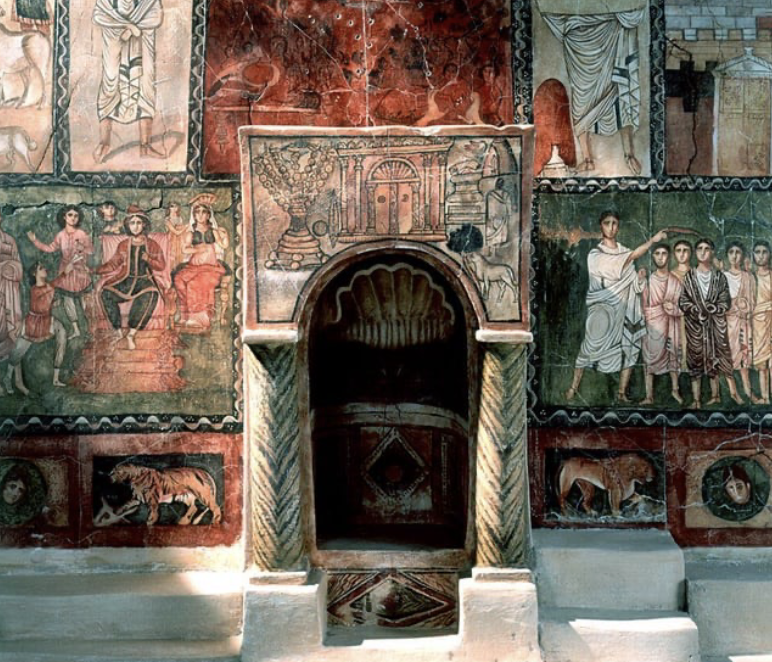

Torah Niche Synagogue
Dura Europos, (245 CE)

Abraham and Isaac - Torah Niche detail
Abe doesn't face us
hand of God stops him --> anionic representation
sacrifice goat instead
represents faithfulness
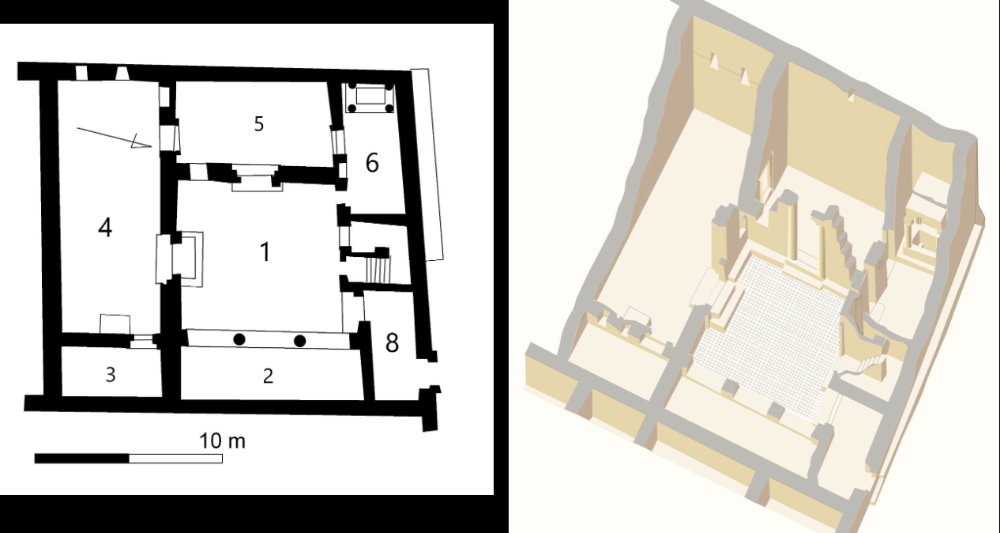
Christian-House Church
Dura Europos, (245 CE), tempra plaster
Christianity needs t be practice privately --> secretive
all paintings cut out and put into Yale%%
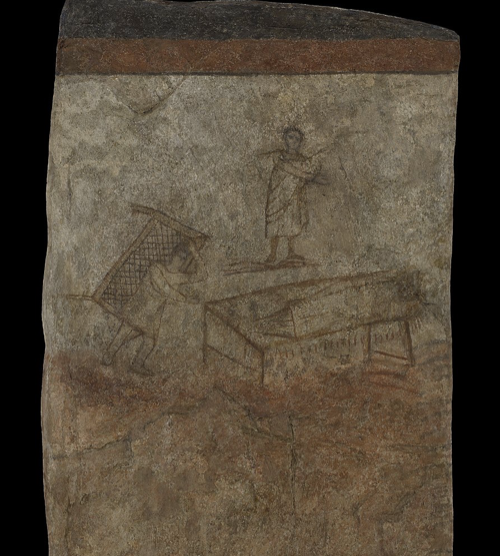

Healing of the Paralytic
Dura Europos, (245 CE), tempra plaster
Christian House-Church wall paintings
Paralytic seen twice
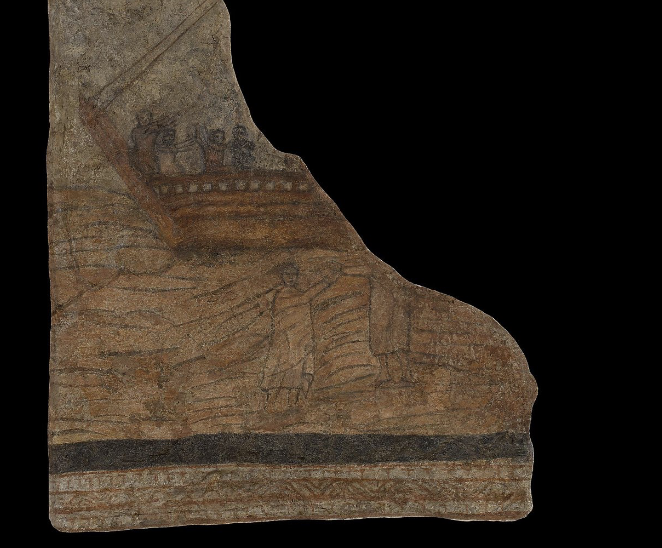

Jesus and Peter Walk on Water
Dura Europos, (245 CE), tempra plaster
Christian House-Church wall paintings %

Baptistery Wall painting
Dura Europos, (245 CE)
Christian worship places have a baptistery
Jesus carrying lamb --> syncretism (taking visual image from another culture and making it one of their own --> lambs sacrifice in archaic and protected in Christianity)
Jesus in tomb
casophagus (bury someone) fill with water for baptism --> symbolic death and rebirth
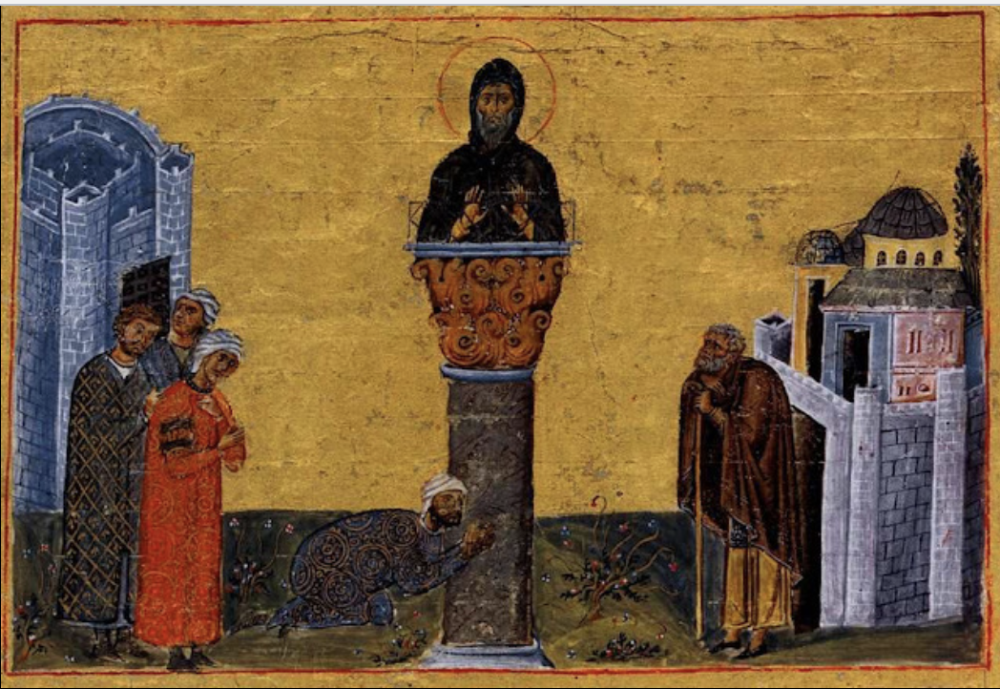

St. Simeon Stylites, Megolian of Basil
decides the world is too much --> withdrawn to be near God
live sup on stylus / pillar and dies up there cause he's a freak%%

Skellig Michael Monastery
ireland, (built 6th - 8th cent CE) --> occupied until 12th cent CE
have to go up 670 steps in the island to monastery
enough for 13 people --> one main person and 12 monks to live there
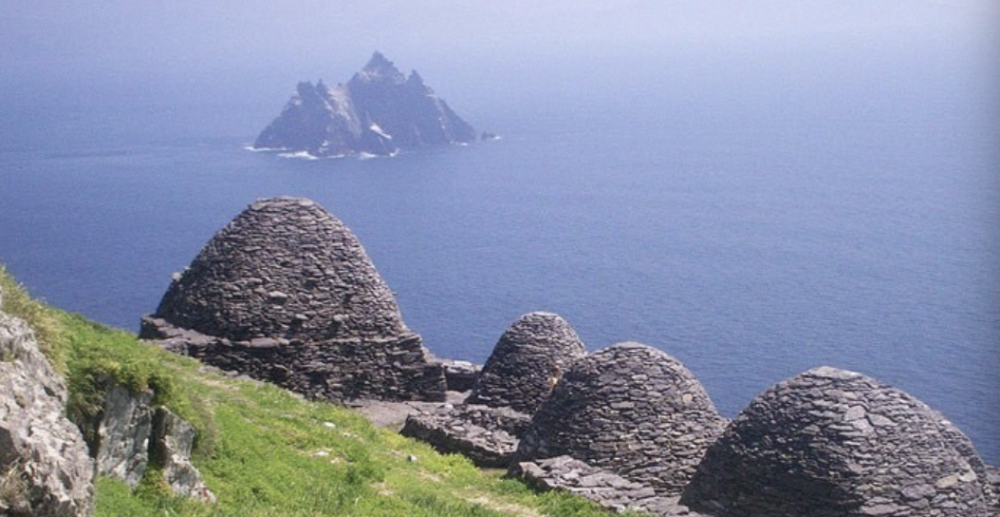

beehive cells
insular = islands / isolation --> no one around (women / distractions), cannot be swayed by other religions, control their own rules, not surprises like VIKINGS who pillage
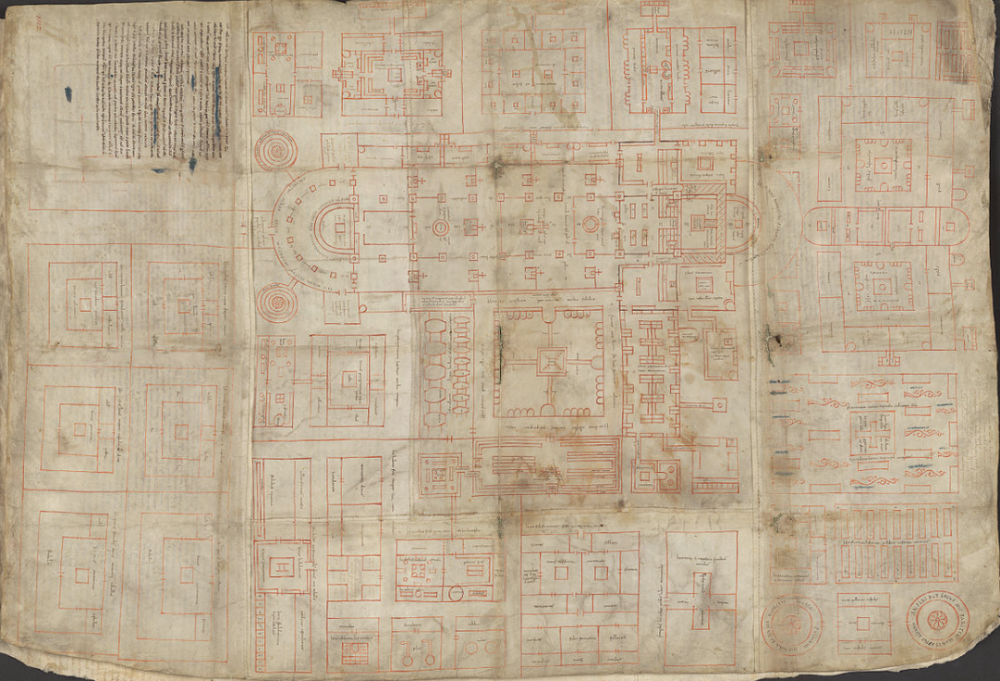
Plan for St. Gall
Medical, (820 CE)
plan for ideal monastery that was never built
completely self-suffcient so the monks can stay isolated
based on Rule of St. Benedict (520 CE)
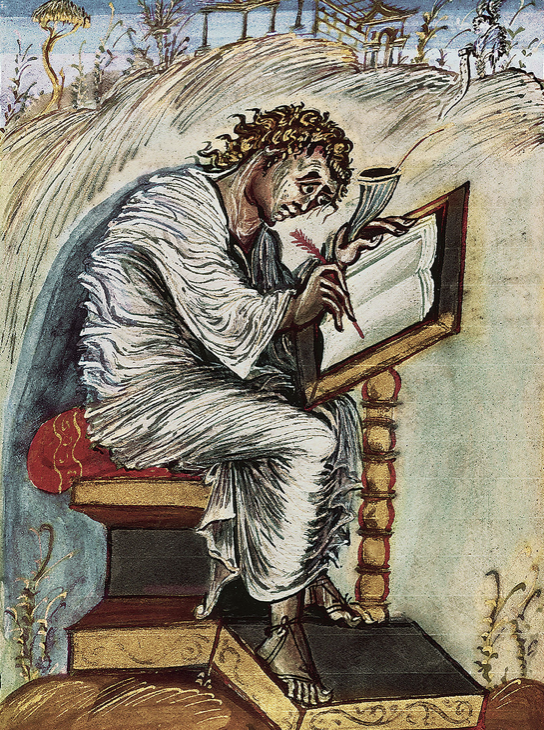

St Matthew - Ebbo Gospels
9th century, ink and tempura on vellum (stretch of animal skin --> holds ink well), in Benedictine Abbey of Hautvillers
St. Matthew nervous or constantly in motion
The incorrupt St. Cuthbert of Linisfarne
12th century

Initial Page of Eadfrith of Lindisfarne
715 - 720 CE, ink on vellum, in Lindisfarne Gospel
first page = initial page
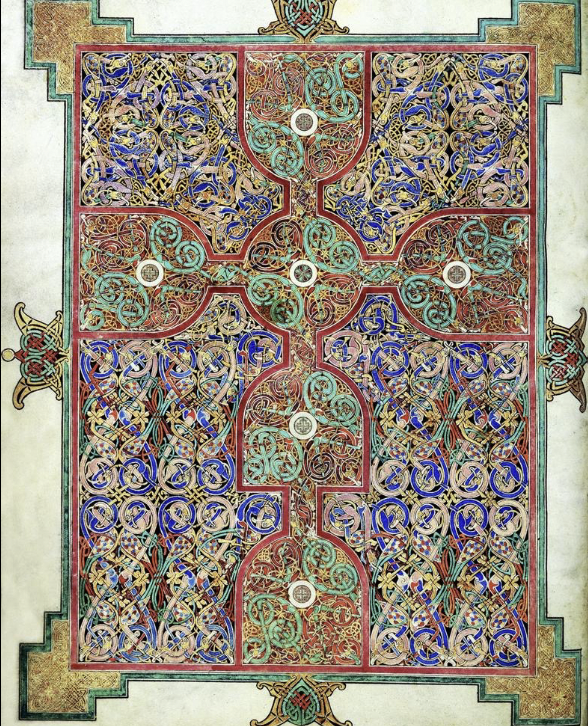

Carpet page of Eadfrith of Lindisfarne
715 - 720 CE, ink on vellum, in Lindisfarne Gospel
carpet page = nonfigural pattern page that separates Gospels from each other
apoptropaic = keeps bad things away --> interlace pattern of carpet page is like a net and keeps bad things out of the Gospel
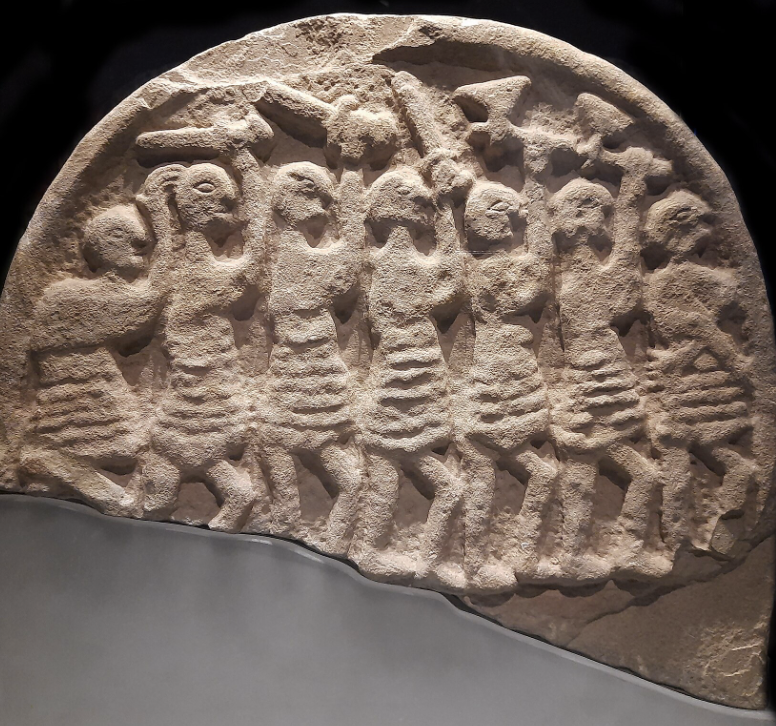

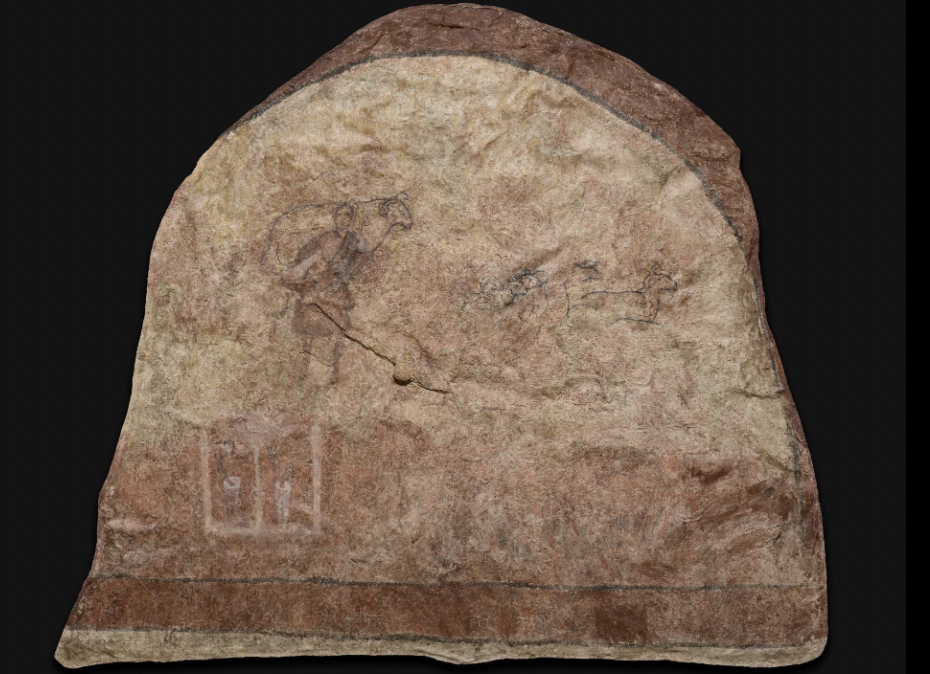
Lindisfarne Stone (Viking Raider Doomsday Stone)
9th century, Northumbrian carved gravestone, found in Lindisfarne
viking raid in Lindisfarne --> destroyed monasteries for expensive things not because of religious reasons

Lindau Gosepls
880 CE, Court of School of Charles the Bald
Jesus on cross and cruciform
repousse = makes things pop out --> turn it over and press it in the stick it out
granulation
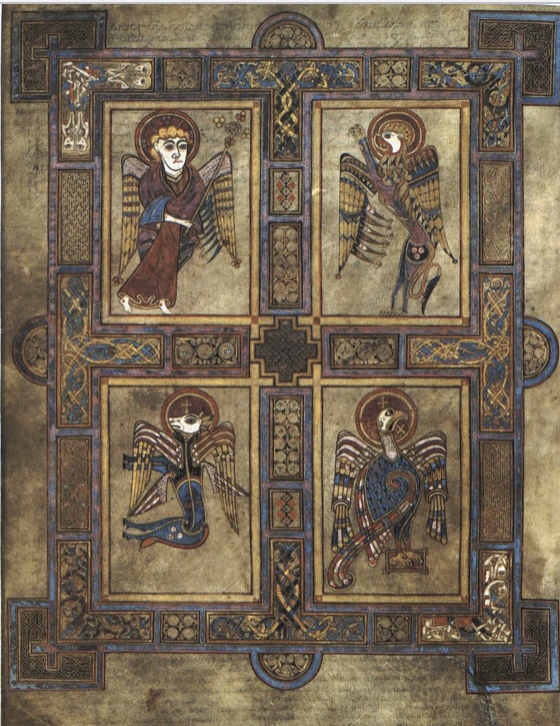

Four Evangelists
800 CE, Book of Kells, illuminated manuscript
Matthew = angel, Mark = lion, Luke = ox, and John = eagle (beasts of apocalypse

Chi-Rho monogram
800 CE, Book of Kells, illuminated manuscript
raids made them stop making illuminated pieces --> what is made in scriptorium
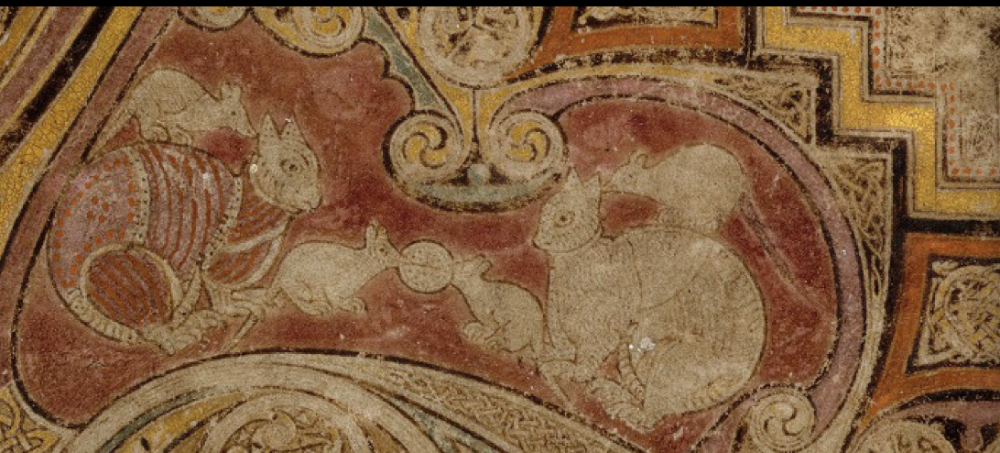

cat and mouse
mice stealing communion
cats stopping them