Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
St. Cath December
front 1 A_____________is used to amplify the light released by the laser scanning the CR image plate before it is sent to a digitizer. PSP | back 1 Photomultiplier |
front 2 Unstable atoms and free electrons are the result of: Meiosis | back 2 Ionization |
front 3 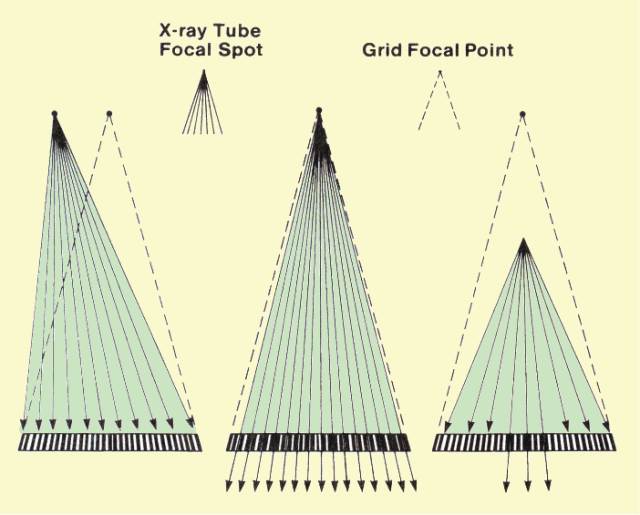 Which of the following grids would be most restrictive on the range of source image distances which can be utilized without demonstrating grid cut-off? 6:1 focused grid | back 3 16:1 focused grid |
front 4 One of the greatest risks to the patient during angiography is blood clot formation on the guide wire or catheter. The best way to keep blood clots from forming is: Using a higher volume of contrast media Injection of heparin Contrast media with a higher concentration of iodine Flushing with sterile saline | back 4 Injection of heparin |
front 5 Detective Quantum Efficiency (DQE) can be defined as: System efficiency of converting an input signal into a useful output signal A histogram of luminance values Shuttering Characteristic of digital imaging comparable to recorded detail | back 5 System efficiency of converting an input signal into a useful output signal |
front 6 For fluoroscopy, the protective curtain or panel must have at least _________lead equivalent between the patient and x-ray personnel. .50mm | back 6 .25mm |
front 7 When the target angle is less than _degrees, the effective focal spot
is smaller than the actual focal spot. | back 7 45 degrees |
front 8 Gas-filled survey instruments used for radiation detection and measurement include: Scintillation detection devices Geiger-Muller counters All of the above Ionization chamber instruments | back 8 All of the above |
front 9 A correctly positioned open-mouth projection of the dens should demonstrate the upper incisors: Superimposed upon the body of the atlas Projected superior to the petrous pyramids Projected superior to the mastoid processes Superimposed upon the cranial base | back 9 Superimposed upon the cranial base |
front 10 Which of the following measurements is easiest to calculate? Entrance skin exposure Organ dose Gonadal dose Bone marrow dose | back 10 Entrance skin exposure |
front 11 The projection of the shoulder demonstrated in the diagram is
the: Acromioclavicular (Pearson) Transthoracic lateral (Lawrence) Axiolateral | back 11 lnferosuperior axial (Lawrence) |
front 12 How many vessels return oxygenated blood to the heart? | back 12 4 |
front 13 Pixel value is defined as: A digital representation of the tissue imaged None of the above The size of the matrix A digital representation of the contrast resolution | back 13 A digital representation of the tissue imaged |
front 14 The structure designated as number 4 on the diagram is the: | back 14 Temporal bone |
front 15 Which of the following photon-tissue interactions results in the ejection of a K-shell electron? Coherent scatter Compton's interaction Photoelectric interaction Pair production | back 15 Photoelectric interaction |
front 16 It is almost always advantageous to perform bedside radiography for
patients in: 1&2 2 3 1 1, 2, &3 | back 16 1&2 |
front 17 The __________ administration of a drug is NOT considered parenteral. Intramuscular Intravenous Subdermal Oral | back 17 Oral |
front 18 When a radiographer declares her pregnancy she should... No longer work in fluoroscopy Wear an extra radiation monitor Be limited to working in clerical areas Wear extra protective apparel | back 18 Wear an extra radiation monitor |
front 19 Determine the missing factor that will produce the same exposure to
the image 200mA 300 mA .3 seconds ---seconds 62 kVp 70 kVp | back 19 .1 |
front 20 The smooth prominence located between the eyebrows and superior to the nasal bones is the: Bregma Inion Nasion Glabella Acanthion | back 20 Glabella |
front 21 Which of the following does NOT directly affect geometrically recorded detail? Focal spot size | back 21 Density |
front 22 Which of the following would best demonstrate the sphenoid sinuses? Lateral projection Parietoacanthial Projection (Waters method) Posterior Profile Position (Stenvers method) PA Axial (Caldwell method) | back 22 Lateral projection |
front 23 Which of the following would describe the Roentgen? 2.58 x 10-4 coulombs/kg 25 x 10-4 coulombs/kg 3.7 x 10-4 coulombs/kg 100 x 1o-4 atomic disintegrations per second | back 23 2.58 x 10-4 coulombs/kg |
front 24 Which of the following would be utilized to demonstrate the axillary region of the ribs with the patient prone? Direct the central ray cephalad Direct the central ray caudad Elevate the unaffected side Elevate the affected side | back 24 Elevate the affected side |
front 25 In terms of radiation protection, the _____________is considered the largest source of scatter in fluoroscopy. Patient | back 25 Patient |
front 26 In order to obtain a projection similar to Radiograph B, the degree
of angulation between the mid-sagittal plane and the plane of the film
should be adjusted to approximately: | back 26 40-45 degrees |
front 27 The exposure timer on a three phase generator can be evaluated using a/an: Synchronous | back 27 spinning top |
front 28 The structure designated as number 1 on the diagram is the: | back 28 Palatine process of maxilla |
front 29 Which of the following types of the acute radiation syndrome would require the greatest amount of exposure for manifestation of effects? Hemopoietic | back 29 Central nervous system |
front 30 A 45 degree right posterior oblique position of the lumbar vertebrae fails to adequately demonstrate the lumbosacral zygapophyseal articulation. In order to demonstrate this area, the patient should be positioned with the mid-coronal plane and the plane of the film forming an angle of: 30 degrees | back 30 30 degrees |
front 31 Which of the following bones of the skull articulates with the spinal column? Sphenoid bone | back 31 Occipital bone |
front 32 Determine the missing factor that will produce the same exposure to
the image 100 mA ---mA . 1 second. 12 second 200 film/screen speed 100 film/screen speed | back 32 150 |
front 33 A_ relationship states that no level of radiation is safe and the degree of damage is not directly proportional. Linear-threshold | back 33 Non-linear-nonthreshold |
front 34 Which of the following is not considered a "negative" contrast agent? Nitrous oxide | back 34 Iodine |
front 35 When is it appropriate for a radiographer to stand in the primary beam? When taking a radiograph of a pediatric patient When taking radiographs of an uncooperative patient Only during emergency room cases Never | back 35 Never |
front 36 To demonstrate the coccyx with the patient prone, the central ray should be directed: 20 degrees caudad | back 36 10 degrees cephalad |
front 37 Cathartics that are commonly used after a barium study include: Biscodyl | back 37 All of these are correct |
front 38 In order to improve Radiograph A, the technologist should: | back 38 Increase patient obliquity |
front 39 Which of the tube-object alignments above would result in the
demonstration of the largest image size? | back 39 2 |
front 40 Which method is used to demonstrate a ligament tear of the ankle joint? Kite | back 40 AP stress studies |
front 41 If an open sterile tray is found unattended it should be: Used immediately | back 41 Discarded |
front 42 Determine the missing factor that will produce the same exposure to
the image 500 mA mA | back 42 300 |
front 43 What effect does a diuretic have on the body? Decrease pain | back 43 Increases urine production |
front 44 The uses aluminum oxide to record radiation dose. TLD | back 44 OSL dosimeter |
front 45 The structure designated as No. 1 on Radiograph A is the: Articular pillar | back 45 Body |
front 46 In the diagram above, which target angle would produce a smaller
effective focal spot? | back 46 No.2 |
front 47 The central ray for an AP projection of the pelvis should be directed to a point 2": Below the iliac crest | back 47 Below the anterior superior iliac spine |
front 48 Which of the following articulates with the base of the first metatarsal? Cuboid | back 48 First cuneiform |
front 49 What happens when a grid is utilized? Patient dose increases and radiographic contrast decreases Patient dose decreases and radiographic contrast decreases Patient dose decreases and radiographic contrast increases Patient dose increases and radiographic contrast increases | back 49 Patient dose increases and radiographic contrast increases |
front 50 The exposure rate at 1 ft. from a fluoroscopic table is 300 mR/hr. The amount of exposure received in 30 min. at 4 ft. from the table would be: 150.20 mR | back 50 9.37 mR |
front 51 Determine the missing factor that will produce the same exposure to
the image 500 Ma 300 mA 1/8 | back 51 1/8 |
front 52  Photoemission occurs at which component of the image intensifier? Photocathode | back 52 Photocathode |
front 53 When evaluating radiographs taken during a small bowel series, the portion of the intestine which appears "feathery" is the Jejunum and Ileum | back 53 Jejunum |
front 54 Tachycardia can be caused by: Inadequate oxygen supply | back 54 All of the above |
front 55 The structure designated as No. 2 on Radiograph B is the: | back 55 Intervertebral foramen |
front 56 Which of the transmission based precautions should be used for an adult patient with active pulmonary tuberculosis? Droplet precautions | back 56 Airborne precautions |
front 57 Lead aprons are needed to protect personnel during fluoro due to: The photoelectric effect | back 57 The Compton effect |
front 58 Increasing the number of turns of wire on the secondary side of the transformer will: Cause an increase in voltage | back 58 Cause an increase in voltage |
front 59 Patients with a diagnosis of possible internal hemorrhage should be monitored closely for: Ketoacidosis | back 59 Shock |
front 60 Following emission of gamma radiation, the atomic number of the atom involved will: Decrease by 1 | back 60 Remain the same |
front 61 Determine the missing factor that will produce the same exposure to
the image 300mA ---mA 1/4 second 1/3 second 200 film/screen speed 400 film/screen speed 45"SID 60" SID | back 61 200 |
front 62 Which of the following would be the acceptable leakage radiation rate at 1 meter from the tube housing? 75 mR/one half hour | back 62 1.66 mR/minute |
front 63 Which area of the body in which temperature can be measured has an average temperature reading of 97.6 degrees Fahrenheit? Rectum | back 63 Axilla |
front 64 Which of the following systems would use thin film transistors? 1. Computed radiography systems 1 only | back 64 2 &3 |
front 65 A patient is placed in a supine position with the knee flexed as far as possible. An image receptor is placed in contact with and parallel to the long axis of the femur. In order to obtain a tangential projection of the patella, the central ray should be directed: Parallel to the long axis of the tibia | back 65 Cephalad |
front 66 The structure designated as number 2 on the diagram is the: | back 66 Zygomatic arch |
front 67 The layers of a CR imaging plate include: Phosphor,Reflective , and Color Color Reflective Phosphor and Reflective Phosphor | back 67 Phosphor and Reflective |
front 68 A patient is positioned in a 45 degree right posterior oblique position. A perpendicular central ray is directed to a point 2" medial and 2" inferior to the upper outer border of the shoulder. This position would best demonstrate the: Right glenoid cavity | back 68 Right glenoid cavity |
front 69 The medial articulation of the head of the radius is with the: Trochlea | back 69 Radial notch |
front 70 A Water's projection of the sinuses is be obtained using the
following: What would be the effect of not using a grid while maintaining 50 mAs? 1. Decreased magnification 1 & 3 | back 70 4 only |
front 71 All of the following are beam limiting devices except: Cones | back 71 Grids |
front 72 The exposure timer on a three phase generator can be evaluated using a/an: 1. spinning top 2. Synchronous spinning top 3. lon chamber 2 and 3 | back 72 2 and 3 |
front 73 Film badge results are reported in to reflect deep and shallow doses. Rem | back 73 Rem |
front 74 The function of filtration is to absorb: High frequency, short wavelength radiation | back 74 Low frequency, long wavelength radiation |
front 75 If the film does not spend enough time in the developer, the film will show. A dichroic stain | back 75 Decreased density |
front 76 When discussing safe transfer methods, the base of support can be described as: A line through the center of gravity The part of the body in contact with the floor The floor A line from the center of the pelvis to the floor | back 76 The part of the body in contact with the floor |
front 77 Which of the following factors is most important in controlling size distortion? OlD | back 77 OlD |
front 78 In order to obtain a lateral projection of the humerus with the patient supine, it would be necessary to: Abduct the humerus slightly and place back of hand against the body Adduct the humerus and flex the elbow Adduct the humerus and place palm of hand flat on table Abduct the humerus and extend the elbow | back 78 Abduct the humerus slightly and place back of hand against the body |
front 79 To decrease OlD for a PA projection of the wrist the: Elbow should be flexed | back 79 Fingers should be flexed |
front 80 Which of the following is NOT a bone that forms a portion of the orbit? Maxilla | back 80 Nasal |
front 81 In order to benefit from the results of the anode heel effect when performing an AP femur exam, the cathode end of the tube should be positioned over: The left side of the femur | back 81 The proximal end of the femur |
front 82 A Water's projection of the sinuses is be obtained using the
following: 10 mAs | back 82 25 mAs |
front 83 Considering the exposure factors below, which of the following statements would be most accurate? (1) 100 mA 1/5 sec 92 kVp 50" SID 12:1 grid #4 would produce greater density than #3 | back 83 #4 would produce greater density than #3 |
front 84 Which of the following is a man-made source of radiation? Radon | back 84 Nuclear fuel |
front 85 What is emitted by the output phosphor of the image intensifier? Visible light | back 85 Visible light |
front 86 Which of the following is not a viral disease? Measles | back 86 Syphilis |
front 87 PACS allow for _______within an imaging department. Digital image display | back 87 All are correct |
front 88 The of a sterile gown is/are considered sterile. 1&2 | back 88 1&2 |
front 89 If you will be sending confidential information via fax, the information should be: Transmitted by e-mail instead | back 89 Preceded by a phone call to the recipient |
front 90 An increase in kVp with compensation of mAs to maintain density will result in: (1) 100 mA 1/5 sec 92 kVp 50" SID 12:1 grid Production of a shorter scale of contrast | back 90 Increased exposure latitude |
front 91 Why is it better to take a PA projection of the skull instead of an AP projection? 1. Less dose to the lens of the eye 1 only | back 91 1 & 2 only |
front 92 Which of the tube-object alignments would result in demonstration of
foreshortening of the radiographic image? | back 92 1 and 3 |
front 93 A_ grid is recommended for digital imaging to obtain the best quality images. High frequency | back 93 High frequency |
front 94 The plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves is the plane. Midsagittal | back 94 Midsagittal |
front 95 The purpose of the tube housing and the oil bath contained in the housing is to: 1. Provide shielding to prevent leakage radiation 3 | back 95 1, 2, &3 |
front 96 Which of the following bones forms a portion of the posterior wall of the nasal cavity? Frontal | back 96 Palatine |
front 97 Select the position/projection which best demonstrates the splenic flexure of the colon. LAO | back 97 LAO |
front 98 A Water's projection of the sinuses is be obtained using the
following: | back 98 Decreased recorded detail |
front 99 A Water's projection of the sinuses is be obtained using the
following: | back 99 Decreased magnification |
front 100 A Water's projection of the sinuses is be obtained using the
following: | back 100 Histogram analysis error |
front 101 An increase in mA will result in: A predictable increase in the number of x-rays produced An unpredictable increase in the number of x-rays produced An increase in the energy of the x-ray beam A decrease in the energy of the x-ray beam | back 101 A predictable increase in the number of x-rays produced |