Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves
front 1 Central Nervous System | back 1  -consists of the brain and spinal cord, which primarily interpret incoming sensory information and issue instructions based on that info and on past experience |
front 2 Peripheral Nervous System | back 2  -consists of the cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, and sensory receptors |
front 3 Two Subdivisions of PNS | back 3 1.Sensory Portion
|
front 4 Sensory Portion | back 4 -consists of nerve fibers that conduct impulses toward the CNS |
front 5 Motor Portion | back 5 -contains nerve fibers that conduct impulses away from the CNS
|
front 6 Somatic Division (sometimes called the voluntary system) | back 6  -controls the skeletal muscles |
front 7 Autonomic Nervous System (often referred to as Involuntary Nervous System) | back 7  -controls smooth and cardiac muscles and glands
|
front 8 Neural Tube | back 8 -epithelial tube developed from the neural plate and forming the central nervous system of the embyro |
front 9 Three major regions of the brain | back 9  1.Forebrain
|
front 10 Ventricles | back 10  -cavities within the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid |
front 11 Cerebral Hemispheres | back 11  -either half of the cerebrum
|
front 12 Gyri | back 12  -elevated ridges of tissue |
front 13 Sulci | back 13  -shallow grooves |
front 14 Fissures | back 14  -deeper grooves |
front 15 Longitudinal Fissure | back 15  -single deep fissure |
front 16 Central Sulcus | back 16 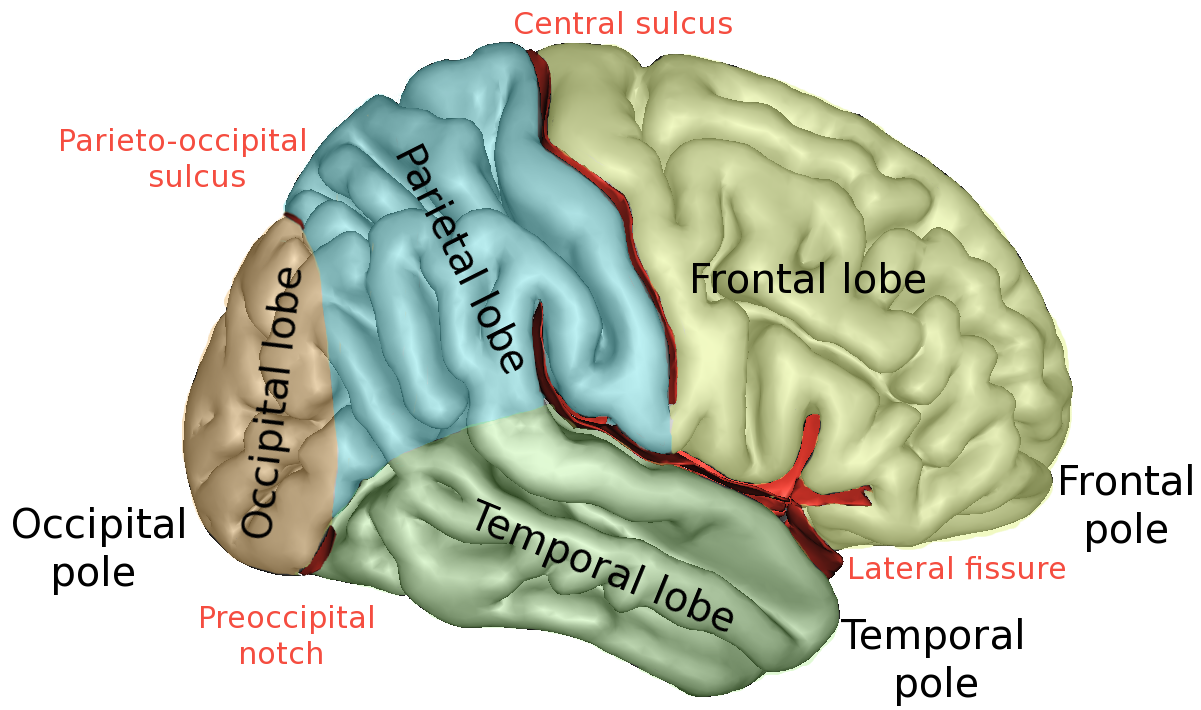 -divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe |
front 17 Lateral Sulcus | back 17 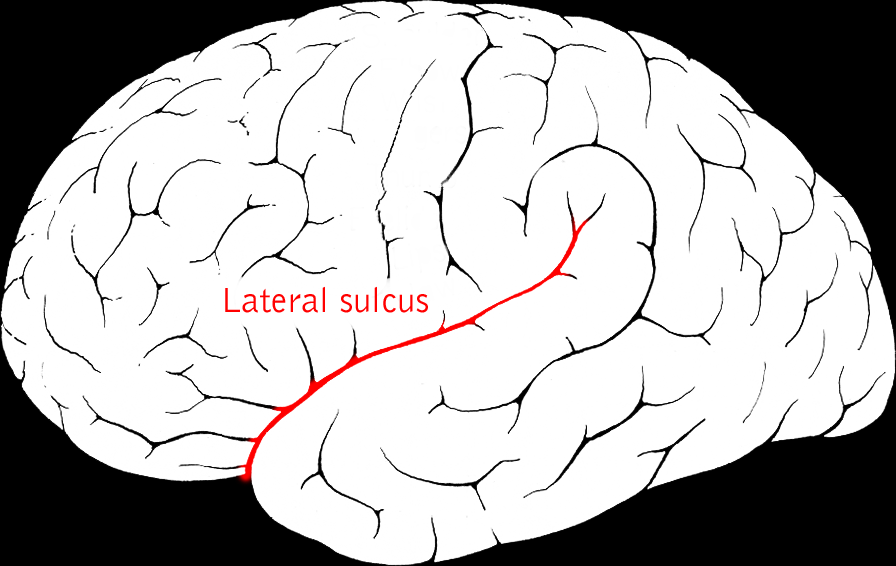 -separates the temporal lobe from the parietal lobe |
front 18 Parieto-occipital Sulcus | back 18  -on the medial surface of each hemisphere divides the occipital lobe from the parietal lobe |
front 19 Insula | back 19 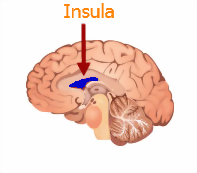 -fifth lobe of each cerebral hemispheres
|
front 20 Primary Somatosensory Cortex | back 20  -region of the brain where nerve signals from the sense of touch are normally received
|
front 21 Somatosensory Association Cortex | back 21 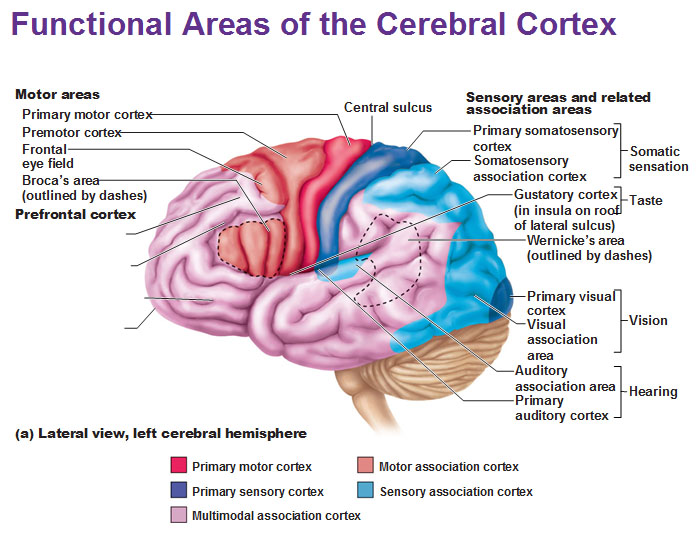 -incoming stimuli is analyzed
|
front 22 Uncus | back 22 - the hooklike anterior end of the hippocampal gyrus on the temporal lobe of the brain |
front 23 Primary Motor Cortex | back 23  - responsible for conscious or voluntary movement of skeletal muscles.
|
front 24 Broca's area | back 24  -specialized speech motor area
|
front 25 Prefrontal Cortex | back 25  -contains many areas involved in intellect, complex reasoning, and personality
|
front 26 Wernicke's Area | back 26  -at the junction of the parietal and temporal lobes
|
front 27 Cerebral Cortex | back 27  -outer layer of gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres
|
front 28 Cerebral White Matter | back 28 -composed of fiber tracts carrying impulses to or from the cortex |
front 29 Diencephalon | back 29  -posterior part of the forebrain that connects the midbrain with the cerebral hemispheres
|
front 30 Olfactory Bulbs | back 30  -the bulblike distal end of the olfactory lobe, where the olfactory nerves begin
|
front 31 Pituitary Gland | back 31  -small oval endocrine gland attached to the base of the vertebrate brain and consisting of an anterior and posterior lobe |
front 32 Mammillary Bodies | back 32  - one of two small round structures on the undersurface of the brain that form the terminals of the anterior arches of the fornix
|
front 33 Brain Stem | back 33 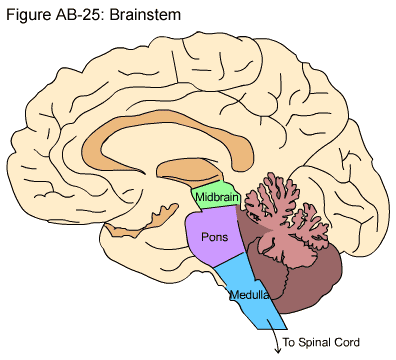 -the stemlike portion of the brain connecting the cerebral hemispheres with the spinal cord
|
front 34 Cerebellum | back 34  -cauliflower-like
|
front 35 Pons | back 35  -consists primarily of motor and sensory fiber tracts connecting the brain with lower CNS centers |
front 36 Medulla Oblongata | back 36 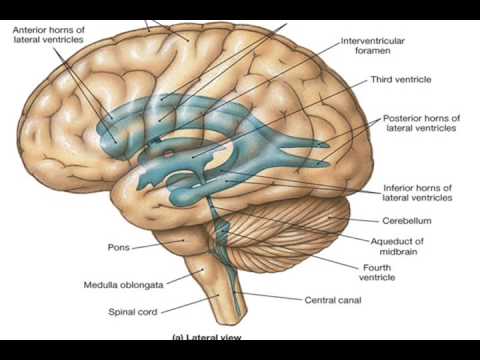 composed primarily of fiber tracts |
front 37 Corpus Callosum | back 37  -major commissure connecting the cerebral hemispheres |
front 38 Fornix | back 38  -bandlike fiber tract concerned with olfaction as well as limbic system functions |
front 39 Septum Pellucidum | back 39  -separates the lateral ventricles of the cerebral hemispheres |
front 40 Thalamus | back 40 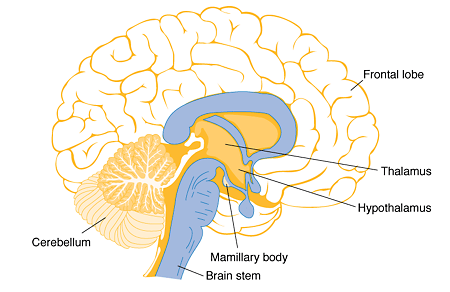 -consists of two large lobes of gray matter that laterally enclose the shallow third ventricle of the brain |
front 41 Hypothalamus | back 41  -makes up the floor and inferolateral walls of the third ventricle
|
front 42 Epithalamus | back 42 -forms the roof of the third ventricle
|
front 43 Cerebral Aqueduct | back 43  -a slender canal traveling through the midbrain
|
front 44 Meninges | back 44  -3 layer of connective tissue membranes covering and protecting the brain and spinal cord |
front 45 Dura Mater | back 45  -outermost meninx double layered membrane
|
front 46 Arachnoid Mater | back 46  -weblike middle meninx
|
front 47 Pia Mater | back 47  -the innermost meninx
|