Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy & Physiology Lab 1: The Axial Skeleton
front 1 Three parts of the Axial skeleton | back 1  1.The Skull
|
front 2 Cranial Bones | back 2 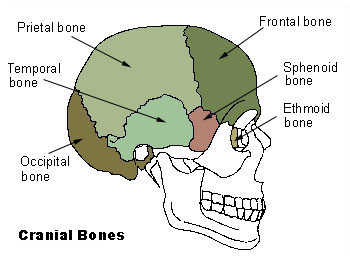 -encloses and protects the fragile brain tissue |
front 3 Facial Bones | back 3 -supports the eyes and position them anteriorly
|
front 4 All but one of the bones of the skull are joined by interlocking joints called ____________. | back 4  Sutures |
front 5 The mandible, or lower jawbone is attached to the rest of the skull by a _______________. | back 5 freely movable joint |
front 6 Cranial Vault/Calvaria | back 6  -the superior, lateral, and posterior walls of the skull |
front 7 Cranial Base | back 7  -forms the skull bottom |
front 8 What are the three distinct depressions of the cranial base? | back 8  1.Anterior cranial fossae
|
front 9 Frontal Bone | back 9 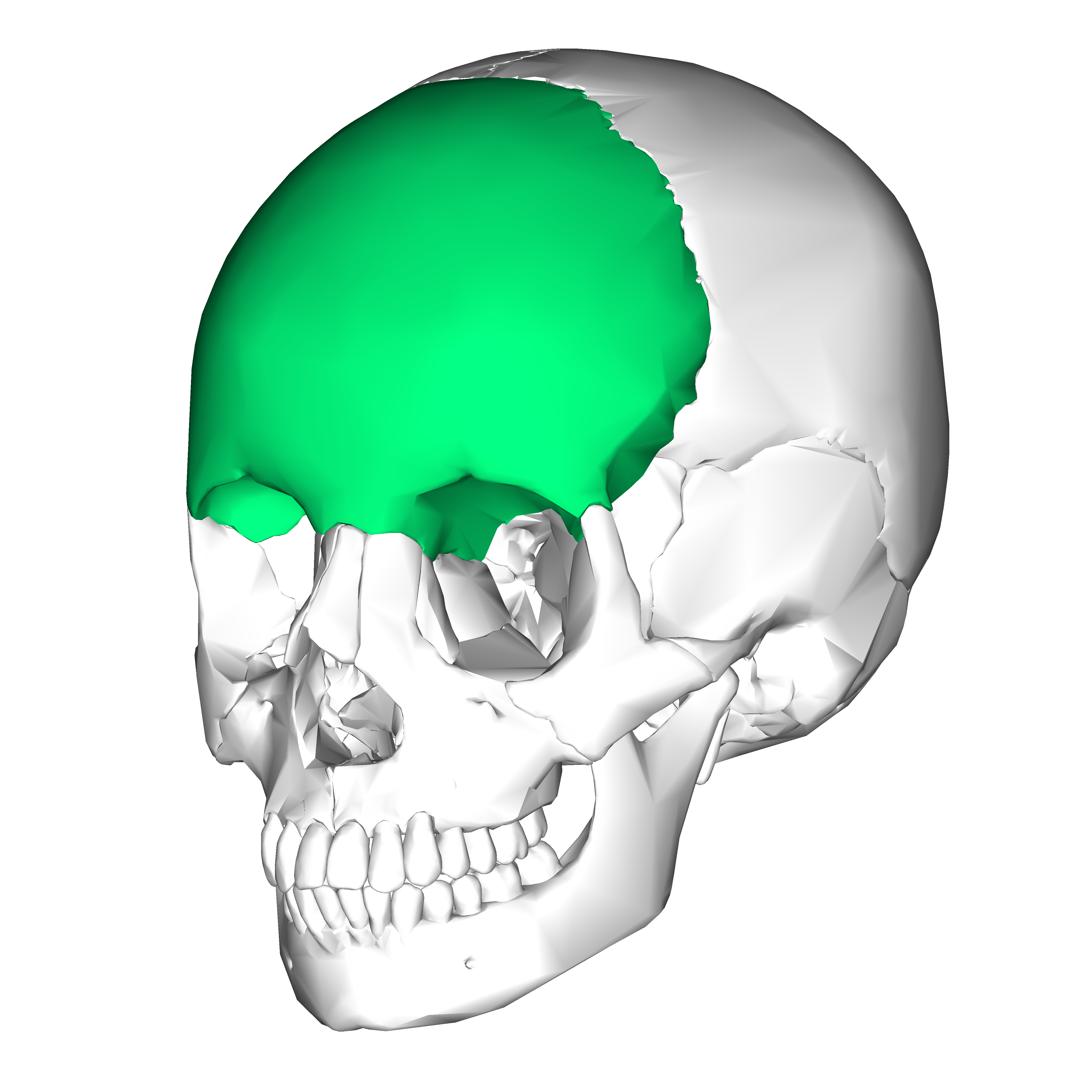 -anterior portion of cranium
|
front 10 Supraorbital foramen (notch) | back 10 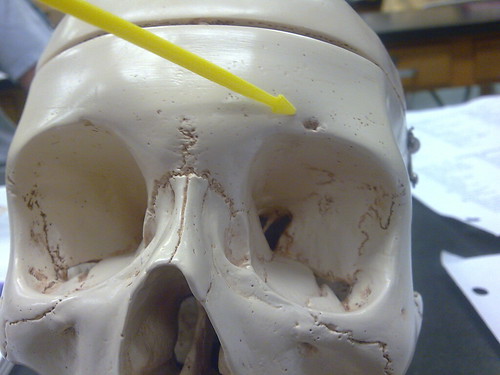 -opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass |
front 11 Glabella | back 11 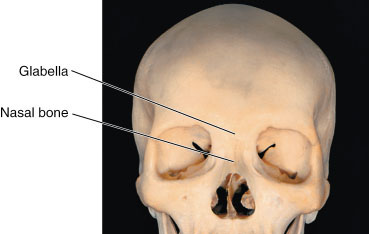 -smooth area between the eyes |
front 12 Parietal Bone (2) | back 12 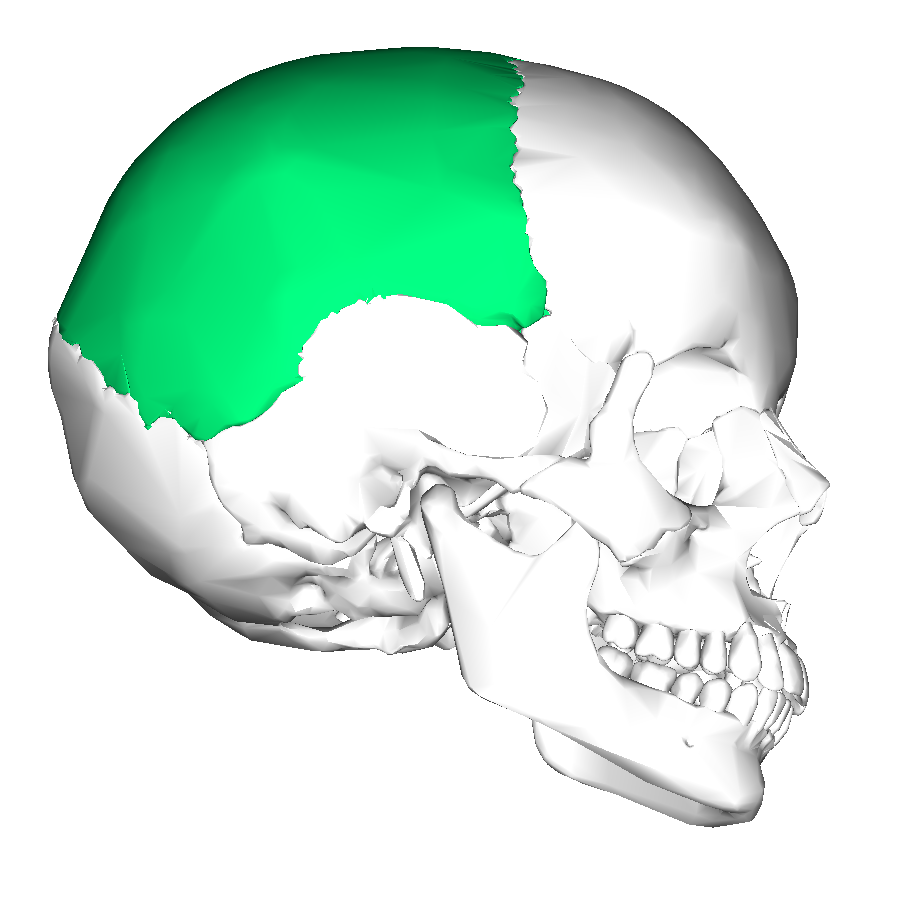 -posterolateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of the cranium |
front 13 Sagittal Suture | back 13 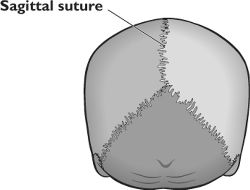 -midline articulation point of the two parietal bones |
front 14 Coronal Suture | back 14 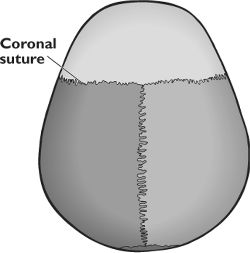 -point of articulation of parietals with frontal bone |
front 15 Temporal Bone | back 15 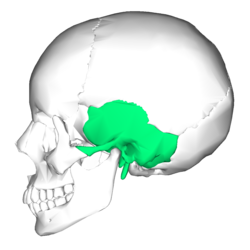 -inferior to parietal bone on lateral skull |
front 16 What are the three major parts of the temporal bone? | back 16  1. Squamous part
|
front 17 Squamous Suture | back 17  -point of articulation of the temporal bone with the parietal bone |
front 18 Zygomatic Process | back 18  - bridgelike projection joining the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) anteriorly |
front 19 Mandibular Fossa | back 19  -rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process
|
front 20 External Acoustic Meatus | back 20  -canal leading to eardrum and middle ear |
front 21 Styloid Process | back 21  -needlelike projection inferior to external acoustic meatus
|
front 22 Jugular Foramen | back 22  -opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI pass |
front 23 Carotid Canal | back 23  -opening medial to the styloid through which the internal carotid artery passes into the cranial cavity |
front 24 Internal Acoustic Meatus | back 24  -opening on posterior aspect (or petrous part) of temporal bone allowing passage of cranial nerves |
front 25 Foramen Lacerum | back 25  -jagged opening between the petrous temporal bone and the sphenoid providing passage for a number of small nerves and for the internal carotid artery to enter the middle cranial fossa |
front 26 Stylomastoid Foramen | back 26  -tiny opening between the mastoid and styloid processes through which cranial nerve VII leaves the cranium |
front 27 Mastoid Process | back 27  -Rough projection inferior and posterior to external acoustic meatus
|
front 28 Occipital Bone | back 28 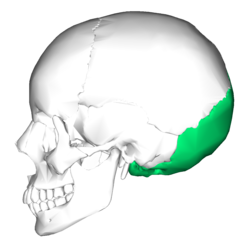 -most posterior bone of the cranium |
front 29 Lambdoid Suture | back 29  -site of articulation of occipital bone and parietal bones |
front 30 Foramen Magnum | back 30  -large opening in base of occipital, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain |
front 31 Occipital Condyles | back 31  -rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas) |
front 32 Hypoglossal Canal | back 32  -opening medial and superior to the occipital condyle through which the hypoglossal nerve pass |
front 33 External Occipital Crest and Protuberance | back 33 .jpg) -midline prominences posterior to the foramen magnum |
front 34 Sphenoid Bone | back 34 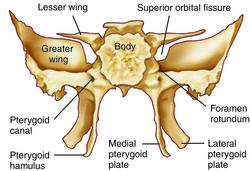 Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull.
|
front 35 Greater Wings | back 35  -portions of the sphenoid seen exteriorly anterior to the temporal and forming a part of the eye orbits |
front 36 Pterygoid Processes | back 36 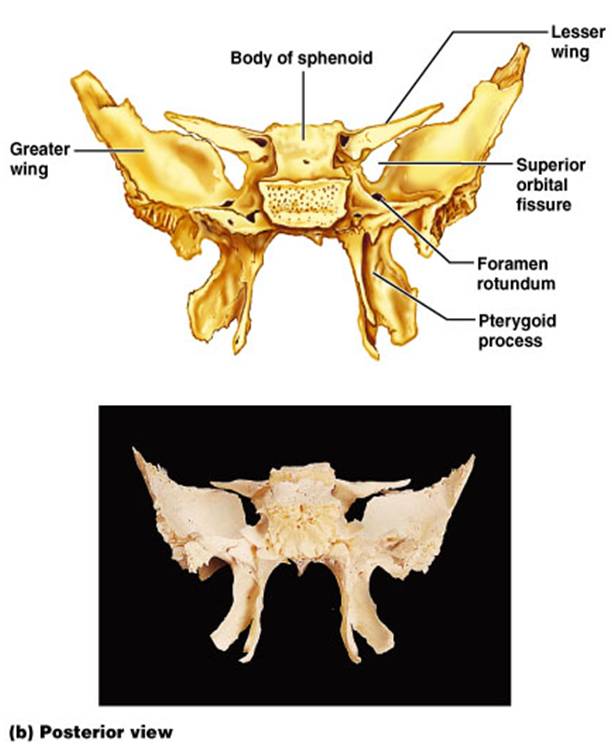 -inferiorly directed trough-shaped projections from the junction of the body and the greater wings |
front 37 Superior Orbital Fissures | back 37  -jagged openings in orbits provding passages for cranial nerves III, IV, V, and VI to enter the orbit where they serve the eye |
front 38 Sella Turcica | back 38 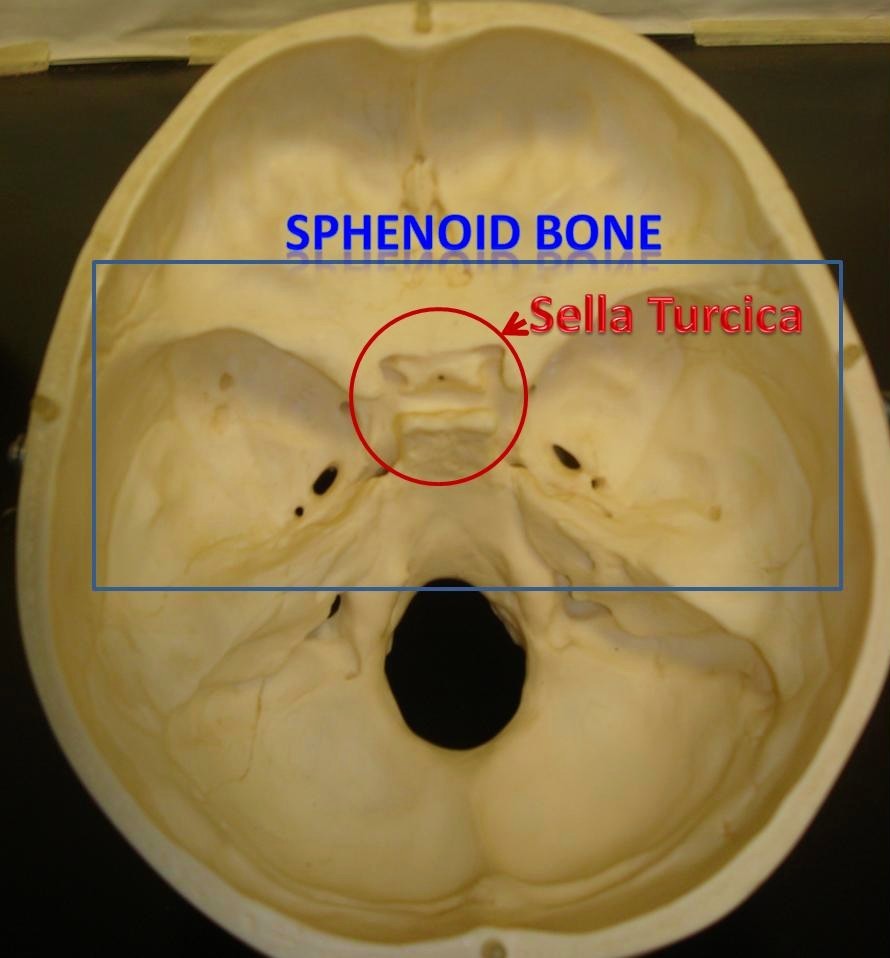 - saddle shaped region in the sphenoid midline |
front 39 Lesser Wings | back 39  -bat shaped portions of the sphenoid bone anterior to the sella turcica |
front 40 Optic Canals | back 40  - openings in the bases of the lesser wings through which the optic nerve (cranial nerve II) enter the orbits to serve the eyes |
front 41 Foramen Rotundum | back 41  - opening lateral to the sella turcica providing passage for a branch of the fifth cranial nerve |
front 42 Foramen Ovale | back 42  opening posterior to the sella turcica that allows passage of the fifth cranial nerve. |
front 43 Foramen Spinosum | back 43  opening lateral to the foramen ovale which the meningeal artery passes |
front 44 Ethmoid Bone | back 44 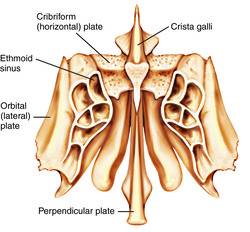 irregularly shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid |
front 45 Crista Galli | back 45  vertical projection providing a point of attachment for the dura meter, helping to secure the brain within the skull |
front 46 Cribriform Plates | back 46  bony plates lateral to the crista galli through which olfactory fibers pass to the brain |
front 47 Perpendicular Plate | back 47  inferior projection of the ethmoid bone that forms the superior part of the nasal septum |
front 48 Lateral Masses | back 48 irregularly shaped and thin-walled bony regions flanking the perpendicular plate laterally |
front 49 Mandible | back 49 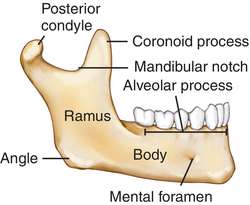 the lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporals in the only freely movable joints of the skull |
front 50 Mandibular body | back 50  horizontal portion; forms the chin |
front 51 Mandibular Ramus | back 51  vertical extension of the body on either side |
front 52 Condylar Process | back 52  articulation point of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone |
front 53 Coronoid Process | back 53  jutting anterior portion off the ramus
|
front 54 Mandibular Angle | back 54 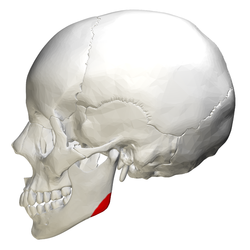 posterior point at which ramus meets the body |
front 55 Mental Foramen | back 55  -prominent opening on the body that transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw |
front 56 Mandibular Foramen | back 56  -permis passage of the nerve involved with tooth sensation |
front 57 Alveolar Process | back 57  superior margin of the mandible, contains sockets in which the teeth lie |
front 58 Maxillae | back 58 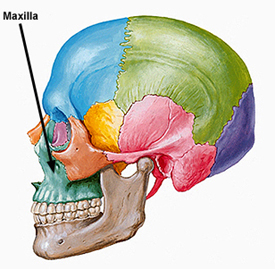 -two bones fused in a median suture
|
front 59 Palatine Processes | back 59  -from the anterior hard palate; meets medially in the intermaxillary suture |
front 60 Infraorbital Foramen | back 60  -opening under the prbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels to the nasal region |
front 61 Lacrimal Bone | back 61  -fingernail sized bones forming part of the medial orbit walls between the maxilla and the ethmoid bone |
front 62 Palatine Bone | back 62 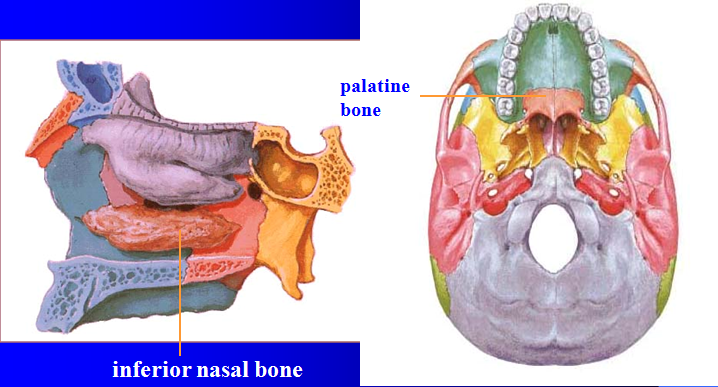 -paired bones posterior to the palatine processes |