Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chemistry in Our Lives
front 1 What does hemoglobin do in the body? | back 1
|
front 2 What does hemoglobin do in the body? (simple answer) | back 2
|
front 3 Why does aspirin relieve headaches? | back 3
|
front 4 Chemistry | back 4
|
front 5 Matter | back 5
|
front 6 Examples of a Chemical Reaction | back 6
|
front 7 Chemicals | back 7
|
front 8 Antioxidants | back 8
|
front 9 Calcium carbonate | back 9
|
front 10 Sorbitol | back 10
|
front 11 Sodium Lauryl Sulfate | back 11
|
front 12 Titanium Dioxide | back 12
|
front 13 Triclosan | back 13
|
front 14 Sodium Fluorophosphate | back 14
|
front 15 Methyl Salicylate | back 15
|
front 16 Which of the following contains chemicals? A. sunlight B. fruit C. milk D. breakfast cereal | back 16 B,C,D
|
front 17 Scientific Method | back 17
|
front 18 Observations | back 18
|
front 19 Hypothesis | back 19
|
front 20 Experiments | back 20
|
front 21 Conclusion | back 21
|
front 22 Ones Place (place value) | back 22 
|
front 23 Tens Place (place value) | back 23 
|
front 24 Tenths Place (place value) | back 24
|
front 25 Hundredths Place (place value) | back 25
|
front 26 Graph | back 26
|
front 27 Positive Number | back 27
|
front 28 Negative Number | back 28
|
front 29 Multiplication and Division of Positive and Negative Numbers | back 29 
|
front 30 Addition of Positive and Negative Numbers | back 30 
|
front 31 Subtraction of Positive and Negative Numbers | back 31 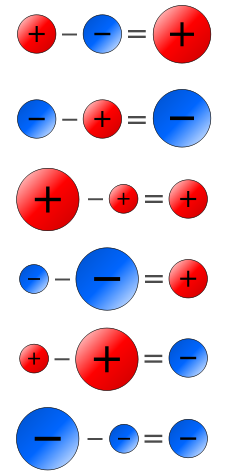
|
front 32 Calculating a Percentage | back 32
|
front 33 Solving Equations | back 33 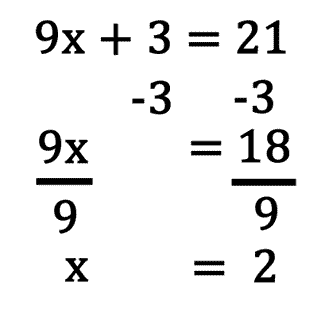
|
front 34 Writing Numbers in Scientific Notation | back 34 
|
front 35 Scientific Notation on Calculator | back 35  |
front 36 Scientific Notation | back 36
|