Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
BIO Lab Ch 1-5 Test 1
front 1  Name H occipital frontal parietal temporal | back 1 occipital |
front 2  Name E. sacral perineal coxal inguinal | back 2 coxal |
front 3  Name I sacral perineal gluteal | back 3 sacral |
front 4  Name B. temporal occipital cervical | back 4 cervical |
front 5  Name K. calcaneal tarsal crural | back 5 calcaneal |
front 6  Name J. popliteal femoral sural | back 6 popliteal |
front 7  Name A. brachial occipital cephalic | back 7 cephalic |
front 8  Name D crural brachial femoral | back 8 femoral |
front 9  Name the region B. middle hypochondriac hypogastric epigastric Umbilical | back 9 Umbilical |
front 10  Name the region A. umbilical right hypochondriac hypogastric | back 10 epigastric |
front 11  Name the region E. right lumbar epigastric left iliac | back 11 left iliac |
front 12  Name the region C. epigastric umbilical hypogastric | back 12 hypogastric |
front 13  Name the region D. Left Hypochondriac epigastric Right Lumbar | back 13 Right Hypochondriac |
front 14  The liver is found in the region labeled: | back 14 A |
front 15  Name the plane D parasagittal midsagittal oblique | back 15 oblique |
front 16  Name the plane E. frontal oblique mid saggital | back 16 frontal |
front 17  Name the plane B. frontal para saggital oblique | back 17 para saggital |
front 18  Name the Plane C transverse sagittal midsagittal | back 18 transverse |
front 19  Name the plane A parasagittal midsagittal transverse | back 19 midsagittal |
front 20  Name the cavity A. cranial vertebral ventral | back 20 cranial |
front 21  Name the cavity C. thoracic abdominal pelvic | back 21 thoracic |
front 22  Name the cavity formed by A and B. ventral dorsal pelvic | back 22 dorsal |
front 23  Name the cavity formed by D and E. abdominopelvic dorsal thoracic | back 23 abdominopelvic |
front 24  Name the cavity formed by C, D and E. cranial ventral abdominopelvic | back 24 ventral |
front 25  Name the cavity E. pelvic abdominal thoracic | back 25 pelvic |
front 26  Produces ATP aerobically. | back 26 B |
front 27  Site of synthesis of lipid and steroid molecules. | back 27 A |
front 28  Source of cell autolysis. | back 28 C |
front 29  Site of enzymatic breakdown of phagocytized material. | back 29 C |
front 30  Replicate for cell division. | back 30 D |
front 31  Packages proteins for insertion in the cell membrane or for exocytosis. | back 31 E |
front 32  Name the structure B. smooth ER rough ER mitochondria | back 32 rough ER |
front 33  Name structure A Lysosome mitochondria nucleus golgi complex | back 33 nucleus |
front 34  Name the structure letter C. rough ER smooth ER golgi complex | back 34 golgi complex |
front 35  Name structure D. mitochondria lysosome golgi complex | back 35 mitochondria |
front 36  Name the structure F. rough ER smooth ER mitochondria | back 36 smooth ER |
front 37  Peripheral protein. | back 37 E |
front 38  Identification "tags" for the cell. | back 38 A |
front 39  Polar region of phospholipid. | back 39 B |
front 40  Glycocalyx. | back 40 A |
front 41  Hydrophilic portion of phospholipid. | back 41 B |
front 42  Nonpolar region of phospholipid. | back 42 C |
front 43  Name the phase prophase interphase anaphase | back 43 prophase |
front 44  Name the phase metaphase anaphse prophase | back 44 metaphase |
front 45  In which phase of the cell cycle is the highlighted cell? metaphase prophase anaphase | back 45 prophase |
front 46  In which phase of the cell cycle is the highlighted cell? prophase interphase anaphase | back 46 anaphase |
front 47  Name the phase anaphase interphase prophase | back 47 Interphase |
front 48  In which phase of the cell cycle is the highlighted cell? anaphase prophase interphase | back 48 metaphase |
front 49  Name the phase anaphase metaphase telophase | back 49 anaphase |
front 50  Name the phase anaphase telophase prophase | back 50 telophase |
front 51  Name the tissue? adipose blood bone | back 51 blood |
front 52  Which tissue is highlighted? reticular connective tissue dense irregular connective tissue dense regular connective tissue | back 52 dense regular connective tissue |
front 53  Name the tissue reticular nerve areolar skeletal muscle | back 53 areolar |
front 54  Which tissue is highlighted? cardiac muscle skeletal muscle elastic tissue | back 54 smooth muscle |
front 55  Which type of tissue is the highlighted region composed of? stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized stratum spinosum dermis | back 55 stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized |
front 56  Which epithelial type is highlighted? pseudostratified columnar epithelium simple columnar epithelium simple squamous epithelium | back 56 simple columnar epithelium |
front 57  Which structure is highlighted? collagenous trabaculae lymphocytes macrophages | back 57 reticular fibers |
front 58  Which structures are highlighted? microvilli goblet cells nuclei | back 58 microvilli |
front 59  Which component of the connective tissue in this field of view is
highlighted? extracellular matrix lacunae collagen fibers | back 59 extracellular matrix |
front 60  Which epithelial type is highlighted? transitional epithelium stratified columnar epithelium stratified cuboidal epithelium | back 60 transitional epithelium |
front 61  Name the tissue simple squamous adipose reticular areolar | back 61 adipose |
front 62  Which structures are highlighted? striations nuclei fibers | back 62 nuclei |
front 63  Name the tissue? stratified squamous dense irregular transtitional | back 63 dense irregular |
front 64  Which structure is highlighted? microvilli lamina propria of villus villus | back 64 simple columnar epithelium |
front 65  What is secreted by the highlighted cell? hormones digestive enzyme mucin | back 65 mucin |
front 66  Which structures are highlighted? skeletal muscle fibers intercalated discs striations | back 66 striations |
front 67  Which epithelial type is highlighted? simple squamous epithelium stratified squamous epithelium stratified cuboidal epithelium | back 67 simple squamous epithelium |
front 68  Which structure is highlighted? stratified squamous epithelium, non-keratinized stratified cuboidal epithelium stratified columnar epithelium | back 68 stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized |
front 69  Name the tissue hyaline cartilage areolar elastic cartilage | back 69 fibrocartilage |
front 70  Which structures are highlighted? striations sarcomeres nuclei | back 70 intercalated discs |
front 71  Which epithelial type is highlighted? transitional epithelium pseudostratified columnar epithelium simple columnar epithelium | back 71 pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
front 72  The highlighted fibers are produced by what cell type? fibroblast mast cell macrophage | back 72 fibroblast |
front 73  Name the tissue stratified cubodial simple squamous stratified squamous | back 73 simple cubodial |
front 74  Which structures are highlighted? simple columnar cells microvilli goblet cells | back 74 goblet cells |
front 75  Which structures are highlighted? pseudostratified columnar epithelium cilia microvilli | back 75 cilia |
front 76  Where capillary loops are found. | back 76 E |
front 77  Site of the dermal ridges that produce epidermal ridges on the epidermal surfaces of the fingers. | back 77 E |
front 78  Region that thickens markedly when one gains weight. | back 78 B |
front 79  What is produced by the highlighted structures? semen sweat sebum | back 79 sweat |
front 80  Which layer of the skin is highlighted? reticular layer of dermis hypodermis epidermis | back 80 papillary layer of dermis |
front 81  Which region of the skin is highlighted? reticular layer of dermis epidermis papillary layer of dermis | back 81 no data |
front 82  Which structure is highlighted? stratum corneum duct of sudoriferous gland Meissner's corpuscle | back 82 duct of sudoriferous gland |
front 83  Which structure is highlighted? follicle wall hair shaft hair root | back 83 follicle wall |
front 84  What is secreted by the highlighted structure? mucus cerumin sweat | back 84 sebum |
front 85  The outermost surface of the hair is called the ________. cortex matrix medulla | back 85 cuticle |
front 86  Which layer of the epidermis is highlighted? stratum spinosum stratum corneum stratum basale | back 86 stratum spinosum |
front 87  Which structure is highlighted? hair root hair follicle hair shaft | back 87 hair papilla |
front 88  Which structure is highlighted? hair root hair papilla hair follicle | back 88 hair follicle |
front 89  Which structure is highlighted? hair bulb hair root arrector pili muscle | back 89 arrector pili muscle |
front 90  Which structure is highlighted? hypodermis reticular layer of dermis papillary layer of dermis | back 90 reticular layer of dermis |
front 91  Which structure is highlighted? papilla hair follicle hair root | back 91 no data |
front 92  Which structures would you expect to find in the highlighted
layer? free nerve endings only blood vessels, free nerve ending, and receptor cells blood vessels only | back 92 blood vessels, free nerve ending, and receptor cells |
front 93  Which layer is highlighted? hypodermis reticular layer of dermis epidermis | back 93 hypodermis |
front 94  Reticular layer of the dermis | back 94 C |
front 95  Hypodermis | back 95 D |
front 96  Epidermis | back 96 A |
front 97  Which structure is highlighted? hair bulb hair follicle hair shaft | back 97 hair bulb |
front 98  Which region of the skin is highlighted? follicle wall dermis stratum corneum | back 98 no data |
front 99  Which layer is highlighted? stratum spinosum stratum basale stratum lucidum | back 99 stratum spinosum |
front 100  Which structure is highlighted? hair follicle hair root hair bulb | back 100 hair root |
front 101 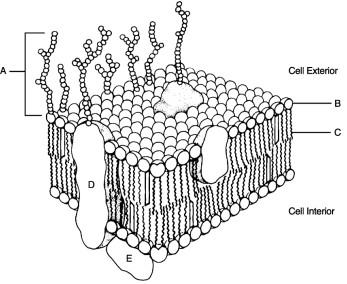 Integral protein | back 101 D |
front 102 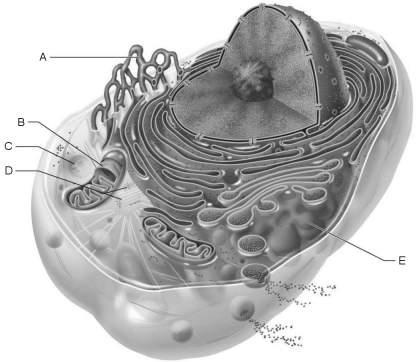 Forms the mitotic spindle | back 102 D |