The Urinary System
________ ______________ main function is to keep the body in homeostasis by controlling the composition and volumes of the blood
Urinary System
__________________ means external or posterior to the peritoneum
Retroperitoneal
The Kidneys lie in a ______________ position (between the dorsal body wall and the parietal peritoneum).
Retroperitoneal
Kidneys ...
- _________ and ______________ selected amounts of water and solutes.
- __________ selected amounts of varios wastes (________, __________)
- Remove
- Restore
- Excrete
- Urea and creatinine
Kidneys...
- Help to regulate blood pressure by balancing __________ levels.
- water
- Because their position next to ____________, right kidneys is __________ than the left.
- Both are protected by the ________ and __________ pairs of ribs.
- liver
- lower
- 11th
- 12th pair of ribs
The kidneys are _______ -shaped, as they are retroperitoneal; ______ layers of tissue protect and support the kidneys.
- _________________ is a fibrous coat.
- _________________ fat deposits around the kidney (12% body fat).
- _________________ fibrous C.T. which anchors the kidneys to the dorsal wall
- bean
- three
- Fibrous Capsule
- Parietal Fat Capsule or Adipose capsule
- Renal Fascia
Kidneys are sectioned in:
- Hilum
- Renal Sinus
- Renal Cortex
- Renal Medulla
__________ is the indentation where the blood vessels enter and exit from the kidneys , and the ureters ________ from the renal pelvis.
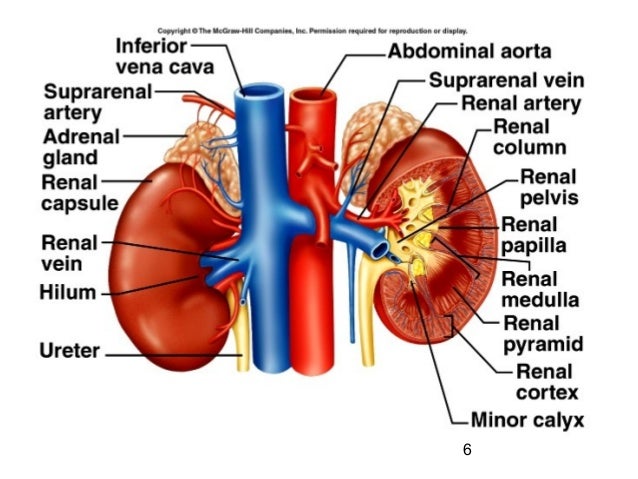
- Hilum
- exit
Renal __________ is a cavity in the Kidney in which the renal pelvis can be found.
- Sinus
____________ is the area or the kidneys from the base of the renal pyramid to the renal capsule
- Cortex
________________ is the area which contains the renal pyramids.
Medulla
- ________________ ______________ is a "Funnel-shaped tube", continuous with the ureter leaving the hilium.
- It is a large central urine collecting area.
- Branching extensions of this structure form the _________.
- Renal Pelvis
- Calyxes
__________________ are the triangular-shaped structures in the medulla which appear _______ due to the presence of collecting ducts and blood vessels.
- Renal Pyramids
- striated
_____ __________ is the tip of the pyramid; the collecting ducts opening is located here.
- Renal Papella
_______ __________ are long portions of the cortex between the pyramids, located in the medullar area
- Renal Collumns
____________ are cup-like extensions of the renal pelvis which encompass each of the renal papillae.
Calyxes
These last areas or structures form part of the __________________ , and are here listed again:
- Renal Pyramid
- Renal papillae
- Renal Column
- Renal Pelvis
- Renal Calyxes (major and minor)
Renal Medulla
_______________ are the functional portion of the kidneys which contains the nephrons (cortex and renal pyramids)
Parenchyma
Which is the functional UNIT of the kidney

The Nephrons
A nephron functions are:
- Filtration
- Reabsorption
- Secretion
Filtration takes place in the _____________ and processes a cell-free and protein-free __________.
- corpuscle
- fitrate
Reabsorption (reclaims what the body needs to keep) is the process of selectively moving substances from the filtrate back into the _________. It takes place in the renal ___________ and collecting __________. Reclaims almost everything from the Filtrate:
- Water
- Salts
- glucose
- AAs
What happens with what is not reabsorbed:
Becomes URINE
Secretion is the process of selectively moving substances from the ___________ into the ______________. It also takes place in the renal ___________ and collecting __________.
- blood
- filtrate
- tubule
- ducts
Nephrons consist of two portions:
- Renal Corpuscle
- Renal Tubule
Renal Corpuscle consists of
- Glomerular capsule
- Glomerulus
Renal Tubule consists of...
- Proximal convoluted tubules
- Distal convoluted tubules
- Loop of Henle
What it the other name for Loop of Henle:
Loop of Nephron
- Glomerular Capsule, also known as _________ ___________ is
composed of:
- parietal layer composed of ____________ ___________ epithelium; which invaginates and becomes _____________ _________
- Bowman's capsule
- simple squamous epithelium
- Visceral layer
- _______________ is a capillary tuft within the spherical glomerular capsule.
- Differs from all other capillary beds in the body in that it is both fed and drained by _____________
- BLOOD enters via the ____________ arteriole, and exits via the ___________ arteriole.
- Glomerulus
- Arterioles
- Afferent
- Efferent
- ________ _________ are wider than _______ _________
- This arrangements maintain the ________ __________ in the glomerulus that is needed for filtration.
- Afferent arterioles
- Efferent artrioles
- High Pressure
The walls of __________ ____________ tubule are formed by cuboidal epithelial cells with dense microvilli. Just as the intestine, this brush border increases the surface area and capacity for REABSORBING water and solutes from the filtrate and secreting substances into it.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
The U-shape __________ loop, also known as The Loop of ________, has _________ and ___________ limbs. Cells have microvilli also (true or false)
- Nephron
- Henle
- descending and
- ascending
- True
- The proximal part of the descending limb is continuous with the ____________ tubule. The rest of the descending limb (the thin limb) consists of _________ ___________ epithelium.
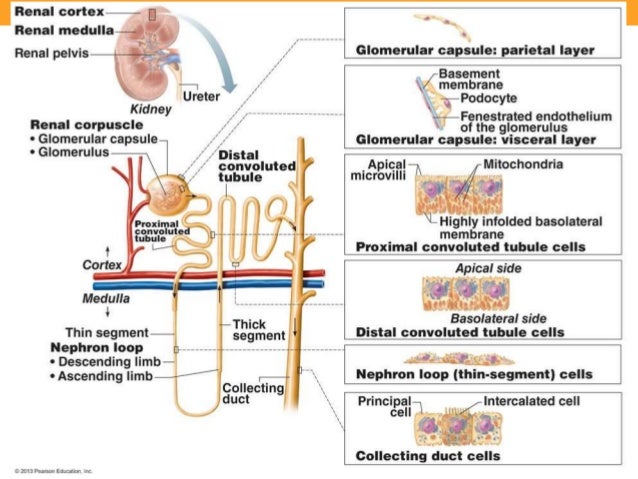
- Proximal
- simple squamous epithelium
_________ ______________ Tubule is made of ____________ cells, almost entirely lack of microvilli.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule
- Cuboidal
___________ duct is a duct where many distal convoluted tubules join and deposit their __________ secretion.
- Collective Duct
- urine
____________ duct is the end of the collecting duct as it terminates at the end of the renal papilla
- Papillary Duct
Nephrons are generally divided into 2 major groups, or there are 2 type of Nephrons :
- Cortical Nephron
- Juxtamedullary Nephron
Cortical Nephron, account _____% of the nephrons. They have their glomerulus in the portion of the _______ and its loop of Henle penetrates into the _________.
- 25%
- Cortex
- Medulla
Juxtamedullary Nephrone originate its glomerulus deep in the ________ and its loop of Henle penetrates the ________ almost to the renal __________.
- Cortex
- Medulla
- Renal Papillae
HISTOLOGY OF THE NEPHRON
1- The endothelial is make of ________ ___________ epithelium which comprises the glomerural ________ ______. This capillary has ___________ or pores ___ or ____ microns in the diameter. These pores are too _______ for blood cells to pass through.
- simple squamous epithelium
- capillary tuft
- finestra
- .5 to 1.0 microns
- small
2- ____________________ is an extracellular fibours glycoprotein matrix which acts as a ______________ membrane. It functions to ________ _____ large molecules from leaving the plasma.
- Basement membrane
- dialyzing membrane (purification)
- screen out
3- _____________ _________ is formed by the protocytes of the visceral layer of the ____________ ____________.
- Extensions from podocytes called ______________, which mean _________ __________ form filtration slits.
- A slit membrane extends across the filtration slits and restricts the passage of ___________ ___________.
- Filtration Slits
- Glomerulus Capsule
- pedicels
- little feet
- medium-size molecules
- Blood circulation to the kidneys is under ____________ control which regulates the ____________ of the capillaries
- _______ __________ transport ____% of the cardiac output (______) to the kidkeys per minute, which represents about _________ ml/min to be cleanse.
- Motor
- diameter
- Renal Arteries
- 25
- blood
- 1,200 ml/min
Blood Pathway through Kidneys
- Renal arteries branch into
- __________ ________ which in the turn branch into
- Interlobal arteries (between pyramids) which branch to form the...
- _________ _________ (at base of the pyramids) which branch to form the
- __________ ________ _________ (in the cortex)
- Renal Artery
- Segment arteries
- Interlobal Arteries
- Arcuate Arteries
- Cortical Radiate Arteries
6- The __________ branch off and enter the glomerular capsule to form the ...
7- ________________ where filtration happens
8- The efferent arteriole now leaves the _____________ and branches into a capillary network called the _____________ ____________
6-Afferent arteries
7-Glomerulus
8-Glomerulus
- Peritubular Capillaries (surrounding the proximal and distal convoluted tubules)
- Vasa Recta (surrounding the loop of the nephrones)
9- Peritubular Capillaries and Vasa Recta unite to form the ___________ ___________ vein.
10- then the _____________ veins
11- Interlobal veins
12- Segmental Vens
13- Renal Veins
9- Cortical Radiate Vein
10- Arcuate veins
11- Interlobal veins
12- segmental veins
13-Renal Veins
In the _______________ apparatus the fluid in the DCT are thought to play a role in controlling blood flow through the afferent arterioles (__________)
- Juxtaglomerulus Apparatus
- feedback
- Afferent arterioles are made of _______________ cells.
- Which contain granules called ___________.
- Its release causes formation of _____________ which constricts the afferent arteriole, there-by controlling blood flow to the nephrone.
_of_a_nephron_p_9681318457485220.jpg)
- Juxtaglomerular cells
- Renin
- angiotensin
- If the flow rate is too slow, the Macula Densa will signal the afferent arteriole to _____________
- If the flow rate is too FAST, the Macula Densa will signal the afferent arteriole to _____________
- Dialate
- Constrict
Physiology of the Nephrons
Nephrons functions are 3:
- Control blood concentration and volume by removing selected amounts of water and solutes.
- Helps to regulate blood pH
- Removes toxic waste from the blood
The main 3 processes require for Urine Formation are:
- Glomerular Filtration
- Tubular resorption
- Tubular secretion
- _________________ occurs by forcing the fluids and dissolved substances through a membrane by an outside pressure.
- Filtration occurs in _________-______ membrane.
- The pressure is because _________ pressure
- The fluid is called _________________
- Filtration
- Endothelial-capsular membrane
- Blood
- Filtrate
- _______________ of renal corpuscles for filtering blood occurs
because of:
- A capsule of highly __________ glomerular capillaries presents a vast surface area for filtration.
- The _________-_________ membrane receives from afferent arterioles __________.
- efferent arteriole is ________ in diameter that the afferent; which brings _________ to outflow of blood from the glomerulus.
- The adaptation
- coiled
- Endothelial-capsule membrane
- blood
- smaller
- resistance
- The glomerular capillaries have the _______ Blood Pressure of all capillaries (_________).
- The endothelial-capsular membrane is very thin (___________) and separates __________ and ___________ from water and smaller solutes to form _____________.
- Highest
- 40-60 mm Hg
- .1 micrometers
- blood cells
- large proteins
- Filtrate
To find the levels of filtration according to hydrostatic pressure, we need to consider these different types of Pressures:
- NFP
- CHP
- BOP
- BGHP
NFP stands for
Net (effective) Filtration Pressure
NFP tells the ____________ which causes filtrate to be formed (to leave the capillary and enter into the glomerular space).
Pressure
CHP stands for
Capsular Hydrostatic Pressure
CHP is the __________ or ___________ which a fluid under pressure exerts on the walls of a container (capsular wall)
force or resistance
BOP stands for
Blood Colloidal Osmotic Pressure
The pressure which develops from water movement into a contained solution. It walways develops in the solution with the higher concentration of solutes.
Blood Colloidal Osmotic Pressure
Since blood has more proteins than the filtrate. Then, water moves _________ the filtrate and _________ the blood vessels.
- out of
- back into
GHP stands for
Glomerular Hydrostatic Pressure
The blood pressure in the glomerulus. This pressure is pushing _________ the walls of the capsule and the filtrate which is already there.
- Glomerular Hydrostatic Pressure
- Tubular Resorption is the movement of the _________ back into the ____________ of the _________ capillaries or ____________ Recta.
- Some of the materials reabsorbed are:
- ___
- ___
- ___
- Filtrate
- Blood
- Peritubular capillaries
- Vasa Recta
- water, glucose, AAs, Na+, K+, Ca+, Cl-
Tm stands for ____________
Tubular Max
- Tubular Max is the _______ amount that can be ______, and the rest is _________.
- This allows the body to ___________ most of its nutrients.
- Maximum
- reabsorbed
- voided
- retain
Keeping the plasma proteins in the capillaries maintains the________ ___________, which prevents the _______ of all its water to the capsular space.
Colloid osmotic (oncotic) Pressure.
The presence of proteins or ______ _______ cells indicate
- Red Blood C.
- A problem with the filtration membrane.
___________ is only partially resorbed, and is derived from the normal breakdowns of amino acids.
Urea
Water accounts for about ____% of urine volume; the remaining ___% consists of solutes.
- The largest component of urine by weight , apart from water is ___________
- 95%
- 5%
- Urea
- ___________ reabsorption probably involves a carrier system
- Na+ ions are resorbed actively from the __________ _________ Tubules back into the ____________ capillaries.
- Glucose
- proximal convoluted
- peri-tubular
- _____________- ____________ tubules contain ___________ which increase the surface area approximately 20x.
- Proximal Convoluted T.
- microvilli
- As Na+ is actively transported through the cells, and into the ___________ capillaries; now that Na+ ion concentrations inside the cell is ______ than in the lumen, so a Na+ ion diffusion gradient is established from the _______ to the insid________ of the cell. Reason why the blood now is slightly more electropositive than the filtrate.
- peri-tubular capillaries
- higher
- tubule
- inside
- Cl- ions follow ______ ions out of the tubule by _________ attraction (also _____ and ______).
- Na+
- electrostatic
- Phosphorus and HCO3- (bicarbonate)
________ follows since the Proximal C.T. are always permeable to it.
H2O
- Due to Na+ being transported ______ ____ the blood, the osmotic pressure of the blood becomes higher than the filtrate.
- Water follows the ______ into the blood to re-establish _________ equilibrium. This is called _______________ Reabsorption.
- back into
- Na+
- Osmotic
- Obligatory
- When blood-water concentration is too low, ______ is released. Which stands for:
- ADH
- Antidiuretic Hormone
- ADH makes the membrane of the _____ and _________ duct _____ permeable to water _______ reabsorption by carrier molecule. This is called _____________ reabsorption.
- DCT
- Collective Ducts
- more
- Facultative
About _____ - ______ ml (volume) are eliminated per day and is influenced by:
- 1000-1800
- Blood Pressure
- Blood Concentrations
- Diet
- Temperature
- Diuretics
- Mental state
- general health
- Tubular secretion is a process which adds materials from the blood in peritubular capillary to the filtrate:___________________________,
- It moves ____________ substances
K+, H+, ammonium ions, urea, creatinine, penicillin, etc.
Selectively
Tubular secretion functions to ______ the body of certain materials as well as help to control the ____________
- rid
- blood pH
The body tries to maintain a pH of ___________
7.35 to 7.45
Normal urine has a pH of
6 pH
To raise the blood in renal tubules secrete _____ ions and _____________ into the filtrate.
- H+
- ammonium ions
Which is the main site of secretion:
PCT
Urine eventually excreted contain both __________ and _____________ substances. With one major exception.
- filtrrated
- secreted
- K+
____________ ________________ is a process which allows the kidneys to secrete hypertonic urine or hypotonic urine.
Countercurrent Multiplier Mechanism
____________ deliver urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
Ureters
- Ureters are aprox. ___ to ___ inches long.
- ___________, hydrostatic pressure and __________ help move urine
- 10 to 12
- Peristalsis
- gravity
In a cross-sectional view of ureters we find different layers of:
- Mucosa
- Muscularis
- Fibrous
Mucosa in the ureter is formed of:
- Transitional epithelium
- Lamina propia
Muscularis is formed of
- longitudinal layer
- circular layer
Fibrous
which holds tu ureters with Adventitia
______________ is a hollow muscular organ held in place by the peritoneum.
Urinary bladder
Urinary bladder consists of 4 coats
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis or Detrusor muscle
- Peritoneum
1- Mucosa is composed of ___________ ______________, contains folds called ______________ which allow the urinary bladder to _____________ as it fills with urine.
- Transitional epithelium
- ragae
- stretch
2- Submucosa is a ____ layer which holds the _______ layer to the ______ coat.
- Connective Tissue
- Mucosa
- Muscular
3- Muscularis or _________ ________ consists of __ layers of ________:
- _____ Longitudinal, ____ -________ and outer __________.
- _________ urethral sphincter
- _________ urethral sphincter
- Detrusor muscle
- 3 layers of
- muscles
- Inner
- middle circular
- longitudinal
- Internal
- External
4- Peritoneum is the external ___________ covering
Serous
________________ is the expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder; urination; voiding.
Micturition
The average urinary bladder capacity is _______
400 to 800 ml
_______________ a smooth mucosal layer; the ureters drain into the urinary bladder at the base corners of this layer (at top)
Trigone
________________ is a tube extending from the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice through which urine is expelled.
Urethra
_____________ is only partially resorbed, and is derived from the normal breakdowns of amino acids.
Urea
_________ occurs when toxic levels of urea in the blood due to the kidneys not functioning correctly
Uremia
____________ is an infection in renal pelvis and calyxes
Pyelitis
_____________ is an infection or inflammation the entire kidney
Pyelonephritis
______ ________ when rapid weight loss removes fat causing the kidney to fall to a lower position
Renal Ptosis
________________ is the back up of urine from ureter obstruction.
Hydronephrosis