Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Experiment 3- Separation of Components of a Mixture
front 1 Purpose of Experiment 3? | back 1 Familiarize w/ the methods of separating substances from one another ...using (DES) techniques: 1. Decantation 2. Extraction 3. Sublimation |
front 2 Purpose of Experiment 2? | back 2 Familiarize w/ procedures used in evaluating physical properties and use of these properties to identify substances. |
front 3 Purpose of Experiment 1? | back 3 To learn the use of common, simple lab equipment. |
front 4 Decantation: | back 4  (process of) separating a liquid from a solid (sediment) by gently pouring the liquid from the solid - so as to not disturb the solid |
front 5 Filtration: | back 5  (process of) separating a solid from a liquid by means of a porous substance (filter) - allows the liquid to pass through but not the solid common filters: paper, layers of charcoal, and sand Silt and sand can be removed from our drinking water by this process |
front 6 Extraction: | back 6 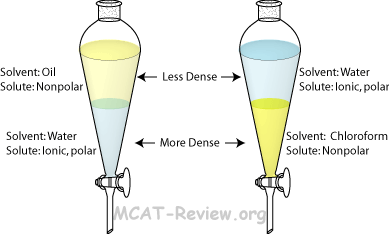 (separation of) a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent By this process, a soluble compound is usually separated from an insoluble |
front 7 Sublimation: | back 7  (process in which) a solid passes directly to the gaseous state and back to the solid state (w/o the appearance of the liquid state) |
front 8 Can all substances be sublimed? Why or why not? | back 8 No, not all substances possess the ability to be sublimed. Iodine, napthalene, and ammonium chloride= common substances easy to sublime |
front 9 Mixture | back 9 A combination of two or more substances in which each substance retains its own chemical identity - and its own properties Pure substances= fixed composition Mixture= compositions vary |
front 10 Two kinds of mixtures? | back 10 Homogenous- sugar water, air - also called a solution Heterogenous- cement, wood, rocks, soil (don't have the same composition, properties, appearance throughout |
front 11 Fundamental properties of mixtures | back 11 1. Each of the substances in the mixture retains its chemical identity 2. separable into these components by physical means |
front 12 Define preponderant. Define impurities | back 12 1. substance whose amount far exceeds the amounts of the other substances in a mixture 2. the other substances in the mixture containing the preponderant |