Chapter 34
Carbon dioxide enters the blood at the _____.
A) capillaries of the lungs
B) capillaries of the abdominal
organs
C) capillaries of the hind limbs
D) capillaries
of the head and forelimbs
E) capillaries of the head,
forelimbs, abdominal organs, and hind limbs
E
The _____ has(have) the thinnest walls.
A) aorta
B)
capillaries
C) inferior vena cava
D) pulmonary artery
E)right ventricle
B
Blood pressure is highest in the _____.
A) aorta
B)
inferior vena cava
C) superior vena cava
D) pulmonary
artery
E) capillaries
A
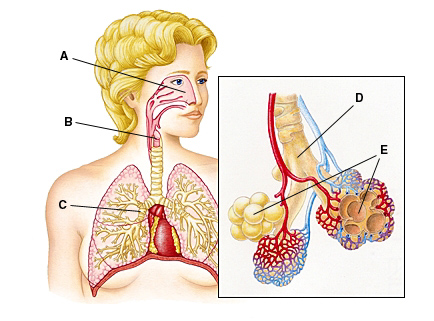
Most gas exchange with blood vessels occurs across the walls of the structure indicated by the letter _____.
E
Blood returns to the heart via the ______.
A) Aorta
B) Pulmonary Arteries
C) Pulmonary Veins
D) Aorta and Pulmonary arteries
E) Aorta and Pulmonary Veins
C
From the pulmonary veins, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
B
From the anterior vena cava, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
A
From the capillaries of the abdominal organs and hind limbs, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
E
What is the function of a circulatory system?
A) It exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide with the outside air.
B) It is the site of blood cell production.
C) It acts as a reservoir for the storage of blood.
D) It brings a transport liquid into close contact with all cells in the body.
D
Why do the circulatory systems of land vertebrates have separate circuits to the lungs and to the rest of the body?
A) The large decrease in blood pressure as blood moves through the lungs may prevent efficient circulation through the rest of the body.
B) Blood is pumped to the lungs to be oxygenated before being pumped to the rest of the body.
C) The circuits increase the amount of surface area available for the diffusion of gases and nutrients in the body.
D) Land vertebrates are bigger and require more tubing to reach all areas of the body.
A
True or false? The circulatory systems of land-dwelling vertebrates are composed of two pumping circuits: the systemic circulation, which is a lower-pressure circuit to the lung, and the pulmonary circulation, which is a higher-pressure circuit to the rest of the body.
A) True
B) False
B
What is the function of the left ventricle?
A) It pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary circulation.
B) It pumps oxygenated blood around the body via the systemic circulation.
C) It receives deoxygenated blood from the lungs.
D) It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
B
Which of the following statements about blood circulation in the body is true?
A) Deoxygenated blood flowing through the pulmonary veins is carried to the right atrium.
B) Valves prevent the backflow of blood into the atria and ventricles.
C) During one cardiac cycle, the two ventricles contract first, and then the two atria contract.
D) As the right ventricle contracts, it sends oxygenated blood through the aorta to all tissues of the body.
B
Which event occurs first during diastole?
A) The atria and ventricles are relaxed, and blood flows into the atria.
B) Blood flows into the relaxed atria while the ventricles contract.
C) The atria contract while blood flows into the relaxed ventricles.
D) The atria and ventricles contract simultaneously.
A
Which event of the cardiac cycle occurs when systolic blood pressure is measured?
A) The atria and ventricles contract simultaneously.
B) The ventricles contract, carrying blood into the aorta, and blood flows into the relaxed atria.
C) The atria contract while blood flows into the relaxed ventricles.
D) The atria and ventricles are relaxed, and blood flows into the atria.
B
True or false? The lungs of humans form from the embryonic foregut.
A) True
B) False
A
True or false? The pressure inside the human chest cavity is always positive, so the lungs stay relatively inflated even upon exhalation.
A) True
B) False
B
Which lung structure is a tiny sac that functions as an interface between air and blood?
A) Alveolus
B) Epithelium
C) Capillary
D) Diaphragm
A
Which barrier(s) must O2 and CO2 cross to pass between air and blood inside lungs?
Check all that apply
1. capillary wall
2. extracellular fluid
3. epithelial cells
4. diaphragm
1, 2, 3
True or false? The driving force for the unloading of oxygen from hemoglobin into tissues is the difference in PCO2levels between the blood and body tissues.
A) True
B) False
B
How is most carbon dioxide transported from tissues to the lungs?
A) As protons (H+)
B) As carbon dioxide gas
C) As carbonic acid
D) As bicarbonate ions (HCO3−).
D
Which of the following statements about the oxygen-hemoglobin interaction is true?
A) The binding of one oxygen molecule to hemoglobin stimulates the unloading of the oxygen molecules that are already bound.
B) Each hemoglobin molecule can bind one oxygen molecule.
C) The binding of one oxygen molecule to hemoglobin stimulates the binding of other oxygen molecules.
D)The oxygen–hemoglobin dissociation curve is exponential, which means that hemoglobin can respond quickly to small changes in oxygen demand.
C
Most carbon dioxide is carried from the body tissues to the lungs _____.
A) as bicarbonate ions (HCO3 -)
B) combined with hemoglobin
C) by the trachea
D) as hydrogen ions (H+)
E) dissolved in blood plasma
A
By picking up hydrogen ions, hemoglobin prevents the blood from becoming too _____.
A) acidic
B) basic
C) thick
D) low in oxygen concentration
E) red
A
In the blood most of the oxygen that will be used in cellular respiration is carried from the lungs to the body tissues _____.
A) as bicarbonate ions (HCO3 -)
B) combined with hemoglobin
C) by the trachea
D) water (H2O)
E) dissolved in blood plasma
B
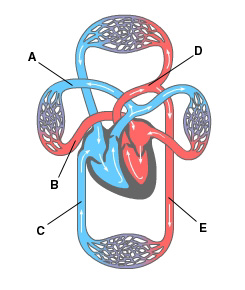
The posterior inferior vena cava is indicated by the letter _____.
C
Arteries carry blood _____.
A) away from capillaries
B) away from the heart and away from the lungs
C) to the heart and away from the lungs
D) to the heart only
E) away from the heart only
E
Blood returns to the heart via the _____.
A) aorta
B) pulmonary arteries
C) pulmonary veins
D) aorta and pulmonary arteries
E) aorta and pulmonary veins
C
From the pulmonary veins, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
B
From the anterior vena cava, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
A
From the capillaries of the abdominal organs and hind limbs, blood flows to the _____.
A) right atrium
B) left atrium
C) aorta
D) capillaries of the lungs
E) posterior vena cava
E
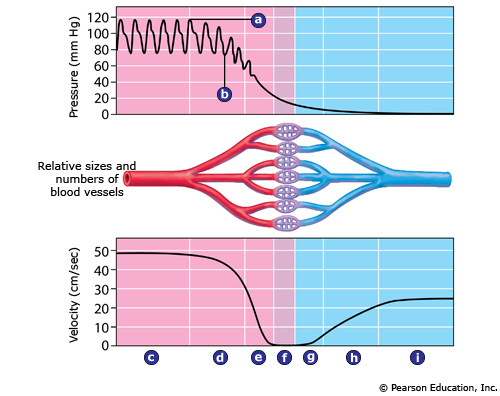
Which letter indicates systolic pressure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) I
A

Which letter indicates diastolic pressure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) I
B

Which letter indicates the arteries?
A) c
B) d
C) e
D) f
B

Which letter indicates the venules?
A) f
B) g
C) h
D) I
B

Which letter indicates the vessels in which blood pressure is the lowest?
A) f
B) g
C) h
D) I
D

Which letter indicates the vessels in which blood velocity is decreasing the most due to an increase in the total combined cross-sectional area of those vessels?
A) d
B) e
C) g
D) h
B

Which letter indicates the vessels in which blood travels the most slowly?
A) e
B) f
C) g
D) h
B

Which letter indicates the vessels in which blood velocity is increasing the most due to a decrease in the total combined cross-sectional area of those vessels?
A) d
B) e
C) g
D) h
D
In which of the following animals are the circulatory fluid and interstitial fluid considered to be the same body fluid?
A) dogs
B) grasshoppers
C) fishes
D) sparrows
E) jellyfish and cnidarians
B
Which of the following best describes an artery?
A) Arteries contain valves.
B) Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
C) Arteries carry blood away from capillaries.
D) Arteries have thin walls compared with veins.
E) Arteries carry oxygenated blood
B
Gas exchange in the aquatic salamander known as the axolotl is correctly described as
A) simple diffusion of oxygen into the salamander from the water.
B) facilitated diffusion of carbon dioxide from the salamander into the water.
C) active transport of carbon dioxide from the salamander into the water.
D) active transport to move oxygen into the salamander from the water.
E) carrier-mediated transport to move oxygen into the salamander from the water.
A
Circulatory systems compensate for
A) the need to cushion animals from trauma.
B) temperature differences between the lungs and the active tissue.
C) the need fetal organisms have for maintaining an optimal body temperature.
D) the slow rate at which diffusion occurs over large distances.
E) the problem of communication systems involving only the nervous system.
D
The fluid that moves around in the circulatory system of a typical arthropod is
A) the cytosol
B) the intracellular fluid
C) the digestive juices
D) the interstitial fluid
E) the blood plasma.
D
Organisms with a circulating body fluid that is distinct from the fluid that directly surrounds the body's cells are likely to have
A) a gastrovascular cavity
B) hemolymph
C) an open circulatory system
D) branched tracheae
E) a closed circulatory system.
E
In which of the following organisms does blood flow from the pulmocutaneous circulation to the heart before circulating through the rest of the body?
A) annelids
B) frogs
C) insects
D) fishes
E) molluscs
B
The only vertebrates in which blood flows directly from respiratory organs to body tissues without first returning to the heart are the
A) mammals
B) birds
C) fishes
D) reptiles
E) amphibians.
C
Which statement regarding the mammalian heart is correct?
A) Blood arrives at the heart via the ventricles
B) Oxygen-loaded blood moves only through the right side of the heart.
C) When the right atrium contracts, it forces blood into the left atrium.
D) Blood is pumped from the heart via the atria.
E) In the adult heart, blood in the right chambers of the heart cannot enter the left chambers without passing through the lungs.
E
Which statement about human blood vessels is correct?
A) Arteries carry blood toward the atria of the heart.
B) Veins transport blood from the heart to the capillaries.
C) Arteries carry oxygenated blood; veins carry oxygen-poor blood.
D) Pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
E) The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
D
A human red blood cell in an artery of the left arm is on its way to deliver oxygen to a cell in the thumb. To travel from the artery in the arm to the left ventricle, this red blood cell must pass through
A) two capillary beds
B) three capillary beds
C) one capillary bed
D)five capillary beds
E) four capillary beds
A
Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow in reptiles and mammals?
A) right ventricle → pulmonary vein → pulmocutaneous circulation
B) right atrium → pulmonary artery → left atrium ventricle
C) pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle pulmonary circuit
D) vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary circuit
E) left ventricle → aorta → lungs → systemic circulation
D
Damage to the sinoatrial node in humans
A) would disrupt the rate and timing of cardiac muscle contractions
B) would block conductance between the bundle branches and the Purkinje fibers.
C) is a major contributor to heart attacks.
D) would have a negative effect on peripheral resistance.
E) would have a direct effect on blood pressure monitors in the aorta.
A
The semilunar valves of the mammalian heart
A) are the attachment site where the pulmonary veins empty into the heart.
B) are the route by which blood flows from the atria to the ventricles.
C) are found only on the right side of the heart.
D) prevent backflow of blood in the aorta and pulmonary arteries.
E) are at the places where the anterior and posterior venae cavae empty into the heart.
D
Heart rate will increase in the presence of increased
A) epinephrine
B) low-density lipoproteins
C) immunoglobulins
D) platelets
E) erythropoietin.
A
Which of the following develops the greatest pressure on the blood in the mammalian aorta?
A) diastole of the right ventricle
B) diastole of the right atrium
C) diastole of the left atrium
D) systole of the left atrium
E) systole of the left ventricle
E
The material present in arterioles that is not present in capillaries is
A) fully oxygenated blood
B) circular smooth muscle cells that can alter the size of the arterioles.
C) plasma in which carbon dioxide has been added.
D) white blood cells and platelets
E) a lining of endothelial cells.
B
The set of blood vessels with the slowest velocity of blood flow is
A) the arterioles
B) the capillaries
C) the metarterioles
D) the veins
E) the arteries
B
The set of blood vessels with the lowest blood pressure driving flow is
A) the metarterioles
B) the arteries
C) the capillaries
D) the veins
E) the arterioles.
D
An increased concentration of nitric oxide within a vascular bed is associated with
A) a decreased amount of blood in the capillaries of that vascular bed
B) vasodilation
C) a reduction in blood flow in that region.
D) vasoconstriction
E) narrowing of the arteries.
B
Among the following choices, which organism likely has the highest systolic pressure?
A) human
B) giraffe
C) hippopotamus
D) rabbit
E) mouse
B
Small swollen areas in the neck, groin, and axillary region are associated with
A) dehydration
B) blood sugar that is abnormally high
C) a broken limb
D) sodium depletion
E) increased activity of the immune system.
E
The blood pressure is lowest in the
A) arteries
B) capillaries
C) arterioles
D) aorta
E) vena cava.
E
What will be the long-term effect of blocking the lymphatic vessels associated with a capillary bed?
A) fewer proteins leaking out of the blood to enter the interstitial fluid
B) the area of the blockage becoming abnormally small
C) more fluid entering the venous capillaries
D) an increase in the blood pressure in the capillary bed
E) the accumulation of more fluid in the interstitial areas
E
Vasoconstriction of blood vessels delivering blood to the gut is a likely response when an individual is
A) eating a meal
B) responding to increased blood pressure
C) stressed and secreting stress hormones
D) lying down after standing up
E) having an allergy attack with lots of histamine secretion.
C
Stroke occurs when _____.
A) the pacemaker of the heart becomes defective, producing an irregular heartbeat
B) the walls of an artery in the leg accumulate deposits and lose their flexibility and elasticity
C) a blood clot enters and blocks one of the coronary arteries
D) a blood clot enters the cerebral circulation, blocking an artery and causing the death of brain tissue
E) a blood clot dislodges from a vein and moves into the lung, where it blocks a pulmonary artery
D
In a healthy human, the typical life span of a red blood cell is
A) 1 month
B) 4 months
C) 24 hours
D) 1 week
E) 80 years or more.
B
The hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells and the organ where this hormone is synthesized are
A) acetylcholine and bone marrow, respectively.
B) cortisol and adrenal gland, respectively.
C) epinephrine and adrenal gland, respectively.
D) growth hormone and pancreas, respectively.
E) erythropoietin and kidney, respectively.
E
The production of red blood cells is stimulated by
A) epinephrine
B) immunoglobulins
C) erythropoietin
D) platelets
E) low-density lipoproteins
C
The meshwork that forms the fabric of a blood clot is
A) thrombin
B) prothrombin
C) chymotrypsin
D) fibrin
E) collagen.
D
Which of the following organisms has no specialized respiratory structures?
A) salmon
B) earthworms
C) crabs
D) alligators
E) ants
B
The smallest airway through which inspired air passes before gas exchange occurs in the mammalian lungs is the _____.
A) trachea
B) bronchus
C) pharynx
D) bronchiole
E) larynx
D
Sponges, cnidarians, and flatworms lack a specialized gas exchange surface because
A) nearly all of their cells are in direct contact with the external environment
B) they do not produce carbon dioxide
C) they live without need for oxygen
D) countercurrent exchange mechanisms cannot function well in their living conditions
E) they are too large for a circulatory system to operate well.
A
In mammals, most gas exchange between the atmosphere and the pulmonary blood occurs in the
A) bronchioles
B) trachea
C) bronchi
D) alveoli
E) larynx
D
Countercurrent exchange is evident in
A) the flow of water across the gills of a fish and that of blood within those gills
B) the flow of air within the primary bronchi of a human and that of blood within the pulmonary veins
C) the flow of water across the skin of a frog and that of blood within the ventricle of its heart
D) the flow of fluid out of the arterial end of a capillary and that of fluid back into the venous end of the same capillary
E) the flow of blood in the dorsal vessel of an insect and that of air within its tracheae.
A
Countercurrent exchange in the fish gill helps to maximize
A) diffusion
B) osmosis
C) blood pressure
D) endocytosis
E) active transport.
A
Air-breathing insects carry out gas exchange
A) across the finest branches of the trachea and cell membranes
B) in the alveoli of their lungs
C) in their specialized external gills
D) in their specialized internal gills
E) across all parts of their thin cuticular exoskeleton.
A
An oil-water mixture works as an insecticidal spray against mosquitoes and other insects because it
A) blocks the openings into the tracheal system
B) interferes with gas exchange across the capillaries.
C) coats their lungs
D) prevents gases from leaving the atmosphere
E) clogs their bronchi.
A
Some human infants, especially those born prematurely, suffer serious respiratory failure because of
A) the incomplete development of the lung surface
B) the sudden change from the uterine environment to the air.
C) mutations in the genes involved in lung formation
D) the overproduction of surfactants
E) lung collapse due to inadequate production of surfactant.
E
_____ in carbon dioxide in your red blood cells, which causes _____ in pH, causes your breathing to speed up.
A) A decrease ... a rise
B) An increase ... a rise
C) A decrease ... a drop
D) An increase ... a drop
E) Actually, it is the rise and fall of oxygen, not carbon dioxide, that controls breathing.
D
Of the following choices, impairment of a mammal's breathing cycle is most likely following neural damage in
A) the adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex.
B) the frontal lobe and the temporal lobe.
C) the medulla oblongata and the pons.
D) the thalamus and the hypothalamus.
E) the cerebrum and cerebellum.
C
Air rushes into the lungs of humans during inhalation because
A) gas flows from a region of lower pressure to a region of higher pressure
B) a positive respiratory pressure is created when the diaphragm relaxes
C) the rib muscles and diaphragm contract, increasing the lung volume
D) pulmonary muscles contract and pull on the outer surface of the lungs
E) the volume of the alveoli increases as smooth muscles contract.
C
The exhalation of air from human lungs is driven by
A) the expansion of the rib cage.
B) a decrease in the residual volume of the lungs.
C) a decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity.
D) the contraction of the diaphragm.
C
Breathing is usually regulated by
A) hemoglobin levels in the blood.
B) CO2 and O2 concentration and pH-level sensors.
C) the concentration of red blood cells.
D) the lungs and the larynx.
E) erythropoietin levels in the blood.
B
Carbon dioxide levels in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid affect their pH. This enables the organism to sense a disturbance in gas levels as
A) the medulla oblongata is able to control the concentration of bicarbonate ions in the blood.
B) the brain directly measures and monitors carbon dioxide and causes breathing changes accordingly.
C) stretch receptors in the lungs cause the medulla oblongata to speed up or slow breathing.
D) the brain alters the pH of the cerebrospinal fluid to force the animal to retain more or less carbon dioxide.
E) the medulla oblongata, which is in contact with cerebrospinal fluid, monitors pH and uses this measure to control breathing.
E
The amount of oxygen bound to hemoglobin _____.
A) is called the Bohr shift
B) increases with increasing acidity at the tissue level
C) decreases in the presence of high concentrations of oxygen
D) increases as the pH of tissues decreases
E) increases in the presence of high concentrations of oxygen
E
Hemoglobin and hemocyanin
A) both transport oxygen
B) are both freely dissolved in the plasma.
C) are both red in color.
D) are both found in mammals
E) are both found within blood cells
A
The epiglottis of a human covers the glottis when he or she is
A) breathing.
B) talking.
C) sleeping.
D) swallowing.
E) yawning.
D
Select the correct statement about capillary beds.
A) Capillary beds have a total cross-sectional area much smaller than the total cross-sectional area of major arteries.
B) Capillary beds are the site of nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues.
C) Capillary beds join arteries and veins.
B
Why does the velocity of blood slow greatly as blood flows from arterioles into capillaries?
A) Because capillary beds have a total cross-sectional area much greater than the total cross-sectional area of the arterioles.
B) Because capillary beds are the site of nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues.
C) Because the narrow capillaries offer great resistance to blood flow.
A
Which statement about lipoproteins is correct?
A) Low-density lipoproteins are the principal component of atherosclerotic plaques.
B) High-density lipoproteins are cholesterol transporters in the blood.
C)High-density lipoproteins are a form of cholesterol considered the “good” type to have in blood plasma.
B
How are gases transported in insect bodies?
A) In closed circulatory systems
B) In tracheal systems
C) In open circulatory systems
B