Ch. 4 amino acids
Dand E are basic amino acids because at neutral pH they
donated a side-chain proton
K and R are considered basic because at neutral pH they have
accepted a side-chain proton
All amino acids are
polyprotic, weak acids
A peptide bond is formed in a condensation reaction between two
two amino acids
Which amino acids are the exceptions when it comes to Geometry and chirality?
Proline and Glycine
Which amino acids falls under nonpolar?
Leucine, Proline, Alanine, Methionine, Tryptophan, Phenylalanine, isoleucine and Valine
Which amino acids are considered polar?
Glycine, Serine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Threonine, Cysteine, and Tyrosine
which amino acids are considered acidic?
Aspartic acid and Glutamic acid
Which amino acids are considered basic?
Lysine, Arginine, and Histidine
At a neutral pH, the alpha amino group and alpha carboxyl group are
charged
If the pH is below the pKa
protonate
If pH is above the pKa
deprotonate
DEHCYKR:
D=3.9, E=4.1, H=6.0, C=8.4, Y=10.5, K=10.5, R= 12.5
All amino acids are chiral except:
glycine
Which amino acid configuration predominates?
L-amino aicds
Absorbance is at___ especially in Tyr and Trp.
280 nm
When a protein in floating freely in an aqueous solution, the
hydrophobic side will be inside the proteins and hydrophilic will be found on the outside of protein
When pH<pKa, it is
(+) charged
When pH>pKa, it is
(-) charged
Cysteine is the only amino acid that participates in
covalent reaction in proteins
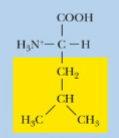
leucine, Leu, L
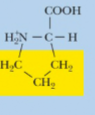
Proline, Pro, P
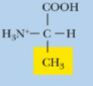
Alanine, Ala, A
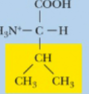
Valine, Val, V
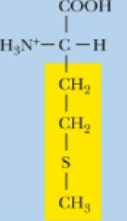
Methionine, Met, M
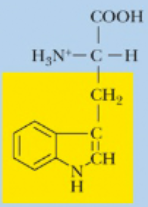
Tryptophan, Try, W
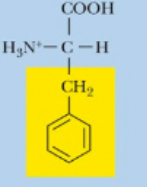
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
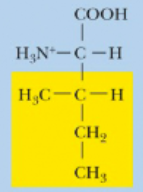
Isoleucine, Ile, I
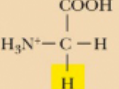
Glycine, Gly, G
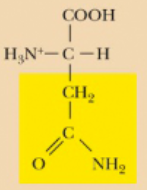
Asparagine, Asn, N
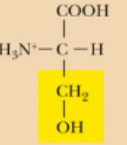
Serine, Ser, S
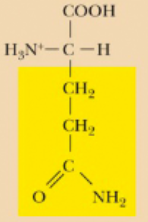
Glutamine, Gln, Q
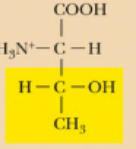
Threonine, Thr, T
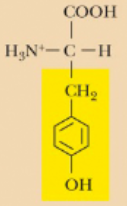
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
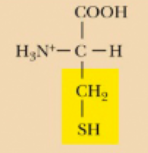
Cysteine, Cys, C
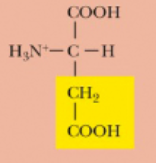
Aspartic acid, Asp, D
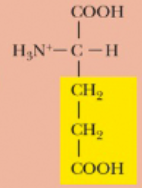
Glutamic acid, Glu, E
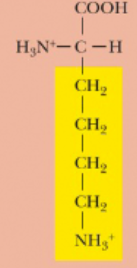
Lysine, Lys, K
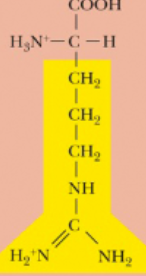
Arginine, Arg, R
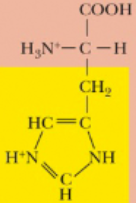
Histidine, His, H