Lab7 (pg. 1-5)
signal of interest must be converted into an analog voltage is done by a ____
transducer
process: voltage usually varies continuously over time and is monitored by the hardware which can modify it by amplification and filtering
signal conditioning
signal conditioning zeroing
involves the removal of an unwanted steady offset voltage from a transducer's output
frequency
the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time
amplitude
height of the wave from baseline to crest
waveform
shape and form of a signal
wavelength
length from the crest of one peak to the crest of the next peak
skeletal muscle cells
make up about 40% of the cell mass of the body
skeletal muscles so the majority of
the work for locomotion and support of the animal skeleton
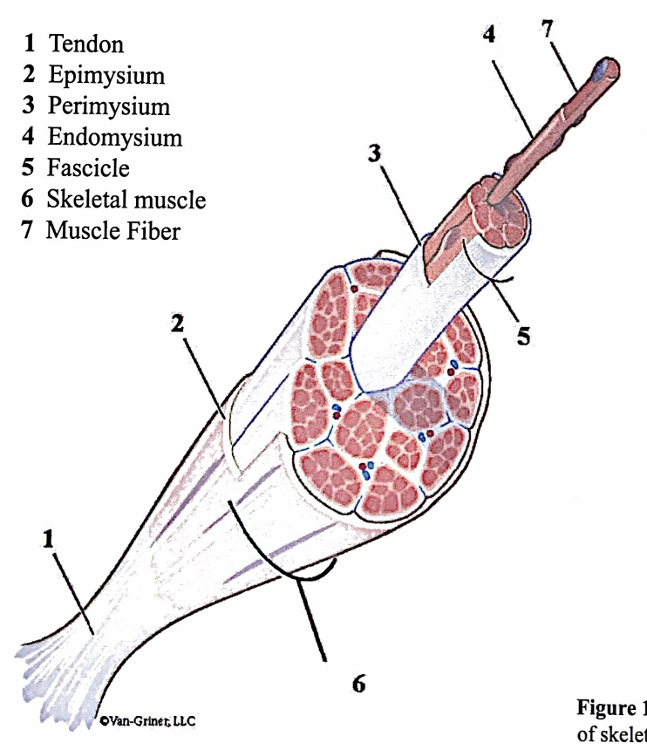
each muscle is made up of individual ____ organized in fascicles.
muscle fibers (muscle cells)
to produce mechanical energy in directed movements,
muscles to the chemical energy stored in ATP
skeletal muscle structure- connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium
disease of muscle are rare and mostly inherited but,
trauma to muscle is very common
upper motor neuron lesions
loss of muscle function as a consequence of strokes damaging neutons in the brain
skeletal muscle is ____
consciously controlled and therefore voluntary, can rapidly contract but tires rapidly.
excitability
all muscle cell membranes have an electric charge differential which can be changed upon stimulation (such as through neurotransmitter binding) to ultimately produce an intracellular muscle response
contractility
all muscle cells shorten when stimulated
extensibility
all muscle cells can also be stretched, sometimes more than their resting length
elasticity
all muscle cells, after being stretched, can recoil to the resting cell length
an entire skeletal muscle, such s the gastrocnemius is an ___
organ and is made up of more than just muscle fibers- it has nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. Nerves and blood vessels enter the muscle near its center and then branch throughout the muscle running through the connective tissue sheaths (epi-, peri-, & endomysium)
tendons
connective tissues that attach muscle to bone. the connective tissue sheaths of muscles are continuous with each other and with tendons to transfer the force of the contracting muscle fibers to the structure (bone) to be moved
muscle attachments can be
direct or indirect
direct attachment
the periosteum or perichondrium is fused with the muscle's epimysium
indirect attachments
more durable, smaller, and are more common. example: tendon or aponeurosis
tendons are mostly
collagen and are rope-like extensions of a muscle's connective tissue
aponeurosis are
similar sheet-like extension instead of rope like
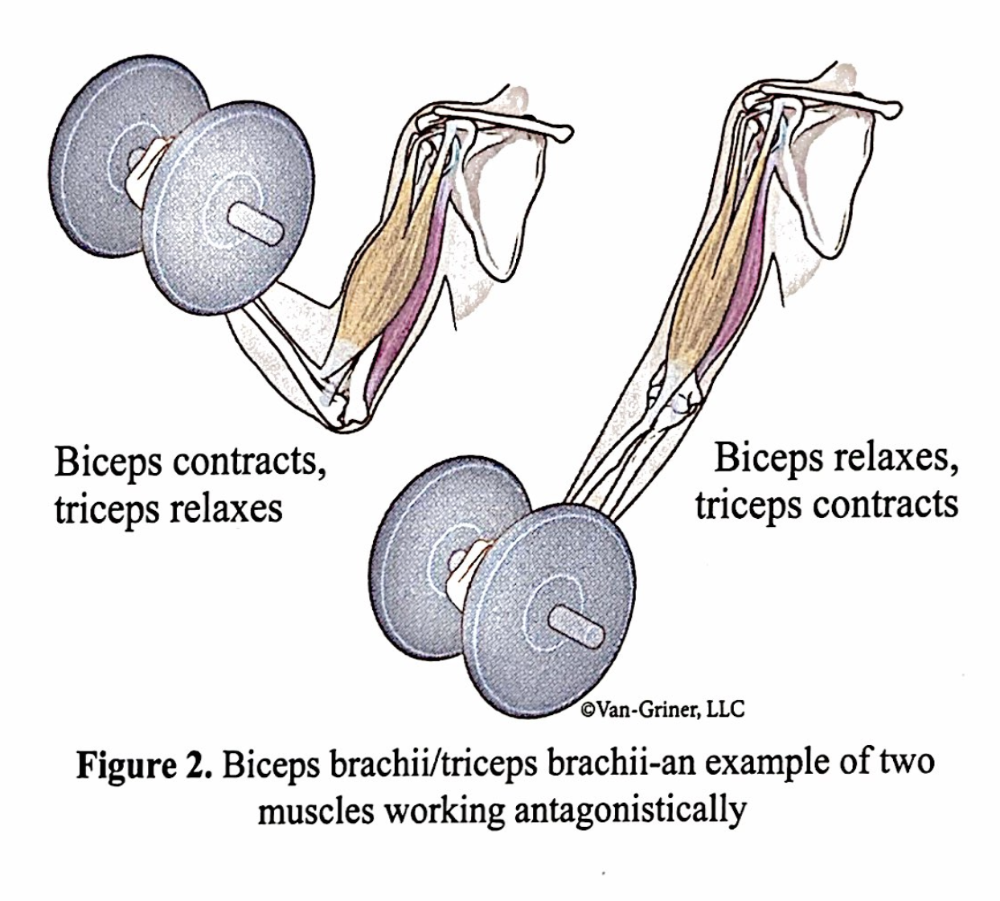
antagonistically
as one muscle contracts and shortens, its antagonist relaxes and elongates (two or more muscles usually work like this)
skeletal muscle fibers are
very large multinucleated cells
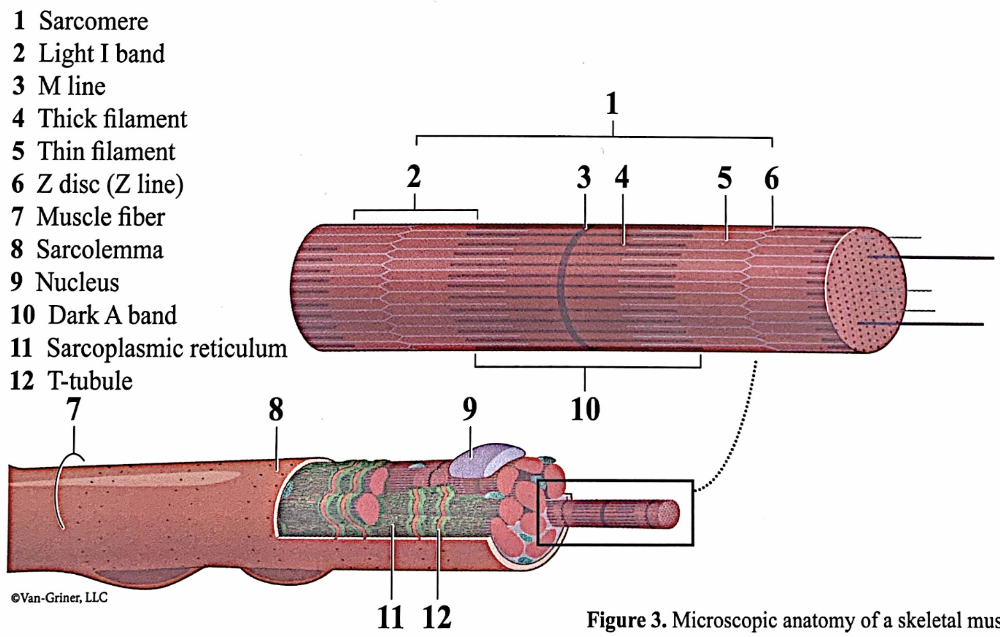
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm
myoglobin
muscle cells contains lots of it, are granules of glycogen that can be broken down to supply ATP from glucose for energy
most of the intracellular volume of skeletal muscle cells is taken up by organelles called ____. they are repeating units of sarcomeres.
myofibrils
sarcomeres
smallest "atomic" contractile units of skeletal muscle fibers
skeletal muscle is striated because the dark ____ and light _____ within the sarcomeres are perfectly lines beside one another.
A bands; I bands
each A band has a middle region that is slightly light called the
H zone (or H band)
biceps brachii/triceps brachii-an example of two muscles working antagonistically
microscopic anatomy of a skeletal muscle fiber
myofilaments' alignment
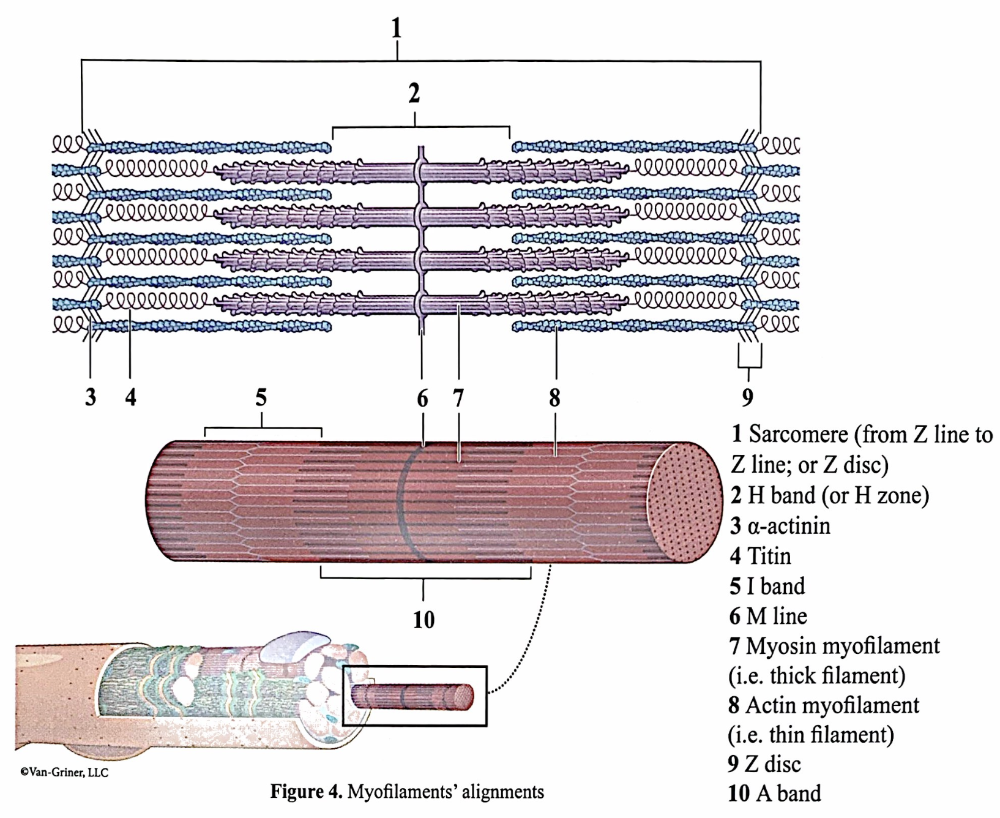
the I and has a dark midline region termed the
Z line (or Z disc)
sarcomere runs from
Z line to Z line OR from each half I band to half I band with an A band in the middle
thick filaments
contain the protein myosin and run the length of the A band
myosin proteins contain
protruding globular heads
each globular head associates
with two light chains
The M line connects thick filaments which
only have myosin heads in areas where actin proteins of the thin filament and myosin heads of the thick filament overlap
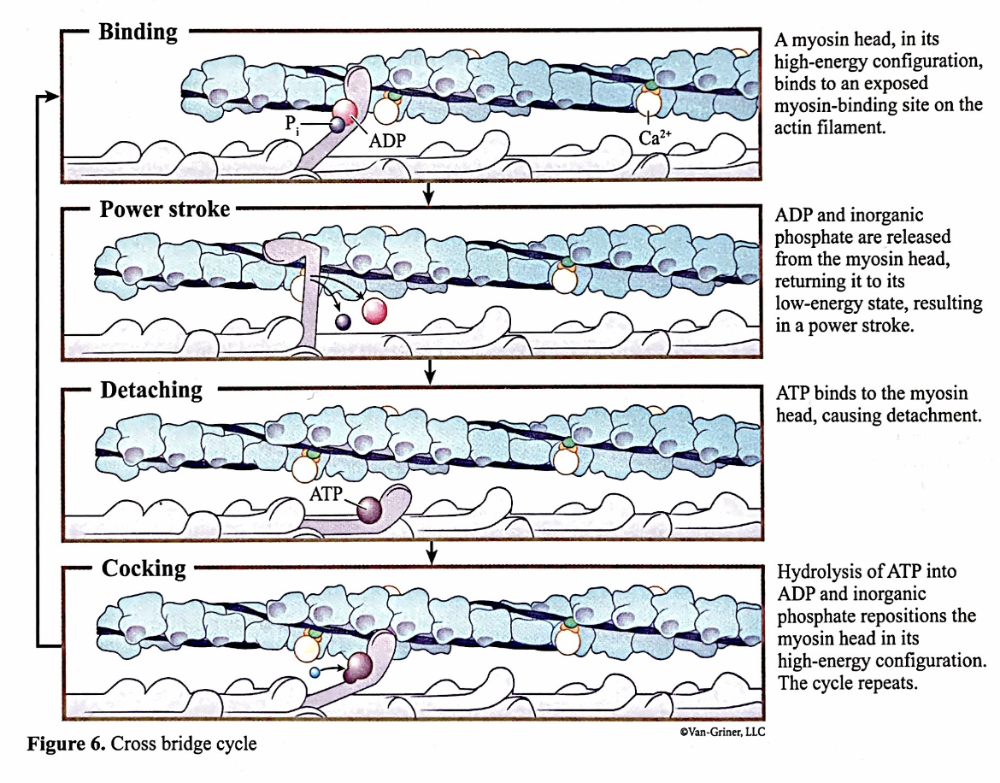
when a muscle contracts, the globular myosin heads link the thick and thin filaments together making ____, and swivel as motors to create force that shortens the sarcomere
cross bridges
each thick filament can contain
over 300 myosin molecules
the thin filament consists of a helix of two actin subunit strands plus the proteins ____ and ____
tropomyosin; troponin
each actin subunit (tropomyosin and troponin) is
a globular actin and contains active sites where myosin heads attach
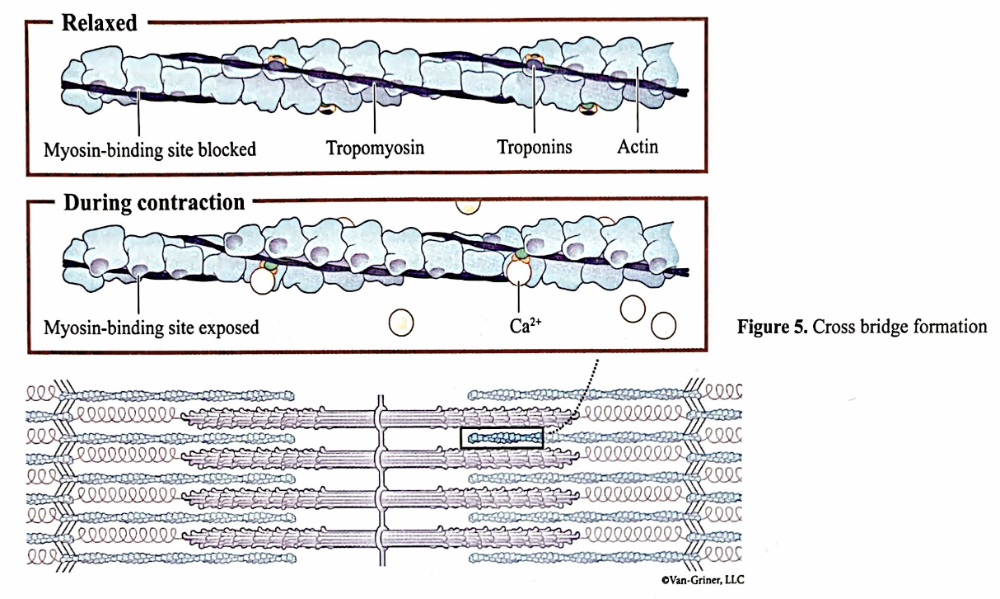
in a relaxed muscle fiber, tropomyosin ___
blocks actin's myosin-binding
troponin is composed of
three globular polypeptides each of which have different function, one polypeptide binds actin, another binds tropomyosin, calcium ions bind to the third which is sandwiched between the other two troponin polypeptides
elastic filaments, made of the protein ____ , run from the Z line to the thick filaments to hold them in place and provide flexible recoil to the sarcomere as it contracts, relaxes, and stretches.
titin
when titin reaches its normal extension, ____
it stiffens and resists further over-stretching of the muscle
cross bridge formation
cross bridge cycle
sarcoplasmic reticulum
in muscle, endoplasmic reticulum becomes very elaborate
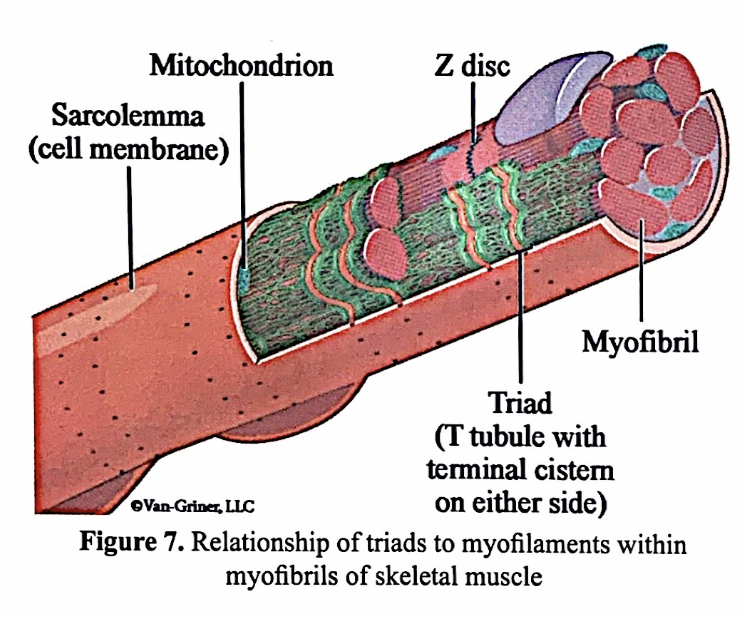
each myofibril is surrounded by
interconnecting sarcoplasmic reticulum
at the A band I band junction, the sarcoplasmic reticulum forms large perpendicular cross channels called ______ which are always found in pairs
terminal cisterns
mitochondria and glycogen granules are highly abundant near the
sarcoplasmic reticulum
sarcoplasmic reticulum controls
calcium levels within the sarcoplasm and stores and releases calcium to control muscle fiber contraction
at the A band and I band junction, elongated tubular extensions of the sarcolemma dice deeply into the cell and are ___
T tubules
triad
the T tubule plus terminal cisterns on either side
when a nerve stimulates a muscle, ____
an electrical signal travels down the sarcolemma and be carried deep into the muscle to every sarcomere.
the elctrical signal causes
the release of calcium from the terminal cisterns which leads to contraction
both the T tubules and terminal cisterns of teh sarcoplasmic reticulum have
integral membrane proteins that protrude into the space between these structures
these integral proteins if the T tubules function as
voltage sensors while the integral proteins of the terminal cisterns create gated channels for the release of calcium
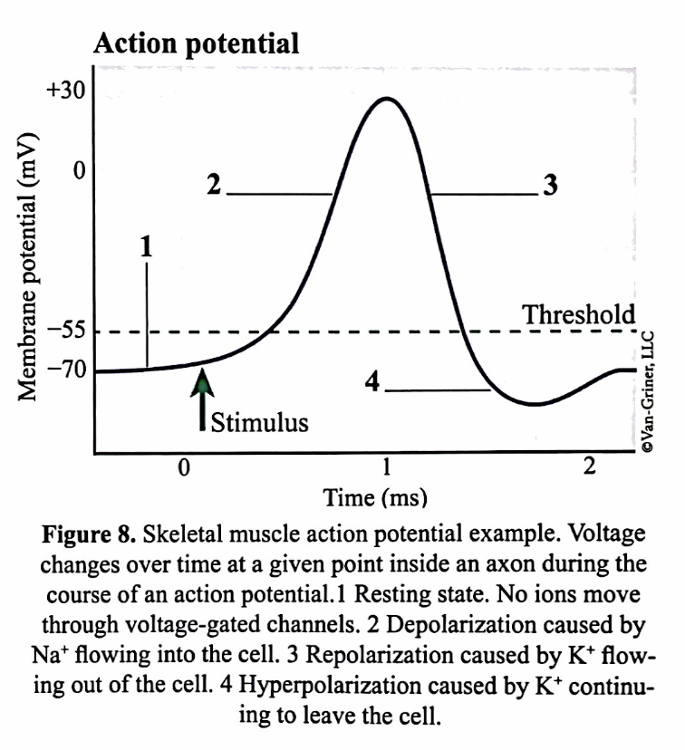
all plasma membranes of all human cells, including the sarcolemma of muscle fibers, carry a resting charge or ____ wehre the inside of the cell is more negative relative to the outside
polarization
the initiation and propagation of a muscle action potential involves three steps
- acetylcholine binds to its receptor opening chemical ligand-gated ion channels for sodium. these events transciently make the inner surface of the sarcolemma less neagtive, termed depolarization. this begins at the end plate and is thus termed the end plate potential.
- voltage-gated sodium channels on the surrounding sarcolemma respond to the change in charge and open allowing positive sodium to enter down its electrochemical gradient. once a threshold potential is achieved, the voltagr change in the membrane becomes sufficient to open further voltage-gated sodium chanels and spread the signal in the form of a depolarization wave along the sarcolemma termed a muscle action potential.
- once the voltage become sufficiently positive, the voltage-gated potassium channels open. the membrane then becomes more negative or repolarizes as positive potassium exits the cell down its concentration gradient. once the membrane becomes sufficiently negative again, this change in charge closes the voltage-gated potassium channels.
relationship of triads to myofilaments within myofibrils of skeletal muscle
skeletal muscle action potential example. voltage changes over time at a given point inside an axon during the course of an action potential. 1- Resting state. no ions move through coltage0gates channels. 2- depolarization cause by Na+ flowing into the cell. 3-repolarization caused by K+ flowing out of the cell. 4- hyperpolarization caused by K+ continuing to leave the cell
the gradient differences for sodium and potassium are restored by ____ which moves sdium out and potassium in
sodium potassium ATPase pump
refractory period
while repolarizing the cell cannot be stimulated again until the membrane is sufficiently negative
consequential contraction
may last for more than 100 times the duration of the electrical signal
muscle action potential travels along the sarcolemma and down the T tubules where the ___ causes voltage-sensitive tubule proteinf to undergo a change in shape which leads to opening of calcium release channels in the terminal cisterns.
depolarization
excitation-contraction coupling: events of contraction of the muscle description -->
ca+ moves into sarcoplasm, removes inhibitory action of tropomyosin as it bind to troponin, changing shape for tropomyosin to move away and expose binding site for myosin on actin thin filaments. myosin binds and cross bridge cycling starts.
repolarizes
voltage sensitive tubule proteins regain their resting configuration, closing the ca+ release channels of terminal cisterns.
muscle relaxation
ca+ pumps back into SR by ATP dependent ca+ punmps in the terminal cistern membrane. once ca+ levels drop, inhibitory effect of tropomyosin is restores so actin and myosin no longer cross bridge
tropomyosin
physically blocks the myosin binding active sites on actin when intracellular ca+ is low
when it is high, it binds to troponin
power stroke
occurs as phosphate and ADP are released from the myosin head allowing the myosin to swivel or stroke from its high energy configuration to a low energy state. this pulls actin filament toward M line. ATP binds to myosin head = myosin head to detach. nerve impulses arrive at muscle in rapid succession, ca+ increase, another contraction before muscle relaxes
cross bridge cycling
occurs many times during a single contraction
muscle tension
defined as the force exerted by a contracting muscle on an object
load
defined as the opposing force applied on the muscle by the mass of the object being moved
each individual muscle fiber is innervated by a branch of a
motor axon
neuronal action potential activates
all of the muscle fibers innervated by the motor neuron and its axonal branches
motor unit
motor neuron, together with all of the individual muscle fibers that it innervates
vary greatly in size, from small motor unit to large motor unit
the small the motor unit, ____
the finner the control of movement in that muscle
small units controls
movements of the fingers and eyes
large motor units controls
large limb muscles
regardless of size, specific motor units contains
only one neuron
activation process involves
initiation of an action potential along the axon of the neuron