Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle
front 1 Skeletal Muscle/Voluntary Muscle | back 1  -attaches to the skeleton
|
front 2 Fibers | back 2  -large, long cylindrical cells that makes up skeletal muscle
|
front 3 Sarcolemma | back 3  -membrane enclosing a striated muscle fiber |
front 4 Myofibrils | back 4  -a contractile fibril of skeletal muscle
|
front 5 Myofilaments | back 5  -composed of actin and myosin, which slide past each other during muscle activity to bring about shortening and contracting of the muscle cells |
front 6 Sarcomere | back 6  -contractile units of muscle
|
front 7 Transverse Tubule (t tubule) | back 7  -deep invagination of the sarcolemma |
front 8 Terminal Cisterns | back 8  -pairs of tranversely oriented channels that are confluent with the sarcotubules, which together with an intermediate T tubule constitute a triad of skeletal muscle |
front 9 Triads | back 9 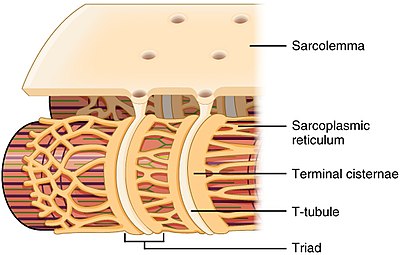 -regions where the sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal borders a t tubule on each side. |
front 10 Endomysium | back 10  -delicate areolar connective tissue that encloses each muscle fiber |
front 11 Perimysium | back 11  -collagenic membrane surrounding several muscle fibers |
front 12 Fascicle | back 12  -bundle of fibers |
front 13 Epimysium | back 13  - large number of fascicles bounded together by dense connective tissue |
front 14 Deep Fascia | back 14 -coarser sheets of dense connective tissue that bind muscles into functional groups |
front 15 Insertion | back 15  -a muscles more movable attachment |
front 16 Origin | back 16  - a muscles immovable attachment |
front 17 Neuromuscular/Myoneural Junction | back 17 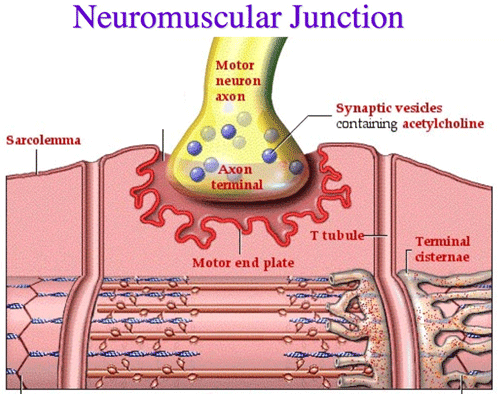 - junction between an axon of a motor neuron and a muscle cell |
front 18 Motor Unit | back 18 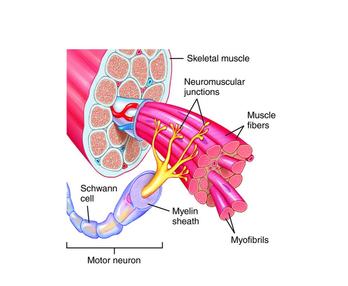 -a neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates |
front 19 Synaptic Cleft | back 19  -small fluid-filled gap separating the neuron and muscle fiber membranes |