Chapter 14
1) What do we mean when we use the terms monohybrid cross and
dihybrid cross?
A) A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a
dihybrid cross involves two parents.
B) A monohybrid cross
produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces two
progeny.
C) A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are
heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only
one.
D) A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation,
whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
E) A
monohybrid cross results in a 9:3:3:1 ratio whereas a dihybrid cross
gives a 3:1 ratio.
Answer: C
2) Why did the F₁ offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look
like one of the two parental varieties?
A) No genes interacted
to produce the parental phenotype.
B) Each allele affected
phenotypic expression.
C) The traits blended together during
fertilization.
D) One phenotype was completely dominant over
another.
E) Different genes interacted to produce the parental phenotype.
Answer: D
3) What was the most significant conclusion that Gregor Mendel drew
from his experiments with pea plants?
A) There is considerable genetic variation in garden peas.
B) Traits are inherited in discrete units, and are not the
results of "blending."
C) Recessive genes occur more
frequently in the F₁ generation than do dominant ones.
D) Genes
are composed of DNA.
E) An organism that is homozygous for many
recessive traits is at a disadvantage.
Answer: B
4) How many unique gametes could be produced through independent
assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 32
E) 64
Answer: B
5) The individual with genotype AaBbCCDdEE can make many kinds of
gametes. Which of the following is the major reason?
A)
segregation of maternal and paternal alleles
B) recurrent
mutations forming new alleles
C) crossing over during prophase I
D) different possible alignments of chromosomes
E) the
tendency for dominant alleles to segregate together
Answer: D
6) Why did Mendel continue some of his experiments to the F₂ or F₃
generation?
A) to obtain a larger number of offspring on which to base
statistics
B) to observe whether or not a recessive trait would
reappear
C) to observe whether or not the dominant trait would
reappear
D) to distinguish which alleles were segregating
E) to be able to describe the frequency of recombination
Answer: B
7) Which of the following differentiates between independent
assortment and segregation?
A) The law of independent assortment
requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
B) The law of segregation requires describing two or more genes
relative to one another.
C) The law of segregation requires
having two or more generations to describe.
D) The law of
independent assortment is accounted for by observations of prophase I.
E) The law of segregation is accounted for by anaphase of mitosis.
Answer: A
8) Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio
for a particular trait. What does this suggest?
A) that the
parents were true-breeding for contrasting traits
B) that the
trait shows incomplete dominance
C) that a blending of traits
has occurred
D) that the parents were both heterozygous for a
single trait
E) that each offspring has the same alleles for
each of two traits
Answer: D
9) A sexually reproducing animal has two unlinked genes, one for head
shape (H) and one for tail length (T). Its genotype is HhTt. Which of
the following genotypes is possible in a gamete from this organism?
A) tt
B) Hh
C) HhTt
D) T
E) HT
Answer: E
10) When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a
single trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an
offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Answer: C
11) Mendel accounted for the observation that traits which had
disappeared in the F₁ generation reappeared in the F₂ generation by
proposing that
A) new mutations were frequently generated in the
F₂ progeny, "reinventing" traits that had been lost in the
F₁.
B) the mechanism controlling the appearance of traits was
different between the F₁ and the F₂ plants.
C) traits can be
dominant or recessive, and the recessive traits were obscured by the
dominant ones in the F₁.
D) the traits were lost in the F₁ due
to dominance of the parental traits.
E) members of the F₁
generation had only one allele for each trait, but members of the F₂
had two alleles for each trait.
Answer: C
12) The fact that all seven of the pea plant traits studied by Mendel
obeyed the principle of independent assortment most probably indicates
which of the following?
A) None of the traits obeyed the law of segregation.
B)
The diploid number of chromosomes in the pea plants was 7.
C)
All of the genes controlling the traits were located on the same
chromosome.
D) All of the genes controlling the traits behaved
as if they were on different chromosomes.
E) The formation of
gametes in plants occurs by mitosis only.
Answer: D
13) Mendel was able to draw his ideas of segregation and independent
assortment because of the influence of which of the following?
A) His reading and discussion of Darwin's Origin of Species.
B) The understanding of particulate inheritance he learned from
renowned scientists of his time.
C) His discussions of heredity
with his colleagues at major universities.
D) His experiments
with the breeding of plants such as peas and fuchsia.
E) His
reading of the scientific literature current in the field.
Answer: E
14) Mendel's observation of the segregation of alleles in gamete
formation has its basis in which of the following phases of cell
division?
A) prophase I of meiosis
B) anaphase II of
meiosis
C) metaphase I of meiosis
D) anaphase I of meiosis
E) anaphase of mitosis
Answer: D
15) Mendel's second law of independent assortment has its basis in
which of the following events of meiosis I?
A) synapsis of
homologous chromosomes
B) crossing over
C) alignment of
tetrads at the equator
D) separation of homologs at anaphase
E) separation of cells at telophase
Answer: C
16) Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). Short tails
(T) are dominant to long tails (t). What fraction of the progeny of
crosses BbTt × BBtt will be expected to have black fur and long tails?
A) 1/16
B) 3/16
C) 3/8
D) 1/2
E) 9/16
Answer: D
17) In certain plants, tall is dominant to short. If a heterozygous
plant is crossed with a homozygous tall plant, what is the probability
that the offspring will be short?
A) 1
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 1/6
E) 0
Answer: E
18) In the cross AaBbCc × AaBbCc, what is the probability of
producing the genotype AABBCC?
A) 1/4
B) 1/8
C) 1/16
D) 1/32
E) 1/64
Answer: E
19) Given the parents AABBCc × AabbCc, assume simple dominance for
each trait and independent assortment. What proportion of the progeny
will be expected to phenotypically resemble the first parent?
A)
1/4
B) 1/8
C) 3/4
D) 3/8
E) 1
Answer: C
20) Which of the following is the best statement of the use of the
addition rule of probability?
A) the probability that two or
more independent events will both occur
B) the probability that
two or more independent events will both occur in the offspring of one
set of parents
C) the probability that either one of two
independent events will occur
D) the probability of producing
two or more heterozygous offspring
E) the likelihood that a
trait is due to two or more meiotic events
Answer: C
21) Which of the following calculations require that you utilize the
addition rule?
A) Calculate the probability of black offspring
from the cross AaBb × AaBb, when B is the symbol for black.
B)
Calculate the probability of children with both cystic fibrosis and
polydactyly when parents are each heterozygous for both genes.
C) Calculate the probability of each of four children having
cystic fibrosis if the parents are both heterozygous.
D)
Calculate the probability of a child having either sickle-cell anemia
or cystic fibrosis if parents are each heterozygous for both.
E)
Calculate the probability of purple flower color in a plot of 50
plants seeded from a self-fertilizing heterozygous parent plant.
Answer: D
22) In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in
the heterozygous (Rr) offspring of red (RR) and white (rr)
homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in
the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white?
A) red × white
B) roan × roan
C) white × roan
D) red × roan
E) The answer cannot be determined from the
information provided.
Answer: B
23) Which of the following describes the ability of a single gene to
have multiple phenotypic effects?
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple alleles
C) pleiotropy
D) epistasis
Answer: C
24) Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive
system, and other organs, resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing
difficulties to recurrent infections. Which of the following terms
best describes this?
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple
alleles
C) pleiotropy
D) epistasis
E) codominance
Answer: C
25) Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
A) pink flowers in snapdragons
B) the ABO blood group in
humans
C) Huntington's disease in humans
D) white and
purple flower color in peas
E) skin pigmentation in humans
Answer: E
26) Hydrangea plants of the same genotype are planted in a large
flower garden. Some of the plants produce blue flowers and others pink
flowers. This can be best explained by which of the following?
A) the knowledge that multiple alleles are involved
B) the
allele for blue hydrangea being completely dominant
C) the
alleles being codominant
D) the fact that a mutation has
occurred
E) environmental factors such as soil pH
Answer: E
27) Which of the following provides an example of epistasis?
A) Recessive genotypes for each of two genes (aabb) results in
an albino corn snake.
B) The allele b17 produces a dominant
phenotype, although b1 through b16 do not.
C) In rabbits and
many other mammals, one genotype (cc) prevents any fur color from
developing.
D) In Drosophila (fruit flies), white eyes can be
due to an X-linked gene or to a combination of other genes.
E)
In cacti, there are several genes for the type of spines.
Answer: C
28) Most genes have many more than two alleles. However, which of the
following is also true?
A) At least one allele for a gene always produces a dominant
phenotype.
B) Most of the alleles will never be found in a
live-born organism.
C) All of the alleles but one will produce
harmful effects if homozygous.
D) There may still be only two
phenotypes for the trait.
E) More than two alleles in a genotype
is considered lethal.
Answer: D
29) How could you best predict the maximum number of alleles for a
single gene whose polypeptide product is known?
A) Search the
population for all phenotypic variants of this polypeptide.
B)
Count the number of amino acids in the polypeptide.
C) Mate all
known genotypes and collect all possible offspring different from the
parents.
D) Measure the rate of new mutations in the species and
estimate the number since it first evolved.
E) Count the number
of DNA nucleotides that are in the code for the polypeptides.
Answer: E
30) An ideal procedure for fetal testing in humans would have which
of the following features?
A) the procedure that can be
performed at the earliest time in the pregnancy
B) lowest risk
procedure that would provide the most reliable information
C)
the procedure that can test for the greatest number of traits at once
D) a procedure that provides a three-dimensional image of the
fetus
E) a procedure that could test for the carrier status of
the fetus
Answer: A
31) A scientist discovers a DNA-based test for one allele of a
particular gene. This and only this allele, if homozygous, produces an
effect that results in death at or about the time of birth. Of the
following, which is the best use of this discovery?
A) Screen
all newborns of an at-risk population.
B) Design a test for
identifying heterozygous carriers of the allele.
C) Introduce a
normal allele into deficient newborns.
D) Follow the segregation
of the allele during meiosis.
E) Test school-age children for
the disorder.
Answer: B
32) An obstetrician knows that one of her patients is a pregnant
woman whose fetus is at risk for a serious disorder that is detectable
biochemically in fetal cells. The obstetrician would most reasonably
offer which of the following procedures to her patient?
A) CVS
B) ultrasound imaging
C) amniocentesis
D) blood
transfusion
E) X-ray
Answer: C
33) The frequency of heterozygosity for the sickle-cell anemia allele
is unusually high, presumably because this reduces the frequency of
malaria. Such a relationship is related to which of the following?
A) Mendel's law of independent assortment
B) Mendel's law
of segregation
C) Darwin's explanation of natural selection
D) Darwin's observations of competition
E) the malarial
parasite changing the allele
Answer: C
34) Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive human disorder in which an
individual cannot appropriately metabolize a particular amino acid.
The amino acid is not otherwise produced by humans. Therefore, the
most efficient and effective treatment is which of the following?
A) Feed them the substrate that can be metabolized into this
amino acid.
B) Transfuse the patients with blood from unaffected
donors.
C) Regulate the diet of the affected persons to severely
limit the uptake of the amino acid.
D) Feed the patients the
missing enzymes in a regular cycle, such as twice per week.
E)
Feed the patients an excess of the missing product.
Answer: C
35) Hutchinson-Gilford progeria is an exceedingly rare human genetic
disorder in which there is very early senility and death, usually from
coronary artery disease, at an average age of approximately 13.
Patients, who look very old even as children, do not live to
reproduce. Which of the following represents the most likely
assumption?
A) All cases must occur in relatives; therefore,
there must be only one mutant allele.
B) Successive generations
of a family will continue to have more and more cases over time.
C) The disorder may be due to mutation in a single
protein-coding gene.
D) Each patient will have had at least one
affected family member in a previous generation.
E) The disease
is autosomal dominant.
Answer: C
36) One of two major forms of a human condition called
neurofibromatosis (NF 1) is inherited as a dominant gene, although it
may range from mildly to very severely expressed. If a young child is
the first in her family to be diagnosed, which of the following is the
best explanation?
A) The mother carries the gene but does not express it at all.
B) One of the parents has very mild expression of the gene.
C) The condition skipped a generation in the family.
D)
The child has a different allele of the gene than the parents.
Answer: B
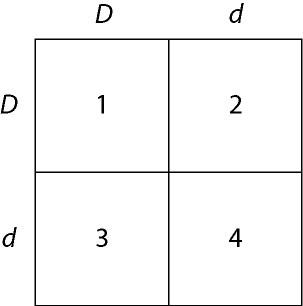
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D.
Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants
with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A
true-breeding dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one,
and the F₁ offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted
outcome of the F₂ is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in Figure
14.1, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to
each box within the square.
37) Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants with dark
leaves?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 4
only
E) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: E

In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D.
Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants
with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A
true-breeding dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one,
and the F₁ offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted
outcome of the F₂ is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in Figure
14.1, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to
each box within the square.
38) Which of the boxes correspond to plants with a heterozygous
genotype?
A) 1
B) 1 and 2
C) 1, 2, and 3
D) 2
and 3
E) 2, 3, and 4
Answer: D

In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D.
Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants
with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A
true-breeding dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one,
and the F₁ offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted
outcome of the F₂ is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in Figure
14.1, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to
each box within the square.
39) Which of the plants will be true-breeding?
A) 1 and 4
only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, 3, and 4
D) 1 only
E) 1 and 2 only
Answer: A

The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
40) What is the genotype of individual II-5?
A) WW
B) Ww
C) ww
D) WW or ww
E) ww or Ww
Answer: C

The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
41) What is the likelihood that the progeny of IV-3 and IV-4
will have the trait?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D)
75%
E) 100%
Answer: C

The following question refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 14.2 for
a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W.
Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
42) What is the probability that individual III-1 is Ww?
A) 3/4
B) 1/4
C) 2/4
D) 2/3
E) 1
Answer: E

Use the following pedigree (Figure 14.3) for a family in which
dark-shaded symbols represent individuals with one of the two major
types of colon cancer. Numbers under the symbols are the individual's
age at the time of diagnosis.
43) What is the genotype of the deceased individual in
generation II?
A) homozygous for a gene for colon cancer
B) homozygous for both cancer alleles from his mother
C)
heterozygous for a gene for colon cancer
D) affected by the same
colon cancer environmental factor as his mother
E) carrier of
all of the several known genes for colon cancer
Answer: C

Use the following pedigree (Figure 14.3) for a family in which
dark-shaded symbols represent individuals with one of the two major
types of colon cancer. Numbers under the symbols are the individual's
age at the time of diagnosis.
44) In each generation of this family after generation I, the
age at diagnosis is significantly lower than would be found in
nonfamilial (sporadic) cases of this cancer (~ 63 years). What is the
most likely reason?
A) Members of this family know to be checked for colon cancer
early in life.
B) Hereditary (or familial) cases of this cancer
typically occur at earlier ages than do nonfamilial forms.
C)
This is pure chance; it would not be expected if you were to look at a
different family.
D) This cancer requires mutations in more than
this one gene.
E) Affected members of this family are born with
colon cancer, and it can be detected whenever they are first tested.
Answer: B

Use the following pedigree (Figure 14.3) for a family in which
dark-shaded symbols represent individuals with one of the two major
types of colon cancer. Numbers under the symbols are the individual's
age at the time of diagnosis.
45) From this pedigree, how does this trait seem to be
inherited?
A) from mothers
B) as an autosomal recessive
C) as a result of epistasis
D) as an autosomal dominant
E) as an incomplete dominant
Answer: D

Use the following pedigree (Figure 14.3) for a family in which
dark-shaded symbols represent individuals with one of the two major
types of colon cancer. Numbers under the symbols are the individual's
age at the time of diagnosis.
46) The affected woman in generation IV is thinking about her
future and asks her oncologist (cancer specialist) whether she can
know whether any or all of her children will have a high risk of the
same cancer. The doctor would be expected to advise which of the
following?
I. genetic counseling
II. prenatal diagnosis when/if she
becomes pregnant
III. testing to see whether she has the allele
IV. testing to see whether her future spouse or partner has the
allele
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) I,
II, and III only
E) III and IV only
Answer: C
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has
red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F₁
individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and
location assort independently.
47) If 1,000 F₂ offspring resulted from the cross, approximately
how many of them would you expect to have red, terminal flowers?
A) 65
B) 190
C) 250
D) 565
E) 750
Answer: B
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has
red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F₁
individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and
location assort independently.
48) Among the F₂ offspring, what is the probability of plants
with white axial flowers?
A) 9/16
B) 1/16
C) 3/16
D) 1/8
E) 1/4
Answer: C
Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a
black female with a brown male, results can be either all black
puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow
puppies.
49) These results indicate which of the following?
A)
Brown is dominant to black.
B) Black is dominant to brown and to
yellow.
C) Yellow is dominant to black.
D) There is
incomplete dominance.
E) Epistasis is involved.
Answer: E
Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a
black female with a brown male, results can be either all black
puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow
puppies.
50) How many genes must be responsible for these coat colors in
Labrador retrievers?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Answer: B
Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a
black female with a brown male, results can be either all black
puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow
puppies.
51) In one type cross of black × black, the results were as
follows:
9/16 black
4/16 yellow
3/16 brown
The
genotype aabb must result in which of the following?
A) black
B) brown
C) yellow
D) a lethal result
E) white
Answer: C
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a
red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple
offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with
long being the dominant characteristic.
52) If true-breeding red long radishes are crossed with
true-breeding white oval radishes, the F₁ will be expected to be which
of the following?
A) red and long
B) red and oval
C)
white and long
D) purple and long
E) purple and oval
Answer: D
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a
red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple
offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with
long being the dominant characteristic.
53) In the F₂ generation of the above cross, which of the
following phenotypic ratios would be expected?
A) 9:3:3:1
B) 9:4:3
C) 1:1:1:1
D) 1:1:1:1:1:1
E) 6:3:3:2:1:1
Answer: E
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a
red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple
offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with
long being the dominant characteristic.
54) The flower color trait in radishes is an example of which of
the following?
A) a multiple allelic system
B) sex linkage
C) codominance
D) incomplete dominance
E) epistasis
Answer: D
Drosophila (fruit flies) usually have long wings (+) but mutations in
two different genes can result in bent wings (bt) or vestigial wings
(vg).
55) If a homozygous bent wing fly is mated with a homozygous
vestigial wing fly, which of the following offspring would you expect?
A) all +bt +vg heterozygotes
B) 1/2 bent and 1/2 vestigial
flies
C) all homozygous + flies
D) 3/4 bent to 1/4
vestigial ratio
E) 1/2 bent and vestigial to 1/2 normal
Answer: A
Drosophila (fruit flies) usually have long wings (+) but mutations in
two different genes can result in bent wings (bt) or vestigial wings
(vg).
56) If flies that are heterozygous for both the bent wing gene
and the vestigial wing gene are mated, what is the probability of
offspring with bent wings only?
A) 1/8
B) 3/8
C) 1/4
D) 9/16
E) 3/16
Answer: E
Tallness (T) in snapdragons is dominant to dwarfness (t), while red
(R) flower color is dominant to white (r). The heterozygous condition
results in pink (Rr) flower color.
57) A dwarf, red snapdragon is crossed with a plant homozygous
for tallness and white flowers. What are the genotype and phenotype of
the F1 individuals?
A) ttRr—dwarf and pink
B) ttrr—dwarf
and white
C) TtRr—tall and red
D) TtRr—tall and pink
E) TTRR—tall and red
Answer: D
Tallness (T) in snapdragons is dominant to dwarfness (t), while red
(R) flower color is dominant to white (r). The heterozygous condition
results in pink (Rr) flower color.
58) If snapdragons are heterozygous for height as well as for
flower color, a mating between them will result in what ratio?
A) 9:3:3:1
B) 6:3:3:2:1:1
C) 1:2:1
D)
27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1
E) 9:4:3
Answer: B
Skin color in a certain species of fish is inherited via a single
gene with four different alleles.
59) How many different types of gametes would be possible in
this system?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
Answer: C
Skin color in a certain species of fish is inherited via a single
gene with four different alleles.
60) One fish of this type has alleles 1 and 3 (S1S3) and its
mate has alleles 2 and 4 (S2S4). If each allele confers a unit of
color darkness such that S1 has one unit, S2 has two units, and so on,
then what proportion of their offspring would be expected to have five
units of color?
A) 1/4
B) 1/5
C) 1/8
D) 1/2
E) 0
Answer: D
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses
with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous
recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second
gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous
recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all.
61) The relationship between genes S and N is an example of
A) incomplete dominance.
B) epistasis.
C) complete
dominance.
D) pleiotropy.
E) codominance.
Answer: B
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses
with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous
recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second
gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous
recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all.
62) A cross between a true-breeding sharp-spined cactus and a
spineless cactus would produce
A) all sharp-spined progeny.
B) 50% sharp-spined, 50% dull-spined progeny.
C) 25%
sharp-spined, 50% dull-spined, 25% spineless progeny.
D) all
spineless progeny.
E) It is impossible to determine the
phenotypes of the progeny.
Answer: A
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cactuses
with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous
recessive ss cactuses have dull spines. At the same time, a second
gene, N, determines whether or not cactuses have spines. Homozygous
recessive nn cactuses have no spines at all.
63) If doubly heterozygous SsNn cactuses were allowed to
self-pollinate, the F2 would segregate in which of the following
ratios?
A) 3 sharp-spined:1 spineless
B) 1 sharp-spined:2
dull-spined:1 spineless
C) 1 sharp-spined:1 dull-spined:1
spineless
D) 1 sharp-spined:1 dull-spined
E) 9
sharp-spined:3 dull-spined:4 spineless
Answer: E
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes, Y and
B, one for pigment on the outside and one for the inside of the
feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or
Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white.
64) A blue budgie is crossed with a white budgie. Which of the
following results is not possible?
A) green offspring only
B) yellow offspring only
C) blue offspring only
D)
green and yellow offspring
E) a 9:3:3:1 ratio
Answer: D
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes, Y and
B, one for pigment on the outside and one for the inside of the
feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or
Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white.
65) Two blue budgies were crossed. Over the years, they produced
22 offspring, 5 of which were white. What are the most likely
genotypes for the two blue budgies?
A) yyBB and yyBB
B)
yyBB and yyBb
C) yyBb and yyBb
D) yyBB and yybb
E)
yyBb and yybb
Answer: C
A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O
positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that
shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the
alleles R and r, respectively. A third gene for the MN blood group has
codominant alleles M and N.
66) Which of the following is a possible partial genotype for
the son?
A) IBIB
B) IBIA
C) ii
D) IBi
E) IAIA
Answer: D
A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O
positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that
shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the
alleles R and r, respectively. A third gene for the MN blood group has
codominant alleles M and N.
67) Which of the following is a possible genotype for the
mother?
A) IAIA
B) IBIB
C) ii
D) IAi
E) IAIB
Answer: D
A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O
positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that
shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the
alleles R and r, respectively. A third gene for the MN blood group has
codominant alleles M and N.
68) Which of the following is a possible phenotype for the
father?
A) A negative
B) O negative
C) B positive
D) AB negative
E) impossible to determine
Answer: C
A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O
positive and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a trait that
shows simple dominance over Rh negative and is designated by the
alleles R and r, respectively. A third gene for the MN blood group has
codominant alleles M and N.
69) If both children are of blood type M, which of the following
is possible?
A) Each parent is either M or MN.
B) Each
parent must be type M.
C) Both children are heterozygous for
this gene.
D) Neither parent can have the N allele.
E) The
MN blood group is recessive to the ABO blood group.
Answer: A
Humanoids on the newly explored planet Brin (in a hypothetical galaxy
in ~50 years from the present) have a gene structure similar to our
own, but many very different plants and animals.
70) One species of a small birdlike animal has an extremely
variable tail length, which is a highly polymorphic trait. Geneticists
have come to realize that there are eight separate genes for tail
length per haploid genome, with each gene having two alleles. One
allele for each gene (a, b, and so on) increases the length by 1 cm,
whereas the other allele (a2, b2, and so on) increases it by 0.5 cm.
One bird was analyzed and found to have the following genotype:
a1a1b2b2c1c2d1d2e2e2f1f2g1g1h1h2
What is the length of its
tail?
A) 6 cm
B) 8 cm
C) 12 cm
D) 24 cm
E) 36 cm
Answer: C
Humanoids on the newly explored planet Brin (in a hypothetical galaxy
in ~50 years from the present) have a gene structure similar to our
own, but many very different plants and animals.
71) One species of green plant, with frondlike leaves, a
spine-coated stem, and purple cup-shaped flowers, is found to be
self-pollinating. Which of the following is true of this species?
A) The species must be haploid.
B) Its reproduction is
asexual.
C) All members of the species have the same genotype.
D) Some of the seeds would have true-breeding traits.
E)
All of its dominant traits are most frequent.
Answer: D
Humanoids on the newly explored planet Brin (in a hypothetical galaxy
in ~50 years from the present) have a gene structure similar to our
own, but many very different plants and animals.
72) If the environmental parameters, such as temperature,
humidity, atmosphere, sunlight, and so on, are mostly Earthlike, which
of the following do you expect of its types of leaves, stems, and
flowers?
A) The genes for them would have originated on Earth.
B) Genes for these traits would have a common ancestor with
those from Earth.
C) Such plants could be safely eaten by
humans.
D) Genotypes for these traits would be identical to
Earth plants with the same traits.
E) Phenotypes would be
selected for or against by these
Answer: E
Humanoids on the newly explored planet Brin (in a hypothetical galaxy
in ~50 years from the present) have a gene structure similar to our
own, but many very different plants and animals.
73) Marfan syndrome in humans is caused by an abnormality of the
connective tissue protein fibrillin. Patients are usually very tall
and thin, with long spindly fingers, curvature of the spine, sometimes
weakened arterial walls, and sometimes ocular problems, such as lens
dislocation. Which of the following would you conclude about Marfan
syndrome from this information?
A) It is recessive.
B) It
is dominant.
C) It has a late age of onset (> 60).
D)
It is pleiotropic.
E) It is epistatic.
Answer: D