COT 6410 Computational Complexity Midterm
Deterministic Finite Automata notation
A = {Q, Σ, δ, q_0, F}
Q - set of states
Σ - alphabet
δ - transition function
q_0 - start state
F - finale state
δ(current state, character) = state you would have transitioned to
δ(current state, character) = state you would have transitioned to
How do you reverse a language represented as a DFA
- Change start state to final state
- Change finale state(s) to start state(s)
- Reverse the transitions
(optional) - create a new state that λ transitions to all the start states
How to tell if something is a Regular Language?
A DFA or NFA can recognize it
Difference between DFA and NFA
DFA due to its deterministic nature must have a transition out of every state for every character in the alphabet, and NO λ transitions. Also note every DFA is technically also an NFA
NFA doesn't have to have a transition for every alphabet character and can have λ transitions. Also note every NFA has an equivalent DFA
some primitive notation
Φ = {}
λ = {λ}
a means where 'a' is in Σ denotes {a}
Closure properties for R and S
R · S
R + S
R*
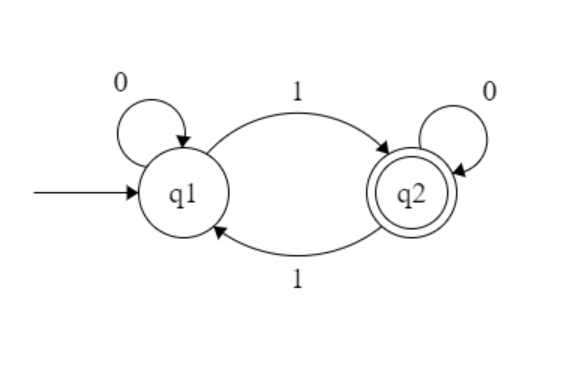
convert this to a reg ex using (R_ij)^k method
in 1-16 notes
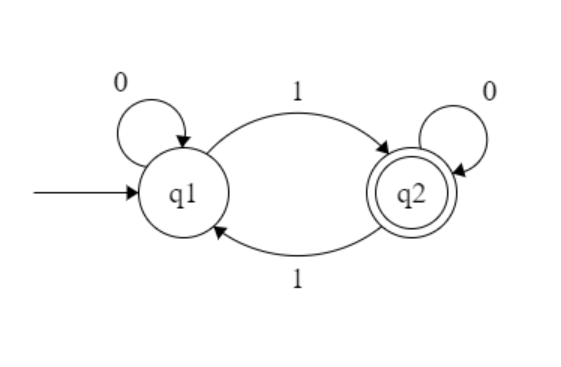
convert this to a reg ex using state ripping
in 1-16 notes

convert this to a reg ex using Arden's
in 1-21 notes
Show the relation between the following family of languages. Regular,
Deterministic Context-Free, Context-
Free, and Context-Sensitive
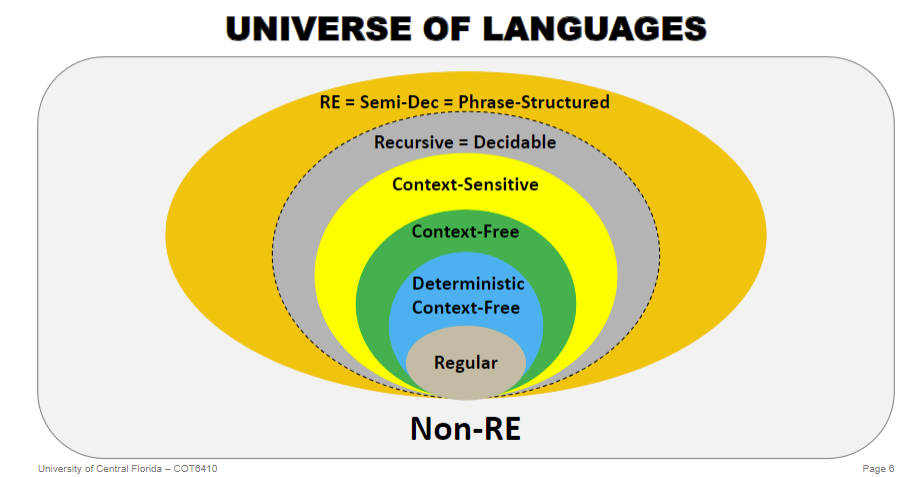
Show the relation between models of computation
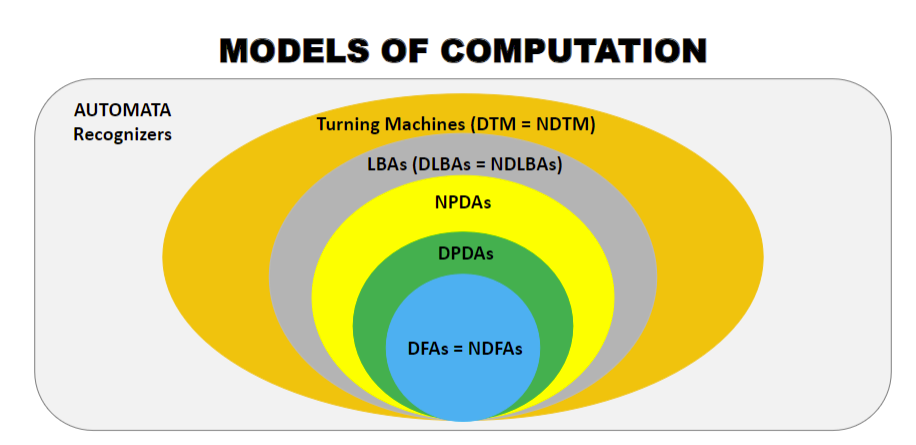
True or False: Every NFA does not have an equivalent DFA
true, you can turn an nfa into usually a nasty much larger dfa with stuff like trap states.
Does an algorithm exist for determining if a grammar is considered ambiguous?
no, ambiguity is undecidable
Whenever a new problem is created, what is it considered inherently?
solvable and unsolved
solved is temporal or inherited
temporal
unsolvable/undecidable is temporal or inherited
temporal
unsolved is temporal or inherited
inherited
if we solve that new problem it moves from
solvable and unsolved
to?
solvable and solved
if we find that new problem is unsolvable it moves from
solvable and unsolved
to?
unsolved and solved
Can the CYK parsing algorithm take any type of grammar as input?
CYK operates only on context-free grammars given in Chomsky normal form
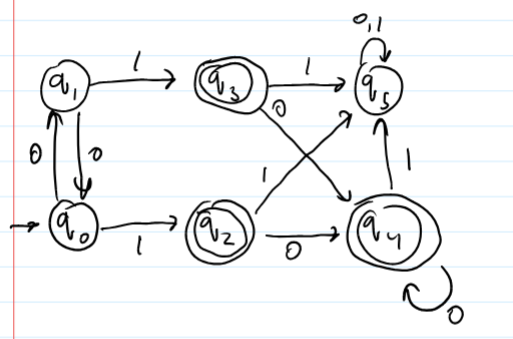
Find the minimal equivalent DFA using the method that was shown in class.
1-23 slides
True or False: The reversal operation is closed under regular languages.
true earlier card says how
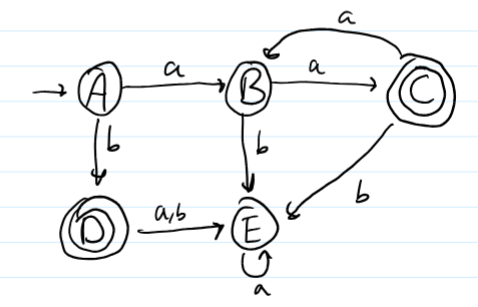
Express the following FSA as a regular expression using Arden's Theorem..
1-21 slides