the replication/copying of cellular DNA occurs during the-
Synthesis phase (s phase) of the cell cycle
The S phase is a necessary process to ensure that-
the instructions in DNA are faithfully passed on to the newly produced cells.
in cell nuclei, DNA and protein complexes known as ____________ make up the ______________
chromatin, chromosomes
replication can ONLY occur on a-
single strand DNA template
the main enzyme that catalyzes the formation of new DNA strands is-
DNA polymerase
what is the function of DNA polymerase?
reads in 3' to 5' to form a complement strand in 5' to 3'
DNA replication is ALWAYS
semi-conservative
why is DNA replication semi- conservative?
uses the template of the original DNA + a newly synthesized strand. (each of the two daughter strands has half new DNA and half old DNA)
the lagging strand is ?
the template strand
the leading strand is?
the new strand
a characteristic of eukaryotic DNA replication is that-
it is bidirectional, and starts in several locations at once
DNA is copied at about-
50 base pairs per second
What is the function of DNA helicase?
unwinds the two strands of DNA in a double helix
what is the function of DNA primases?
synthesizes RNA primers to start DNA replication
what is the function of DNA polymerases?
adds complementary bases to template strand, therefore creating a new DNA strand
what is the function of exonucleases?
remove RNA fragments (Okazaki fragments), also act as a proofreader which removes nucleotides that are not a part of the double helix. (removes mismatched residues, edits DNA)
What is the function of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins?
prevents DNA from binding back together
What is the function of DNA ligase?
seals complementary strands
what is the function of topoisomerases?
facilitates unwinding
what is the function of telomerase?
synthesis of telomeres (caps the ends of a chromosome)
What is the first 4 steps in DNA synthesis?
DNA helicase, DNA primase, DNA polymerase, Exonucleases
What are the last four steps of DNA synthesis?
Single-stranded DNA binding proteins,DNA ligase, Topoisomerases,, Telomerases
what base is found in RNA that is NOT found in DNA?
Uracil (U)
RNA is a-
single strand
Chain ELONGATION is carried out by-
DNA polymerases
What is the specific function of DNA polymerases?
select the nucleotide that is added to the 3'-OH end of the growing chain and catalyze the formation of the phosphodiester bond.
Exonucleases enhance the fidelity of DNA replication by-
rechecking the correctness of base pairing before proceeding with polymerization
eukaryotic DNA replication is also-
a semi discontinuous process.
why is DNA replication a semidiscontious process?
because the leading strand is synthesized CONTINUOUSLY, while the lagging strand is synthesized DISCONTINUOUSLY (Okazaki fragments)
a NEW strand of DNA is always synthesized in the _________ direction
5' to 3'
A strand is READ from the ___ end toward the __ end
3' , 5'
ALL DNA polymerases function in the same manner in which they-
READ parental strand in 3' to 5' and SYNTHESIZE a complementary antiparallel new strand in 5' to 3'
the leading strand is the one in which-
5' to 3' synthesis proceeds in the SAME direction as replication fork movement
the lagging strand is the one in which-
DNA is 5' to 3' synthesized in short fragments in the opposite direction of the replication fork movement
okazaki fragments are about ___ to ____ nucelotide long
100, 200
Overall chain growth occurs at the-
the base of the replication fork (but synthesis of the lagging strand occurs discontinuously in the opposite direction with exclusive 5'-3' polarity)
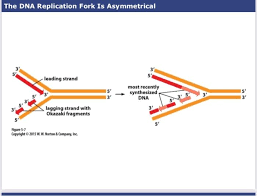
on the lagging strand, okazaki fragments are synthesized sequentially with fragments-
nearest to the replication fork being the most recently made
what is annealing?
the ability of two complementary nucleic acids to align in an opposing orientation to form hydrogen bonds with bases of the complementary strand
what keeps the strands of DNA replication protected until complementary strands are produced?
single-stranded DNA proteins
why is DNA ligase so important?
it is important because it creates the final phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides on a strand of DNA
super twisting of DNA is removed by which enzyme?
topoisomerases
what is the function of topoisomerase I ?
catalyzes breaks in only ONE strand of the double-stranded DNA
what is the function of topoisomerase II?
catalyzes breaks in BOTH strands of the double stranded DNA
both topoisomerases function similarly in that-
they allow the unwinding of the broken strand and catalyze the formation of new phosphodiester bonds
Telomerase is an enzyme that-
helps maintain the telomere
the telomere shortens as-
we get older
what allows the cell to distinguish intact chromosomes from broken chromosomes and protect them from degradation
telomeres
DNA damage can result from-
endogenous and exogenous causes
most DNA damage is ________ before DNA is replicated
repaired
Mutagenic agents are most effective during which phase of the cell cycle?
synthesis phase
rate of endogenous mutations is termed-
the basal mutation rate
what can contribute to errors in DNA replication?
spontaneous tautomeric shifts (changes from one natural form to another)
what are examples of an exogenous agent?
ionizing radiation, hydrocarbons, oxidative free radicals, chemotherapy
DNA repair is important because cells are-
continuously exposed to environmental mutagens and because cell mutations occur spontaneously in every cell during relplication
cells use undamaged strands of DNA as a template to
correct the mistakes in DNA
when both strands of DNA are damged, the cell uses-
the sister chromatid (2nd copy of DNA present in diploid cells) or an error-prone recovery system
Define mismatch repair-
corrects the mismatches of normal bases that fail to maintain correct DNA pairing. (usually DNA polymerase is at fault)
Proteins that can recognize a mismatch are
MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS1, PMS2 genes
mutations in MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS1, PMS2 genes can lead to a predespotition in
hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) at a young age
what corrects the spontaneous depurination and spontaneous deamination that happens to bases present in DNA
base excision repair
spontaneous deamination of cytosine in DNA causes-
a conversion to uracil (which is only in RNA)
Nucleotide excision repair is-
when an entire nucleotide is wrong
nucleotide excision repair is specifically used to remove-
UV light-induced DNA damage, and damage from environmental chemicals
UV light can form ________ from adjacent pyrimidine bases (C and G) in DNA
pyrimidine-pyrimidine dimers which can cause sunburn and skin cancer
Nucleotide excision repair is also necessary to-
recognize chemically induced bulky additions to DNA that distort the shape of DNA which causes mutations
what are two types of repair mechanisms that exist to correct DNA damage
homologous recombination and nonhomologous end joining
homologous recombination-
takes advantage of sequence information available from the unaffected homologous chromosome for proper repair of breaks
what proteins normally play a role in the homologous recombination process? mutations in these proteins/genes increase breast cancer risk.
BRCA 1 and 2
Nonhomologulos end joining is when-
the joining of ends even if the sequence is not similar. this is very error-prone and can cause mutation during repair
oncogenes are-
mutated genes that can cause cancer and primarily encode cell cycle-related proteins
what helps prevent uncontrolled dividing?
oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes help prevent uncontrolled dividing