Outside Hours Mosby's Essential Sciences for Therapeutic Massage
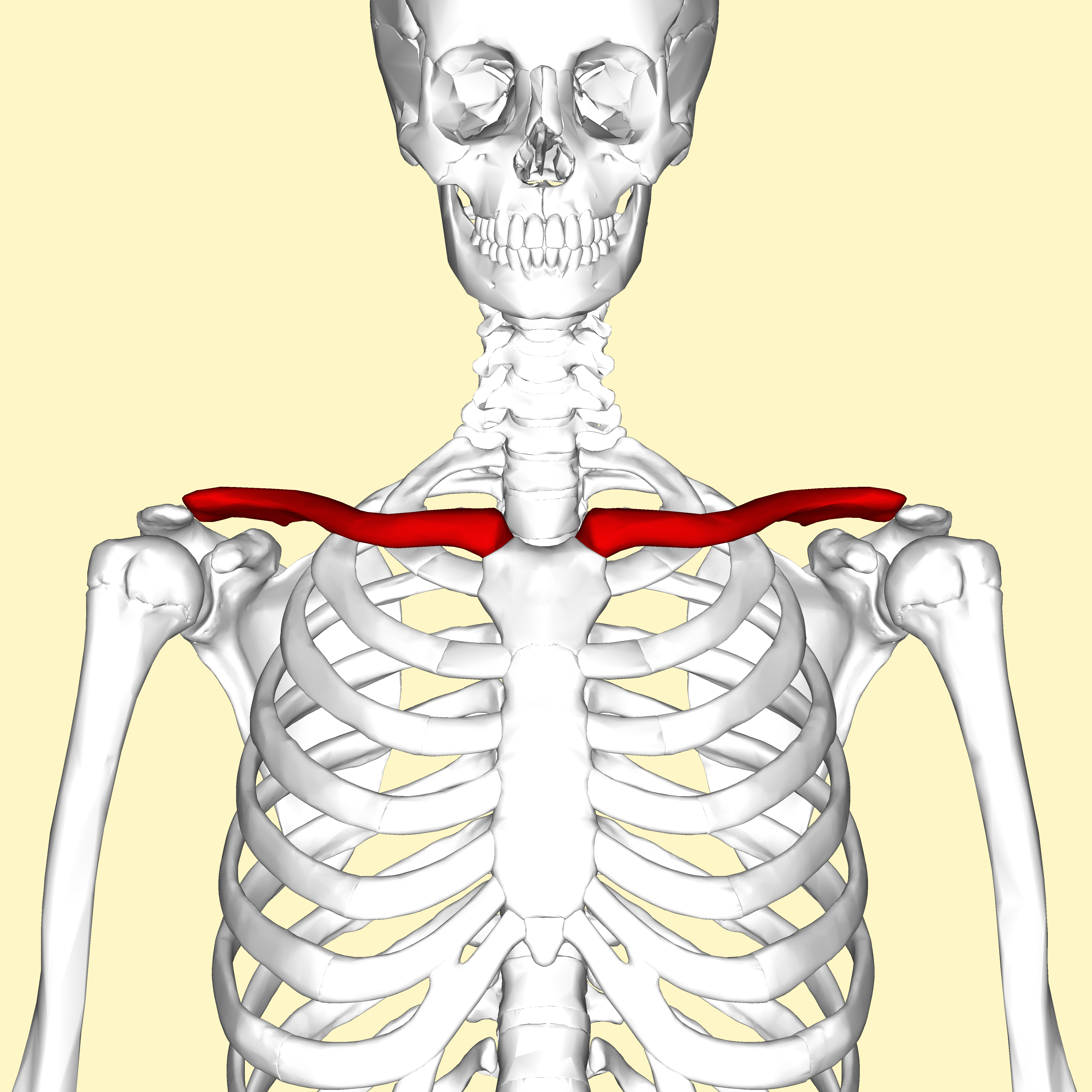
1. sternal end
2. acromial end

- spine
- acromion
- coracoid process
- gleniod cavity
- supraspinous fossa
- infraspinous fossa
- subscapular fossa

- head
- anatomical neck
- surgical neck
- greater tubercle
- lesser tubercle
- deltoid tuberosity
- trochlea
- capitulum
- coronoid fossa
- olecranon fossa
- medial epicondyle
- lateral epicondyle

ulna
- olecranon
- coroniod process
- trochlear notch
- radial notch
- ulnar tuberosity
- head
- styloid process

radius
- head
- neck
- radial tuberosity
- ulnar notch
- styloid process

Carpals
- scaphoid
- lunate
- triquetrum
- pisiform
- hamate
- capitate
- trapezoid
- trapezium

Metacarpals

Phalanges
- proximal
- middle
- distal

- body
- spinous process
- transverse process
- vertebral foramen
- superior articular facets
- inferior articular facets

cervical vertebrae
- atlas
- axis

thoracic vertebrae
- costal facets
lumbar vertebrae
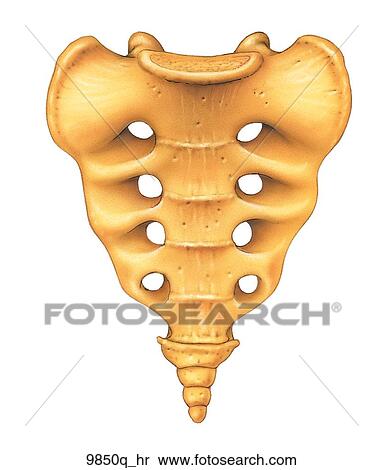
sacrum
- sacral promontory
- coccyx

- manubrium
- body
- xiphoid process
- jugular notch
- cavicular notch
- articulating facets for costal cartilage

- head
- articular facets
- neck
- sternal end

Hyoid

Middle Ear
- malleus
- incus
- stapes

- ilium
- iliac crest
- anterior superior iliac spine
- anterior inferior iliac spine
- posterior superior iliac spine
- posterior superior iliac spine
- greater sciatic notch
- articular surface
- ischium
- ischeal tuberosity
- pubis
- pubic symphysis
-
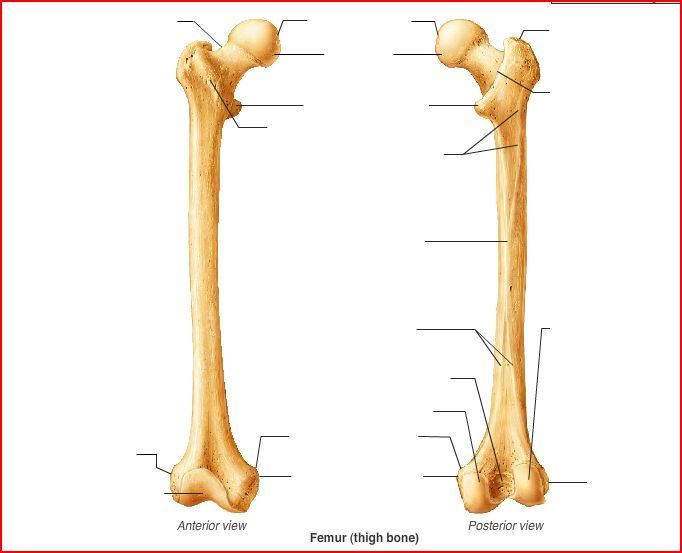
femur
head - neck
- greater trochanter
- lesser trochanter
- linea aspera
- later condyle
- medial condyle
- intercondylar fossa
- lateral epicondyle
- medial epicondyle
- patellar groove

- tibia
- later condyle
- medial condyle
- tibial tuberosity
- medial malleolus
- fibula
- head
- lateral malleolus

- Tarsals
- calcaneous
- talus
- navicular
- cuboid
- medial cuneiform
- middle cuneiform
- lateral cuneiform
- metatarsals
- phalanges
- proximal
- middle
- distal
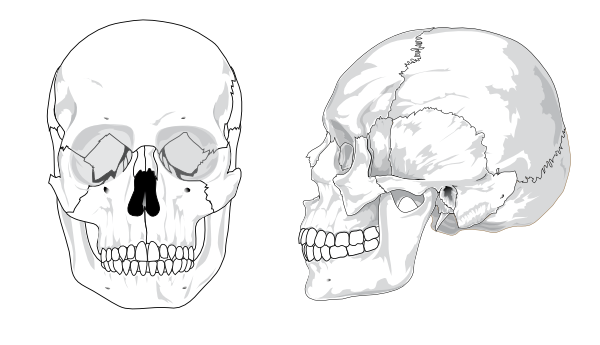
- Frontal Bone
- Parietal Bones
- Temporal bones
- Zygomatic process
- mastiod
- styloid
- mandibular fossa
- Occipital bone
- occipital condyles
- ethmoid
- sphenoid
- zygoma
- maxilla
- palatine
- vomer
- nasal
- lacrimal
- inferior nasal concha
- mandible
- mandibular process
- Coronal suture
- sagittal suture
- squamous suture
- lambdiodal suture
- fontanels

occipitofrontalis
O: Two occipital bellies and two frontal bellies
I: Galea
aponeurotica
A: Raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
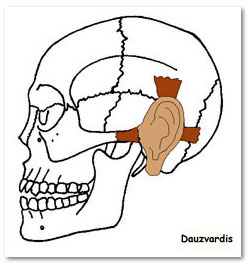
auricularis anterior
O: Temporal fascia
I: Major Helix (ear)
A: Pulls
ear forward

auricularis posterior
O: Mastoid Process
I: Posterior ear
A: Pulls ear backward

auricularis superior
O: Temporal fascia
I: Above the ear
A: Pulls ear upward

orbicularis oculi
O: frontal bone; medial palpebral ligament; lacrimal bone
I:
lateral palpebral raphe
A: closes eyelids

orbicularis oris
O: Maxilla and mandible
I: Skin around the lips
A: It is
sometimes known as the kissing muscle because it is used to
pucker the lips.

buccinator
O: from the alveolar processes of the maxillary bone and mandible,
temporomandibular joint
I: in the fibers of the orbicularis
oris
A: The buccinator compresses the cheeks against the teeth
and is used in acts such as blowing. It is an assistant muscle of
mastication (chewing) and in neonates it is used to suckle.

platysma
O: subcutaneous tissue of infraclavicular and supraclavicular
regions
I: base of mandible; skin of cheek and lower lip; angle
of mouth; orbicularis oris
A: Draws the corners of the mouth
inferiorly and widens it (as in expressions of sadness and fright).
Also draws the skin of the neck superiorly when teeth are clenched
masseter
O: zygomatic arch and maxilla
I: coronoid process, ramus of
mandible, cementomaxillary tendon and cementomandibular tendon
A:
elevation (as in closing of the mouth) and protraction of mandible

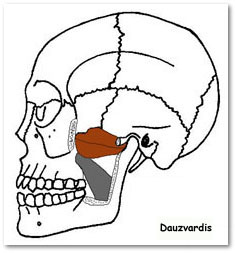
temporalis
O: Temporal lines on the parietal bone of the skull and the superior
temporal surface of the sphenoid bone.
I: Coronoid process of the
mandible.
A: Elevation and retraction of mandible
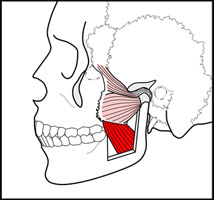
lateral pterygoid
O: Great wing of sphenoid and pterygoid plate
I: Condyloid
process of the mandible
A: depresses mandible, protrude mandible,
side to side movement of mandible
medial pterygoid
O: deep head: medial side of lateral pterygoid plate
behind the upper teeth, superficial head: pyramidal process
of palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity
I: medial angle of the
mandible
A: elevates mandible, closes jaw, helps lateral
pterygoids in moving the jaw from side to side

sternocleidomastoid
O: Manubrium sterni and medial portion of the clavicle
I:
Mastoid process of the temporal bone, superior nuchal line
A:
Unilaterally; cervical rotation to opposite side, cervical lateral
flexion to same side, Bilaterally; cervical flexion, raises the
sternum and assists in forced inspiration
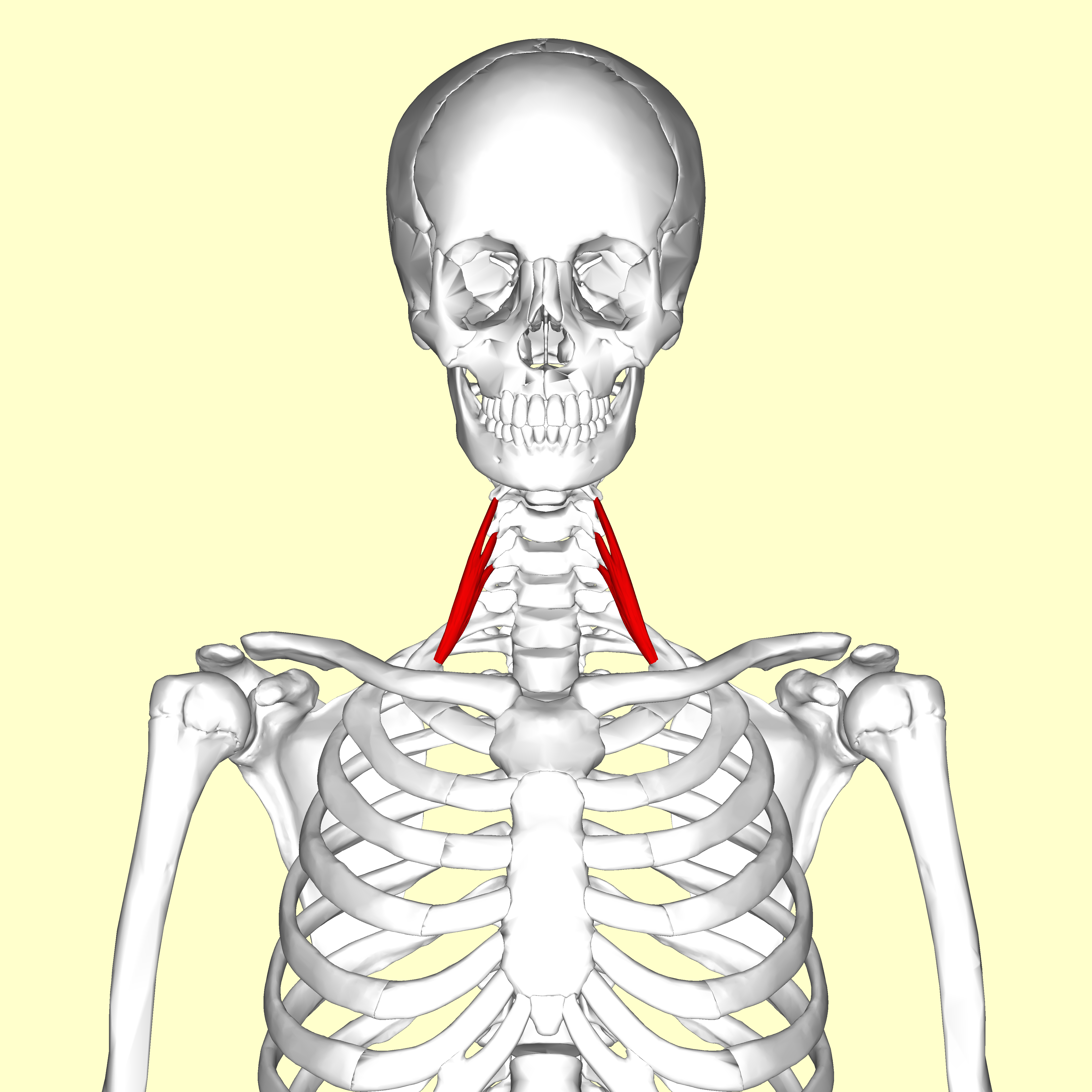
anterior scalene
O: Transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth
cervical vertebræ (C3, C4, C5 and C6)
I: First rib
A:
Elevates first rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side

middle scalene
O: Posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the lower six
cervical vertebræ (C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 and C7)
I: Upper surface of
the first rib
A: Elevate 1st rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side

posterior scalene
O: Transverse processes of C4, C5 and C6
I: Second rib
A:
Elevate second rib, tilt the neck to the same side
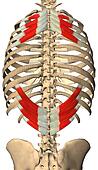
serratus posterior superior
O: Nuchal ligament (or ligamentum nuchae) and the spinous processes
of the vertebrae C7 through T3
I: The upper borders of the 2nd
through 5th ribs
A: Elevates the ribs which aids in inspiration

serratus posterior inferior
O: Vertebrae T11 - L2
I: The inferior borders of the 9th
through 12th ribs
A: Depress the lower ribs, aiding in expiration

diaphragm
O: Attaches to the sternum and xiphoid process
anteriorly, the L1 through the L3 lumbar vertebrae and the arcuate
ligaments posteriorly, and the costal margin peripherally
I:
Attaches to the central aponeurotic tendon
A: Inspiration
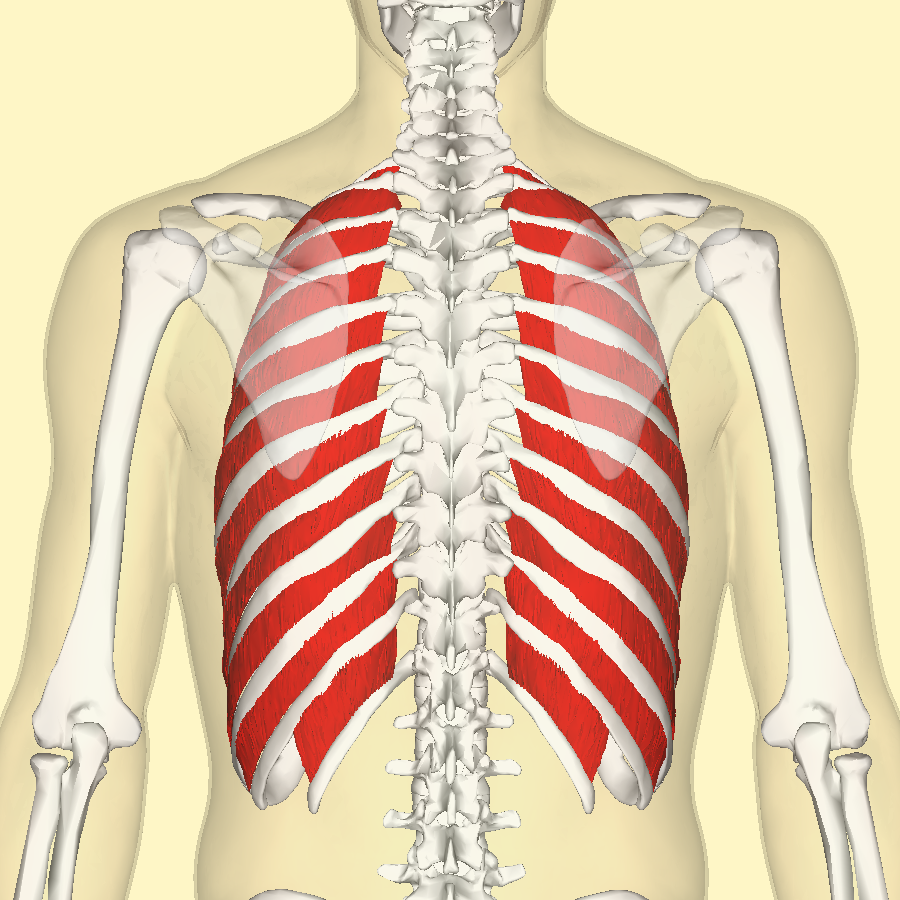
external intercostals
O: lower border of ribs
I: upper border of rib below
A: Inhalation
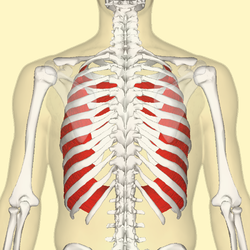
internal intercostals
O: Rib - inferior border
I: Rib - superior border
A: Hold
ribs steady
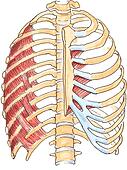
transversus thoracis
O: Costal cartilages of last 3-4 true ribs, body of sternum and
xiphoid process
I: Ribs/costal cartilages 2-6
A: Depresses ribs
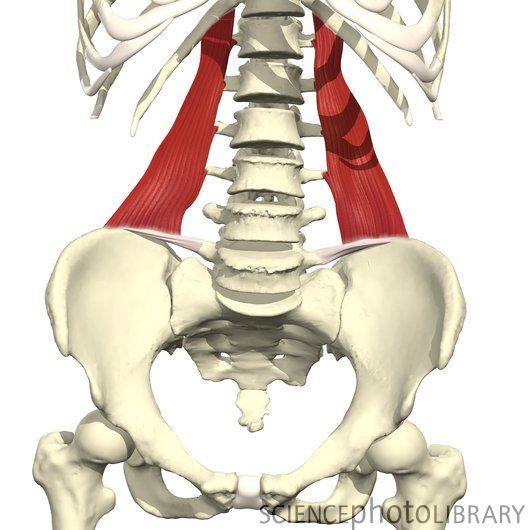
quadratus lumborum
O: iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament
I: Last rib and
transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
A: Alone, lateral
flexion of vertebral column; Together, depression of thoracic rib cage
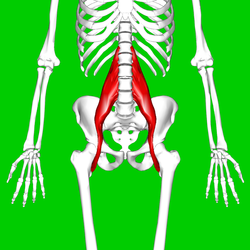
Psoas Major (iliopsoas)
O: Transverse processes of T12-L5 and the lateral aspects of the
discs between them
I: In the lesser trochanter of the
femur
A: Flexion in the hip joint

Iliacus (iliopsoas)
O: upper two-third of the iliac fossa
I: base of the lesser
trochanter of femur
A: flexes and rotates laterally thigh

1. external abdominal oblique
O: Ribs 5-12
I: Iliac crest, Pubic tubercle, Linea
alba
A: Contralateral rotation of torso

2. internal abdominal oblique
O: Inguinal ligament, Iliac crest and the Lumbodorsal
fascia.
I: Linea alba, Pecten Pubis (via Conjoint tendon) and
ribs 10-12
A: Compresses abdomen; unilateral contraction rotates
vertebral column to same side

3. transversus abdominis
O: Iliac crest, inguinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia, and costal
cartilages 7-12
I: Xiphoid process, linea alba, pubic crest and
pecten pubis via conjoint tendon
A: Compresses abdominal contents

4. Rectus abdominis
O: crest of pubis
I: Costal cartilage of ribs 5-7, xiphoid
process of sternum
A: Flexion of the lumbar spine

splenius capitis
O: Nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T3
I: Mastoid
process of temporal and occipital bone
A: Extend, rotate, and
laterally flex the head
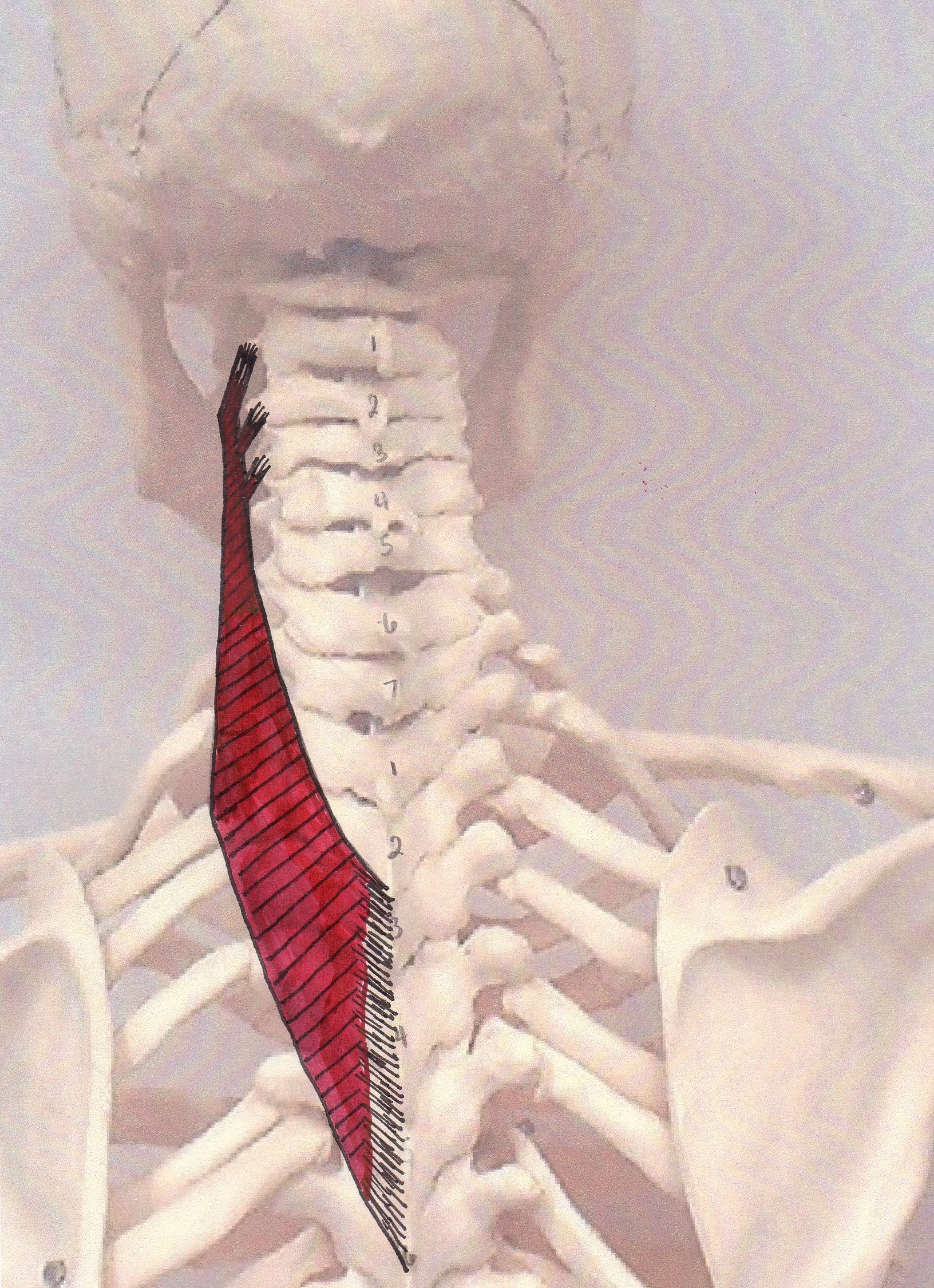
splenius cervicis
O: Spinous processes of T3-T6
I: Transverse processes of
C1-C3
A: Bilaterally: Extend the head & neck, Unilaterally:
Lateral flexion to the same side, Rotation to the same side.
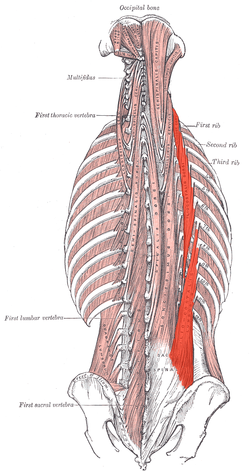
iliocostalis (erector spinae group)
O: Sacrum/Illiac Crest/Spinous Processes of lower lumbar/thoracic
vertebrae
I: Ribs
A: Unilaterally: Flex the head and neck to
the same side. Bilaterally: Extend the vertebral column.

longissimus (erector spinae group)
O: transverse process
I: transverse process
A: Laterally:
Flex the head and neck to the same side. Bilaterally: Extend the
vertebral column.

spinalis (erector spinae group)
O: Thoracis: Spinous process of upper lumbar and lower thoracic
vertebrae. .Cervicis: nuchal ligament and spinous process of
C7
I: Thoracis: Spinous process of upper thoracic vertebrae.
Cervicis: Spinous process of cervical vertebrae except atlas.
A:
Laterally: Flex the head and neck to the same side. Bilaterally:
Extend the vertebral column.

semispinalis
O: Transverse processes of lower cervical and higher thoracic
columna
I: Area between superior and inferior nuchal line
A:
Extends the head
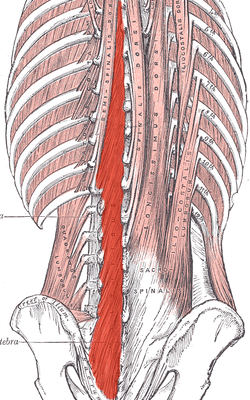
multifidus
O: Sacrum, Erector spinae Aponeurosis, PSIS, and Iliac
crest
I: spinous process
A: Provides proprioceptive
feedback and input due to high muscle spindle density

suboccipital group

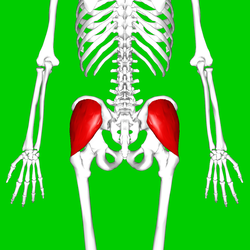
gluteus maximus
O: Gluteal surface of ilium, lumbar fascia, sacrum, sacrotuberous
ligament
I: Gluteal tuberosity of the femur and iliotibial
tract
A: External rotation and extension of the hip joint,
supports the extended knee through the iliotibial tract, chief
antigravity muscle in sitting and abduction of the hip
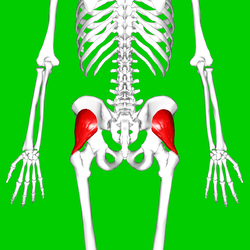
gluteus medius
O: Gluteal surface of ilium, under gluteus maximus
I: Greater
trochanter of the femur
A: abduction of the hip; preventing
adduction of the hip. Medial rotation of thigh.
gluteus minimus
O: From area in between the anterior gluteal line and inferior
gluteal line of Gluteal surface ilium, under gluteus medius.
I:
Greater trochanter of the femur
A: Works in concert with gluteus
medius: abduction of the hip; preventing adduction of the hip. Medial
rotation of thigh.

tensor fascia latae
O: Iliac crest
I: Iliotibial tract
A: Thigh - flexion,
medial rotation, abduction. Trunk stabilization.

piriformis (deep lateral rotator group)
O: Sacrum
I: Greater trochanter
A: External rotator of
the thigh

obturator internus (deep lateral rotator group)
O: Ischiopubic ramus & obturator membrane
I: Medial
aspect of the greater trochanterA: Abducts & laterally rotates
the extended hip and abducts the flexed thigh at the hip, and
stabilizer of the hip during walking

obturator externus (deep lateral rotator group)
O: obturator foramen and obturatory membrane
I:
trochanteric fossa of femur
A: adduct thigh, rotate laterally thigh
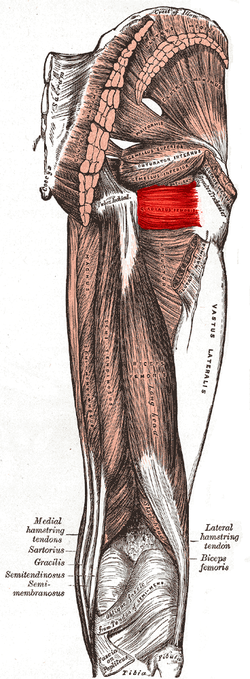
quadratus femoris (deep lateral rotator group)
O: Ischial tuberosity
I: Intertrochanteric crest
A:
lateral rotation and adduction of thigh

gemellus superior (deep lateral rotator group)
O: spine of the ischium
I: Obturator Internus
tendon
A: Rotates laterally thigh

gemellus inferior (deep lateral rotator group)
O: Ischial tuberosity
I: Obturator internus tendon
A:
Rotates laterally thigh
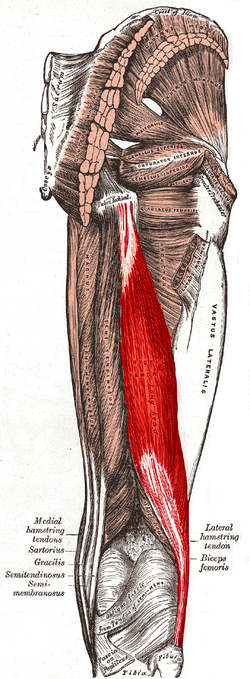
biceps femoris (hamstring group)
O: tuberosity of the ischium, linea aspera, femur
I: the
head of the fibula which articulates with the back of the lateral
tibial condyle
A: flexes knee joint, laterally rotates knee
joint (when knee is flexed), extends hip joint (long head only)
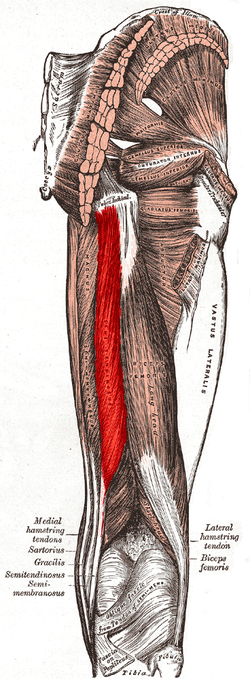
semitendinosus (hamstring group)
O: Tuberosity of the ischium
I: Pes anserinus
(tibia)
A: Flexion of knee, extension of the hip joint
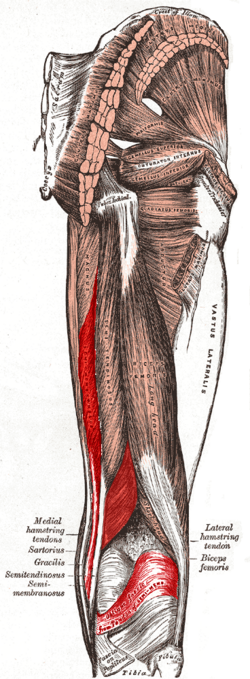
semimembranosus
O: Ischial tuberosity
I: Medial tibial condyle
A:
Extension of hip and flexion of knee
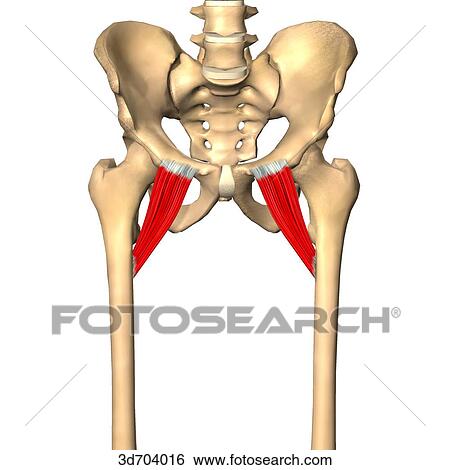
pectineus
O: Pectineal line of the pubic bone
I: Pectineal line of
the femur
A: Thigh - flexion, adduction

adductor brevis (adductor group)
O: anterior surface of the inferior ramus and body of the
pubis
I: the lesser trochanter and linea aspera of the
femur
A: adduction of hip

adductor longus (adductor group)
O: pubic body just below the pubic crest
I: middle third of
linea aspera
A: adduction of hip, flexion of hip joint

adductor magnus (adductor group)
O: Pubis, tuberosity of the ischium
I: Linea aspera and
adductor tubercle of femur
A: Adduction of hip (both portions),
flexion of hip (adductor portion), extension of hip (hamstring portion)

gracilis
O: ischiopubic ramus
I: tibia (pes anserinus)
A:
flexes, medially rotates, and adducts the hip, flexes the knee
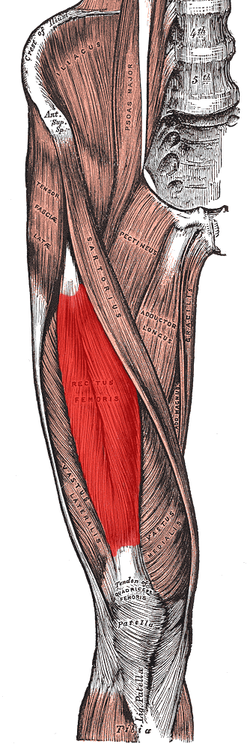
rectus femoris (quadriceps group)
O: anterior inferior iliac spine and the exterior surface of the
bony ridge which forms the groove on the iliac portion of the
acetabulum
I: inserts into the patellar tendon as one of the four
quadriceps muscles
A: knee extension; hip flexion
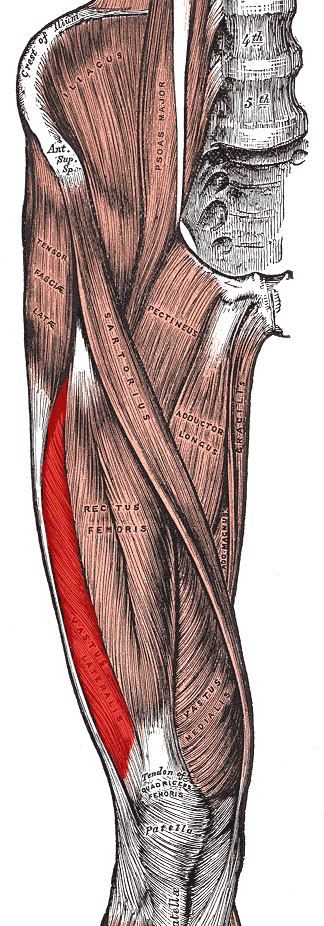
vastus lateralis (quadriceps group)
O: Greater trochanter, Intertrochanteric line, and Linea aspera
of the Femur
I: Patella via the Quadriceps tendon and Tibial
tuberosity via the Patellar ligament
A: Extends and stabilizes knee
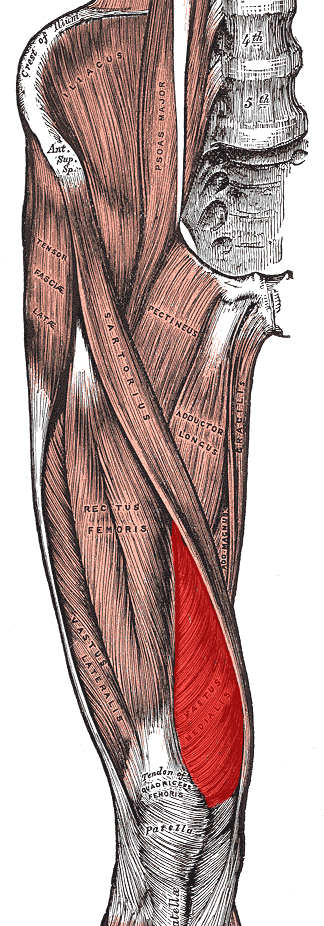
vastus medialis (quadriceps group)
O: Medial side of femur
I: Quadriceps tendon
A:
Extends leg

vastus intermedius (quadriceps group)
O: antero/ lateral femur
I: Quadriceps tendon
A:
Extension of knee joint

tibialis anterior
O: Upper 1/2 & Lateral Condyle of Tibia
I: medial cuneiform
and first metatarsal bones of the foot
A: Dorsiflexion and
Inversion of the foot
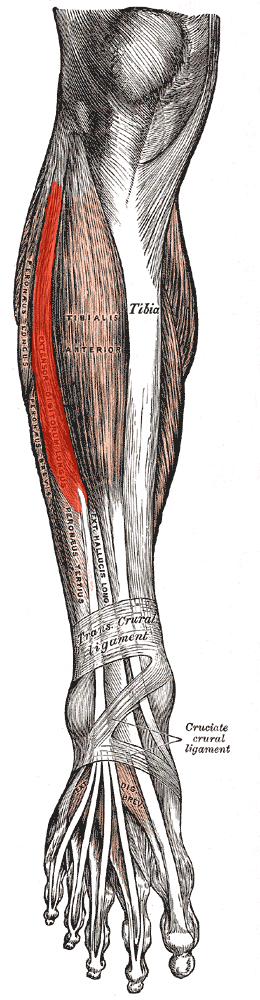
extensor digitorum longus
O: Anterior lateral condyle of tibia, anterior shaft of fibula
and superior 3⁄4 of interosseous
membrane
I: Dorsal surface; middle and distal phalanges of
lateral four digits
A: extension of toes and dorsiflexion of ankle
extensor hallicus longus
O: Arises from the middle portion of the fibula on the anterior
surface and the interosseous membrane
I: Inserts on the dorsal
side of the base of the distal phalanx of the big toe
A: Extends
the big toe and assists in dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle. Also
is a weak evertor/ invertor

fibularis (peroneus) tertius
O: distal anterior surface of the fibula also the interosseous
membrane
I: dorsal surface of metatarsal 5
A: dorsiflexion
and eversion of the foot

fibularis (peroneus) longus
O: Upper lateral shaft of fibula
I: first metatarsal,
medial cuneiformA: plantarflexion, eversion, support arches

fibularis (peroneus) brevis
O: Lower two-thirds of lateral fibula
I: Fifth
metatarsal
A: Plantarflexion, eversion
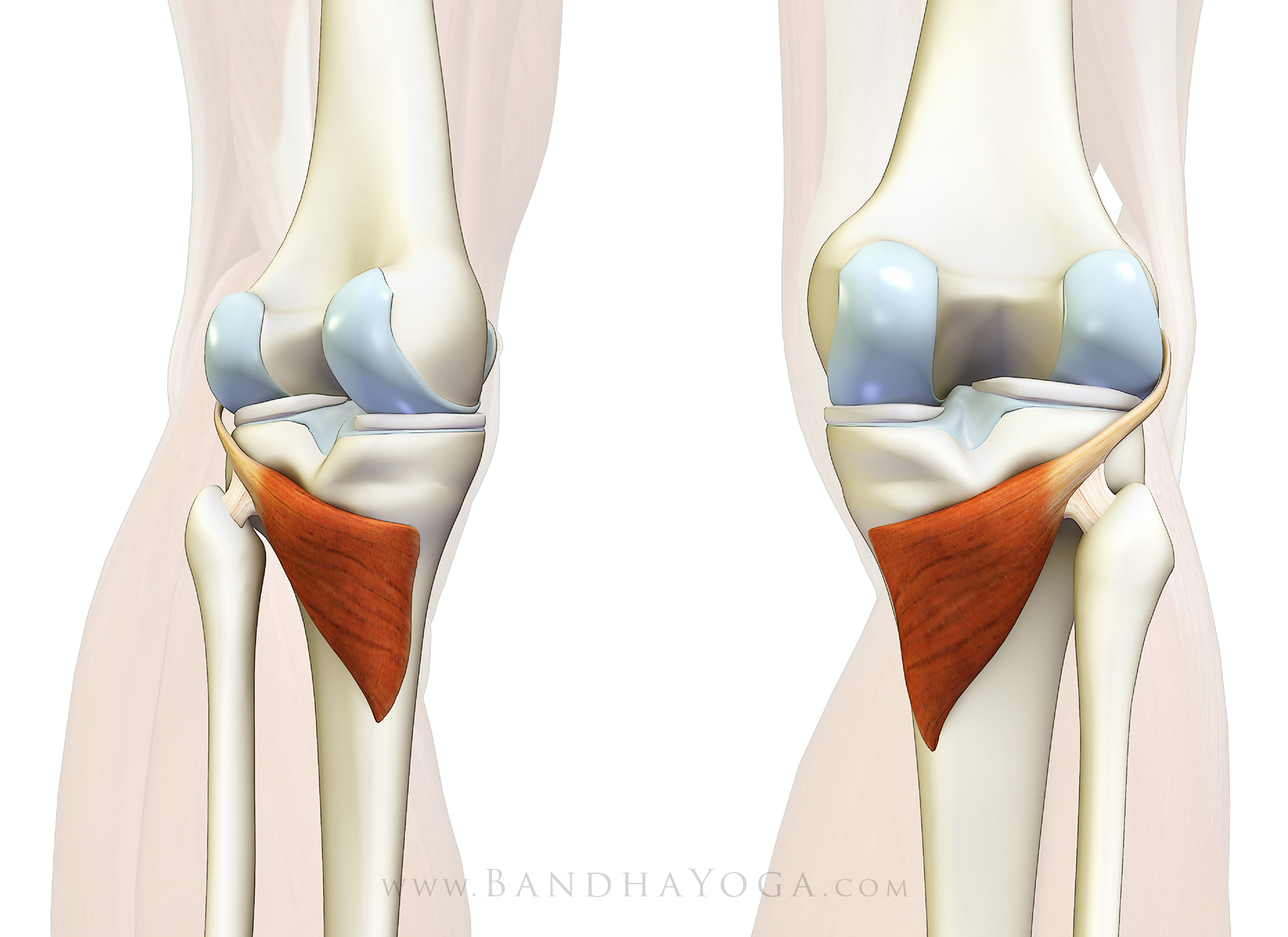
popliteus
O: Lateral condyle of the femur, and the lateral meniscus and
joint capsule
I: posterior surface of upper tibia
A:
Medially rotates tibia on the femur if the femur is fixed (sitting
down) or laterally rotates femur on the tibia if tibia is fixed
(standing up), unlocks the knee to allow flexion (bending), helps to
prevent the forward dislocation of the femur while crouching
tibialis posterior
O: Tibia and fibula
I: Navicular and medial cuneiform
bone
A: Inversion of the foot and plantar flexion of the foot at
the ankle

flexor digitorum longus
O: Posterior surface of the body of the tibia
I: Plantar
surface; base of the distal phalanges of the four lesser toesA:
Primary action is Flex digits
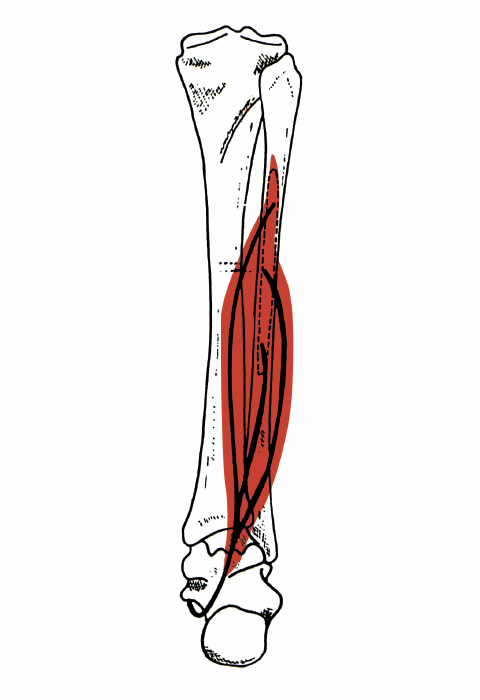
flexor hallicus longus
O: fibula, posterior aspect of middle 1/3
I: Plantar
surface; base of distal phalanx of hallux
A: flexes all joints
of the big toe, plantar flexion of the ankle joint
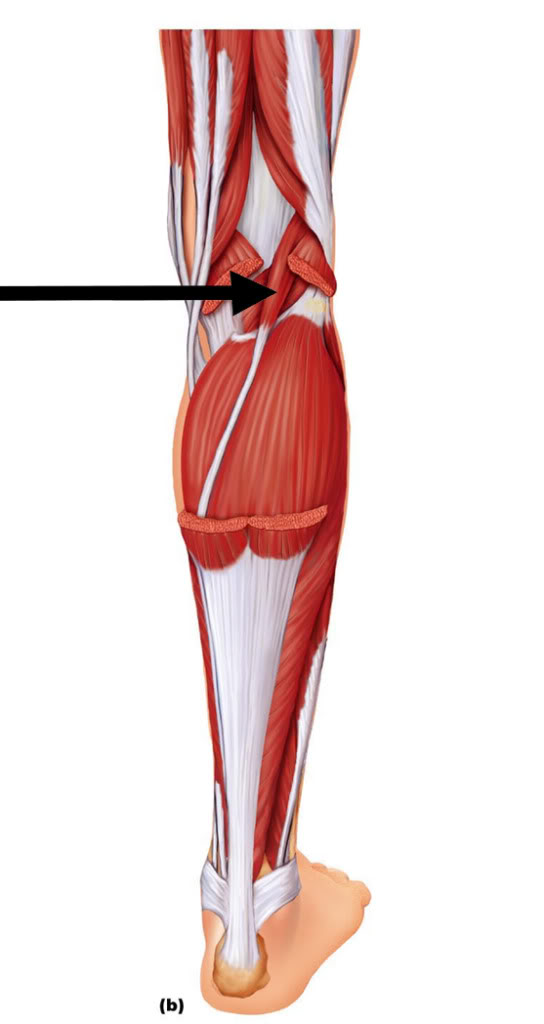
plantaris
O: Lateral supracondylar ridge of femur above lateral head of
gastrocnemius
I: Tendo calcaneus (medial side, deep to
gastrocnemius tendon)
A: Plantar flexes foot and flexes knee
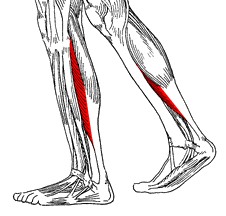
soleus
O: fibula, medial border of tibia (soleal line)
I: tendo
calcaneus
A: plantarflexion
gastrocnemius
O: superior to articular surfaces of lateral condyle of femur and
medial condyle of femur
I: tendo calcaneus (achilles tendon) into
mid-posterior calcaneus
A: plantar flexes foot, flexes knee
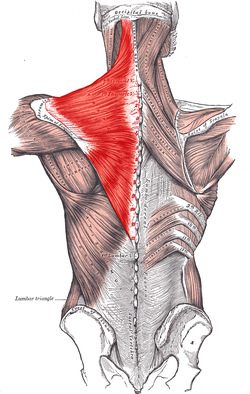
trapezius
O: external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, medial
superior nuchal line, spinous processes of vertebrae C7-T12
I:
posterior border of the lateral third of the clavicle, acromion
process, and spine of scapula
A: rotation, retraction,
elevation, and depression of scapula

rhomboid major
O: spinous processes of the T2 to T5 vertebrae
I: medial
border of the scapula, inferior to the insertion of rhomboid minor
muscle
A: Retracts the scapula and rotates it to depress the
glenoid cavity. It also fixes the scapula to the thoracic wall.
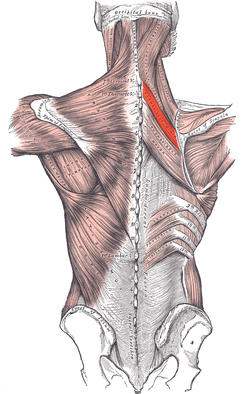
rhomboid minor
O: nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7–T1
I: Medial
border of scapula, superior to the insertion of rhomboid major
muscle
A: Retracts and rotates scapula, fixes scapula to thoracic wall

levator scapula
O: Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1 - C4
vertebrae
I: Superior part of medial border of scapula
A:
Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula
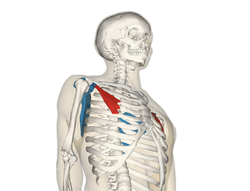
pectoralis minor
O: Third to fifth ribs, near their costal cartilages
I:
Medial border and superior surface of the coracoid process of the
scapula
A: Stabilizes the scapula by drawing it inferiorly and
anteriorly against the thoracic wall, Rises ribs in inspiration
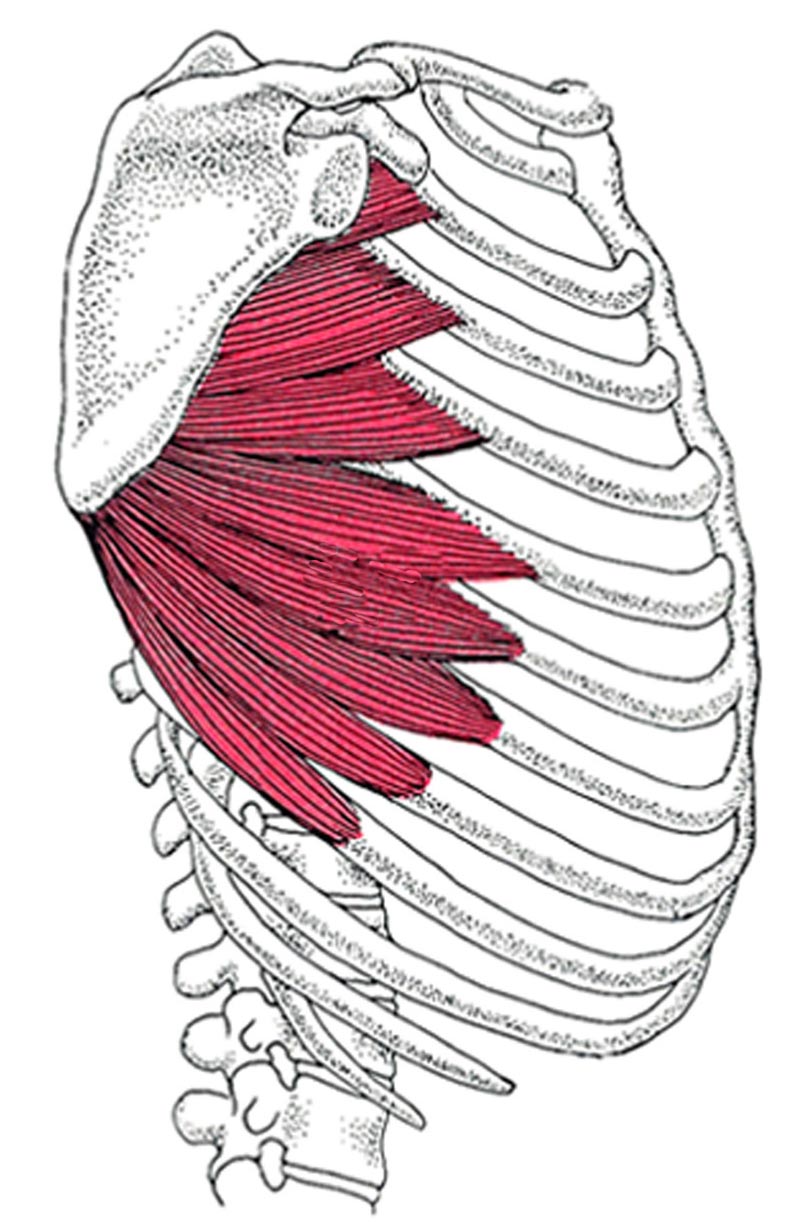
serratus anterior
O: fleshy slips from the outer surface of upper 8 or 9
ribs
I: costal aspect of medial margin of the scapula
A:
protracts and stabilizes scapula, assists in upward rotation.
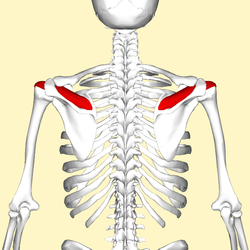
supraspinatus
O: supraspinous fossa of scapula
I: superior facet of
greater tubercle of humerus
A: abduction of arm and stabilizes
humerus see part on controversy of action.
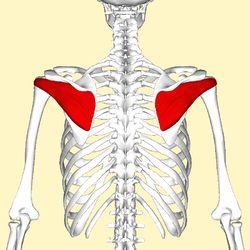
infraspinatus
O: infraspinous fossa of the scapula
I: middle facet of
greater tubercle of the humerus
A: Lateral rotation of arm and
stabilizes humerus

teres minor
O: lateral border of the scapula
I: inferior facet of
greater tubercle of the humerus
A: laterally rotates the arm,
stabilizes humerus
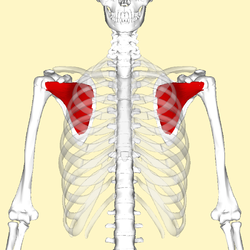
subscapularis
O: Subscapular fossa
I: Lesser tubercle of humerus
A:
Internally (medially) rotates humerus; stabilizes shoulder

deltoid
O: the anterior border and upper surface of the lateral third of
the clavicle, acromion, spine of the scapula
I: deltoid
tuberosity of humerus
A: shoulder abduction, flexion and extension

pectoralis major
O: Clavicular head: anterior surface of the
medial half of the clavicle. Sternocostal head:
anterior surface of the sternum, the superior six costal cartilages,
and the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
I: Lateral
lip of the bicipital groove of the humerus
A: As a whole,
adducts and medially rotates the humerus. It also draws the scapula
anteriorly and inferiorly.

subclavius
O: first rib and cartilage
I: subclavian groove of clavicle
A: depression of clavicle

latissimus dorsi
O: Spinous processes of vertebrae T7-L5, thoracolumbar fascia,
iliac crest, inferior 3 or 4 ribs and inferior angle of
scapula
I: Floor of intertubercular groove of the
humerus
A: Adducts, extends and internally rotates the arm when
the insertion is moved towards the origin. When observing the muscle
action of the origin towards the insertion, the lats are a very
powerful rotator of the trunk
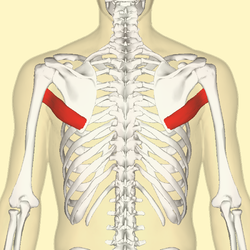
teres major
O: Posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the scapula
I:
Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
A:
Internal rotation (medial rotation) of the humerus, Protracts scapula,
Depress shoulder

coracobrachialis
O: Coracoid process of scapula
I: Medial humerus
A:
adducts humerus , flexes the arm at glenohumeral joint
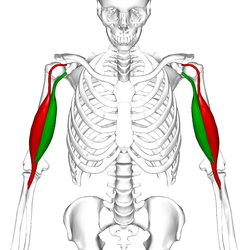
biceps brachii
O: Short head: coracoid process of the scapula
Long head: supraglenoid tubercle
I: Radial
tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis into deep fascia on medial part
of forearm
A: Flexes elbow, flexes and abducts shoulder and
supinates radioulnar joint in the forearm
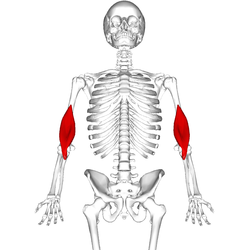
brachialis
O: anterior surface of the humerus, particularly the distal half
of this bone
I: coronoid process and the tuberosity of the
ulna
A: flexion at elbow joint

brachioradialis
O: Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
I: Distal
radius (Radial styloid process)
A: Flexion of Elbow

pronator teres
O: humeral head: medial epicondyle of humerus (common
flexor tendon) ulnar head: coronoid process of ulna
I:
Middle of the lateral surface of the body of the radius
A:
pronation of forearm, flexes elbow

supinator
O: Lateral epicondyle of humerus, supinator crest of ulna, radial
collateral ligament, annular ligament
I: Lateral proximal radial
shaft
A: Supinates forearm

pronator quadratus
O: medial, anterior surface of the ulna
I: lateral, anterior
surface of the radius
A: pronates the forearm
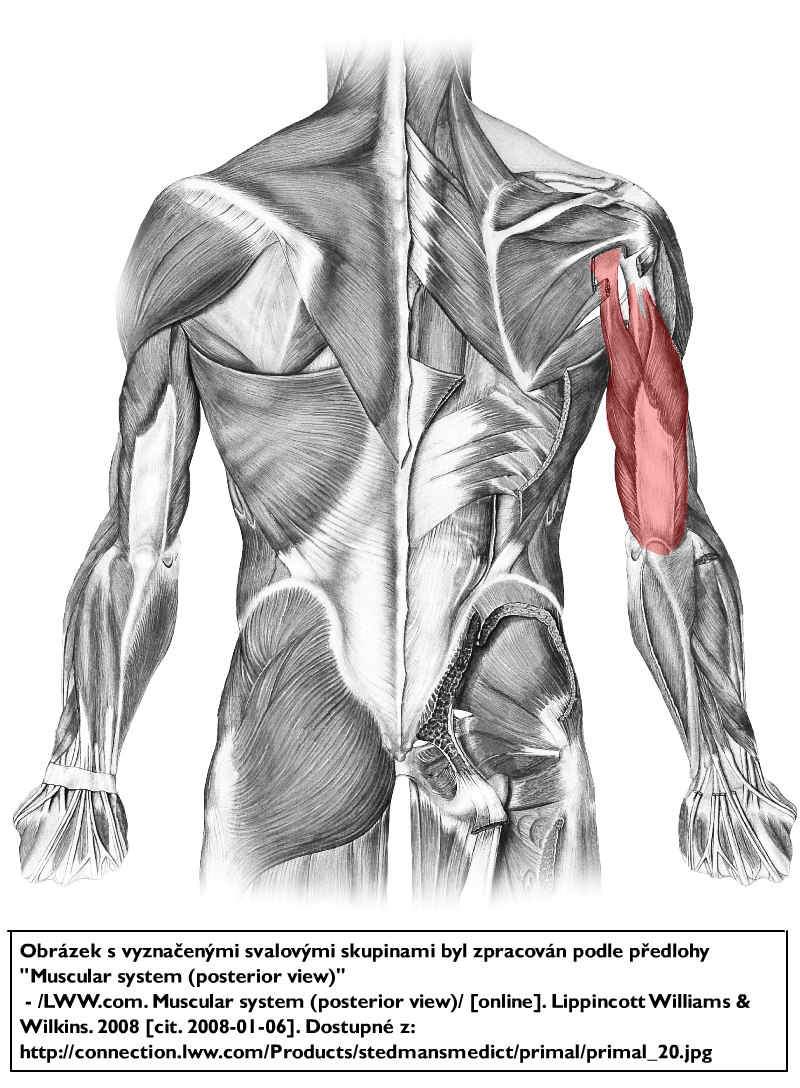
triceps brachii
O: Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
Lateral head: above the radial sulcus
Medial head: below the radial sulcus
I:
Olecranon process of ulna
A: Extends forearm, long head
extends,adducts arm ,Extendsshoulder

anconeus
O: lateral epicondyle of the humerus proximally
I: lateral
surface of the olecranon process and the superior part of the
posterior ulna distally
A: It is partly blended in with the
triceps, which it assists in extension of the forearm.

flexor carpi radialis
O: medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon)
I:
Bases of second and third metacarpal bones
A: Flexion and
abduction at wrist
palmaris longus
O: medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon)
I:
palmar aponeurosis
A: wrist flexor

flexor carpi ulnaris
O: medial epicondyle (common flexor tendon) and medial margin on
olecranon of ulna
I: pisiform, hook of the hamate, base of the
fifth metacarpal bone
A: flexion and adduction of wrist
flexor digitorum superficialis
O: medial epicondyle of the humerus (common flexor tendon) as well
as parts of the radius and ulna.
I: anterior margins on the bases
of the middle phalanges of the four fingers
A: flexor of fingers
(primarily at proximal interphalangeal joints)

flexor digitorum profundus
O: upper 3/4 of the volar and medial surfaces of the body of the
ulna, interosseous membrane and deep fascia of the forearm
I:
base of the distal phalanges of the fingers
A: flex hand,
interphalangeal joints

flexor pollicis longus
O: The middle 2/4 of the volar surface of the radius and the
adjacent interosseus membrane.
I: The base of the distal phalanx
of the thumb
A: Flexion of the thumb.

extensor carpi radialis longus
O: lateral supracondylar ridge
I: 2nd metacarpal
A:
extensor at the wrist joint, abducts the hand at the wrist

extensor carpi radialis brevis
O: humerus at the anterior of lateral epicondyle (common extensor
tendon)
I: Posterior base of the 3rd metacarpal
A: extensor
and abductor of the hand at the wrist joint

extensor digitorum
O: lateral epicondyle (common extensor tendon)
I: extensor
expansion of middle and distal phalanges of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th
fingers
A: extension of hand, wrist and fingers
extensor digiti minimi
O: the anterior portion of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
(common extensor tendon)
I: at the extensor expansion, located at
the base of the proximal phalanx of digit V on the dorsal side
A:
extends the wrist and the little finger at all joints

extensor carpi ulnaris
O: Common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle), ulna
I: 5th
metacarpal
A: extends and adducts the wrist

extensor pollicis brevis
O: radius and the interosseous membrane
I: thumb, proximal
phalanx
A: extension of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint
abductor pollicis longus
O: ulna, radius, Interosseous membrane
I: first
metacarpal
A: abduction, extension of thumb

extensor pollicis longus
O: Middle third of posterior surface of ulna, interosseous
membrane
I: thumb, distal phalanx
A: extension of the thumb
(metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal)
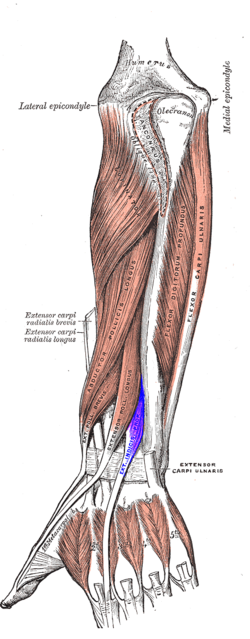
extensor indicis
O: posterior distal third of ulna and interosseous membrane
I:
index finger (extensor hood)
A: extends index finger, wrist