Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Water Cycle
front 1  Absorb | back 1 To soak up or take something in. |
front 2 Atmosphere | back 2 The layer of gas surrounding a planet that is held in place by gravity. |
front 3  Condensation | back 3 The change from a gas state to a liquid state. |
front 4 Crystallization | back 4 The formation of highly ordered, solid structures from particles in a solution. |
front 5  Evaporation | back 5 Change of a liquid to a vapor or gas. |
front 6 Gravity | back 6 The force that causes objects with mass to attract one another. |
front 7 Groundwater | back 7 Water that collects in cracks and pores in underground soil and rock layers. |
front 8 Percolation | back 8 When water soaks into the ground and moves downward through spaces in soil and rocks. |
front 9 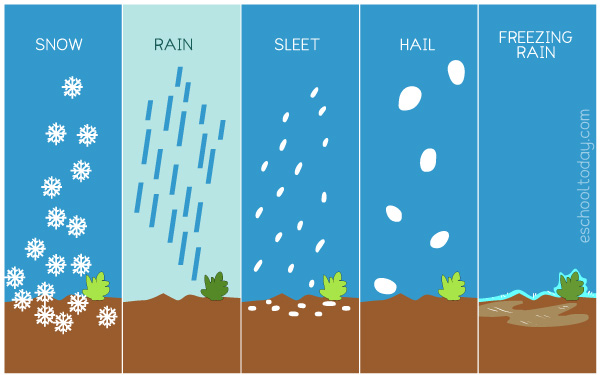 Precipitation | back 9 Rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls from clouds in the sky. |
front 10 Radiant Energy | back 10 Energy from the Sun that reaches Earth as visible light, ultraviolet radiation and infrared (heat) radiation. |
front 11  Runoff | back 11 Rainfall and surface water that drains or flows from the land into streams, rivers, lakes or the ocean. |
front 12  Thermal Energy | back 12 The total kinetic (motion) energy of the tiny particles that make up matter; the faster the particles move, the warmer the matter becomes. |
front 13  Transpiration | back 13 The process by which plants lose water (water vapor) through that stomata in their leaves |
front 14 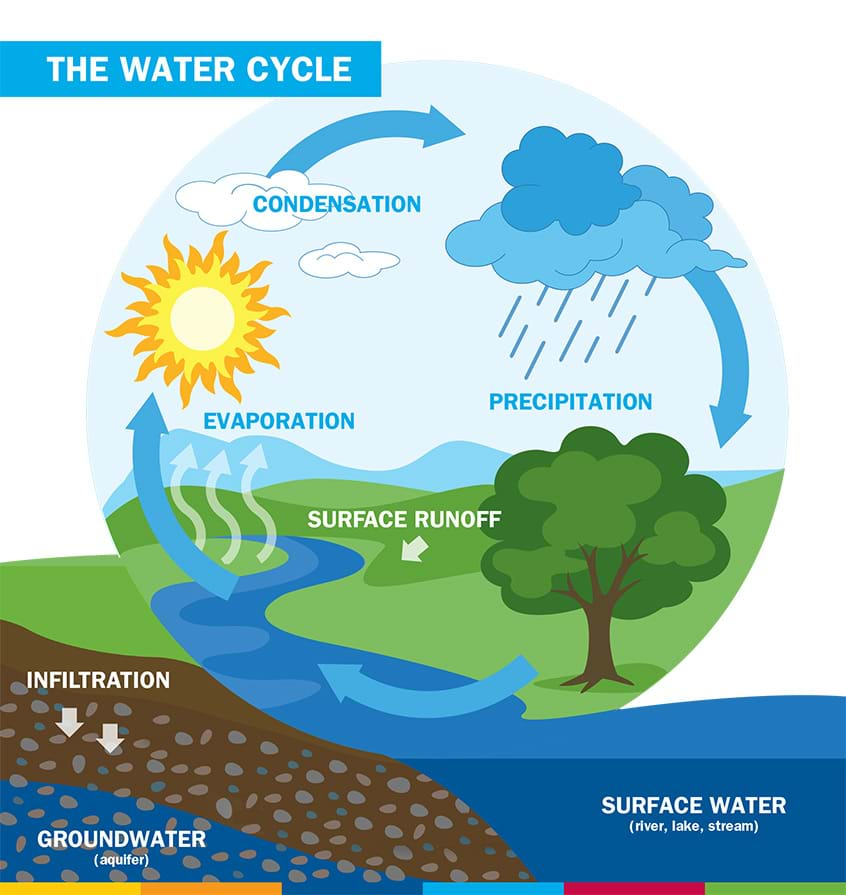 Water Cycle | back 14 The constant movement of water through the land, air, oceans, and living things. |