Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microbiology Lab Quiz #3
front 1 Eosin Methylene Blue Agar | back 1 -Purpose: Eosin methylene blue agar (EMB) is a selective and differential medium used to isolate fecal coliforms. -Selective: inhibits the growth of gram [+] -Differential: coliform from non-coliform- if it is coliform it means it ferments lactose which produces a shiny green appearance to the growth. If it's non-coliform-it means that its not inhibited by the dyes but also did not ferment lactose, retains normal color or takes on color of medium -Contains: -Digest of gelatin: organic carbon and nitrogen -Lactose: fermented to acid end-products by coliforms -Dyes eosin Y: inhibit growth of Gram [+] and reacts w/ vigorous lactose fermenters Methylene Blue: inhibits growth of Gram [+] -Gram positive or negative?- Gram [-] because the dyes eosin Y is used partly to inhibit the growth of Gram [+] -Inhibiting factor?- Dyes eosin Y inhibits the growth of Gram [+] -Procedure: -What purpose does the inoculation of the NA plate serve?-as a comparison for growth quality -Organisms Result: Enterobacter aerogenes: dark purple w/ metallic green sheen- ferments lactose/or sucrose w/ acid production-coliform -good growth-gram [-], not inhibited by eosin/ methylene blue- positive result Staphylococcus epidermidis: colorless- does not ferment lactose or sucrose- non coliform -no growth-inhibited by EMB- Gram [+] E. coli: Pink/mucoid- ferments lactose w/ little acid production- coliform -good growth- Gram [-] and not inhibited by EMB -Grow or not grow= testing Gram -Changes color= fermenter -What purpose do the sugars provide in this medium?-encourage growth of enteric bacteria and to differentiate them based on color reactions when combined with the dyes Enzyme?- |
front 2  Phenol Red Broth | back 2 -Purpose: to detect carbohydrate fermentation that is indicated by a color change in the medium form orange-red to yellow acid end products Used to detect ability of an organism to ferment different carbohydrates FERMENTATION TEST Differential: used to determine whether a bacteria is capable of fermentation Contains: Peptone: Enables microorganisms to grow in broth. Carbohydrate: lactose, glucose, sucrose Phenol red: pH indicator [below 6.8=yellow], [above 7.4=pink-magenta], [6.8-7.4=red] Procedure: Tubes of PR broth contain small inverted Durham tube to trap gas produced What indicates fermentation?- production of acid [color] and gas production [bubbles] How is fermentation of carbohydrates detected in this test?- acid production from fermentation of the carbohydrates lowers pH below the neutral range of the indicator makes medium yellow Lactose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose Results: acid/gas=bubbles acid/no gas=yellow no reaction [no acid or gas]=bright orange Alkaline [peptone degradation]=pinkish red enzyme?- |
front 3 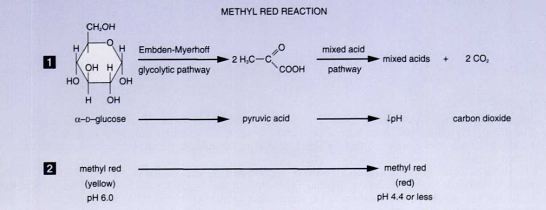 Methyl Red and Voges- Proskauer Tests | back 3 Purpose: used to distinguish between members of the family Escherichia and differentiate them from enterobacter aerogenes Different bacteria convert dextrose and glucose to pyruvate using different metabolic pathways MR: If the organism uses the mixed acid fermentation pathway and produces stable acidic end-products, the acids will overcome the buffers in the medium and produce an acidic environment in the medium. VP: detects organisms that utilize the butylene glycol pathway and produce acetoin. When the VP reagents are added to MR-VP broth that has been inoculated with an organism that uses the butylene glycol pathway, the acetoin end product is oxidized in the presence of potassium hydroxide (KOH) to diacetyl. Contains: Peptone: protein w/ nitrogen glucose: fermentation w/ nitrogen Phosphate buffer: pH indicator Differential: between mixed acid fermenters and others- verified by the addition of methy red indicator dye following incubation What is indicator?- phosphate buffer which turns red when the broth becomes acidic VP Test: designed to test for organisms that ferment glucose, but quickly convert acid to acetoin, 2,3-Buendol A positive VP test: is red A negative VP test: no color change or a copper color Enzyme: creatine as a catalyst |
front 4  Starch Hydrolysis | back 4 TEST DETECTING HYDROLYTIC ENZYMES It is a polysaccharide alpha- D- glucose subunits is the building blocks The test allows us to determine the presence of which enzymes?- Hydrolyze the starch, alpha- amylase, and oligo-1, 6-glucosidase in the area surrounding the growth Enzyme functions?- ability to hydrolyze starch by breaking the glycosidic linkages between sugar subunits These are exoenzymes why are they important?- enzyme secreted from the organism to catalyze reactions outside the cell- Starch is too large to pass through bacterial cell membrane to be of a metabolic value to bacteria it first must split into smaller fragments or individual glucose molecule. Exoenzyme break down starch into individual alpha-glucose subunits Role of Gram's iodine in the experiment- The reagent iodine is used to detect the presence or absence of starch in the vicinity around bacterial growth. Iodine reacts w/ starch and produces a blue or dark brown color. Any Microbial starch hydrolysis will be revealed as a clear zone surrounding the growth Iodine binds to starch- purple black clearing around growth- amylase is present [+] no clearing around growth- no amylase present [-] Organisms- E. coli: [-] no clearing around growth Bacillus cereus: [+] clearing around growth |
front 5  Urea Hydrolysis Test | back 5 Purpose: ability to hydrolyze urea w/ enzyme Differential: differentiate rapid urease- positive bacteria from slower urease-positive and urease-negative bacteria Contains: Urea: a product of decarboxylation of certain amino acids Peptone: provide nutrients Potassium phosphate: buffer to resist alkalization Glucose: provide nutrients Phenol red: pH indicator yellow Urea hydrolyzes urea to ammonia which changes the color of phenol red from yellow to pink Result: Positive: pink, urea hydrolysis, strong urease production Negative: No urea hydrolysis, urea is absent, yellow Urea----[urease +H20]---> 2NH3 + CO2 [ammonia]: Urea can be hydrolyzed to ammonia [NH3] and carbon dioxide [CO2] by bacteria containing the enzyme urease Ammonia is used by many bacteria as a source of what element?-nitrogen: protects against and acidic environment Organisms: Klebsiella pneumoniae: pink [+]- rapid hydrolysis, strong urease production E. coli: orange [-]- no urea hydrolysis, does not produce urease or cannot live in broth |
front 6  SIM Medium | back 6 Purpose: determination of 3 bacterial activities: sulfur reduction, indole production from tryptophan, motility Hydrolysis of tryp results in the production of indole w/ the help of tryptophanase enzyme Production of indole tested and positive result?- Tryptophan hydrollysis in SIM medium can be detected by the addition of Kovac's reagent [DMABA]. DMABA reacts w/ any indole present and produces quinoidal compound- reagent red- fromation of a red color= positive result Differential: identify bacteria that are capable of indole production w/ tryptophanase sulfur reducing members- cyesine desulfurase and thiosulfate motility H2S +FeSO4--> H2SO4 +FeS precipitate indicator?- Indicator reaction for H2S production [hydrogen sulfide], a colorless gas, can be detected when it reacts with ferrous sulfate in the medium to produce black precipitate ferric sulfate Positive result: Black in medium- sulfur reduction- cyesine desulfurase or thiosulfate reductase Which ingredient could be eliminated if the SIM medium was used strictly for testing motility among sulfur reducers?- tryptophanase- casein/ animal tissue Which ingredient could be eliminated if the SIM medium was used strictly for testing motility among indole producers?- sodium thiodulfate Bacteria accomplish sulfur reduction to H2S in 2 ways?- cystein desulfurase [enzyme] and thiosulfate reductase [enzyme] Sulfur reduction result: E. Coli: black precipitate present, [+], sulfur reduction-H2S produced Proteus Mirabilis: black precipitate present, [+], sulfur reduction-H2S produced Indole Production Result: E. coli: no red color, [-], organism does not produce tryptophanase and tryptophan not hydrolyized Proteus mirabilis: red color present, [+], organism produces tryptophanase and hydrolyzes tryptophan into indole and pyruvate Motility Result: E. Coli: Blackened medium-not determined Proteus mirabilis: growth radiating outward from stabline- positive |
front 7 Triple Sugar Iron Agar | back 7 Purpose: It is used to differentiate enterics based on the ability to reduce sulfur and ferment carbohydrates. Differential: Differentiate bacteria based on the basis of lactose fermentation, glucose fermentation, sucrose fermentation, and sulfur reduction Provides both anaerobic and aerobic Contains: Glucose/lactose/sucrose: sugars animal proteins: provide carbon/ nitrogen [beef and yeast extract, peptone] ferrous sulfate [oxidized sulfur]: iron is hydrogen sulfide indicator sodium thiosulfate [oxidized sulfur]: source of reducible sulfur Phenol red: pH indicator Basic results: Glucose only= red/yellow all sugars= yellow Sulfur reduction= black Fermentation= acidic conditions Glucose is a good food source so if there is only little it will be faster and easier to see if it can ferment all three [.1% of glucose instead of 1%] reversion raises pH by producing NH3 Why is it inoculated with a both stab and a streak?- to try not to introduce excessive air and to make sure the bacteria reacts w/ all of the medium In this test how would you know that your organism only fermented glucose and not the other two sugars?- If the slant produces a red slant and yellow butt after 24 hrs indicates that the bacteria ferments glucose but not lactose and sucrose Why does all bacteria that ferments lactose or sucrose always ferment glucose as well?- Lactose and sucrose are disaccharides. Glucose is a monomer of both lactose and sucrose Results: E. coli: yellow slant/butt= glucose/lactose/sucrose fermented w/ acid accumulation in slant/butt Morganella morganii: red slant/yellow butt= glucose fermentation w/ acid production, proteins catabolize aerobically [slant] w/ alkaline product- reversion Pseudomonas aeruginosa: red slant/ no color butt= no fermentation, peptone catabolized aerobically w/ basic products not Enterobacteriaceae Proteus mirabilis: red slant/ yellow butt= red slant/yellow butt= glucose fermentation w/ acid production, proteins catabolize aerobically [slant] w/ alkaline product- reversion, sulfur reduction |
front 8 Motility Test | back 8 Purpose: Some bacteria have the ability to propel themselves through liquids by means of flagella ( flagellum = singular). These long fibers of protein are found on many bacteria, including most supported by this simulation. However, not all bacteria are able to "swim", even if they have flagella. The purpose of this test is to see if the microbe can "swim" by means of flagella. Detected: as diffused growth radiating from central stab line Differential: differentiate between motile bacteria and non-motile bacteria The concentration agar is reduced from 1.5% to .4% why?- Just enough to maintain its form while allowing movement of motile bacteria Role of tetrazolium salt? - to make interpretation easier -used by bacteria as an electron acceptor -oxidized form: colorless -soluble when reduce: red Procedure indicate that you should stab agar and the move loop up along the same line where you stabbed because?- Lateral movement of the needle will interpretation more difficult to read Basic result: A positive result for motility indicated when red [reduced] TTC is seen radiating outward from central stab Organisms Results: Proteus mirabilis: red diffuse growth radiating outward from stabline- [+] organism is motile Micrococcus luteus: red growth only along the stab line- [-} organism is non-motile |
front 9 Coliform | back 9 members of Enterobacteriaceae that ferments lactose |
front 10 Selective Medium | back 10 allow certain types of organisms to grow, and inhibit the growth of other organisms |
front 11 Differential Medium | back 11 are used to isolate or identify particular organisms |
front 12 Hydrolytic Enzyme | back 12 reaction that uses water to split complex molecules |
front 13 Tryptophan | back 13 amino acid used in indole production |
front 14 Reversion | back 14 process that takes up to 18 to 24 hrs as glucose diminishes the organisms located in aerobic region[slant] will begin to break down available amino acids producing ammonia [NH3] and raising pH |
front 15 Enterics | back 15 bacteria of the intestines |