
Using the words provided, complete each sentence describing the
digestive process.
Then place the sentences in the correct order
of occurrence.


Each term relates to either mechanical digestion/propulsion or to chemical digestion. Drag each label into the appropriate box.


Label only the organs of the digestive system that comprise the alimentary tract.


Label only the accessory organs of the digestive system.

Identify the roles of the asscessory organs and digestive tract


Place the following anatomical structures in the correct order, following the path that food would take.


Place the following anatomical structures in the correct order, following the path that food would take, starting with the stomach.


Label the layers of the digestive tract wall and associated structures.

Which layer of the digestive tract is composed of epithelial tissue and may contain folds and mucus-secreting glands?
mucosa

Complete the following sentences that describe the alimentary canal and its walls. Then place the sentences in order, listing structures/layers from deep to superficial, starting with the small intestinal lumen.

What is peristalsis?
A propulsive movement of contents of the lumen from one area to another

Label the features of the head and neck in the midsagittal section.


Label the tonsils in this midsagittal section


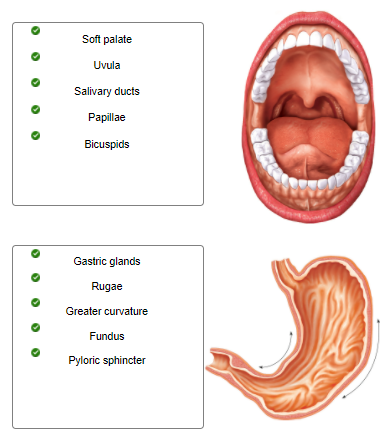
Identify whether the structures are associated with the oral cavity or the stomach by dragging each label into the appropriate position.
What structure is pulled upward during swallowing to close the opening between the nasal cavity and pharynx?
uvula

Label the upper and lower teeth.

What part of the tooth is composed of cellular tissue similar to bone, but harder?
dentin

Place the teeth in the proper order as they are arranged in the jaw, starting from the midline.


Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound.


Indicate where each enzyme (or its inactive precursor) is produced.


Classify each enzyme based on the substrate it decomposes.


The figures depict the stages of swallowing. Place the figures in the proper order.

The figure shows the posterior view of the pharynx. Label the pharyngeal muscles and nearby structures.
Label parts of the upper GI tract and associated structures.
Complete the sentences and put them in order to describe the process of deglutition (swallowing).
What is the term to describe the mass of chewed food mixed with saliva?
Bolus
Label the structures shown in the transverse section of the abdomen.
Drag each label into the appropriate position, identifying where each secretion enters the GI tract.
Where are sensory signals from the stomach and small intestine sent to trigger a vomiting reflex?
Medulla oblongata
Label the following figure of the pancreas, bile ducts, and other surrounding structures.
Complete the sentences describing regulation of pancreatic and gallbladder secretions.
Label the structures seen in the inferior view of the liver.
Label associated structures of a hepatic lobule.
Label the structures associated with blood and bile flow through the hepatic lobule.
Complete each sentence describing the blood flow to and from the liver.
Label the events that lead to bile secretion.
Drag each label onto the appropriate figure, identifying whether the structure is associated with the large or small intestine.
Complete the sentences describing the absorption of nutrients from the intestines.
In the small intestine, ______ impulses stimulate peristaltic movements, while ______ impulses inhibit movements.
Parasympathetic; sympathetic
Label the organs and membranes indicated in the anterior view of the abdominal cavity.
Label the parts of an intestinal epithelial cell.
Label the wall of the small intestine.
Complete the sentences describing the mesentery.
Label the peritoneal formations in the sagittal section of the abdominal cavity.
Label the organs seen in the sagittal section of the abdominopelvic cavity.
Label the structures associated with an intestinal villus.
Label the steps of lipid absorption.
Match the nutrient with the mode of transport for absorption.
Label the structures associated with the large intestine.
Complete the following sentences describing the movements and reflexes of the large intestine.
Deficiency symptoms can develop due to malabsorption of a vitamin or nutrient. Match the symptoms with the appropriate vitamin or nutrient.
1.What stimulates the secretion of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach?
2.The release of secretin can be stimulated by which of the following?
3. What enzyme is produced by the stomach?
4. When chyme enters the duodenum, gastric secretions increase.
5. Gastrin functions to increase the production of HCl in the stomach.
1. the smell of food, the taste of food, the distention of the stomach,
2. hydrochloric acid in chyme.
3. pepsin
4. False
5. True
Before looking at diagnostic images, take a moment to identify digestive organs in the illustration.
Label the following x-ray of the stomach.
1. What is the plane of section for the image above?
2. In the image, which direction is posterior to the section?
3. The star is on what organ?
1. Axial (transverse)
2. To the bottom of the image
3. Liver.
The enzyme __________ begins digestion of protein in the stomach.
Pepsin
Label the radiograph of the abdomen.
What part of a tooth often thins from years of brushing, teeth grinding, and eating acidic foods?
Enamel
Where are haustra found?
Large intestine
Increased peristaltic activity in the small intestine is due to __________ nervous stimulation and distension of the __________ wall.
Parasympathetic; stomach
What are the three phases of gastric activity?
Cephalic, gastric, intestinal
What is the correct order of vessels as blood flows through the liver?
Sinusoids, central vein, hepatic vein
Complete each sentence describing the sphincters located throughout the digestive tract. Then rearrange the sentences in order from proximal to distal through the digestive tract.
Complete each sentence describing the vessels that enter or leave the liver.
Identify the digestive organ shown in each image below. Then, for each label, decide which organ is being described. Drag and drop each description onto the appropriate image.

For each label, determine whether it describes the actions of secretin or the actions of cholecystokinin. Drag and drop each label into the correct category.

Determine whether each statement is true or false about the aging of the digestive system.
1. Thickening of the mucosal layer
2. Decreased absorption of nutrients
3. Increased susceptibility to infections and toxins
4. Blood supply decreases
5. Increased motility
6. Exposed dentin of teeth
1. FALSE
2. TRUE
3. TRUE
4. TRUE
5. FALSE
6. TRUE
Why does the superior part of the esophagus contain skeletal muscle instead of smooth muscle?
The first phase of swallowing is under voluntary control.
In the intestinal lumen, triglycerides are digested to fatty acids and monoglycerides. These two components are absorbed through the intestinal mucosa and enzymatically reunited to re-form triglycerides. These triglycerides, along with other lipids, enter the lacteals as part of particles called __________.
Chylomicrons
Which of the following is needed to digest fats?
Lipase

What is the organ indicated in the figure?
Pancreas

What duct is indicated in the figure?
Bile duct

What gland is indicated in the figure?
Parotid gland
Which of the following is an effect of secretin on the pancreas?
The pancreas releases more bicarbonate in the pancreatic juice.

The structure indicated in the image secretes a watery solution containing an enzyme that breaks down __________ in response to __________ stimulation.
carbohydrates; parasympathetic