Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Chapter 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues
front 1 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.-[. | back 1 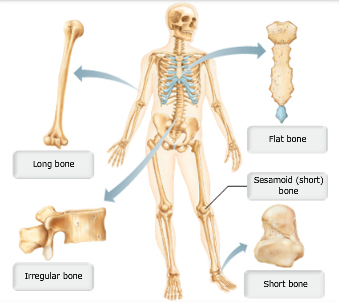 |
front 2 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 2  |
front 3 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 3  |
front 4 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 4  |
front 5 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. | back 5  |
front 6  Which of the following substances is NOT a component of the osteoid material secreted by the cells indicated by the arrow in panel A? | back 6 calcium |
front 7  The illustrated bone-forming process would be associated with which of the following bones? | back 7 parietal |
front 8  During bone growth, which event is most significant at the surface indicated by the letter A? | back 8 expansion of the cartilage matrix |
front 9  During bone growth, which significant event occurs at the surface indicated by the letter C? | back 9 appositional growth |
front 10 Hematopoiesis is a term for which of the following physiological processes? | back 10 blood cell formation |
front 11 Which of the following hormones is currently thought to decrease plasma calcium levels in pregnant women and children? | back 11 calcitonin |
front 12 PTH promotes the formation of which hormone? | back 12 calcitriol |
front 13 Which of the following would NOT be a way that parathyroid hormone (PTH) could alter plasma calcium levels? (Which one of the following is FALSE?) | back 13 increase osteoblasts on bone |
front 14 Which hormone works directly in the intestine to increase plasma calcium levels? | back 14 calcitriol |
front 15 Which of the following refers to a bone disorder found most often in the aged and resulting in the bones becoming porous and light? | back 15 osteoporosis |
front 16 When chondrocytes in lacunae divide and form new matrix, it leads to an expansion of the cartilage tissue from within. This process is called ________. | back 16 interstitial growth |
front 17 Which type of cartilage covers and protects the ends of bones at freely moveable joints? | back 17 hyaline cartilage |
front 18 Cartilage grows in two ways, appositional and interstitial. What is appositional growth? | back 18 the secretion of new matrix against the external face of existing cartilage |
front 19 Which of the following statements best describes interstitial growth? | back 19 Chondrocytes in the lacunae divide and secrete matrix, allowing the cartilage to grow from within. |
front 20 Choose the FALSE statement. | back 20 Long bones include all limb bones except the patella. |
front 21 The main role of the appendicular skeleton is to protect and support vital organs. | back 21 False |
front 22 The periosteum is a tissue that serves only to protect the bone because it is not supplied with nerves or blood vessels. | back 22 False |
front 23 The term osteoid refers to the organic part of the matrix of compact bones. | back 23 True |
front 24  Which of the following bones are formed by the illustrated process? humerus | back 24 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 25 What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo? | back 25 hyaline cartilage |
front 26  The arrow in the figure is pointing to which of the following structures? | back 26 the epiphyseal plate |
front 27 Each consecutive bone lamella has collagen fibers that wrap in alternating directions. | back 27 True |
front 28 Bones are classified by whether they are weight bearing or protective in function. | back 28 False |
front 29 Ossification of the ends of long bones ________. | back 29 is produced by secondary ossification centers |
front 30  The structure indicated by the arrow is composed primarily of what material? | back 30 hyaline cartilage |
front 31 Cartilage has a flexible matrix that can accommodate mitosis of chondrocytes. | back 31 True |
front 32 Which of the following is stored in bones? | back 32 phosphate |
front 33 Hyaline cartilage ________. | back 33 is found on the ends of bones that form movable joints |
front 34 The structural unit of compact bone (osteon) resembles the growth rings of a tree trunk. | back 34 True |
front 35 What indicates that a long bone has reached its adult length? | back 35 closure of the epiphyseal plate |
front 36 Osteoclasts ________. | back 36 break down bone |
front 37  In which of the labeled parts of the adult long bone would hematopoietic tissue be located? | back 37 B |
front 38 The canal that runs through the core of each osteon (the Haversian canal) is the site of ________. | back 38 blood vessels and nerve fibers |
front 39 Sixty-five percent of the mass of bone is a compound called hydroxyapatite. | back 39 True |
front 40 A fracture in the shaft of a bone would be a break in the ________. | back 40 diaphysis |
front 41 The notable hardness of bone is attributed to ________. | back 41 the presence of inorganic hydroxyapatites |
front 42 The axial skeleton includes the ________. | back 42 ribs |
front 43  Which of the following is the major component of the part of the bone labeled E? | back 43 adipose tissue |
front 44 Which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system? | back 44 communication |
front 45 The periosteum is secured to the underlying bone by dense connective tissue called ________. | back 45 perforating (Sharpey's) fibers |
front 46  The above figure depicts which of the following bone-forming processes? | back 46 intramembranous ossification during embryonic development |
front 47 The cell responsible for secreting the matrix of bone is the ________. | back 47 osteoblast |
front 48 The structure of bone tissue suits the function. Which of the following bone tissues is adapted to support weight and withstand tension stress? | back 48 compact bone |
front 49 The notable hardness of bone is attributed to ________. | back 49 the presence of inorganic hydroxyapatites |
front 50 Cartilage has a flexible matrix that can accommodate mitosis of chondrocytes. | back 50 True |
front 51 What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo? | back 51 hyaline cartilage |
front 52 Use the figure to match the following descriptions. | back 52  |
front 53  The arrow in the figure is pointing to which of the following structures? | back 53 the epiphyseal plate |
front 54 The structure of bone tissue suits the function. Which of the following bone tissues is adapted to support weight and withstand tension stress? | back 54 compact bone |
front 55 Yellow bone marrow contains a large percentage of ________. | back 55 fat |
front 56  The structure indicated by the arrow is composed primarily of what material? | back 56 hyaline cartilage |
front 57  Which of the following bones are formed by the illustrated process? femur | back 57 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 58 Bones do NOT have a role in ________. | back 58 glycogen production |
front 59 Ossification of the ends of long bones ________. | back 59 is produced by secondary ossification centers |
front 60  The structures in the figure collectively form a structural unit termed a(n) ______. | back 60 osteon |
front 61 Which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system? | back 61 communication |
front 62 Each consecutive bone lamella has collagen fibers that wrap in alternating directions. | back 62 True |
front 63  The above figure depicts which of the following bone-forming processes? | back 63 intramembranous ossification during embryonic development |
front 64  Osteocytes are connected to each other through which structure? | back 64 canaliculi |
front 65 Choose the TRUE statement. | back 65 Endochondral ossification converts hyaline cartilage "bone" models into true bones (i.e., hyaline cartilage serves as a template for bone formation). |
front 66  A step in which bone-forming process is shown in the figure? | back 66 endochondral ossification |
front 67 Which bone cells form bone? | back 67 osteoblasts |
front 68  The indicated osteocyte is located within layers of bony matrix termed ______. | back 68 lamellae |
front 69 What tissue forms the model for endochondral ossification? | back 69 cartilage |
front 70 The epiphyseal plate is ________. | back 70 where long bone lengthening occurs |
front 71 What is the structural unit of compact bone? | back 71 osteon |
front 72 Which of the following is a bone projection? | back 72 trochanter |
front 73 The trabeculae of spongy bone are oriented toward lines of stress. | back 73 True |