Fundamentals of Nursing
What is a therapeutic index?
Drugs desired therapeutic effects and it's adverse effects
What is the difference between a narrow and wide therapeutic index?
A narrow index is more difficult to manage
- may require close monitoring for toxicity or adverse effects
- EX. seizure meds
A wider therapeutic index is safer and requires less monitoring
- EX is antibiotics and propranolol
Type of Drug Responses:
Graded

biological effects that can be measured continually up to the maximum responding capacity of the biological system
- BLOOD PRESSURE
- HEART RATE
Type of Drug Responses:
Quantal

biological effects are present or not present
effects of a response that may or may not happen
- SEIZURES
- RASH
What is Pharmacodynamics?
What are some factors of Pdyamics?
What the drug does to the body
- Ease of titration
- Therapeutic index
- A narrow therapeutic index is more difficult to manage.
- seizure medications
- A wider therapeutic index is safer and requires less monitoring.
- Like antibiotics
What is pharmacokinetics?
What are factors of Pkinetics?
The movement of the drug to the bodies circulation
- Distribution
- Ability to cross blood–brain barrier
- Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism
- Renal elimination
- Dose–concentration curve
- Half-life
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption
What is Absorption?
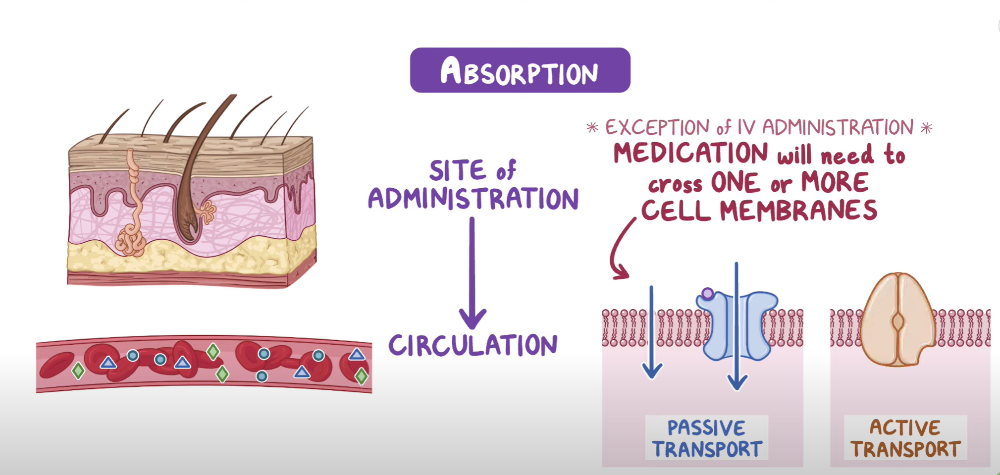
The movement of the drug to the body's circulation
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption
What are things to consider with Absorption of a drug?
**think how you administer it & how body absorbs it
Things to consider:
-
Route of Administration
- IV, IM, oral, sublingual, intranasal
- ***IV fastest method of drug absorption
-
Site of Administration
- Topical- targets the site
- Inhaler- goes straight to lungs
- Ophthalmic- goes to the eyes
-
Bioavailability
- % of the drug that is truly absorbed/administered
- IV- 100% vs Oral 10-90%
- "availability of drug that is truly absorbed"
-
Peak blood levels
- highest level of drug in the body
Pharmacokinetics: Distribution
What is Distribution?
What is required for adequate distribution of a drug?
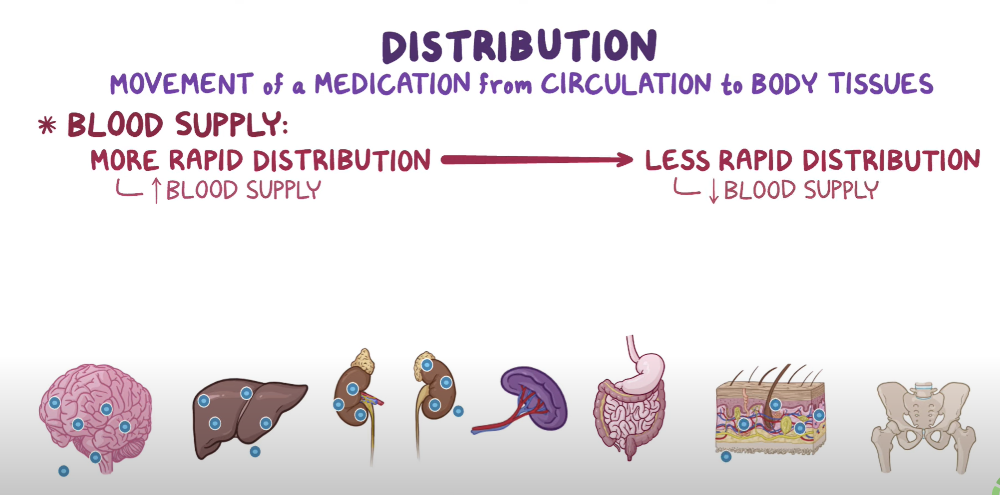
The movement of the drug to the target organ/tissues
- Good blood supply
- Drug distributed to areas of high blood flow first then to low blood flow areas
- EX: Kidneys, liver first then adipose tissue
Pharmacokinetics: Distribution
What are things to consider with Distribution ?
**think size, environment, and how it gets around
Size of molecule
- smaller molecules are better able to diffuse than larger molecules in passive diffusion
Acid & Base Environments
Protein binding
- Plasma proteins in blood
- Albumin is a major protein in the blood
- Consider pts with renal/ liver disease because proteins are produced less or excreted
Transporters
-
influenced by transporters, membrane proteins that
facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell membranes
Volume of Distribution
Pharmacokinetics: Distribution
What are things to consider when crossing the blood brain barrier & placental barrier?
Blood-Brain Barrier
- very protected- impenetrable
- only lipid soluble drugs can pass
Placental Barrier
- Many drugs can pass barrier
- Low molecular weight drugs pass easier
Pharmacokinetics: Distribution
Things to consider with protein binding?
Drugs exists in bound or unbound status
Travel when bound and cross membranes when unbound
- Drug action occurs when drug is unbound
Highly protein bound drug means that less of the drug is available
Low plasma protein (low albumin d/t decrease liver, renal fnx, malnourished, cancer pts-cells feed off body) will result in more free drug
Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism
What is metabolism?
Chemical alteration of drug to metabolites
Metabolism increase or decreases onset, duration, and toxicity of the drug
The breakdown of the drug in the liver
Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism
What does first pass mean and half-life?
First pass IS FOR ORAL DRUGS
- Concentration of the medication function that is reduced before it reaches circulation
- Occurs in the liver or gut
- first pass may break down most function of drug so may need to consider another route of administration
Half life
- Time it takes for 50 % of the drug to be eliminated
Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism
What is CYP450 and things to consider?
It is a major drug metabolizing enzyme
Organized into numbered families
Enzymes can slow or increase drug metabolism
Concurrent administration w/ inhibitor or inducer can alter metabolism of medication
Pro-drugs-- need to go through metabolism to become an active form of drug
Pharmacokinetics: Metabolism
Factors that affect metabolism?
***person, environment
- Age
- Genetics
- Pregnancy
- Diet
- ETOH
- Liver disease
- Environment
- Timing
- Drug Interactions
Pharmacokinetics: Excretion
What is excretion?
What organs eliminate drugs?
Removal of drug from body to organs of elimination
***The drug moving to the potty
- Kidney
- GI
- Lungs- ETOH, Ketosis
- Skin- Sweat
- Saliva
- Mammary Glands- via breast milk
Pharmacokinetics: Excretion
Factors that affect renal excretion?
Kidney function
Age
- Infants/Older adults @ risk for ADR bc renal function (immature or decreased)
Hydration
Cardiac Output
Pharmacodynamics
What is a dose curve response?
Read graph from left to right to represent increase dose concentration
- Dose- response curve shows the relationship between drug dose and magnitude on effect
- Dose below the curve do not produce a pharmacological response
- Dose above the curve do not
produce additional pharmacological response
- May have unwanted side effects = toxicity
Expressing a drug response
What is potency?
What is efficacy?
What is intrinsic activity?
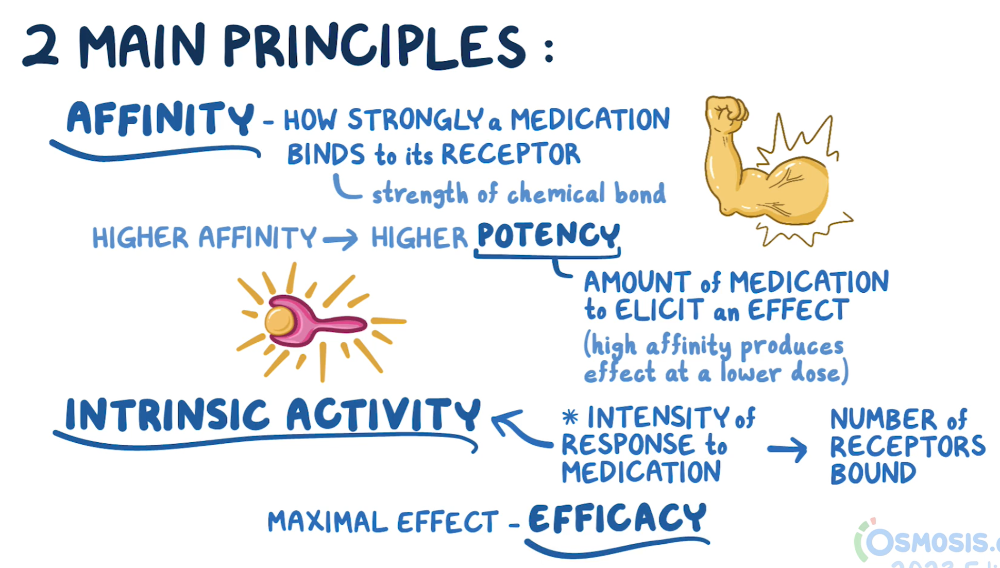
Potency: the amount of the drug needed to produce a biological effect
Efficacy: The maximum effect a drug can produce
Intrinsic activity: ability to produce a response once the drug is attached to the receptors
Drug Selectivity
What is drug selectivity?
What is minimum effective concentration?
What is minimum toxic concentration?
What is therapeutic index?
Ratio of the dose producing undesired effects
Minimum effective concentration (MEC): level below therapeutic effects will not occur
Min toxic concentration (MTC): level above which toxic effects occur
Therapeutic Index: ratio of MTC to MEC
What are the components to rational drug selection?
***think Problem, Plan, Educate
Define the patient problem
Specify the therapeutic objective
Collaborate with the patient
Choose the treatment
Educate the patient
Monitor effectiveness
Define the patient problem
What are the ANP actions to define the problem?
Assess the patient
Develop differential diagnosis
Use diagnostic test to confirm
Specify the therapeutic objective
What is your goal of treatment?
Cure the disease?
Help relieve S/S
Long term prevention
Replace what is needed- Insulin, Vitamin D
make the patient comfortable with palliative therapy
Collaborate with the patient
What does the World Health Organization recommend?
The World Health Organization recommends including the patient in developing the therapeutic objectives of drug therapy.
Choose the treatment
What are things to consider before choosing the drug therapy?
- first determine what the appropriate therapy would be using evidence-based guidelines
- second, individualize the drug
choice for the specific patient
- consider pharmacokinetics & -dyamics
- Determine the cost of the drug
- When writing a prescription, discuss whether patient has ability to pay for prescription.
Educate the patient
What should you educate the patient about?
What does poor adherence to meds result in?
**think about what i educate about insulin
- Patient education should be at the 5th or 6th grade level.
-
Include in
education:
- Purpose of medication
- Instructions for administration
- Adverse drug reactions (ADRs)
- Poor adherence contributes to worsening disease, hospital admissions, and death.
***purpose of insulin is to control BG, how to administer insulin, SE of hypoglycemia. IF do not take medication- can contribute to worsen diabetes, hospital readmission, death
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Monitor the
effectiveness of the drug
What is passive & active monitoring?
- Passive monitoring: Passive monitoring includes educating the
patient on the expected outcome of the drug therapy and instructing
the patient to contact the provider if the treatment is not
effective or if adverse drug effects occur
- EX antibiotics
- Active monitoring: Follow-up laboratory tests
or monitoring to measure therapeutic effectiveness.
- EX seizure medications, anticoags
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Therapeutics Factors
What are sources to find evidence of therapeutic factors of a medication?
-
therapeutic impact of a drug is reviewed in the literature and
observed in
the individual patient - Evidence for therapeutic impact
- Clinical trials
- Clinical practice guidelines
- Systematic reviews
- Randomized controlled trials
- Extrapolate with caution because tend to use
healthy individuals when in reality, patients are complex
- Extrapolate with caution because tend to use
healthy individuals when in reality, patients are complex
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Safety
What are safety platforms and considerations for patients
- The safety profile of a drug is taken into consideration
and weighed against
other factors when prescribing. -
Safety is initially determined in clinical trials and is
outlined in the precautions and contraindications in the drug
monograph. - Safety may vary with the
population.
- Tetragons
- Liver or renal disease
- Drug allergies
-
The U.S. Food and
Drug Administration (FDA) collects information on
and monitors the safety of drugs via postmarketing surveillance by the
MedWatch program - The FDA issues a “Public Health Advisory” when there is drug safety information that needs to be conveyed to patients or caregivers.
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Cost
What are things to consider with drug cost?
- Cost to patient
- High drug cost = patient may decrease adherence
- Ask about prescription drug coverage
- Consider $4 retail pharmacy lists
- Cost to society
- Thoughtful prescribing considers cost to healthcare system
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Patient factors
Previous experience w/ ADRs
- ADRs can be a significant factor in nonadherence
- Renal pts more at risk for ADRs
Health Beliefs
Current Drug Therapy
- Drug interactions
- If a patient is on a complex medication regimen, consultation with a pharmacist or PharmD who has access to drug interaction software is warranted for patient safety.
Age
- either the very young or the very old
Pregnant
DRUG FACTORS INFLUENCING DRUG
SELECTION: Provider factors
- Ease of prescribing or monitoring
- Formularies
- Nurse practitioners need to be familiar with the formularies they are allowed to prescribe.
- Personal formulary: Each provider develops a small list of drugs they are comfortable prescribing.
INFLUENCES ON RATIONAL PRESCRIBING
- Pharmaceutical promotion
- May influence prescribing
- Changes in prescribing recommendations
- When guidelines change, providers may need to be coached or reeducated regarding appropriate prescribing.
What is pharmacogenetics?
- Pharmacogenomics is the branch of pharmacology that deals with the influence of genetic variations on drug response in patients by correlating gene expression with a drug’s efficacy or toxicity.
- In other words, drugs and drug combinations are optimized for each individual’s unique genetic makeup.
What is Heterogeneity?
What system mostly metabolizes drugs?
Genetic makeup contribute to many variations in pharmacokinetics
Most drugs are metabolized through cytochrome P450 enzyme system
various factors contribute to specific observable pharmacodynamics differences
What are basic concepts of CYP450?
- CYP450 enzymes are involved in about 75% of drug metabolism and bioactivation in the liver
- Some CYPs metabolize only one (or a very few) drug(s), whereas others may metabolize multiple drugs
- The CYP3A subfamily is responsible for over 50% of drug metabolism
- Race, gender, environmental factors, and drugs may alter the gene expression of individual CYP450 families and subfamilies
- 40% of Asians display drug polymorphism
What are Inhibitors and Inducers of CYP450?
- What are the clinical implications when substrates inhibit CYP450 enzymes?
- An inhibitor may decrease the metabolism of substrates and generally lead to increased drug effect.
- What are the clinical implications
when substrates induce CYP450 enzymes
- An inducer may increase the metabolism of substrates and generally lead to decreased drug effect.
What are the different types of Metabolizers?
- Poor metabolizers
- break down meds slowly
- experience side effects at the standard dose
- Intermediate metabolizers
- may have too much medication on board at a standard dose, causing side effects
- Extensive metabolizers
- normal rate of metabolism
-
Ultra-rapid
metabolizers
- meds are rapidly broken down
- meds may be removed from the system before providing any symptom relief
What is Pharmacoeconomics?
- Pharmacoeconomics defined
- Provides a framework for evaluating drug treatments in terms of comparing one treatment with another
- Pharmacoeconomics studies
- Generic drugs
Generic Drugs
General concepts
- Generic drugs may or may not be less expensive.
- Pharmacy coverage may determine whether a generic drug is used.
- Tiered benefit
- Many benefit plans have a two- or three-tiered benefit, in which the patient pays a greater co-payment for brand-name drugs than for generic equivalent prescriptions
- Lower co-pay for generic drugs
- Retail prescription drug programs.
Generic substituition
What are prescribers influenced by?
- 69% of prescriptions filled with generic drugs
- Prescriber influenced by:
- Innovator company
- Payer
- Patient
- Innovator companies support for health care
Bioequivalence
- FDA regulates and sets standards for bioequivalence
- Be bioequivalent (an equal rate and extent of drug absorbed in the bloodstream)
- FDA Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations is:
- Available online
- Searched by active ingredient
- Searched by proprietary name
- Updated daily
What are concepts of pharmacoeconomics to consider in practice
- Prescribing generic vs brand-name drugs
- Pharmacist may substitute a less expensive drug that is therapeutic equivalent
- “Dispense as written”
- Patients may switch due to costs and prescription benefit.
- Retail drug programs
- Walmart, Target, Kroger, Sam’s Club
- $4 for a 30-day supply of common generic drugs for Metoformin vs 70% brand name