| |
| |
| |
| back 8 - one meter is equal to 39.4 inches
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 m = 39.4 in.
- 1 m = 1.09 yd
|
| back 9 - a smaller unit of length
- commonly used in
chemistry
- about equal to the width of your little finger
-
2.54 cm = 1 in.
|
| back 10 - the amount of space a substance occupies
- 1 qt = 946
mL
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- 1 L = 1.06 qt
|
| back 11 - slightly larger than a quart (qt)
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- 1 L = 1.06 qt
|
| back 12 - smaller and more convenient
- commonly used in labs and
hospitals
- 1000 mL = 1 L
|
| back 13 - a measure of the quantity of material it contains
-
SI UNIT
- kilogram (kg)
- used for
larger masses, such as body mass
-
METRIC SYSTEM
- 1000 g = 1
kg
- 1 kg = 2.20 lb
- 454 g = 1 lb
|
| back 14 - a measure of the gravitational pull on an object
-
EXAMPLE:
- an astronaut with a mass of 75.0
kg has a weight of 165 lb
|
| back 15 - tells us how hot or cold something is
-
METRIC SYSTEM
- celsius (℃)
- water
freezes at 0℃ and boils at 100℃
- whereas on the
Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32℉ and boils at
212℉
-
SI UNIT
|
| back 16 - measured by second (s) on both systems
|
| back 17 - the numbers you obtain when you measure a quantity
-
SUCH AS:
- height
- weight
- temperature
|
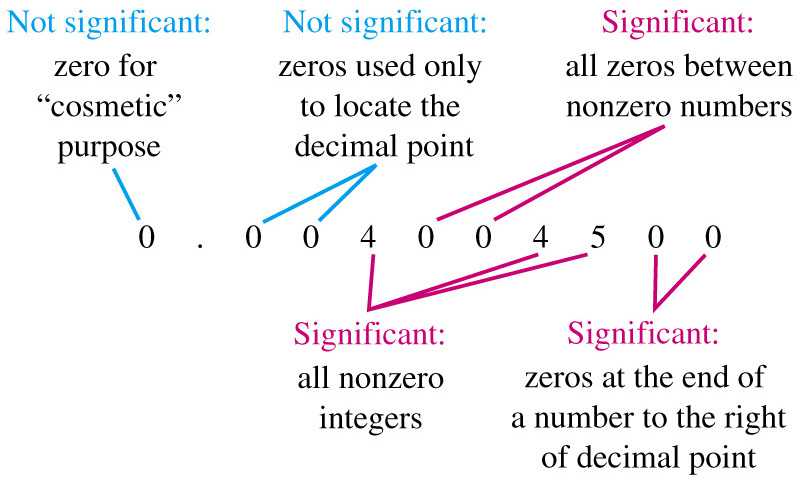
| back 18 -
SIGNIFICANT FIGURE RULES:
- all
the digits including the estimated digit
-
all nonzero digits and zeros between digits
-
zeros at the end of a decimal number
-
A ZERO IS NOT A SIGNIFICANT FIGURE
- at the beginning of a decimal number
-
used as a placeholder in a larger number without a decimal
point
- not zeros that act as placeholders
before digits
|
front 19 Scientific Notation and Significant Zeros | back 19 - when one or more zeros in a large number are significant, they
are shown clearly by writing the number in scientific notation
|
| back 20 - numbers obtained by counting items
- not measured
- do not have limited number of significant figures
- do
not affect the number of significant figures in a calculated
answer
|
front 21 Examples of Some Exact Numbers | back 21 - 8 doughnuts
- 2 baseballs
- 5 capsules
- 1
L = 1000 mL
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 kg = 1000 g
- 1
ft = 12 in
- 1 qt = 4 cups
- 1 lb = 16 oz
|
| back 22 - If the first digit to be dropped is 4 or
less, then it and all the following digits are simply
dropped from the number
- If the first digit to be dropped is
5 or greater, then the last retained
digit of the number is increased by 1
|
front 23 Multiplication and Division with Measured Numbers pg. 32 | back 23 - In multiplication or division, the final answer is written so
that it has they same number of significant figures as the
measurement with the fewest significant figures
|
front 24 Adding Significant Zeros pg. 32 | back 24 - When the calculator display contains fewer SFs than needed, add
one or more significant zeros to obtain the correct number of
significant figures
|
front 25 Addition and Subtraction with SFs pg.32 | back 25 - In addition or subtraction, the final answer is written so that
it has the same number of decimal places as the measurement with the
fewest decimal places
|
| back 26 - can be placed in front of any unit to increase or decrease its
size by some factor of 10
-
EXAMPLES:
- milli....milligram (mg)
- micro....microgram (mcg)
|
front 27 Prefixes That Increase the Size of the Unit | back 27 - tera (T)
- numerical value: 1,000,000,000,000
- scientific notation: 1012
- equality: 1 Ts
= 1 x 1012 s or 1 s = 1 x 10-12 Ts
- giga (G)
- numerical value: 1,000,000,000
- scientific notation: 109
- equality: 1 Gm
= 1 x 109 m or 1 m = 1 x 10-12 Gm
- mega (M)
- numerical value: 1,000,000
- scientific notation: 106
- equality: 1 Mg
= 1 x 106 g or 1 g = 1 x 10-6 Mg
- kilo (k)
- numerical value: 1,000
- scientific notation: 103
- equality: 1 km
= 1 x 103 m or 1 m = 1 x 10-3 km
|
front 28 Prefixes That Decrease the Size of the Unit | back 28 - deci (d)
- numerical value: 0.1
- scientific
notation: 10-1
- equality: 1 dL = 1 x
10-1 L or 1 L = 10 dL
- centi (c)
- numerical value: 0.01
- scientific notation:
10-2
- equality: 1 cm = 1 x 10-2 m or
1m = 100 cm
- milli (m)
- numerical
value: 0.001
- scientific notation: 10-3
- equality: 1 ms = 1 x 10-3 s or 1 s = 1 x
103 ms
- micro (µ*)
- numerical value: 0.000001
- Scientific notation:
10-6
- equality: 1 µg = 1 x 10-6 g or
1 g = 1 x 106 µg
- nano (n)
- numerical value: 0.000000001
- scientific notation:
10-9
- equality: 1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m or
1 m = 1 x 109 nm
- pico (p)
- numerical value: 0.000000000001
- scientific
notation: 10-12
- equality: 1 ps = 1 x
10-12 s or 1 s = 1 x 1012 ps
|
| back 29 - show the relationship between two units that measure the same
quantitiy
- 1 m = 100 cm.... = 1 x 102 cm
- 1 m = 1000 mm... 1 x 103 mm
- 1 cm = 10
mm... 1 x 101 mm
|
front 30 Cubic Centimeter
(abbreviated: cm3 or cc) | back 30 - the volume of a cube whose dimension are 1 cm on each side
- has the same volume as a millimeter
- 1 cm3 or
cc = 1 mL
|
| back 31 - 1 kg = 1000 g... = 1 x 103 g
- 1 g = 1000
mg... = 1 x 103 mg
- 1 g = 100 cg... = 1 x
102 cg
- 1 mg = 1000 mcg... = 1 x 103
mcg
|
| back 32 - any equality written as fraction, with one of the quantities in
the numerator and the other in the denominator
|
| back 33 - uses two different units to describe the same measure
amount
- written for relationship between units of the metric
system, U.S. units, or between metric and U.S. units
-
EXAMPLES:
- 1 m = 1000 mm
- 1 lb = 16
oz
- 2.20 lb = 1 kg
|
front 34 Equalities: Conversion Factors & SF | back 34 - the numbers in:
- any equality between two metric units
or between two U.S system units are obtained by definition and
are exact number
- a definition are exact and are not
used to determine SFs
- an equality between metric and
U.S units contain one number obtained by measurement and count
toward the significant figures
-
Exception: The equality 1 in. = 2.54 cm has been defined
as an exact relationship, 2.54 is an exact
number
|
front 35 Conversion Factors From a Percentage | back 35 - a percent factor gives the ratio of the parts to the whole and
uses
- the same unit in the numerator and denominator
- uses the value of 100 and can be written as two factors
|
front 36 Problem Solving Using Unit Conversion | back 36 - requires one or more conversion factors to change a given unit
to the needed unit
-
problem solving requires indentification of:
-
the given quantity units
-
the units needed
-
conversion factors that connect the given and needed
units
-
given unit x one or more conversion factors = needed
unit
|
| back 37 - compares the mass of an object to its volume
|
| back 38 - A solid
- completely emerged in eater displaces its own
volume of water
- has a volume calculated from the volume
difference
|