Chapter 3 Transducers - Notes
Q-factor formuala
operating frequency/bandwidth
fractional bandwidth formula
bandwidth/operating frequency
Bandwidth formula
max frequency - min frequency
SPL
SPL = nc/f
NZL
NZL = (D^2 * f) / 6
speed of crystal
c = fo * (2 * thickness)
Operating frequency formula
fo = c/(2*thickness)
thickness formula
thickness = c/(2*fo)
Axial Resolution formula
1/2 SPL
If a transducer diameter is doubled, what happens to the NZL?
If a transducer diameter is doubled, the near zone length will quadruple?
If a transducer diameter is doubled, what happens to the depth of the focus?
If a transducer diameter is doubled, the focus is 4 times as deep.
If the operating frequency is doubled, what happens to the NZL?
If the operating frequency is doubled, the NZL is doubled.
focus beamwidth formula
focus beamwidth = 1/2 transducer diameter
True or False?
The U/S beam is razor thin.
False
beam has
length
width
height (thickness)
Transducer
device that converts energy from one form to another
electric motor
electricity to kinetic
people
chemical to kinetic
light bulb
electricity to light (heat)
Sound transducer
converts electricity to sound & vice versa
Audible transducer
speaker - electricity to sound
microphone - sound to electricty
amber - fossilized plant resin
quartz
rochelle salts
tourmaline
naturally occurring Piezoelectric materials
ceramics - lead zirconate titanante (PZT)
barium titanate
polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)
Man-made piezoelectric material
ferroelectric material
piezoelectric material
Piezoelectric principle
applied pressure (echo) comes back to the transducer, converted to electric energy.
Reverse Piezoelectric principle
when a matter is deformed by an applied voltage it produces a pulse.
when you control the electricity going in, you control the strength of the pulse.
What is the most commonly used piezoelectric material in U/S?
ceramics - lead zirconate titanante (PZT)
PZT
Piezoelectric element
ceramic
Piezoelectric element
crystal
Piezoelectric element
element
Piezoelectric element
Creation of Piezoelectric material
Heat to currie point
polling
cool it
polling
placing a material in a very strong electrical field while the material is at a high temperature
curie point
360 degrees
the temperature where piezoelectric materail loses it's piezoelectric properties.
Heat sterilize
Never
element will lose it's piezoelectric properties
when electricity is applied to PZT
vibrates then creates a mechanical longitudinal wave
Increases & decreases in alternating current change the voltage within the crystal
Piezoelectric Effect
One cycle of the operating (drive) voltage creates how many U/S pulses
2 or 3
How many cycles of (drive) voltage is required for Doppler?
5 to 30
Placing a material in a very strong electric field while the material is at a high temperature.
A) poling
B) curie point
C) piezoelectric
D) autoclaving
A) poling
Frequency of the driving voltage
equals the voltage of the sound produce by the transducer
preferred frequency
voltage of the sound produce by the transducer
operating frequency
voltage of the sound produce by the transducer
resonant frequency
voltage of the sound produce by the transducer
natural frequency
voltage of the sound produce by the transducer
What 2 things determine operating frequency
propagation speed of material - 4 to 6 mm/μs
thickness of the transducer - .2 - 1 mm
propagation speed of material
4 to 6 mm/μs
thickness of the transducer
.2 - 1 mm
thickness formula
thickness = .5λ
wavelength formula
λ = c/f
thickness (f)
thickness = .5c/f
Relationship between thickness and frequency
inverse
Relationship between thickness and wavelength
direct
pulses per second
PRF
voltage pulses per second
VRF
relationship between PRF & VRF
PRF = VRF
formula Pd
pd = nt
SPL formula
SPL = nλ
*decrease the number of cycles = decrease SPL
Dampening

material placed behind the element which reduces # of cycles, Pd & SPL
What is dampening material made of
epoxy resin + tungstun
metal powder + plastic or epoxy.
What is the purpose of damping material?
short pulses create better images
damping material stops pulse
*think of grabbing a bell while it rings
dampening and axial resolution
dampening improves axial resolution
dampening and amplitude
dampening reduces amplitude
dampening and sensitivity
dampening decreases sensitivity
dampening and efficiency
dampening decreases efficiency
dampening and SPL
dampening decreases SPL
dampening and Pd
dampening decreases Pd
Which of the following is positive?
A) reduced amplitude
B) decrease # of cycles
C) decrease sensitivity
D) decrease efficiency
B) decrease # of cycles
impedance
propagation speed * density
what is the purpose of gel?
without gel 80% of intensity of a pulse is reflected off the skin
gel eliminates loss from reflection at the surface of the skin
Matching layer

matching layer eliminates loss from reflection at the surface of the transducer
matching layer thickness formula
thickness = .25λ
or
thickness = .25c/f
list impedance from highest to lowest
element > matching layer > gel > skin
impedance of matching layer
halfway between element and skin
ex. if element is 16 rayls a skin is 1 rayl
matching layer is 8 rayls
What determines the matching layer λ?
A) c/f
B) f/c
C) c * f
A) c/f
Matching layer thickness .25λ.
What is f?
A) operating pulse
B) pulse repetition frequency
C) frame frequency
A) operating pulse
Matching layer thickness .25λ.
What is c?
A) soft tissue
B) piezoelectric element
C) matching layer material
D) gel
E) rubber
C) matching layer material
What type of transducers do not need damping?
continuous wave
therapeutic
what is most desirable to get the maximum sound into the tissue?
A) low impedance crystals
B) multiple matching layers
C) little damping
B) multiple matching layers
Bandwidth
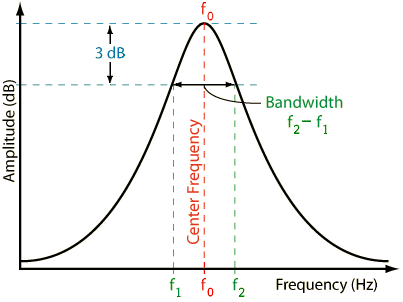
range of frequencies the transducer produces
bandwidth determined by
transducer and the machine electronics
relationship between Pd and bandwidth
inverse
bandwidth formula
max frequency - min frequency
middle frequency
center frequency
fractional bandwidth formula
bandwidth/operating frequency
Q factor
operating frequency/bandwidth
relationship between Q factor and bandwidth
inverse
Quality factor
unitless # describing the degree of damping
approximately the # of cycles in a pulse
low Q transducers
imaging transducers
decrease Pd
low SPL
low Q
widebandwidth
How many pulses in Q factor
1-3
when are transducers broadband?
fractional bandwidth is greater than 80%
Broadband transducers are ___________ sensitive.
less
Why are broadband transducers less sensitive
due to damping
The highest frequency is 6 MHz. The lowest frequency is 2 MHz. What is the bandwidth?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 12
C) 4
6 MHz - 2 MHz = 4 MHz
The highest frequency is 6 MHz. The lowest frequency is 2 MHz. if the center frequency is 4 what is the fractional bandwidth?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
A) 1
bandwidth/operating f
4 MHz / 4 = 1
Advantages of Broad bandwidth
*Multi-Hz transducers can be used
*duplex can use low frequency for Doppler & higher frequencies for B-mode
*dynamic frequency tuning - decreasing frequency with increasing depth
* harmonics can be used if bandwidth includes both frequencies
Types of Resolution
Detail
*axial
*lateral
Contrast
Temporal
Detail resolution
ability to detail fine detail
- the smaller the machine can image the better it is
Axial - depth
lateral - side
section thickness - side
What is detail resolution dependent on?
axial resolution
lateral resolution
matrix size
instrument electronics
display device
Axial resolution
ability to distinguish between two objects that lie next to each other in the depth plane.
Which is frequently better axial or lateral resolution?
axial resolution
What is axial resolution dependent on?
SPL
Synonyms for axial resolution
longitudinal resolution
range resolution
radial resolution
depth resolution
Units of axial resolution
mm
How does SPL improve axial resolution?
shortening the pulse length prevents the echoes from combining as they return to the transducer
How to improve axial resolution?
higher frequency
Decrease SPL by decreasing cycle or wavelength
Lateral resolution
minimum distance that two objects can lie side by side and still be seen as two objects
synonyms for lateral resolution
angular resolution
transverse resolution
azimuthal resolution
What is the prime factor for lateral resolution
beam width
lateral resolution varies with depth.
Where is it best?
at the focus or near zone.
Units of lateral resolution
mm
Symbol for lateral resolution
R L
primary method of reducing beam width
focusing.
How does focusing improve lateral resolution?
by decreasing beam width
Contrast resolution
the ability to see structures with different reflection intensity values as separate items.
Detail resolution is dependent on?
amount of memory
pre & post processing
decibel range
display system
detail resolution
Does urine have low or high impedance mismatch?
Low
Does bone have low or high impedance mismatch
high
SPL a function of
pulse duration
frequency
wavelength
SPW a function of
crystal diameter
Partial thickness artifact
partial volume artifact
(thickness) due to 3D aspect of transducer
Temporal resolution
the ability to accurately located moving structures at any particular instant in time.
resolution pertaining to time
Temporal resolution is dependent in time
Frame rate
depth of penetration
sector size
lines per frame
number of focuses
pulse repetition frequency
SPL
A) The ability to see two items side by side as separate
B) The ability to see two items above and below each other as separate items
C) The ability to see two separate events as separte events
B) The ability to see two items above and below each other as separate items
Huygens Wavelet
Produced by a tiny source
wave diverges into this shape
Huygens Principle
According to Huygens the hourglass shape of a sound beam is the result of constructive and destructive inference of many sound wavelets
Aperture
width of the beam
AKA width of the element
near zone
is the area from the transducer to the focus.
the area of convergence
focus
the smallest part of the beam
1/2 size of element
far zone
the area of divergence
is the area from the focus to the end of the beam.
What shape are sound waves produced by imaging transducers?
hourglass
What is the Fresnel zone?
Near zone
What is the Fraunhofer zone?
far zone
When does the beam stop divergence?
when it reaches its original size
What does width determine?
lateral resolution
What changes top to bottom?
lateral resolution
The width perpendicular to the scan plane determines what?
section thickness artifact.
Formula for axial resolution
1/2 SPL
Grating lobes
Significant intensity that travels out in some direction not included in the beam
What type of transducer causes grating lobes?
Array
What type of transducer causes side lobes
single element transducers
What are some other names for near field?
focal length
focal depth
What happens to the near field when you increase diameter?
increases
What happens to the near field when you increase frequency?
increases
NZL formula
Focal zone length
(f*d^2)/6
f 5 MHz d 5mm? 1 NZL
A) 4 mm
B) 4 cm
C) 125 mm
D) 125 cm
E) 2 mm
F) 2 cm
F) 2 cm
=(5*5^2)/6
=(5*25)/6
=125/6
=20 micrometer
=.02 cm
What is the relationship between near zone length and diameter?
direct
What is the relationship between near zone length and frequency?
direct
For and unfocused beam where are the intensities the highest?
at the focus
For and unfocused beam at any given point, Beam diameter is dependent on what?
frequency
element diameter
depth
When frequency is low beam divergence is __________.
wide
When frequency is high beam divergence is __________.
narrow
When diameter is high beam divergence is __________.
narrow
When diameter is low beam divergence is __________.
wide
Does a smaller frequency gives a shorter or longer near zone?
shorter
variable aperture
increases # of elements fired
What is the relationship between Beam divergence and frequency?
indirect
What is the relationship between Beam divergence and diameter?
indirect
Name the 3 way to focus a transducer
* curve the face
* add a lens
* phase the firing sequence electronically
What type of focusing are the following?
* curve the face
* add a lens
fixed
conventional
mechanical
Focal region
an area on either side of the focal point which is within 25& or 6 dB of SPL
Focused transducers and lateral resolution
worst lateral resolution due to mechanical focusing
what is the value of focusing?
to improve resolution
What improves lateral resolution?
decrease size of focal zone
decrease width of beam
Automatic scanning
method by which transducers rapidly collect information
*creating multiple adjacent scan lines
*rapidly
*repeatedly
*real time scanning - depends on frame rate
What are the two ways rapid motion is accomplished in real time scanning?
Mechanically
* motor unit
* fluid inside
Electronically
* no motor
* no moving parts
* no fluid
Mechanical Motion in fixed focus
mechanical steering has to fo with curvature of PZT

1. linear array
2. sector steered
3. curved linear
4. vector
Electronic scanning sequence
because elements are fixed focus is fixed
all elements fired at once act as one pulse
fires element in sequence until one frame is built.
During electronic scanning phasing
If delay is from left to right pulse angle to the ___________.
right
What does phasing control?
beam direction
focus level
Haygens law
multiple spherical wavelengths create a wave form produce a wave and the wave travels in a direction - orthogonal to the wave form.
where are electronic phased delay patterns produced?
in the beam former
how does phasing control aperture?
some electricity is turned off. This changed the size of the element
How is focus changed with phasing?
by curving the pattern
phasing
When focus is great the focus is ___________.
shallow
Vector
sector with flat top
vector converted from a linear rectangular format into a vector format
Annular array
multiple circular elements with wobble motor sweeps across
What format are annular arrays displayed in?
sector
Annular arrays
Steering is mechanical or electronic?
mechanical
Annular arrays
focus is mechanical or electronic?
electronic
dynamic apodization
changing the amplitude as focusing & steering changes to decrease grating lobe
dynamic focusing
delay correction is changed "on the fly"
transducer sets listening focus, as you cnage the depth
dynamic aperture
using more or less elements to change the diameter of the entire face.