Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology 191 Final Review - Midterm Exam II
front 1 A molecule that has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions is: | back 1 Amphipathic |
front 2 The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is: | back 2 Osmosis |
front 3 The ___ is dissolved in the ___. | back 3 Solute...solvent |
front 4 All cells are separated from their surroundings by: | back 4 A plasma membrane |
front 5 Which of the following extracellular matrix components is embedded in a cell's phospholipid bilayer? | back 5 Integrins |
front 6 What does cholesterol do in a plasma membrane environment that is in a cold environment? | back 6 Increases membrane fluidity |
front 7 What does cholesterol do in a plasma membrane that is in a warm environment? | back 7 Decreases membrane fluidity |
front 8 Glycoproteins are formed when carbohydrates are attached to proteins using: | back 8 Covalent bonds |
front 9 What protein facilitates the passive transport of water across a membrane? | back 9 Aquaporins |
front 10 Glycoproteins that will wind up on a cell's surface have their carbohydrates attached in the: | back 10 Golgi Apparatus |
front 11 The First Law of Thermodynamics states that: | back 11 Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. |
front 12 The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that: | back 12 The total amount of disorder in the universe is constantly increasing. |
front 13 The change in the Gibbs Free Energy for a reaction is defined as: | back 13 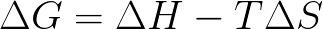 |
front 14 A reaction that has a positive delta G is: Favorable
| back 14 None of the above |
front 15 A chemical reaction that releases energy is: | back 15 Exergonic |
front 16 How do enzymes work to speed up chemical reactions? | back 16 Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for the reaction to start. |
front 17 The position on an enzyme molecule that catalyzes its chemical reaction is the: | back 17 Active site |
front 18 A molecule that binds to an enzyme (but does NOT bind to the position that #17 asked about) and slows down the enzyme's catalytic activity, is: | back 18 An allosteric inhibitor |
front 19 How do cells make energetically unfavorable reactions proceed? | back 19 They couple unfavorable reactions to favorable ones, so the overall change in free energy is negative. |
front 20 ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of G = -7.2kCal/mol. Suppose a cell uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to power a multistep anabolic reaction with delta G = +21.6kCal/mol. At Least how many molecules of ATP must be hydrolyzed during the synthesis? (HINT: remember what the 2nd law of thermodynamics says about real-world efficiency!) | back 20 4 molecules (it's not 3 due to inefficiency) |
front 21 Consider the combustion of natural gas in your stove: CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O +heat. Which component in this reaction is the reducing agent? | back 21 CH4 |
front 22 In the same reaction in #21, what component is the oxidizing agent? | back 22 O2 |
front 23 What is the proper order for all the stages of mitochondrial respiration? | back 23 Glycolysis => Pyruvate Oxidation => Citric Acid Cycle => Oxidative Phosphorylation |
front 24 During glycolysis, how many molecules of ATP must the cell invest to begin digesting glucose? | back 24 2 molecules |
front 25 What are the net products of glycolysis? | back 25 2 ATP
|
front 26 During the process of respiration, when are the first molecules of CO2 released? | back 26 Pyruvate Oxidation |
front 27 During the process of respiration, what step produces the most molecules of ATP? | back 27 Oxidative Phosphorylation |
front 28 True or false: during the Citric Acid Cycle, the two carbon atoms added to the cycle are released as CO2 during the same round that they were added. | back 28 False |
front 29 Which reaction releases the most energy during the process of respiration? | back 29 NADH => NAD+ |
front 30 In respiration, the molecules of ATP that are not produced by oxidative phosphorylation are all produced by: | back 30 Substrate-level phosphorylation |
front 31 Which enzyme produced the most molecules of ATP in respiration? | back 31 ATP synthase |
front 32 During oxidative phosphorylation, Protein Complexes I-IV pump protons from the ___ into the ___. | back 32 Mitochondrial matrix...intermembrane space |
front 33 What is the energy source that directly powers ATP synthesis in oxidative phosphorylation? | back 33 A proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial space. |
front 34 What molecule is the terminal electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain? | back 34 O2 |
front 35 How does a cell doing alcohol fermentation benefit by converting Pyruvate to CO2 + ethanol? | back 35 It regenerates NAD+ needed to continue glycolysis. |
front 36 Suppose you found a new species of plant whose chloroplasts contained an additional pigment that could absorb green light. What color would the plant most likely be? | back 36 Black |
front 37 ___ can produce their own energy while ___ get their energy from consuming material from other organisms. | back 37 Autotrophs...heterotrophs |
front 38 The two main processes of photosynthesis are the Light reactions and: | back 38 The Calvin Cycle |
front 39 What are the reagents used by the light reactions of photosynthesis? | back 39 ADP
|
front 40 What are the products created by the light reactions of photosynthesis? | back 40 ATP
|
front 41 Which answer is true of photons?
| back 41 The longer the wavelength, the lower the energy |
front 42 The organelle where photosynthesis takes place in eukaryotes is the: | back 42 Chloroplast |
front 43 The Calvin Cycle takes place inside the: | back 43 Stroma |
front 44 In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is captured by: | back 44 Ribulose Biphosphate Carboxylase(RuBisCo) |
front 45 At least how many photons must be captured for each molecule of NADPH synthesized during photosynthesis? | back 45 2 molecules |
front 46 What does NOT happen during the Calvin Cycle? | back 46 Splitting of water |
front 47 CAM plants do photosynthesis differently, in order to use what resource more efficiently? | back 47 H2O |
front 48 During the light reactions of photosynthesis, what is the only thing that crosses the membrane to enter the thylakoid space? | back 48 Protons |
front 49 A molecule emitting a photon of a different(longer) wavelength than it absorbed is: | back 49 Fluorescence |
front 50 True or false: glucose is the first carbohydrate released by the Calvin Cycle: | back 50 False (it's G3P) |