The Skull

identify this.
what nerve passes through here?
infraorbital nerve (small sensory branch of V2, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve)
which foramen are associated with the sphenoid bone?

ovale, spinosum, rotundum, optic canal and superior orbital fissure
What is the mneumonic to remember cranial nerves?
Oh! Oh! Oh! to touch and feel very good velvet. Ah, heavenly.
name the bones of the bony orbit
(7)

frontal, lacrimal, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, palatine, sphenoid
know lacrimal groove
what is the mneumonic to help with remembering if cranial nerves are sensory, motor or both?
some say money matters but my brother says big brains matter most
name the twelve cranial nerves along with each type (sensory, motor or both)
olfactory sensory
optic sensory
oculomotor motor
trochlear motor
trigeminal both
v1 opthalmic sensory
v2 maxillary sensory
v3 mandibular both
abducens motor
facial both
vestibulocochlear sensory
glossopharyngeal both
vagus both
accessory motor
hypoglossal motor
name each cranial nerve and the foramen through which it enters the skull
olfactory cribiform foramina in cribiform plate
optic optic canal (foramen)
oculomotor superior orbital fissure
trochlear superior orbital fissure
trigeminal jugular foramen
v1 opthalmic superior orbital fissure
v2 maxillary foramen rotundum
v3 mandibular foramen ovale
abducens superior orbital fissure
facial internal acoustic meatus, through facial canal, exists at stylomastoid foramen
vestibulocochlear internal acoustic meatus
glossopharyngeal jugular foramen
vagus jugular foramen
accessory jugular foramen
hypoglossal hypoglossal canal

What goes through these holes?

olfactory nerve; cribiform foramina

what is this? what passes through here?
(two things)

optic canal/foramen; optic nerve and opthalmic artery

what is this? what passes through here?

optic canal; optic nerve and opthalmic artery

what is the blank? which nerves pass through here? which vein passes through here?

superior orbital fissure; oculomotor, trochlear, opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, and abducens nerve
opthalmic vein

what is the blank? which nerves pass through here? which vein passes through here?

superior orbital fissure; oculomotor, trochlear, opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, and abducens nerve
opthlamic vein

what is this? what nervepasses here?
foramen rotundum; maxillary division of trigeminal nerve

label these


label this


label this


what is this? which nerves pass through here?
foramen ovale; mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve

what is this? which nerves pass through here?
foramen ovale; mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve

what is this? which nerve passes here?
internal acoustic meatus; facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)

what is this? what nerve passes through here?
stylomastoid foramen; facial nerve

what is this? what nerves passes through here?
jugular foramen; glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), accessory (XI)

what is this? what passes through here?
jugular foramen; glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), accessory (XI) and internal jugular vein

what is this? what nerves passes through here?
hypoglossal canal; hypoglossal nerve (XII)

what is this? what nerves passes through here?
hypoglossal canal; hypoglossal nerve (XII)

what is this? what passes through here?
middle meningeal artery; foramen spinosum

what is this? what passes through here?
middle meningeal artery; foramen spinosum

what is this? what passes through here?
foramen lacerum; nothing, it is filled with cartilage after birth

what is this? what passes through here?
foramen lacerum; nothing it is filled with cartilage after birth

what is this? what passes through here?
foramen magnum; vertebral arteries and spinal cord

what is this? what passes through here?
foramen magnum; vertebral arteries and spinal cord

what is this? what passes through here?
carotid canal; internal carotid artery

what is this? what passes through here?
carotid canal; internal carotid artery
how many bones make up the skull? How many form the braincase and how many form the face?
22; braincase 8 14 face
what are the seven associated bones of the skull>
six are auditory ossicles enclosed in the temporal bones and one is the hyoid bone
what eight bones make up the cranium?
occipital bone, parietal bone, frontal bone, right and left temporal bones, sphenoid, and ethmoid
what 14 bones make up the face?
2 maxillae, 2 palatine bones, 2 nasal bones, 2 inferior nasal conchae, 2 zygomatic bones, 2 lacrimal bones, vomer, and mandible
which suture is found between the two parietal bones and the occipital bone
lambdoidal sture

what is this?
lambdoidal suture
which suture is located along the midsagittal plane?
sagittal suture

what is this?
sagittal suture
which nerve provides sensation for forehead?
supraorbital nerve from opthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve

what bone is this?
frontal bone
which bone forms root/superior aspect of bony orbit?
frontal bone

what is this?
superciliary arch (of the frontal bone)

what is this?
supraorbital notch/foramen
which muscle originates on superior and inferior temporal lines?
temporalis muscle

what are these?
superior and inferior temporal line

what is this?
parietal bone

what is this?
parietal bone
____________ are two bones in the human skull which, when joined together at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the cranium.
parietal bones

what is this?
occipital bone

what is this?
occipital bone
the ______ articulate with the _______ to perform the nodding motion of the head
occipital condyles; C1
which muscle originates on the external occipital protuberance?
trapezius
vertebral arteries pass through the ________ to form the posterior circulation of the brain
transverse foramen
What forms the skull to jaw joint?
say features and bones
mandibular fossa of the temporal bone and condylar process of the mandible

label the greys



what forms the zygomatic process? which part is most anterior?

the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and temporal process of zygomatic bone; temporal process of zygomatic bone

label the greys


label the greys

what are the paired and unpaired bones of the cranium?

unpaired: frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid
paired: temporal, parietal
what composes the calvaria?
frontal bone, parietal bones, occipital bone
what are the four major sutures of the skull?
coronal, squamosal, lambdoidal, and sagittal
what type of joint is found between bones of the skull?
fibrous joints - sutures

which suture is in red?

coronal suture

which suture is in red?

squamosal suture
what forms the ptergoid process?
the lateral and medial plates of the sphenoid bone
in which part of the temporal bone are structures of hearing found?
petrous part
what sits in the sella turcica? in which bone is the sella turcica found?
the ptuitary gland; sphenoid bone

label the greys


label the foramen and what passes through them


label the structures


label foramen and list what passes through


label


label

which foramen are associated with the sphenoid bone?
ovale, spinosum, rotundum,
which parts of the brain sit in the middle cranial fossa?
left and right temporal lobes
what part of the brain is found in the anterior cranial fossa?
frontal lobe
what parts of the brain are found in the posterior cranial fossa?
cerebellum and brainstem
which foramen are associated with the ethmoid bone?
the cribiform foramina the ethmoid bone

label

perpendicular plate participates in the formation of _________
the nasal septum
what bones form the anterior cranial fossa?

mostly frontal bone, some ethmoid and the lesser wing of sphenoid
what bones form the middle cranial fossa?

greater wing of sphenoid bone, parietal bone, and half of temporal bone
what bones form the posterior cranial fossa?

occipital bone, half of temporal bone, and some parietal
what are the paired and unpaired bones of the face?
paired:
nasal
maxillae
lacrimal
zygomatic
palatine
inferior nasal concha
UNPAIRED:
vomer
mandible

what is this?
maxillary bones

label features of the maxillary bones
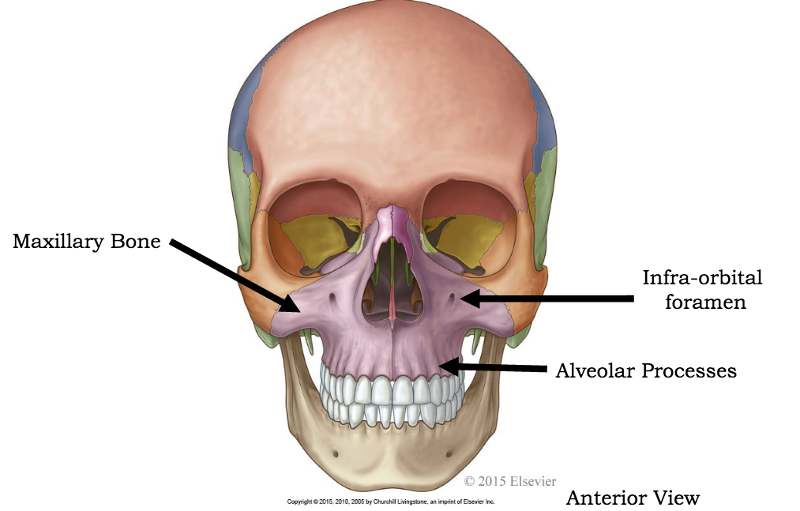
what passes through the infraorbital foramen?
infraorbital nerve (small sensory branch of V2, maxillary division of trigeminal nerve)
infraorbital artery
infraorbital vein
what forms the hard palate?

palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plates of the palatine bones



what is the bone in green?
nasal bone

label

name the bones of the bony orbit
frontal, lacrimal, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, palatine, sphenoid

label bones of bony orbit


what is this bone?
zygomatic

what is this area called? which muscle sits here?
temporal fossa; temporalis muscle
what area is inferior and deep to zygomatic arch? many arteries and nerves pass through here
infratemporal fossa

what is this bone? which gland is found superior and lateral?
lacrimal bone; lacrimal gland
which bones form outer rim, lateral to medial of the bony orbit? which bones form inner part of bony orbit?
front, zygomatic, maxillary, sphenoid
ethmoid lacrimal palatine
which bone forms inferior portion of the nasal septum?
vomer

name this bone
vomer

name this bone
vomer
what is the nasal septum composed of?
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, vomer bone, and septal cartilage

label

what passes through the mental foramen?
mental nerve, division of V3 (mandibular division) of trigeminal nerve
where is the genoid tubercle? what is on the genoid tubercle?
on the inner side of the mandible, behind mental protuberance. muscles of the tongue insert here.
which nerve supplies lower teeth with sensation?
inferior alveolar nerve, division of mandibular nerve (v3)

what is this?
mandibular foramen
describe pathway of inferior alveolar nerve
branches from the mandibular nerve and runs through mandibular foramen. exits through mental foramen as mental nerve
soft fibrous areas where several sutures unite
fontanelles
name the four fontanelles of the infant

anterior fontanelle
posterior fontanelle
mastoid fontanelle (2)
sphenoid fontanelle (2)

label

which foramen are located on the sphenoid?
superior orbital fissure
optic canal
rotundum
ovale
spinosum
on which bone is foramen lacerum located?
between the sphenoid, temporal and occipital bones
what forms the superior portion of the nasal septum?

perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone

what is highlighted in red?
alveolar processes
what does mental nerve supply with sensation?

front of chin and lower lip
which holes are associated with temporal bone?
external acoustic meatus, carotid canal, and stylomastoid foramen

identify
glabella

identify


articular tubercle

identify
frontal process of zygomatic bone

identify blacked out structures




