Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 4
front 1 The element present in all organic molecules is | back 1 Answer: C |
front 2 The complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to | back 2 Answer: A |
front 3 The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations
presumes that | back 3 Answer: E |
front 4 Differences among organisms are caused by | back 4 Answer: B |
front 5 Which of the following people was the first to synthesize an organic
compound, urea, from inorganic starting materials? | back 5 Answer: C |
front 6 Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments proved that | back 6 Answer: B |
front 7 Hermann Kolbe's synthesis of an organic compound, acetic acid, from
inorganic substances that had been prepared directly from pure
elements was a significant milestone for what reason? | back 7 Answer: E |
front 8 Stanley Miller's 1953 experiments assumed that early Earth's
atmosphere contained | back 8 Answer: B |
front 9 When Stanley Miller applied heat and electrical sparks to a mixture
of simple inorganic compounds such as methane, hydrogen gas, ammonia,
and water vapor, what compounds were produced? | back 9 Answer: E |
front 10 How many electron pairs does carbon share in order to complete its
valence shell? | back 10 Answer: D |
front 11 A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other
atoms? | back 11 Answer: C |
front 12 Which of the following statements best describes the carbon atoms
present in a seed-eating bird? | back 12 Answer: E |
front 13 Which of the following statements best describes the carbon atoms
present in a seed-eating bird? | back 13 Answer: D |
front 14 Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water? | back 14 Answer: B |
front 15 How many structural isomers are possible for a substance having the
molecular formula C₄H₁₀? | back 15 Answer: B |
front 16 Which of the following statements correctly describes cis-trans
isomers? | back 16 Answer: A |
front 17 Research indicates that ibuprofen, a drug used to relieve
inflammation and pain, is a mixture of two enantiomers; that is,
molecules that | back 17 Answer: B |
front 18 What determines whether a carbon atom's covalent bonds to other atoms
are in a tetrahedral configuration or a planar configuration? | back 18 Answer: B |
front 19 Compared to a hydrocarbon chain where all the carbon atoms are linked
by single bonds, a hydrocarbon chain with the same number of carbon
atoms, but with one or more double bonds, will | back 19 Answer: B |
front 20 Organic molecules with only hydrogens and five carbon atoms can have
different structures in all of the following ways except | back 20 Answer: E |
front 21 A compound contains hydroxyl groups as its predominant functional
group. Which of the following statements is true concerning this
compound? | back 21 Answer: B |
front 22 Which of the following is a false statement concerning amino groups?
| back 22 Answer: D |
front 23 Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids? | back 23 Answer: C |
front 24 Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional
group? | back 24 Answer: C |
front 25 A carbon skeleton is covalently bonded to both an amino group and a
carboxyl group. When placed in water it | back 25 Answer: D |
front 26 Which functional groups can act as acids? | back 26 Answer: C |
front 27 Testosterone and estradiol are | back 27 Answer: B |
front 28 Testosterone and estradiol are male and female sex hormones,
respectively, in many vertebrates. In what way(s) do these molecules
differ from each other? | back 28 Answer: C |
front 29 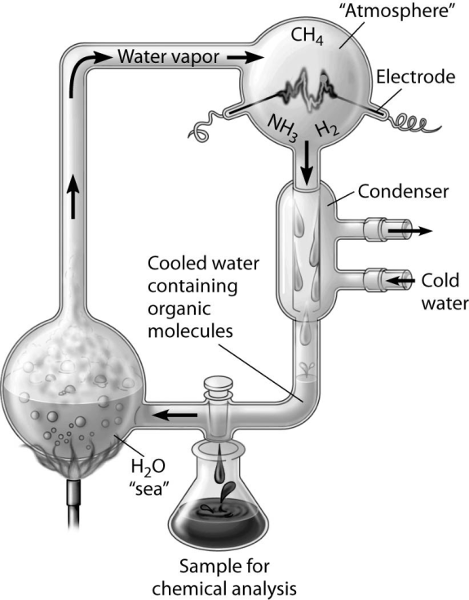 Which of the following people used this apparatus to study the
formation of organic compounds? | back 29 Answer: A |
front 30  The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
| back 30 Answer: C |
front 31  The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These
two molecules differ in the | back 31 Answer: C |
front 32  The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. These
two molecules are | back 32 Answer: D |
front 33 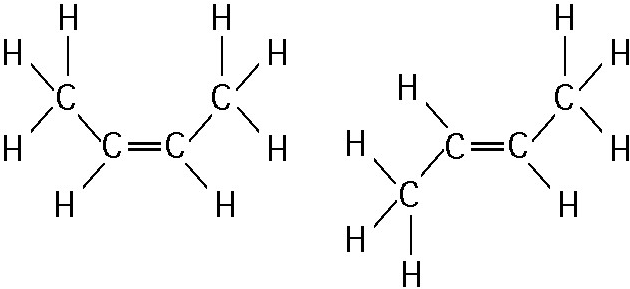 The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
| back 33 Answer: E |
front 34  Three or four of the following illustrations depict different
structural isomers of the organic compound with molecular formula
C₆H₁₄. For clarity, only the carbon skeletons are shown; hydrogen
atoms that would be attached to the carbons have been omitted. Which
one, if any, is NOT a structural isomer of this compound? | back 34 Answer: C |
front 35  Which of the pairs of molecular structures shown below depict
enantiomers (enantiomeric forms) of the same molecule? | back 35 Answer: D |
front 36  Which of the pairs of molecular structures shown below do NOT depict
enantiomers (enantiomeric forms) of the same molecule? | back 36 Answer: C |
front 37  Which pair of molecules shown below are not enantiomers of a single
molecule? | back 37 Answer: B |
front 38  Thalidomide and L-dopa, shown below, are examples of pharmaceutical
drugs that occur as enantiomers, or molecules that | back 38 Answer: B |
front 39  What is the name of the functional group shown in the figure above?
| back 39 Answer: D |
front 40 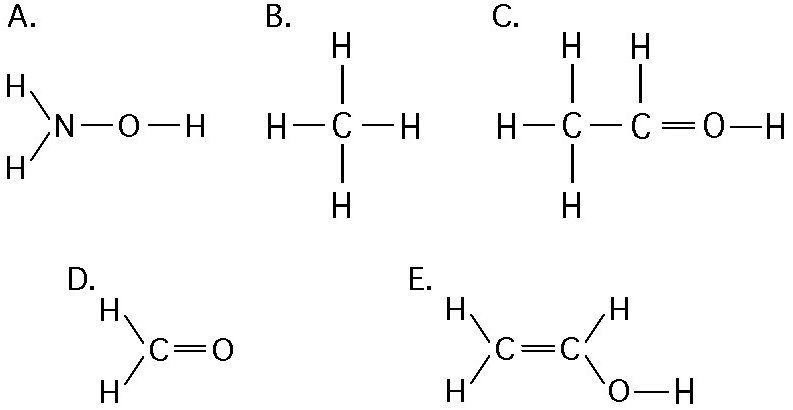 Which of the structures illustrated above is an impossible covalently
bonded molecule? | back 40 Answer: C |
front 41  Which of the structures illustrated above contain(s) a carbonyl
functional group? | back 41 Answer: D |
front 42  In which of the structures illustrated above are the atoms bonded by
ionic bonds? | back 42 Answer: E |
front 43  Which of the structures illustrated above cannot form hydrogen bonds
with water molecules? | back 43 Answer: B |
front 44  Which functional group shown above is characteristic of alcohols?
| back 44 Answer: A |
front 45  Which functional group(s) shown above is (are) present in all amino
acids? | back 45 Answer: E |
front 46  Which of the groups shown above is a carbonyl functional group?
| back 46 Answer: B |
front 47  Which of the groups shown above is a functional group that helps
stabilize proteins by forming covalent cross-links within or between
protein molecules? | back 47 Answer: E |
front 48  Which of the groups above is a carboxyl functional group? | back 48 Answer: C |
front 49  Which of the groups above is an acidic functional group that can
dissociate and release H⁺ into a solution? | back 49 Answer: C |
front 50  Which of the groups above is a basic functional group that can accept
H⁺ and become positively charged? | back 50 Answer: D |
front 51  Which molecule shown above would have a positive charge in aqueous
solution at pH 7? | back 51 Answer: E |
front 52  Which molecule(s) shown above is (are) ionized in aqueous solution at
pH 7? | back 52 Answer: A |
front 53  Which molecules shown above contain a carbonyl group? | back 53 Answer: B |
front 54  Which molecule shown above has a carbonyl functional group in the
form of a ketone? | back 54 Answer: C |
front 55  Which molecule shown above has a carbonyl functional group in the
form of an aldehyde? | back 55 Answer: B |
front 56  Which molecule shown above contains a carboxyl group? | back 56 Answer: D |
front 57  Which molecule shown above can increase the concentration of hydrogen
ions in a solution and is therefore an organic acid? | back 57 Answer: D |
front 58  Which molecule shown above can form a dimer linked by a covalent
bond? | back 58 Answer: B |
front 59  Which molecules shown above will form hydrogen bonds with water?
| back 59 Answer: D |
front 60  Which molecule shown above contains an amino functional group, but is
not an amino acid? | back 60 Answer: A |
front 61  Which molecule shown above is a thiol? | back 61 Answer: B |
front 62  Which molecule shown above contains a functional group that cells use
to transfer energy between organic molecules? | back 62 Answer: D |
front 63  Which molecule shown above can function as a base? | back 63 Answer: A |
front 64 A chemist wishes to make an organic molecule less acidic. Which of
the following functional groups should be added to the molecule in
order to do so? | back 64 Answer: D |
front 65 Organic chemistry is currently defined as | back 65 Answer: B |
front 66  Which functional group is not present in this molecule? | back 66 Answer: B |
front 67 Which chemical group is most likely to be responsible for an organic
molecule behaving as a base? | back 67 Answer: D |
front 68 Which of the following hydrocarbons has a double bond in its carbon
skeleton? | back 68 Answer: D |
front 69  Choose the term that correctly describes the relationship between
these two sugar molecules: | back 69 Answer: A |
front 70  Identify the asymmetric carbon in this molecule. | back 70 Answer: B |
front 71  Which action could produce a carbonyl group? | back 71 Answer: A |