A&P Final part 2
If you find an error
let me know by leaving a comment, so I can fix it! Good Luck!!
If the length of the absolute refractory period in cardiac muscle
cells was the same as it is for skeletal muscle cells ________.
A) it would be much longer before cardiac cells could respond to
a second stimulation
B) contractions would last as long as the refractory period
C) tetanic contractions might occur, which would stop the heart's pumping action
D) it would be less than 1-2 ms
C) tetanic contractions might occur, which would stop the heart's pumping action
During contraction of heart muscle cells ________.
A)
the action potential is initiated by voltage-gated slow calcium channels
B) some calcium enters the cell from the extracellular space and triggers the release of larger amounts of calcium from intracellular stores
C) the action potential is prevented from spreading from cell to cell by gap junctions
D) calcium is prevented from entering cardiac fibers that have been stimulated
B) some calcium enters the cell from the extracellular space and triggers the release of larger amounts of calcium from intracellular stores
Small muscle masses attached to the chordae tendineae are the
________.
A) trabeculae carneae
B) pectinate muscles
C)
papillary muscles
D) venae cavae
C) papillary muscles
Damage to the ________ is referred to as heart block.
A) SA node
B) AV valves
C) AV bundle
D) AV node
D) AV node
Select the correct statement about the structure of the heart wall.
A) The fibrous skeleton forms the bulk of the heart.
B) Connective tissue in the heart wall aids in the conduction of the action potential.
C) The heart chambers are lined by the endomysium.
D) The myocardium is the layer of the heart that actually contracts.
D) The myocardium is the layer of the heart that actually contracts.
Select the correct statement about the function of myocardial cells.
A) The entire heart contracts as a unit or it does not
contract at all.
B) Each cardiac muscle cell is innervated by a sympathetic nerve ending so that the nervous system can increase heart rate.
C) The refractory period in skeletal muscle is much longer than that in cardiac muscle.
D) The influx of potassium ions from extracellular sources is the initiating event in cardiac muscle contraction.
A) The entire heart contracts as a unit or it does not contract at all.
Compared to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle ________.
A) has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium
B) lacks striations
C) has more nuclei per cell
D) cells are larger than skeletal muscle cells
A) has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium
Which of the following is not an age-related change affecting the
heart?
A) atherosclerosis
B) decline in cardiac reserve
C) fibrosis of cardiac muscle
D) thinning of the valve flaps
D) thinning of the valve flaps
The left ventricular wall of the heart is thicker than the right wall
in order to ________.
A) accommodate a greater volume of blood
B) expand the thoracic cage during diastole
C) pump blood with greater pressure
D) pump blood through a smaller valve
C) pump blood with greater pressure
The tricuspid valve is closed ________.
A) while the ventricle is in diastole
B) when the
ventricle is in systole
C) while the atrium is contracting
D) by the movement of blood from atrium to ventricle
B) when the ventricle is in systole
The term for pain associated with deficient blood delivery to the
heart that may be caused by the transient spasm of coronary arteries
is ________.
A) ischemia
B) pericarditis
C) myocardial infarct
D) angina pectoris
D) angina pectoris
Select the correct statement about the heart valves.
A)
The mitral valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
B) The tricuspid valve divides the left atrium from the left ventricle.
C) Aortic and pulmonary valves control the flow of blood into the heart.
D) The AV valves are supported by chordae tendineae so that regurgitation of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction does not occur.
D) The AV valves are supported by chordae tendineae so that regurgitation of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction does not occur.
If cardiac muscle is deprived of its normal blood supply, damage
would primarily result from ________.
A) decreased delivery of oxygen
B) a decrease in the
number of available mitochondria for energy production
C) a
lack of nutrients to feed into metabolic pathways
D) an
inadequate supply of lactic acid
A) decreased delivery of oxygen
The P wave of a normal electrocardiogram indicates ________.
A) ventricular repolarization
B) ventricular
depolarization
C) atrial repolarization
D) atrial depolarization
D) atrial depolarization
The absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine is enhanced by increasing the surface area of the mucosal lining. Which of the following accomplish this task?
A) plicae circulares and intestinal villi
B) the vast array of digestive enzymes
C) Brunner's glands
D) the rugae
A) plicae circulares and intestinal villi
Surgical cutting of the lingual frenulum would occur in which part of
the body?
A) tongue
B) esophagus
C) nasal cavity
D) salivary glands
A) tongue
Pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme, is secreted by the ________.
A) chief cells of the stomach
B) parietal cells of the
duodenum
C) Brunner's glands
D) goblet cells of the
small intestine
A) chief cells of the stomach
When we ingest large molecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, and
proteins, they must undergo catabolic reactions whereby enzymes split
these molecules. This series of reactions is called ________.
A) absorption
B) secretion
C) chemical digestion
D) mechanical digestion
C) chemical digestion
The ________ contains lobules with sinusoids (lined with macrophages)
that lead to a central venous structure.
A) liver
B)
spleen
C) pancreas
D) stomach
A) liver
The function of the goblet cells is to ________.
A) absorb
nutrients from digested food and store them for future use
B)
produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the
effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion
C)
secrete buffers in order to keep the pH of the digestive tract close
to neutral
D) provide protection against invading bacteria and
other disease-causing organisms that enter the digestive tract in food
B) produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion
In addition to storage and mechanical breakdown of food, the stomach ________.
A) initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
B) is the first site where absorption takes place
C) is the only place where fats are completely digested
D) is the first site where chemical digestion of starch takes place
A) initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by which of the secretory cells of the stomach?
A) chief cells
B) parietal cells
C) serous cells
D) mucous neck cells
B) parietal cells
Which vitamin requires intrinsic factor in order to be absorbed?
A) B12
B) K
C) A
D) C
A) B12
The capillaries that nourish the epithelium and absorb digested
nutrients lie in the ________.
A) muscularis mucosae
B)
serosa
C) adventitia
D) lamina propria
D) lamina propria
The sheets of peritoneal membrane that hold the digestive tract in
place are called ________.
A) mesenteries
B) lamina
propria
C) serosal lining
D) mucosal lining
A) mesenteries
Peristaltic waves are ________.
A) segmental regions of the
gastrointestinal tract
B) churning movements of the
gastrointestinal tract
C) pendular movements of the
gastrointestinal tract
D) waves of muscular contractions that
propel contents from one point to another
D) waves of muscular contractions that propel contents from one point to another
________ is (are) not important as a stimulus in the gastric phase of gastric secretion.
A) Distension
B) Carbohydrates
C) Peptides
D) Low acidity
B) Carbohydrates
Hormones or paracrines that inhibit gastric secretion include
________.
A) ACh
B) secretin
C) gastrin
D) histamine
B) secretin
From the esophagus to the anal canal, the walls of every organ of the alimentary canal are made up of the same four basic layers. Arrange them in order from the lumen.
A) muscularis externa, serosa, mucosa, and submucosa
B) serosa, mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis externa
C) submucosa, serosa, muscularis externa, and mucosa
D) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
D) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
Which of the following is not true of saliva?
A) cleanses the
mouth
B) contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of proteins
C) moistens food and aids in compacting of the bolus
D)
dissolves food chemicals so they can be tasted
B) contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of proteins
Triglycerides found in foods such as butterfat molecules in milk are
split by a specific enzyme in preparation for absorption. Which of the
following enzymes is responsible?
A) rennin
B) pepsin
C) lipase
D) cholecystokinin
C) lipase
Chemical digestion in the small intestine involves ________.
A) a significant amount of enzyme secretion by the intestinal mucosa
B) cholecystokinin (CCK), an intestinal hormone responsible for gallbladder contraction
C) secretions from the spleen that contain all enzymes necessary for complete digestion
D) bile salts that help emulsify carbohydrates so that they can be easily digested by enzymatic action
B) cholecystokinin (CCK), an intestinal hormone responsible for gallbladder contraction
Which of the following enzymes is specific for proteins?
A) dextrinase
B) amylase
C) trypsin
D) lipase
C) trypsin
Which of the following is an essential role played by large intestine bacteria?
A) produce gas
B) absorb bilirubin
C) synthesize vitamin K and B-complex vitamins
D) synthesize vitamins C and D
C) synthesize vitamin K and B-complex vitamins
The chemical and mechanical processes of food breakdown are called ________.
A) digestion
B) absorption
C) ingestion
D) secretion
A) digestion
There are three phases of gastric secretion. The cephalic phase occurs ________.
A) before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
B) immediately after food enters the stomach, preparing the small intestine for the influx of a variety of nutrients
C) at the end of a large meal, and the juices secreted are powerful and remain in the GI tract for a long period of time
D) when the meal is excessively high in acids and neutralization is required
A) before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
The terminal portion of the small intestine is known as the ________.
A) duodenum
B) ileum
C) jejunum
D) pyloric sphincter
B) ileum
Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the
liver were severely damaged?
A) lipids
B) carbohydrates
C) proteins
D) starches
A) lipids
Which of the following produce intrinsic factor?
A) parietal cells
B) zymogenic cells
C) mucous neck
cells
D) enteroendocrine cells
A) parietal cells
Select the correct statement about digestive processes.
A) Enterogastrone is a hormone that helps increase gastric motility.
B) Pepsin is an enzyme produced by the stomach for the purpose of starch digestion.
C) Chyme entering the duodenum can decrease gastric motility via the enterogastric reflex.
D) All commonly ingested substances are significantly absorbed by the mucosa of the stomach.
C) Chyme entering the duodenum can decrease gastric motility via the enterogastric reflex.
The mechanical and chemical receptors that control digestive activity are located ________.
A) in the glandular tissue that lines the organ lumen
B) in the walls of the tract organs
C) in the pons and medulla
D) only in the esophagus because this is the only part of the tract that needs to change to accommodate food passage
B) in the walls of the tract organs
A fluid secreted into the small intestine during digestion that
contains cholesterol, emulsification agents, and phospholipids is
________.
A) bile
B) pancreatic juice
C)
intestinal juice
D) gastric juice
A) bile
The layer of the digestive tube that contains blood vessels,
lymphatic nodes, and a rich supply of elastic fibers is the ________.
A) mucosa
B) submucosa
C) muscularis externa
D) serosa
B) submucosa
The salivary glands are composed of which two types of secretory cells?
A) goblet cells and squamous epithelial cells
B) parietal cells and glial cells
C) serous cells and mucous cells
D) cuboidal epithelium and ciliated columnar cells
C) serous cells and mucous cells
Chyme is created in the ________.
A) mouth
B) stomach
C) esophagus
D) small intestine
B) stomach
The lamina propria is composed of ________.
A) loose
connective tissue
B) dense irregular connective tissue
C)
dense regular connective tissue
D) reticular connective tissue
A) loose connective tissue
Which hormone causes an increased output of enzyme-rich pancreatic
juice and stimulates gallbladder contraction to release bile?
A) gastrin
B) secretin
C) cholecystokinin CCK
D) gastric inhibitor peptide
C) cholecystokinin CCK
You have just eaten a meal high in complex carbohydrates. Which of
the following enzymes will help to digest the meal?
A) gastrin
B) amylase
C) cholecystokinin
D) trypsin
B) amylase
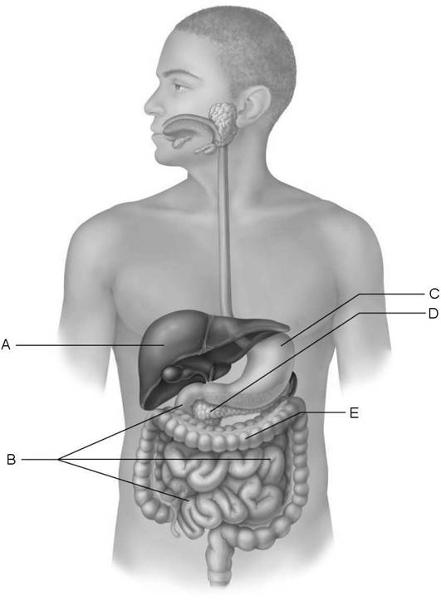
Using Figure 23.3, match the following:
17) Produces enzymes that break down all categories of
foodstuffs.
18) Increases surface area for absorption via villi and
microvilli.
19) Bacteria process undigested chyme from the small intestine.
20) Only digestive structure with three muscle layers.
21) Receives blood via the hepatic portal system.
22) Contains the brush border enzymes that complete digestion of
carbohydrates and proteins.
17) D
18) B
19) E
20) c
21) A
22) B
Match the following:
A) Peristalsis
B) Absorption
C) Digestion
D) Hydrolysis
13) Wavelike smooth muscle contractions that move foodstuffs
through the alimentary tube.
14) Chemical or mechanical process of breaking down foodstuffs
to substances that can be absorbed.
15) Enzymatic breakdown of any type of food molecule.
16) Process by which the products of digestion pass through the
lumen of the gastrointestinal tract into the blood or lymph.
13. A
14. C
15. D
16. B
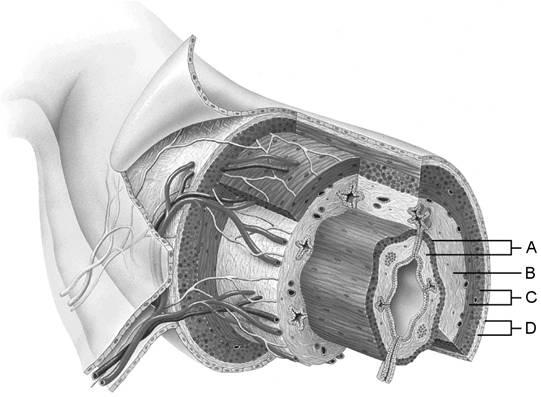
Using Figure 23.1, match the following:
1) Mucosa.
2) Smooth muscle layer.
3) Serosa.
1) A
2) C
3) D
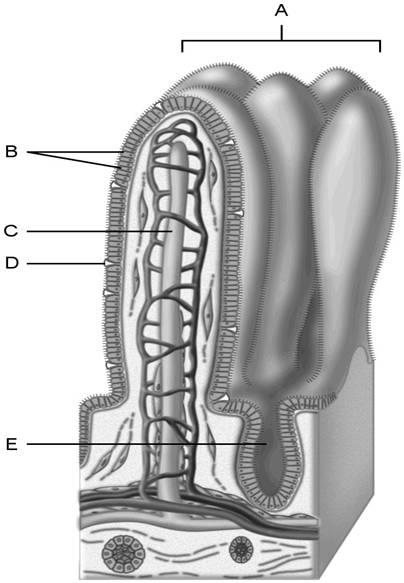
Using Figure 23.2, match the following:
8) Absorptive cells that line the intestinal tract.
9) Structures that increase the absorptive area of the small
intestine.
10) Wide lymph capillary located in the villus.
8) B
9) A
10) C
Which of the following determines lung compliance?
A) airway opening
B) flexibility of the thoracic cage
C) muscles of inspiration
D) alveolar surface tension
D) alveolar surface tension
Possible causes of hypoxia include ________.
A) too little
oxygen in the atmosphere
B) obstruction of the esophagus
C) taking several rapid deep breaths
D) getting very cold
A) too little oxygen in the atmosphere
Select the correct statement about the pharynx.
A) The pharyngeal tonsil is located in the laryngopharynx.
B) The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx.
C) The laryngopharynx blends posteriorly into the nasopharynx.
D) The palatine tonsils are embedded in the lateral walls of the nasopharynx.
B) The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx.
The nose serves all the following functions except ________.
A) as a passageway for air movement
B) as the initiator
of the cough reflex
C) warming and humidifying the air
D) cleansing the air
B) as the initiator of the cough reflex
Complete the following statement using the choices below. Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is
A) less than the pressure in the atmosphere.
B) greater than
the pressure in the atmosphere.
C) equal to the pressure in the
atmosphere.
D) greater than the intra-alveolar pressure.
B) greater than the pressure in the atmosphere.
The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, type I
and type II. The function of type II is to ________.
A) secrete
surfactant
B) trap dust and other debris
C) replace
mucus in the alveoli
D) protect the lungs from bacterial invasion
A) secrete surfactant
Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________.
A) pressure within the pleural cavity
B) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs
C) negative pressure in the intrapleural space
D) difference between atmospheric pressure and respiratory pressure
B) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs and through all
cell membranes by ________.
A) osmosis
B) diffusion
C) filtration
D) active transport
B) diffusion
41) Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for gas
exchange?
A) alveolar sacs
B) alveoli
C)
respiratory bronchioles
D) alveolar ducts
B) alveoli
Which of the following is not an event necessary to supply the body with O2 and dispose of CO2?
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) blood pH adjustment
C)
internal respiration
D) external respiration
B) blood pH adjustment
Which of the choices below determines the direction of respiratory
gas movement?
A) solubility in water
B) partial pressure
gradient
C) the temperature
D) molecular weight and size
of the gas molecule
B) partial pressure gradient
Tidal volume is air ________.
A) remaining in the lungs after
forced expiration
B) exchanged during normal breathing
C) inhaled after normal inspiration
D) forcibly expelled after normal expiration
B) exchanged during normal breathing
Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the
trachea?
A) surface tension of water
B) surfactant
C) cartilage rings
D) pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
C) cartilage rings
The most powerful respiratory stimulus for breathing in a healthy
person is ________.
A) loss of oxygen in tissues
B)
increase of carbon dioxide
C) pH (acidosis)
D) pH (alkalosis)
B) increase of carbon dioxide
The lung volume that represents the total volume of exchangeable air is the ________.
A) tidal volume
B) vital capacity
C) inspiratory capacity
D) expiratory reserve volume
B) vital capacity
Respiratory control centers are located in the ________.
A)
midbrain and medulla
B) medulla and pons
C) pons and
midbrain
D) upper spinal cord and medulla
B) medulla and pons
The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is
called ________.
A) reserve air
B) expiratory reserve
C) inspiratory reserve
D) vital capacity
C) inspiratory reserve
Nerve impulses from ________ will result in inspiration.
A) the ventral respiratory group
B) the chemoreceptor center
C) Broca's center
D) the preoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus
A) the ventral respiratory group
The loudness of a person's voice depends on the ________.
A)
thickness of vestibular folds
B) length of the vocal folds
C) strength of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles
D) force
with which air rushes across the vocal folds
D) force with which air rushes across the vocal folds
The statement, "in a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the
sum of the individual partial pressures of gases in the mixture"
paraphrases ________.
A) Henry's law
B) Boyle's law
C) Dalton's law
D) Charles' law
C) Dalton's law
For gas exchange to be efficient, the respiratory membrane must be
________.
A) at least 3 micrometers thick
B) 0.5 to 1
micrometer thick
C) between 5 and 6 micrometers thick
D)
The thickness of the respiratory membrane is not important in the
efficiency of gas exchange.
B) 0.5 to 1 micrometer thick
Which statement about CO2 is incorrect?
A) Its concentration in the blood is decreased by hyperventilation.
B) Its accumulation in the blood is associated with a decrease in pH.
C) More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs.
D) CO2 concentrations are greater in venous blood than arterial blood.
C) More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs.
Which of the choices below is not a role of the pleura?
A) allows the lungs to inflate and deflate without friction
B) helps divide the thoracic cavity into three chambers
C) helps limit the spread of local infections
D) aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs
D) aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs
The relationship between the pressure and volume of gases is given by
________.
A) Boyle's law
B) Henry's law
C)
Charles' law
D) Dalton's law
A) Boyle's law
Which of the choices below is not a functional process performed by the respiratory system?
A) pulmonary ventilation
B) transport of respiratory gases
C) external respiration
D) pulmonary respiration
B) transport of respiratory gases
Which of the following is not a stimulus for breathing?
A) rising carbon dioxide levels
B) rising blood pressure
C) arterial Po2 below 60 mm Hg
D) arterial pH resulting
from CO2 retention
B) rising blood pressure
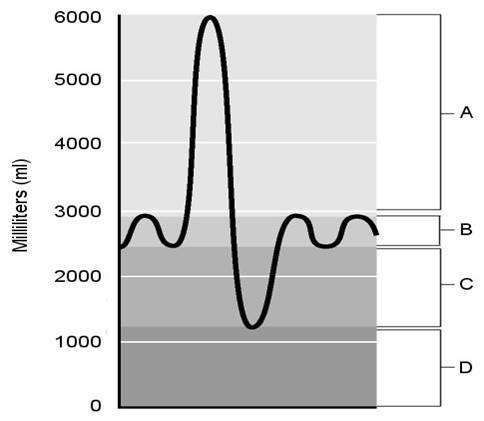
6) Tidal volume.
7) Inspiratory reserve volume.
8) Residual volume.
9) Expiratory reserve volume.
10) Air that does not participate in the exchange of gases.
6) b
7) a
8) d
9) c
10) d
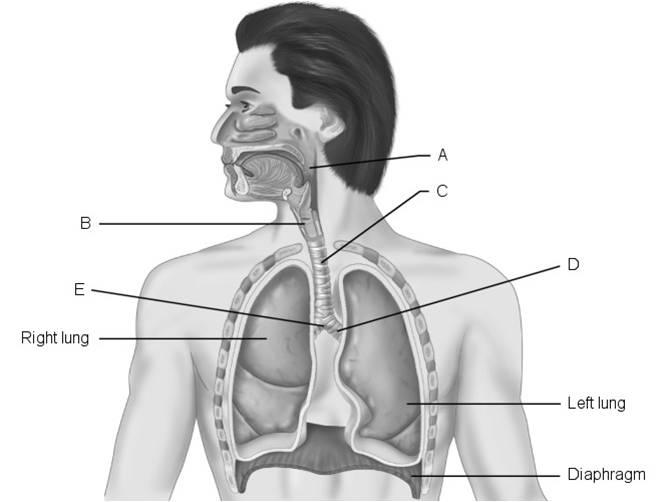
Using Figure 22.1, match the following:
1) Main (primary)
bronchus.
2) Pharynx.
3) Larynx.
4) Carina of trachea.
5) Trachea.
1) d
2) a
3) b
4) e
5) c
A) Respiratory bronchioles
B) Type I cells
C) Segmental
bronchi
D) Alveolar duct
11) No exchange of gases
occurs here.
12) Where the respiratory zone of the lungs begins.
13) Composed of simple squamous epithelium.
14) Terminates in alveoli.
15) The respiratory membrane is composed of fused basement membrane of the capillary walls and ________.
11) c
12) a
13) b
14) d
15) b
Match the following:
A) Epicardium
B) Parietal layer
C) Myocardium
D) Endocardium
14) The inner lining of the heart.
15) Heart muscle.
16) Serous layer covering the heart muscle.
17) The outermost layer of the serous pericardium.
14) A
15) C
16) D
17) B
Match the following:
A) Purkinje fibers
B) AV
bundle
C) SA node
D) AV node
18) The
pacemaker of the heart.
19) Found in the
interventricular septum.
20) The point in the conduction
system of the heart where the impulse is temporarily delayed.
21) damage to it is a heart block
18) C
19) B
20) D
21) D
A) Aortic valve
B) Tricuspid valve
22) Prevents backflow into the left ventricle.
23) Prevents backflow into the right atrium.
22) A
23) B
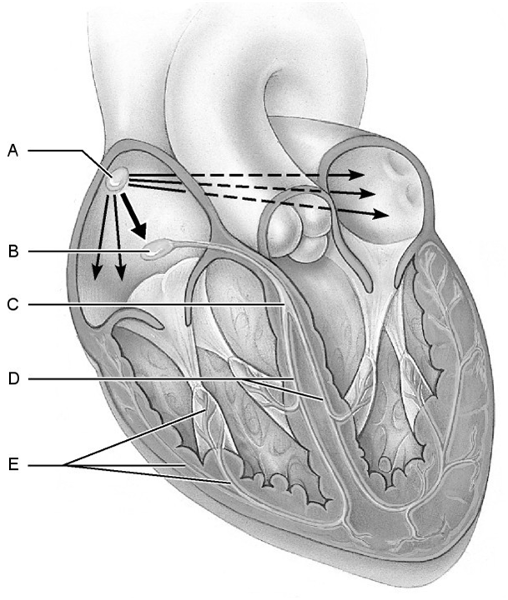
match the following:
1) Purkinje fibers.
2) SA node.
3) AV
bundle.
4) AV node.
5) Bundle branches.
1. Answer: E
2. Answer: A
3. Answer: C
4. Answer: B
5. Answer: D
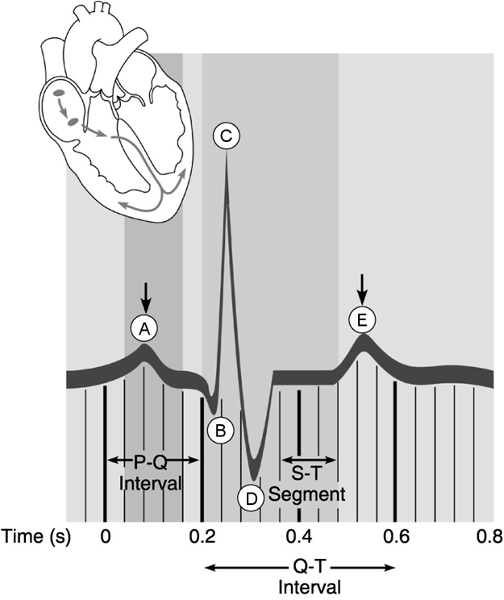
match the following:
6) Atrial depolarization.
7) Point after which pressure begins to rise in the aorta.
8) Ventricular repolarization.
9) Point
that represents the "dup" sound made by the heart.
6. Answer: A
7. Answer: D
8. Answer: E
9. Answer: E
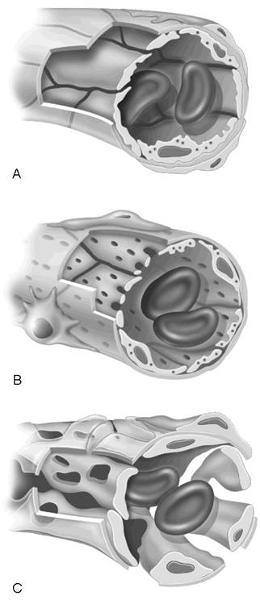
match the following:
1) Sinusoid capillary.
2) Capillary found in endocrine organs that allows hormones to
gain rapid entry into the blood.
3) Capillary with
intercellular clefts found in the skin and muscles.
4)
Capillary that may contain Kupffer cells in the lining.
5) Capillary found where active capillary absorption of filtrate occurs.
1) C
2) B
3) A
4) C
5) B
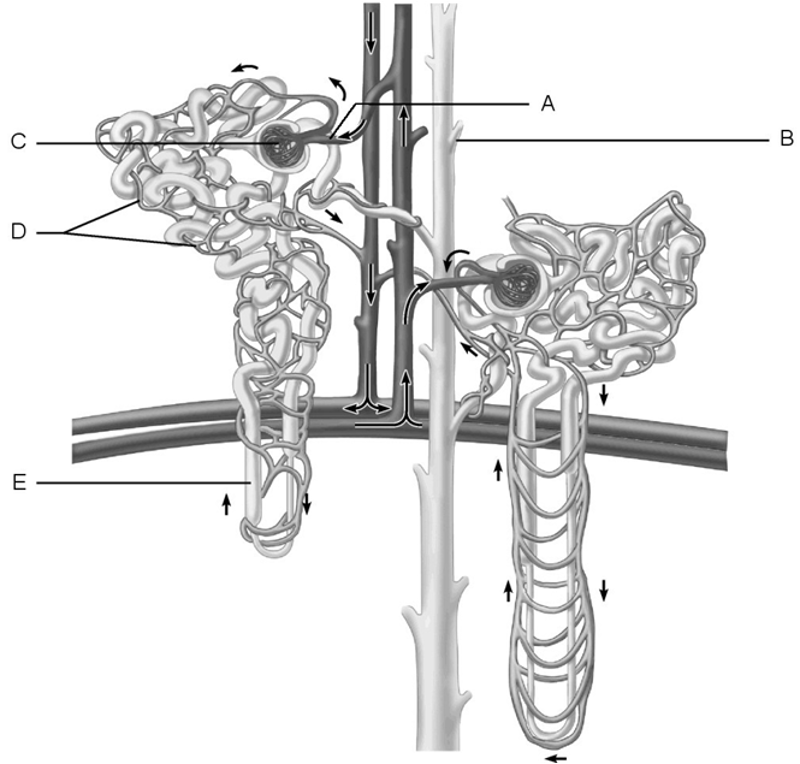
1) Glomerulus.
2) Afferent arteriole.
3) Collecting duct.
4) Loop of Henle.
5) Peritubular capillaries.
6) Structure most closely associated with granular cells.
7) Medulla of the kidney.
1. Answer: C
2. Answer: A
3. Answer: B
4. Answer: E
5. Answer: D
6. Answer: A
7. Answer: E
Match the following:
A) Site at which most of the tubular reabsorption occurs.
B) Blood supply that directly receives substances from the
tubular cells.
C) Site of filtrate formation.
D) Site
that drains the distal convoluted tubule.
17) Proximal convoluted tubule.
18) Glomerulus.
19) Peritubular capillaries.
20) Collecting duct.
Answers:
17) A
18) C
19) B
20) D
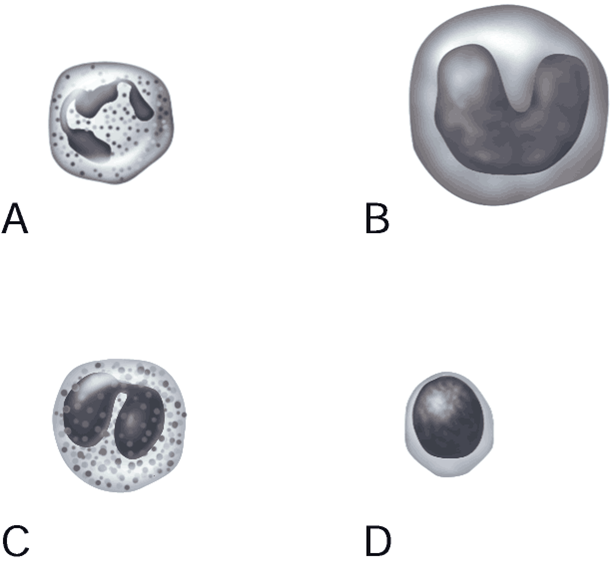
1) Monocyte.
2) Lymphocyte.
3) Eosinophil.
4) Neutrophil.
5) Most common white blood cell found in whole blood.
6) Mounts an immune response by direct cell attack or via
antibodies.
7) Kills parasitic worms.
8) Becomes a macrophage.
9) Main bacteria killer during acute infections.
1) Answer: B
2) Answer: D
3) Answer: C
4) Answer: A
5) Answer: A
6) Answer: D
7) Answer: C
8) Answer: B
9) Answer: A
Match the following:
A) Leukemia
B) Anemia
C)
Embolism
1) Cancerous condition involving white blood cells
2) Condition in which blood has abnormally low oxygen-carrying capacity.
3) Free-floating thrombus in the bloodstream
1) a
2) b
3) c
The source of blood carried to capillaries in the myocardium would be
the ________.
A) coronary sinus
B) fossa ovalis
C) coronary
arteries
D) coronary veins
C) coronary arteries