Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Campbell Biology Chapter 15 (powell_h)
front 1 1) When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F₁ generation flies
to each other, the F₂ generation included both red- and white-eyed
flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the
explanation for this result? | back 1 Answer: B |
front 2 2) Sturtevant provided genetic evidence for the existence of four
pairs of chromosomes in Drosophila in which of these ways? | back 2 Answer: B |
front 3 3) Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of
inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century? | back 3 Answer: B |
front 4 4) Thomas Hunt Morgan's choice of Drosophila melanogaster has been
proven to be useful even today. Which of the following has/have
continued to make it a most useful species? | back 4 Answer: E |
front 5 5) A woman is found to have 47 chromosomes, including three X
chromosomes. Which of the following describes her expected phenotype? | back 5 Answer: D |
front 6 6) Males are more often affected by sex-linked traits than females
because | back 6 Answer: D |
front 7 7) SRY is best described in which of the following ways? | back 7 Answer: C |
front 8 8) In cats, black fur color is caused by an X-linked allele; the
other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is
tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross
of a black female and an orange male? | back 8 Answer: D |
front 9 9) Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in
humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son.
What are the genotypes of the parents? | back 9 Answer: E |
front 10 10) Cinnabar eyes is a sex-linked recessive characteristic in fruit
flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type
male, what percentage of the F₁ males will have cinnabar eyes?
| back 10 Answer: E |
front 11 11) Calico cats are female because | back 11 Answer: B |
front 12 12) In birds, sex is determined by a ZW chromosome scheme. Males are
ZZ and females are ZW. A recessive lethal allele that causes death of
the embryo is sometimes present on the Z chromosome in pigeons. What
would be the sex ratio in the offspring of a cross between a male that
is heterozygous for the lethal allele and a normal female? | back 12 Answer: A |
front 13 13) Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY region of the Y
chromosome. An abnormality of this region could allow which of the
following to have a male phenotype? | back 13 Answer: B |
front 14 14) In humans, clear gender differentiation occurs, not at
fertilization, but after the second month of gestation. What is the
first event of this differentiation? | back 14 Answer: D |
front 15 15) Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by a gene on the
human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time
because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein.
They rarely live past their 20s. How likely is it for a woman to have
this condition? | back 15 Answer: D |
front 16 16) Women (and all female mammals) have one active X chromosome per
cell instead of two. What causes this? | back 16 Answer: A |
front 17 17) Which of the following statements is true of linkage? | back 17 Answer: A |
front 18 18) How would one explain a testcross involving F₁ dihybrid flies in
which more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring are
produced? | back 18 Answer: A |
front 19 19) What does a frequency of recombination of 50% indicate? | back 19 Answer: A |
front 20 20) What is the reason that linked genes are inherited together?
| back 20 Answer: A |
front 21 21) Three genes at three loci are being mapped in a particular
species. Each has two phenotypes, one of which is markedly different
from the wild type. The unusual allele of the first gene is inherited
with either of the others about 50% of the time. However, the unusual
alleles of the other two genes are inherited together 14.4% of the
time. Which of the following describes what is happening? | back 21 Answer: D |
front 22 22) The centimorgan (cM) is a unit named in honor of Thomas Hunt
Morgan. To what is it equal? | back 22 Answer: B |
front 23 23) Recombination between linked genes comes about for what reason?
| back 23 Answer: D |
front 24 24) Why does recombination between linked genes continue to occur?
| back 24 Answer: C |
front 25 25) Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate
physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons?
| back 25 Answer: A |
front 26 26) Which of the following two genes are closest on a genetic map of
Drosophila? | back 26 Answer: E |
front 27 27) If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis II during gametogenesis, what
will be the result at the completion of meiosis? | back 27 Answer: C |
front 28 28) One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to
join a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this alteration called?
| back 28 Answer: D |
front 29 29) A nonreciprocal crossover causes which of the following products?
| back 29 Answer: D |
front 30 30) In humans, male-pattern baldness is controlled by an autosomal
gene that occurs in two allelic forms. Allele Hn determines
nonbaldness, and allele Hb determines pattern baldness. In males,
because of the presence of testosterone, allele Hb is dominant over
Hn. If a man and woman both with genotype HnHb have a son, what is the
chance that he will eventually be bald? | back 30 Answer: E |
front 31 31) Of the following human aneuploidies, which is the one that
generally has the most severe impact on the health of the individual?
| back 31 Answer: A |
front 32 32) A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic
counseling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a
portion of his chromosome 4 that has been exchanged with a portion of
his chromosome 12. Although he is normal because his translocation is
balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm
will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm? | back 32 Answer: A |
front 33 33) Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors.
Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to
different control regions. Which of the following might then occur to
make the cancer worse? | back 33 Answer: B |
front 34 34) An inversion in a human chromosome often results in no
demonstrable phenotypic effect in the individual. What else may occur?
| back 34 Answer: B |
front 35 35) What is the source of the extra chromosome 21 in an individual
with Down syndrome? | back 35 Answer: D |
front 36 36) Down syndrome has a frequency in the U.S. population of ~1/700
live births. In which of the following groups would you expect this
frequency to be significantly higher? | back 36 Answer: E |
front 37 37) A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years
old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most
probable cause of the child's condition? | back 37 Answer: D |
front 38 38) In 1956 Tijo and Levan first successfully counted human
chromosomes. What is the reason it took so many years to do so?
| back 38 Answer: E |
front 39 39) At which phase(s) is it preferable to obtain chromosomes to
prepare a karyotype? | back 39 Answer: E |
front 40 40) What is a syndrome? | back 40 Answer: C |
front 41 41) Which of the following is known as a Philadelphia chromosome? | back 41 Answer: A |
front 42 42) At what point in cell division is a chromosome lost so that,
after fertilization with a normal gamete, the result is an embryo with
45, X? | back 42 Answer: E |
front 43 43) Which of the following is true of aneuploidies in general?
| back 43 Answer: B |
front 44 44) A gene is considered to be non-Mendelian in its inheritance
pattern if it seems to "violate" Mendel's laws. Which of the
following would be considered Mendelian? | back 44 Answer: D |
front 45 45) Genomic imprinting is generally due to the addition of methyl
(–CH3) groups to C nucleotides in order to silence a given gene. If
this depends on the sex of the parent who transmits the gene, which of
the following must be true? | back 45 Answer: D |
front 46 46) Correns described that the inheritance of variegated color on the
leaves of certain plants was determined by the maternal parent only.
What phenomenon does this describe? | back 46 Answer: B |
front 47 47) Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins
needed for electron transport. Therefore, in which body systems would
you expect most mitochondrial gene mutations to be exhibited? | back 47 Answer: D |
front 48 48) A certain kind of snail can have a right-handed direction of
shell coiling (D) or left-handed coiling (d). If direction of coiling
is due to a protein deposited by the mother in the egg cytoplasm, then
a Dd egg-producing snail and a dd sperm-producing snail will have
offspring of which genotype(s) and phenotype(s)? | back 48 Answer: A |
front 49 49) Which of the following produces a Mendelian pattern of
inheritance? | back 49 Answer: E |
front 50 50) Suppose that a gene on human chromosome 18 can be imprinted in a
given pattern in a female parent but not in a male parent. A couple in
whom each maternal meiosis is followed by imprinting of this gene have
children. What can we expect as a likely outcome? | back 50 Answer: D |
front 51 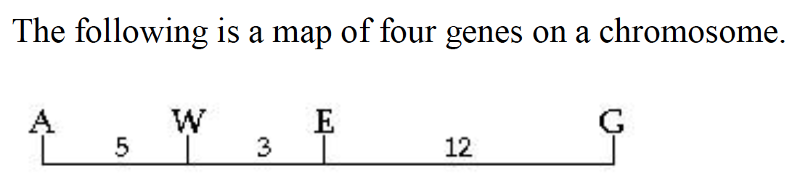 This a map of four genes on a chromosome (See Image) | back 51 Answer: E |
front 52 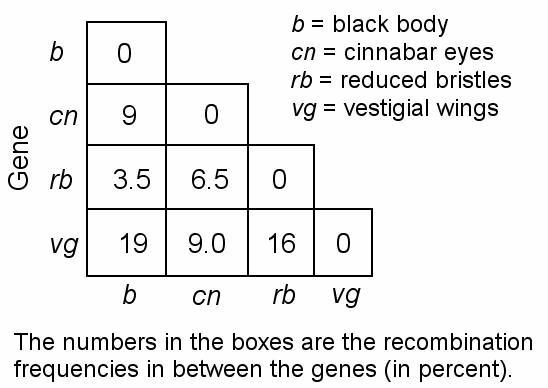 52) In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies
for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown
in Figure 15.2. What is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
| back 52 Answer: D |
front 53 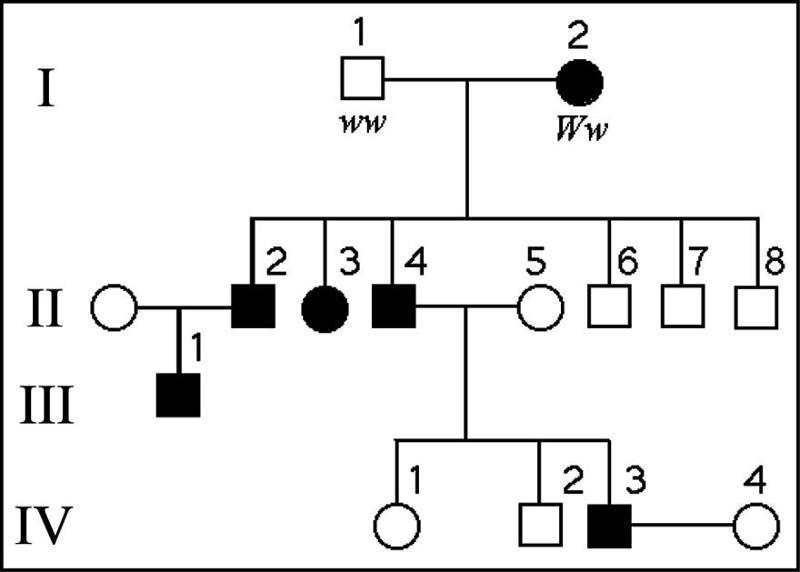 53) The pedigree in Figure 15.3 shows the transmission of a trait in
a particular family. Based on this pattern of transmission, the trait
is most likely | back 53 Answer: A |
front 54 A man who is an achondroplastic dwarf with normal vision marries a
color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was 6 feet tall,
and both the woman's parents were of average height. Achondroplastic
dwarfism is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is
X-linked recessive. | back 54 Answer: B |
front 55 A man who is an achondroplastic dwarf with normal vision marries a
color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was 6 feet tall,
and both the woman's parents were of average height. Achondroplastic
dwarfism is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is
X-linked recessive. | back 55 Answer: B |
front 56 A man who is an achondroplastic dwarf with normal vision marries a
color-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was 6 feet tall,
and both the woman's parents were of average height. Achondroplastic
dwarfism is autosomal dominant, and red-green color blindness is
X-linked recessive. | back 56 Answer: E |
front 57 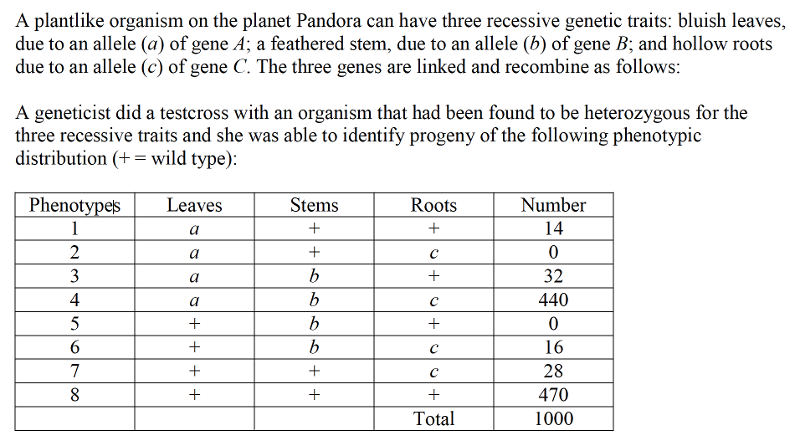 A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive
genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a
feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due
to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine
as follows: | back 57 Answer: C |
front 58  A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive
genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a
feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due
to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine
as follows: | back 58 Answer: A |
front 59  A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive
genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a
feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due
to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine
as follows: | back 59 Answer: B |
front 60  A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive
genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a
feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due
to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine
as follows: | back 60 Answer: C |
front 61  A geneticist did a testcross with an organism that had been found to
be heterozygous for the three recessive traits and she was able to
identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild
type): (See Image) | back 61 Answer: D |