genetics exam 1 (slides)
When did microscopy work begin and what did it lead to?
It started in the 1950s and led to the description of the nucleus and the description of chromosomes.
Who was Gregor Mendel?
He was the father of genetics, and he published an explanation of hereditary transmission in plants. He also studied pea plants
Who were the 3 botanist that rediscovered mendel's work?
Correns, de vries, and von tschermak
Who described the inheritance of alkaptonuria?
Garrod in 1901
Who recognized that the trait for alkaptonuria must be rare and recessive?
Bateson
Who discovered how chromosomes moved during cell division and how the pattern paired with transmission of mendelian hereditary units
Flemming, Sutton, and Boveri
What are the 4 phases of modern genetics?
1. Identification of the cellular and chromosomal basis of hereditary
2. Identification of DNA as hereditary material
3. Central dogma of biology
4. Genomic era
Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan?
He talked about the chromosome theory of inheritance
What are chromosomes?
They are long molecules of double-stranded DNA and
protein,
which contain genes
What are homologous pairs?
They carry genes for a trait (in sexually reproducing organisms)
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
They both have DNA and chromosomes
Prokaryotic - an attachment site
Eukaryotic - histones, and a nucleus
What cells contain mitochondria?
plant and animals
What cells contain chloroplast?
plant
Who discovered the structure of DNA
Watson, Crick, and Franklin
When did gene cloning and recombinant DNA technology progress?
1960-1970s
When was gel electrophoresis first used?
In 1949 by Linus Pauling
What is the study of genomics?
focusing on the sequencing, interpretation, and comparison of genomes from different organisms
What is proteomics?
Focuses on the study of the complete set of proteins encoded in a genome
What is transcriptomics?
studies the complete set of genes that undergo transcription in a cell
What is metabolomics?
studies chemical processes involving metabolites in a specific
cell,
tissue, organ, or organism
What leads to natural selection?
overproduction and variation
Natural selection leads to?
inheritance
What biological findings supported Darwins principles of population?
1. Phenotypic variation reflects genetic variation
2. Offspring inherit and express the alleles of their parents
3. Organisms carrying certain allele variants favored
by
natural selection have a reproductive advantage
over
those who do not
What 4 processes lead to a change in allele frequency?
1. genetic mutation
2. gene flow
3. genetic drift
4. natural selection
What is the modern synthesis of evolution?
It merges evolutionary theory with experimental, mathematical, and molecular population biology
What are the three domains of life and give description
1. Eukarya (true nucleus, multiple chromosomes)
2. Bacteria (no
true nucleus, single chromosome)
3. Archaea (no true nucleus,
single chromosome)
What is the blending theory of inheritance (Mendel)
it viewed the traits in offspring as an intermediate mixture of the parental traits. (Mendel's results rejected this)
What is the steps of the scientific method?
1. Make initial observations about a phenomenon
or
process
2. Formulate a testable hypothesis
3. Design
a controlled experiment to test the hypothesis
4. Collect data
from the experiment
5. Interpret the experimental results,
comparing them to
those expected under the hypothesis
6.
Draw a conclusion and reformulate the hypothesis if
necessary
What are the keys to success in blending the pea plants?
Controlled crosses, used pure-breeding strains to begin experimental controlled crosses, selection of dichotomous traits, quantification of results, and used replicate, reciprocal and test crosses
What are pure breeding or true breeding strains?
These are strains that consistently produce the same phenotype. (p, f1,f2 generation)
What is homozygous?
Pure-breeding individuals that have identical copies of the two alleles for a trait
What is heterozygous?
The F1 plants had different alleles from each parent
What are the results of the f1 generation?
Dominance of one phenotype over the other in the F1 generation.
100% dominance
What are the results of the f2 generation?
1. Reemergence of the recessive phenotype in the F2
generation
2. A ratio of approximately among F2 phenotypes (3:1)
What is the theory of particulate inheritance?
The theory stated that plants carry two discrete hereditary units(alleles) for each trait
What di the two alleles for each trait determine?
the phenotype of the individual
What is a monohybrid cross?
a cross in which the two organisms crossed are both heterozygous for one gene. (G/g) x (G/g)
What is the phenotypic and genotypic ratio predicted for the F2 generation?
3:1 phenotypic ratio and a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio
What is a punnett square?
A method of diagramming a genetic cross is a simple tool of genetic analysis
What was Mendel's first law and explain.
The law of segregation. It says the units of heredity, their separation into gametes, and the random union of the gametes into progeny in predictable proportions
What was Mendel's second law and explain(what is the ratio).
The law of independent assortment. alleles of two or more different genes separate independently from the other into gametes that reproduce sexually (9:3:3:1 ratio)
Practice monohybrid, dihybrid, and trihybrid crosses.
kk
What was the forked line diagram?
It is used to determine gamete genotypes and frequencies
What are the 4 rules of probability theory?
Product rule(multiplication), sum rule, conditional probability, and binomial probability
What is the multiplication(product) rule?
If two or more events are independent of one another, the likelihood of their simultaneous or consecutive occurrence is the product of their individual probabilities
What is the sum (addition) rule?
It defines the joint probability of occurrence of any two or more mutually exclusive events
What is conditional probability?
It involves questions asked after a cross has been made and is applied when information about the outcome modifies the probability calculation
What is Binomial probability?
It predicts the likelihood of a series of events (for which there are two or more possible outcomes each time)
What is the binomial expansion formula?
p = frequency of the outcome
q = frequency of the alternative outcome
(p+q)=1 (if there's only 2 outcomes)
(p+q)^n (can expand when n is the number of successive events)
What is the chi-square test? (X^2)
It is used for quantifying how closely an experimental observation matches the expected outcome
X^2 = (O-E)^2/E
(O=observed, E=expected values)
What is found using the X^2 test?
The p (probability) value. low X^2 means high p value
It is the probability that the results of another experiment of the same size and structure will deviate as much or more from the expected results by chance
What is the degree of freedom?
It helps determine the p-value. It is equal to the number of outcome classes, n, minus 1
When any experimental result has less than 5% probability, the hypothesis of chance is what?
rejected
What is autosomal inheritance?
the transmission of genes carried on autosomes, chromosomes
found
in both males and females
How many pairs of autosomes and sex chromosomes are there in each human?
22 - autosomes
1 - X or Y sex-determining chromosome
Why are model organisms good to use?
1. short generation (life) time
2. easy to grow and maintain in a restricted space
3. easy to understand development and growth
4. closely resembles other organisms
What are some common model organisms?
yeast, worms, fruitflies (D. melanogaster), zebrafish, mustard weed, and mouse
What are pedigrees?
They are a way of tracing the inheritance of traits in humans and some animals
Know the symbols for the pedigrees
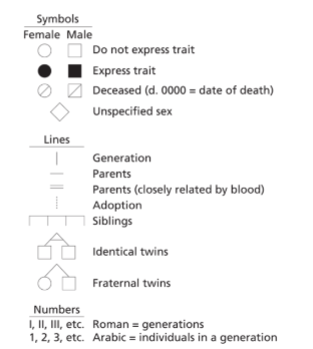
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance characteristics
1. Males and females have the trait in approximately equal
frequency
2. Each individual who has the trait has at least one
parent with the trait
3. Either gender can transmit the trait to
a child
4. If neither parent has the trait, none of their
children will have it
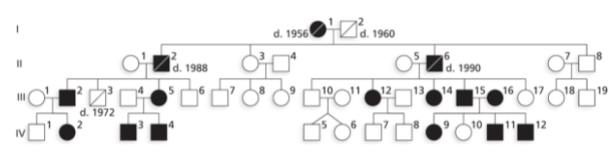
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance characteristics
1. Males and females have the trait in approximately equal
frequency
2. Individuals who have the trait are often born to
parents who do not (parents are heterozygous)
3. If both parents
have the trait, all children will have it
4. The trait is not
usually seen in each generation, rather it is typically seen among siblings
Transmission of alleles is equated with transmission of variable DNA sequences that act through ______ to produce proteins responsible for phenotypes
mRNA
What is sbe1?
Produces an enzyme that converts a linear starch molecule (amylose) into a complex, branched form (amylopectin). (has to do with seed shape)
What leads to a winkled appearance in the seeds?
The amylose
What gene produces the giberellin(an enzyme involved in production of the plant growth hormone) for stem length?
The Le gene
What gene produce an enzyme involved in the breakdown of chlorophyll so that initially green seeds lose chlorophyll and turn yellow as they mature?
The Sgr gene
For flower color, what gene is a transcription factor that activates expression of certain genes? (specifically purple pigment)
The b H L H gene
What is mitosis?
the process of cell division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells from one original parental cell
What are the phases of the cell cycle? (please please make a taco)
Interphase (G1, S phase, G2), prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
What happens in G1 and G0?
G1 - active gene expression/activity and preparation for DNA synthesis
G0- cell remains specialized by does not divide, will eventually die (apoptosis)
What happens in the s phase and G2?
s phase - DNA is replicated and chromosomes are duplicated
G2 - prepares for cell division
What happens during the G1 checkpoint?
Can pass through if the cell size is good and full or nutrients and growth factors are present
What happens in the s phase checkpoint?
Can pass of DNA replication is completes and there is no base pair error
What happens in the G2 checkpoint?
Can pass if the cell size is good and chromosome replication is successful.
What happens in the metaphase checkpoint?
Can pass if all chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle
When do chromosomes condense in the cell cycle?
A little in prophase but mostly in metaphase
What are centrosomes?
Barrel shape structures that focus on the main microtubule organizing center.
What are centrioles?
They are small structures made of microtubules in the centrosome that help organize the microtubules.
What are centromeres?
The part that holds the chromosomes together. The help separate the sister chromatids during cell division
What is a kinetochore?
they are large protein assemblies that connect chromosomes to microtubules of the mitotic and meiotic spindles in order to distribute the replicated genome from a mother cell to its daughters.
What are kinetochore microtubules?
they help provide an attachment site for chromosomes for cellular division
What are polar microtubules?
They are polarized structures with a minus end that help pull the sister chromatids apart.
What are astral microtubules?
They come from the centriole and help orient and position the spindle in the cell
What is cohesin?
a 4-subunit protein that coats sister chromatids along their entire length, with the greatest concentration at the centromeres
What is seperase?
It is an enzyme that helps break down cohesin and separate the sister chromatids in anaphase
What is the purpose of mitosis and where does it occur?
Produce genetically identical cells for growth and maintenance in somatic cells
What happens to homologous chromosomes in mitosis?
They dont pair and rarely undergo recombination
What happens to sister chromatids in mitosis?
Attach to spindle fibers from opposite poles in metaphase Separate and migrate to opposite poles at anaphase
What is the product of mitosis?
Two genetically identical diploid daughter cells that continue to divide by mitosis
Describe the steps of prophase in mitosis
Chromatin condenses, making chromosomes and centromeres visible. The nucleus also disappears.
Describe the steps of prometaphase in mitosis
The nuclear envelope breaks down, and microtubules extend from opposite poles. Chromomses move towards the middle of the cell, and cohesin binds the sister chromatids.
Describe the steps of metaphase in mitosis
Chromosomes are aligned in the metaphase plate and are fully condensed. The kinetochores and microtubules are fully extended, and the complete mitotic spindle is in place.
Describe the steps of anaphase in mitosis
Anaphase A - Sister chromatids separate (disjunction), and the daughter chromosomes move towards the poles.
Anaphase B - polar microtubules extend in length
Describe the steps of telophase and cytokinesis in mitosis
Daughter chromosomes reach the poles and from two new nuclei. Cytokinesis divides cytoplasm to create 2 new cells. (plants- cell walls/animal cells- cleavage furrow)
Practice identifying the pics of mitosis and meiosis
okkk
Meiosis starts diploid and ends what?
diploid
What is the purpose and location of meiosis?
Produce gametes for sexual reproduction that are genetically different in germ line cells
What do homologous chromosomes do in meiosis? (3 key events)
They fuse in prophase I, cross over in prophase I, and separate in anaphase I
When homologous chromosomes seperates what happens
They reduce to haploid numbers
What so sister chromatids do in meiosis?
1. Attach to spindle fibers from the same pole in metaphase I
2.
Migrate to the same pole in anaphase I
3. Attach to spindle
fibers from opposite poles in metaphase II
4. Separate and
migrate to opposite poles in anaphase II
What is the product of meiosis?
Four genetically different haploid cells that mature to form gametes and unite to form diploid zygotes
What is the main purpose meiosis I?
to separate homologous chromosomes
What are the stages of meiosis I?
prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I
What are the five stages of prophase I and explain it
leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis
Chromosomes condense in leptotene, and meiotic spindle forms and extend out. The nuclear envelope disintegrates in zygotene. Homologous chromosomes fuses (synapsis). Crossing over occurs between nonsister chromatids and nuclear envelope continues to break down In pachytene. In diplotene, crossing over is complete, leaving the chiasmata to hold nonsister chromatids together. 4 chromatids of homologous pairs are visible, and the nuclear envelope is fully broken down. In diakinesis the mitotic spindle is established and tetrads move towards the middle of the cell.
What is the synaptonemal complex?
the protein bridge that forms between homologous chromosomes
True or false. non sister chromatids belong to different members of a homologous pair
true
Describe the steps of metaphase I
The chiasmata between homologs are resolved and crossing over is complete. Homologs align on apposite sides of the metaphase plate and kinetochore microtubules attach to both sister chromatids.
Describe the steps of anaphase I
Sister chromatids are firmly attached by cohesin and homologs move to opposite poles of the cell
Describe the steps of telophase I
chromosomes gather at the poles of the cells and the cytoplasm divides.
Why can X and Y chromosomes fuse (synapsis) during prophase I?
Because of pseudoautosomal regions (PARs). There are 2 PARs on each chromosomes - PAR1 and PAR2
What is the main purpose of meiosis II?
Separate sister chromatids (To divide haploid daughter cells into 2 haploid cells similar to mitosis.)
Describe the steps of prophase II
The nuclear envelope breaks down and centrosomes duplicate. Kinetochores and microtubules are produced, and chromosome recondensation takes place.
Describe the steps of metaphase II
sister chromatids attach to kinetochore microtubules from opposite poles. The microtubule pull, and cohesin leads chromosomes to align on the metaphase plate.
Describe the steps of anaphase II
Sister chromatids sperate after cohesin breaks down by seperase. When sister chromatids move towards opposite poles, polymerization of nonkinetochore microtubules elongates the cell
Describe the steps of telophase II and cytokinesis
Chromosomes begin to condense, and the nuclear envelope re-forms. Cytokinesis separates newly formed nuclei and divides cytoplasmic material.
Who proposed that chromosomes behavior in meiosis mirrors hereditary transmission of genes?
Sutton and Boveri
Who studies fruit flies and why?
Morgan and to test Mendel's rules on natural species
What does wild type signify?
the most common phenotype in a population
Why are males hemizygous?
because they only have one X
What is sex determination?
The genetic and biological processes that produce the male and female characteristics of a species
What does the X/A(autosomal) ratio determine
It determines the gender based on the number of X chromosomes to sets of autosomes. Males - 0.5 and females -1
Sex determination depends on what?
The SRY gene found on the Y chromosome (male) because it initiates the testicular development and without it the expression is female
True or false. placental mammals have a X and Y chromosomes
True
What system is used for many animals?
Z/W system
Females - ZW
Males - ZZ
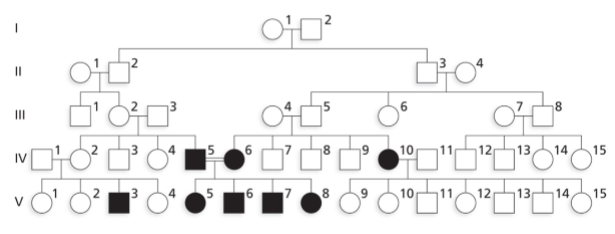
What is X-linked recessive inheritance?
Females homozygous for the recessive allele and males hemizygous for it display the recessive phenotype. (more often in males)
What is X-linked dominant inheritance?
Females heterozygous and males hemizygous for the dominant allele express the dominant phenotype
What is Y-linked inheritance?
They are passed father to son
True or false Hemophilia A is an X-linked recessive trait
True
What is hemophilia A cause by...
A mutation in the factor VIII gene on the X chromosome. The mutant allele produces a nonfunctional blood clotting protein
Congenital hypertrichosis )CGH) is a what?
A rare X-linked dominant disorder that leads to a increase in the number of hair follicles on the body (affected males have more body hair than females)
What is dosage compensation?
Any mechanism that compensates for the difference in number of copies of genes between males and females. There are 4 different mechanisms
What is the random X inactivation hypothesis?
When one of the two X chromosomes in each female somatic cell is randomly inactivated in mammalian development.
It is also called the Lyon hypothesis.
What is a barr body?
The inactive X chromosome is visible near the nuclear wall.
Visualized by Murray Barr
What is a mosaic?
When a person has 2 or more genetically different sets of cells. An example is cats
Why do cats have patches?
X inactivation in heterozygous females leads to a pattern of orange and black patches that is unique to each individual
Random X inactivation requires what X-linked gene?
XIST (X-inactivation specific transcript) and it can only act on the chromosome that is being transcribed.
What does the XIST gene do?
It produces large R N A molecules that spread out and cover (or paint) the chromosome to be inactivated