Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
General Surgery Chapter 14 Nissen to Hemorrhoidectomy
front 1 What does TEP stand for | back 1 Totally Extraperitoneal Patch
|
front 2 What is a surgical procedure that is performed to correct a hiatal hernia | back 2  Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication
|
front 3 Who inserts the bougie dilator for a Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication because they cannot be passed from the sterile field | back 3 Anesthesia |
front 4 What can also treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)as well as a hiatal hernia | back 4 Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication |
front 5 Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication unique supplies | back 5 Abdominal Lap drape
|
front 6 What occurs when the esophageal hiatus is weak, which allows the abdominal esophagus and superior portion of the stomach to protrude into the thoracic cavity. | back 6 Hiatal hernia |
front 7 What surgery does the surgeon wraps (plicates) the top of the stomach (fundus) around the bottom of the esophagus and stitches it in place (wrap) | back 7 Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication |
front 8 What is the surgical creation of an opening (fistula tract) from the gastric mucosa to the skin and is performed to provide nutrition “feeding” to the patient or to decompress and drain the stomach | back 8 A gastrostomy
|
front 9 What is the timeline for a gastrostomy | back 9 Long term or temporary depending on technique and condition |
front 10 What are the layers of the stomach:
| back 10  serosa |
front 11 What is the main purpose of a gastrostomy | back 11 Create an opening to bypass the esophagus |
front 12 What type of suture pattern do they use for a PEG procedure | back 12 Pursestring |
front 13 Often tumors of the larynx, pharynx, esophagus, and proximal stomach, as well as esophageal stricture, dictate the timeline for a ......... | back 13 A gastrostomy |
front 14 What are the ways a gastrostomy can be created | back 14 Open
|
front 15 What gastrostomy is a surgically placed feeding tube in the stomach | back 15 Stamm Gastrostomy
|
front 16 What does PEG stand for | back 16 Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
|
front 17 What type of feeding tube is used for patients on a ventilator, who may have a spinal cord injury, dementia, or cerebral palsy | back 17  Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy |
front 18 What is a tube that is passed through the nose and down through the nasopharynx and esophagus into the stomach | back 18 Nasogastric tubes |
front 19 What is the removal of part or all of the stomach | back 19  Gastrectomy |
front 20 What is the surgical removal of the distal portion of the stomach and the pylorus
| back 20  Gastroduodenostomy Billroth I
|
front 21 What is the surgical removal of the distal portion of the stomach and the pylorus.
| back 21  Gastrojejunostomy Billroth II
|
front 22 Stomach anatomy | back 22  |
front 23 What involves removal of the stomach and re-constitution of the alimentary tract | back 23  Total gastrectomy
|
front 24 What requires an upper midline incision, bilateral subcostal incision (chevron), or thoracoabdominal incision | back 24 Total gastrectomy |
front 25 When doing abdominal cases what is the best technique to employ | back 25 Bowel technique |
front 26 What is a term used to describe the contraction of the muscles that mix and propel contents in the gastrointestinal tract | back 26 Motility disorders |
front 27 Pathology of the Esophagus - what causes
| back 27 Motility disorders |
front 28 What is a disease of the muscle of the esophagus | back 28 Achalasia |
front 29 What is a condition where the pea-sized, bulging pouches in the inner lining of the bowel become inflamed | back 29  Diverticulitis |
front 30 What is the medical or biological term for an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body | back 30 Diverticula |
front 31 What is connected to the lesser curvature of the stomach and extends to the posterior surface of the liver to hold the stomach in place. | back 31 The lesser omentum |
front 32 What extends from the diaphragm to the cardia of the stomach to also help keep the stomach in normal anatomic position | back 32 The gastrophrenic ligament |
front 33 What is the inferior border of stomach called | back 33 The greater curvature. |
front 34 What is the attachment of two ends of approximately the same sized structures
| back 34  End-to-end anastomosis |
front 35 What is the attachment of the end of one section of bowel into the side of another section (T-like)
| back 35  End-to-side anastomosis |
front 36 What is the creation (attachmen) of parallel opening in two sections of bowel with anastomosis
| back 36  Side-to-side anastomosis |
front 37 What is a specific technique of anastomosis that allows for a variety of applications in gastric, intestinal, biliary, and pancreatic surgery often referred to as gastric bypass | back 37  Roux-en-Y
|
front 38 What is inspected to ensure good blood flow to the remaining segments of bowel | back 38  The mesentery
|
front 39 The mesentery is a fold of membrane that attaches the intestine to the abdominal wall and holds it in place | back 39  The mesentery |
front 40 An elevated white blood cell count and fever are common symptoms for | back 40 Appendectomy |
front 41 After which surgery are all instruments placed in a basin and removed from the immediate field. The basin is placed in a predefined area on the back table and left there until the case is completed. Instruments and needles are counted by pointing, not by touching. This includes any specimens removed | back 41 Appendectomy
|
front 42 Where are the appendix located | back 42 Right lower quadrant |
front 43 What incision is used for an open appendectomy | back 43 McBurney's |
front 44 After the appendix has been removed what suture is used and procedure performed to the stump | back 44 Stump is sutured with a purse string suture and inverted inside itself |
front 45 Appendectomy:
| back 45  |
front 46 What is the anatomy of the colon:
| back 46  |
front 47 What begins at hepatic flexure, travels across top of abdominal cavity, and ends at splenic flexure | back 47 Transverse colon |
front 48 What occurs (in toddlers) when a portion of the intestine folds inside another part. This causes a blockage in the colon | back 48  Intussusception |
front 49 Colon resection options:
| back 49  |
front 50 What is a section of bowel that communicates with the outside of the abdominal cavity that is created to divert the fecal stream | back 50 A stoma (“ostomy”) |
front 51 What is a surgically created opening to divert feces to the outside temporarily or permanently | back 51 A Stoma |
front 52 What are created from either an end section or loop of the ileum (ileostomy) or colon (colostomy). | back 52  Stomas |
front 53 What is the name for the colostomy that the bowel is pulled out onto the abdomen and held in place with an external device. The bowel is then sutured to the abdomen and two openings are created in the one stoma: one for stool and the other for mucus. | back 53 Loop colostomy (Diversion) |
front 54 What is the name for the stoma that is created from one end of the bowel. The other portion of the bowel is either removed or sewn shut | back 54 End colostomy (End)
|
front 55 What is constructed from a terminal portion of ileum, can be temporary or permanent | back 55 End ileostomy |
front 56 What is primarily a TEMPORARY stoma for fecal diversion | back 56 Loop ileostomy |
front 57 What is a modification of the loop method in which the loop is divided with a linear cutter and both ends are brought out through the skin incision | back 57 End-loop ileostomy |
front 58 What is created from the descending COLON and sigmoid | back 58 End colostomy |
front 59 What utilizes the transverse COLON
| back 59 Loop colostomy |
front 60 What is a modification of the loop method in which the loop is divided with a linear cutter and both ends are brought out through the skin incision | back 60 End-loop colostomy |
front 61 What is the most common type of permanent colostomy
| back 61 Sigmoid colostomy |
front 62 What is a chronic form of perianal abscess that fails to heal after draining and becomes an inflammatory tract | back 62  Fistula-in-ano |
front 63 What is a tear in the lining of the lower rectum | back 63 Anal fissure |
front 64 What is a cyst or abscess near or on the natal cleft of the buttocks that often contains hair and skin debris | back 64  Pilonidal disease |
front 65 What are the most common anal lesions, can be internal or external vascular structures in the anal canal | back 65  Hemorrhoids |
front 66 What is the membranous layer of subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen, it is attached to iliac crest, linea alba, pubis | back 66  Scarpa’s fascia |
front 67 What separates aponeurosis of external oblique muscle from overlying tissues and contains the intercrural fibers | back 67 Interparietal fascia |
front 68 What separates aponeurosis of external oblique muscle from overlying tissues and contains the intercrural fibers | back 68 Innominate fascia |
front 69 What is a thin layer of fascia lining the transversus abdominis muscle | back 69 Transversalis fascia |
front 70 Where do we see the following fascia:
| back 70 McVay (Cooper Ligament) Inguinal Herniorraphy |
front 71 What is an anatomic triangle formed by cystic duct, common hepatic duct, and inferior borderof liver; used to locate the cystic artery, which is usually within the triangle | back 71 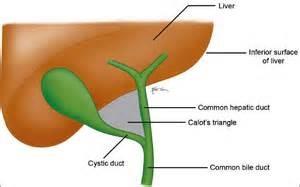 Triangle of Calot |
front 72 What is performed for managing tumors of the head of the pancreas, the most common site of pancreatic cancer | back 72 The Whipple procedure |
front 73 What is the medical name for a Whipple
| back 73  Pancreaticoduodenectomy |
front 74 What is the surgical cutting of the vagus nerve to reduce acid secretion in the stomach | back 74  Vagotomy |
front 75 Mouth
| back 75 Basic steps through the alimentary canal |
front 76 What is the largest parenchymal organ in the abdominal cavity | back 76 Liver |
front 77 It's function is to reabsorb fluids and process waste products | back 77 Colon |
front 78 What organ is the single largest mass of lymphatic tissue in the abdominal cavity | back 78 Spleen |
front 79 What organ is responsible for both the storage and purification of red blood cells | back 79 Spleen |
front 80 What means in a direction towards the head | back 80 Cephalad |
front 81 What means in a direction towards the feet | back 81 Caudal |
front 82 What is the semifluid mass of partly digested food that is expelled by the stomach into the duodenum | back 82 Chyme |
front 83 What is a solid mass of indigestible material that accumulates in your digestive tract, sometimes causing a blockage | back 83 Bezoar |
front 84 What is difficulty swallowing | back 84 Dysphagia |