Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
CH 460 Final Exam Review
front 1 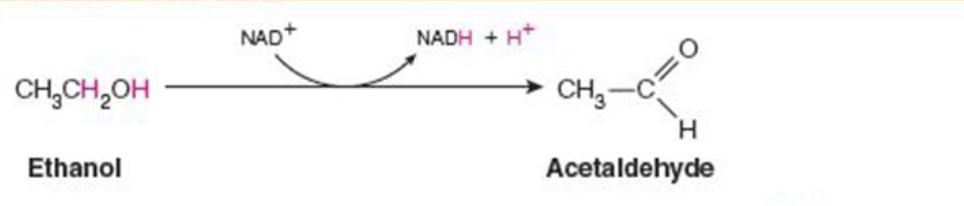 Name the enzyme: catalyze oxidation reduction reactions | back 1 Oxidoreductases Ex. alcohol dehydrogenase (oxidation with NAD+) |
front 2 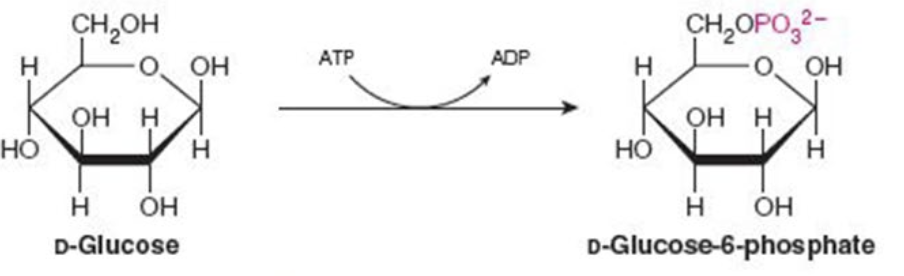 Name the enzyme: catalyze transfer of functional groups from one molecule to another | back 2 Transferases Ex. Hexokinase (phosphorylation) |
front 3 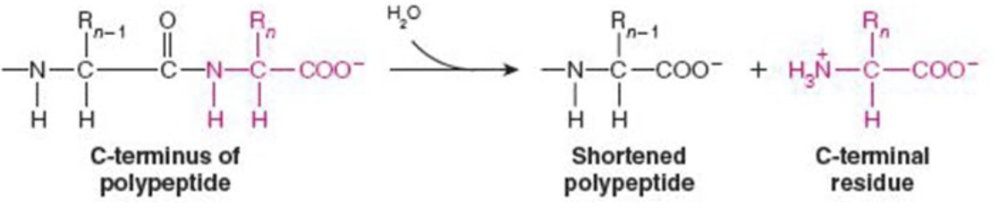 Name the enzyme: catalyze hydrolytic cleavage | back 3 Hydrolases Ex. carboxypeptidase A (peptide bond cleavage) |
front 4 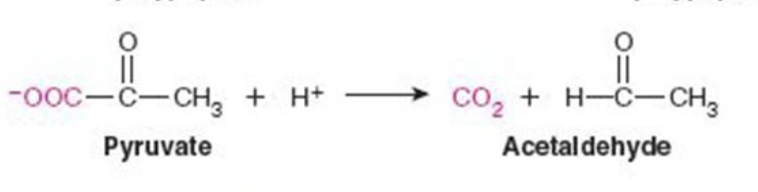 Name the enzyme: Catalyze removal of a group from or addition of a group to a double bond or other cleavage involving electron rearrangement | back 4 Lyases Ex. Pyruvate decarboxylase (decarboxylation) |
front 5 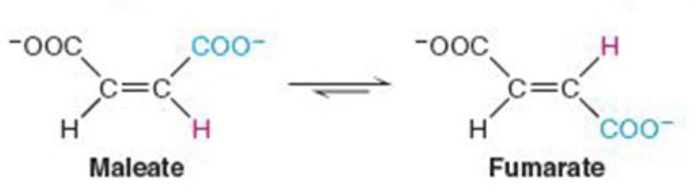 Name the enzyme: catalyze intramolecular arrangement of molecule | back 5 Isomerases Ex. maleate isomerase (cis-trans isomerization) |
front 6 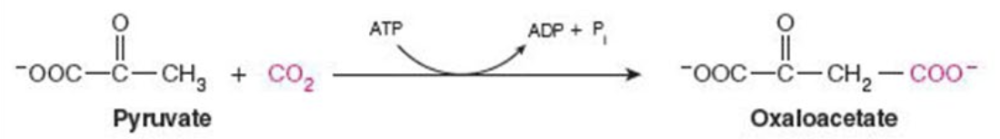 Name the enzyme: Catalyze reactions in which 2 molecules are joined | back 6 Ligase Ex. pyruvate carboxylase |
front 7 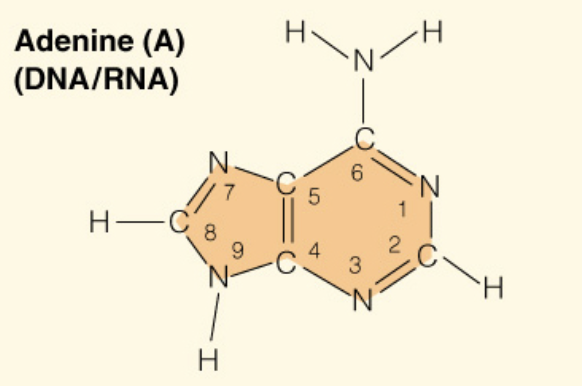 Name the base: | back 7 Adenine (Purine - 2 rings) |
front 8 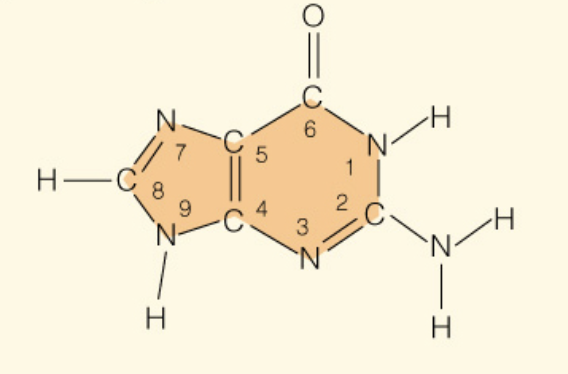 Name the base: | back 8 Guanine (Purine - 2 rings) |
front 9 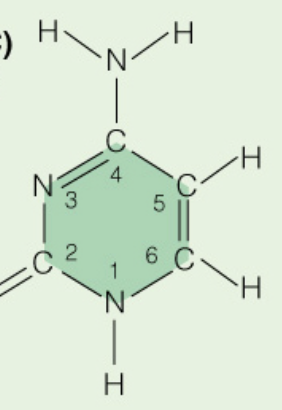 Name the base: | back 9 Cytosine (Pyrimidine) |
front 10 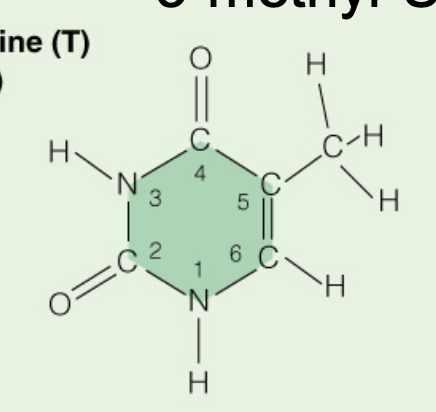 Name the base: | back 10 Thymine (Pyrimidine) |
front 11 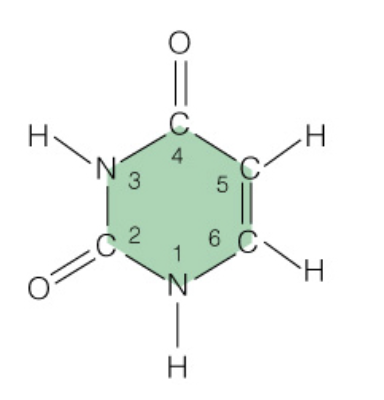 Name the base: | back 11 Uracil (RNA Only - Pyrimidine) |
front 12 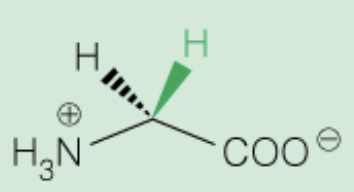 Name the amino acid | back 12 Glycine (Gly, G) - smallest molecule, achiral - Nonpolar, aliphatic |
front 13 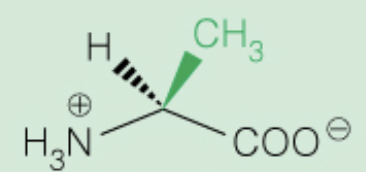 Name the amino acid | back 13 Alanine (Ala,A) - Nonpolar, alipathic |
front 14 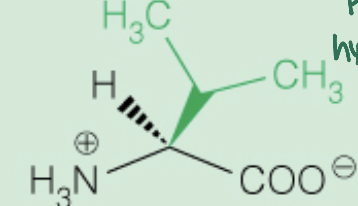 Name the amino acid | back 14 Valine (Val,V) Nonpolar, Aliphatic |
front 15 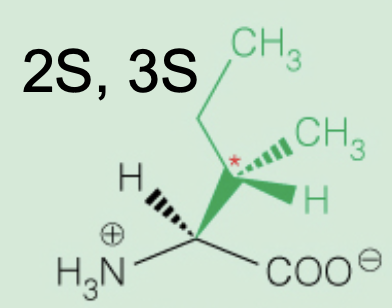 Name the amino acid | back 15 Isoleucine (2S,3S) Nonpolar, Aliphatic Ile, I |
front 16 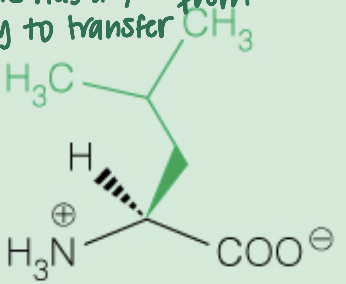 Name the amino acid | back 16 Leucine (Leu,L) Nonpolar, Aliphatic |
front 17 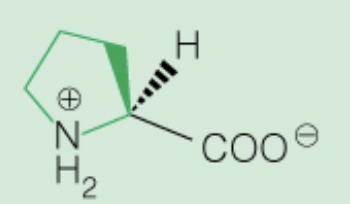 Name the amino acid | back 17 Proline (Pro, P) Nonpolar, only amino acid with secondary amine ring in backbone |
front 18 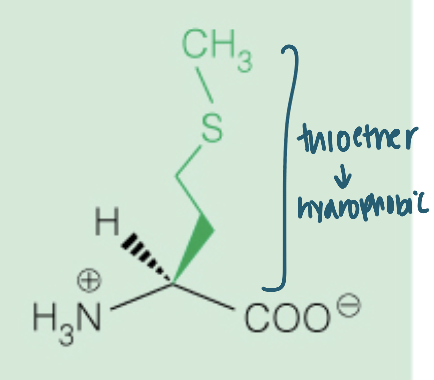 Name the amino acid | back 18 Methionine (Met, M) Nonpolar |
front 19 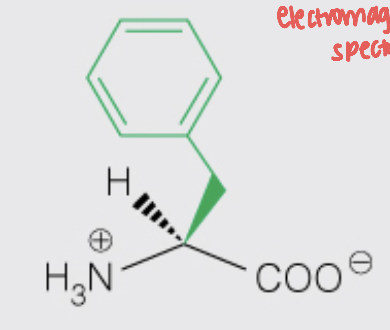 Name the amino acid | back 19 Phenylalanine (Phe, F) - Nonpolar, Aromatic |
front 20 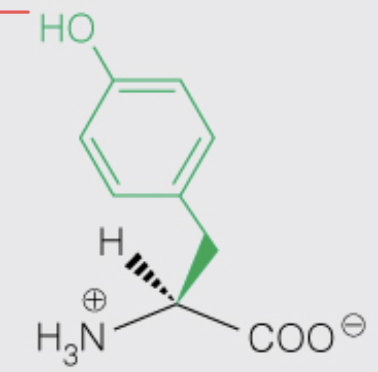 Name the amino acid | back 20 Tyrosine (Tyr, Y) - Nonpolar, Aromatic - OH can be phosphorylated |
front 21 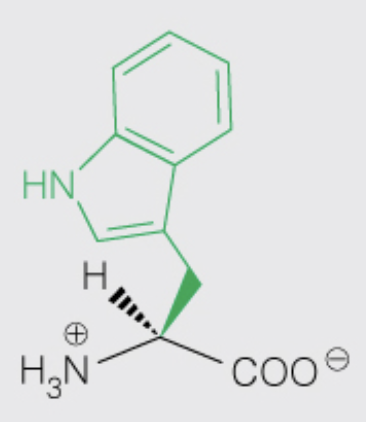 Name the amino acid | back 21 Tryptophan (Trp, W) - Nonpolar, Aromatic - contributes the most to UV absorbance at 280 nm compared to Tyr |
front 22 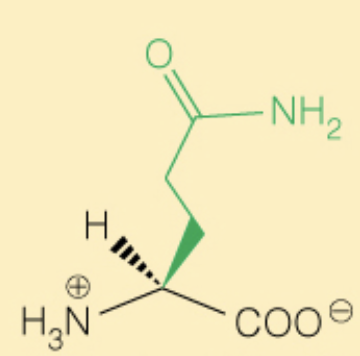 Name the amino acid | back 22 Glutamine (Gln, Q) - Polar |
front 23 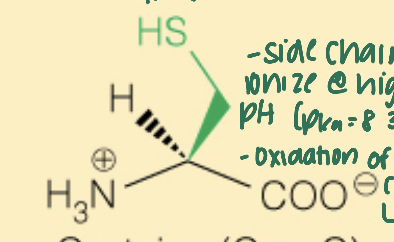 Name the amino acid | back 23 Cysteine (Cys, C) - Polar - 2 cysteine molecules can form a disulfide bond (with -SH, thiol) |
front 24 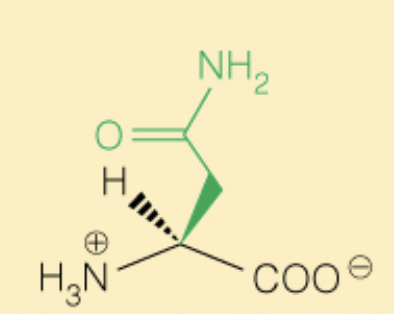 Name the amino acid | back 24 Asparagine (Asn, N) - Polar |
front 25 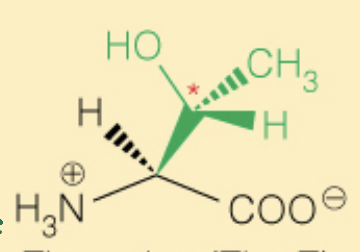 Name the amino acid | back 25 Threonine (Thr, T) - OH can be phosphorylated - Polar - 2S, 3R |
front 26 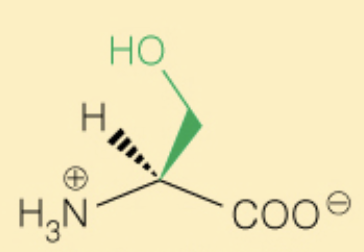 Name the amino acid | back 26 Serine (Ser, S) - OH can be phosphorylated - Polar |
front 27 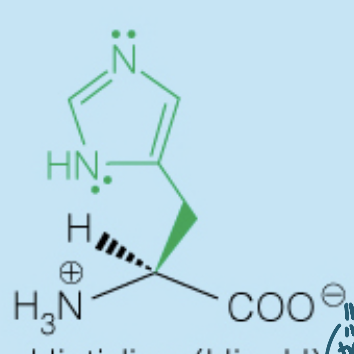 Name the amino acid | back 27 Histidine (His, H) - Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic - Used in many enzymes catalysis since the side chain pKa (6) is around the physiological pH |
front 28 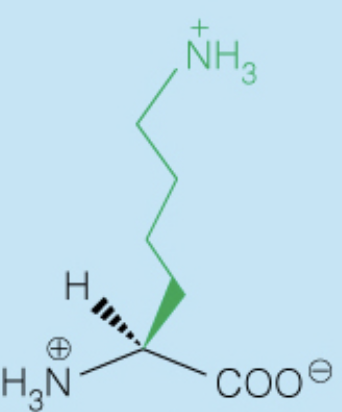 Name the amino acid | back 28 Arginine (Arg, R) - Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic |
front 29 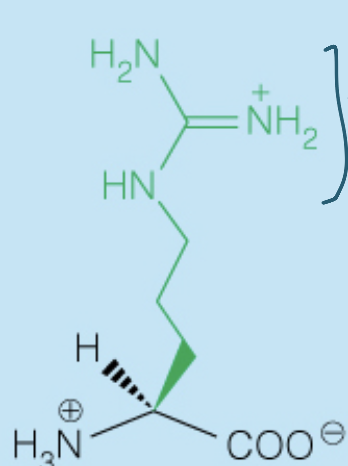 Name the amino acid | back 29 Lysine (Lys, K) - Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic |
front 30 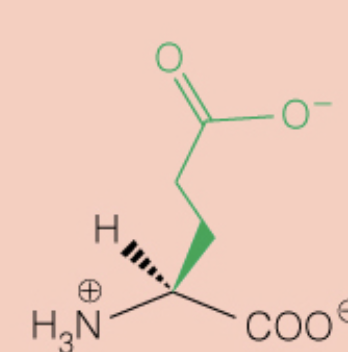 Name the amino acid | back 30 Glutamic Acid (Glu, E) - Polar, Negatively Charged, Acidic |
front 31 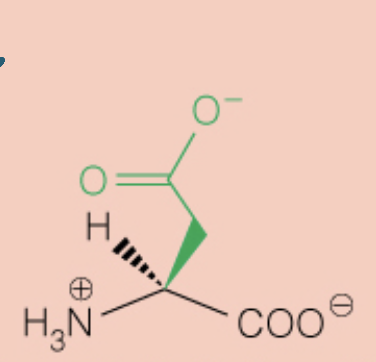 Name the amino acid | back 31 Aspartic Acid (Asp, D) - Polar, Negatively Charged, Acidic |
front 32 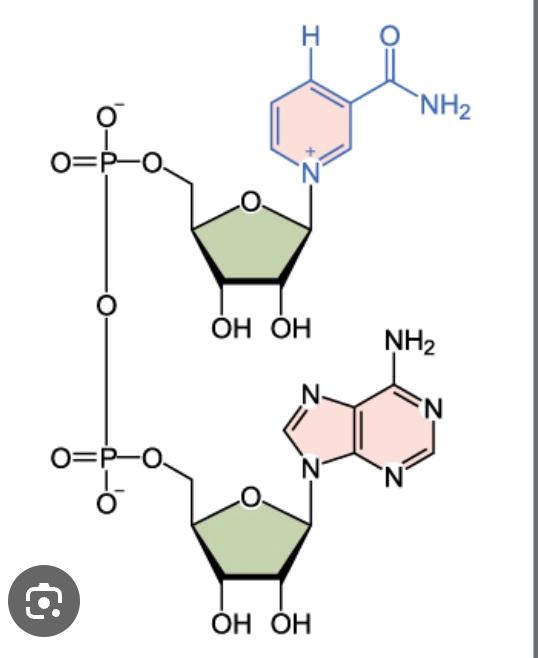 Name the structure | back 32 NAD+ |
front 33 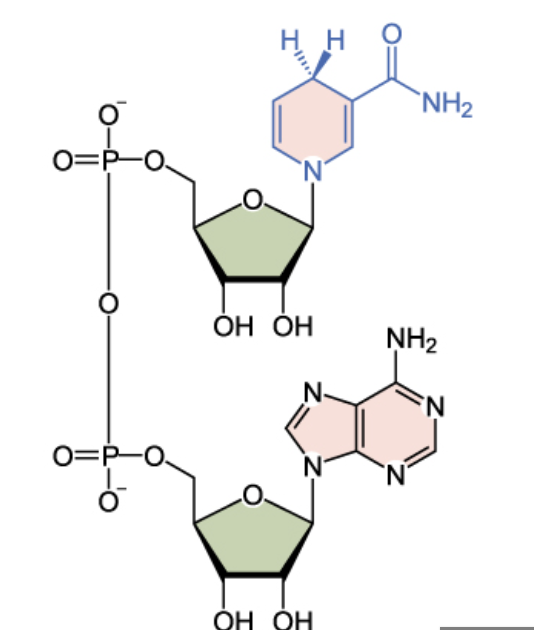 Name the structure | back 33 NADH |
front 34 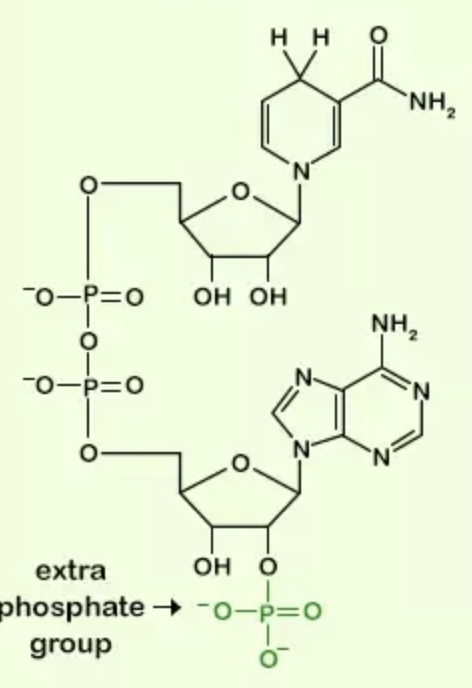 Name the structure | back 34 NADPH |
front 35 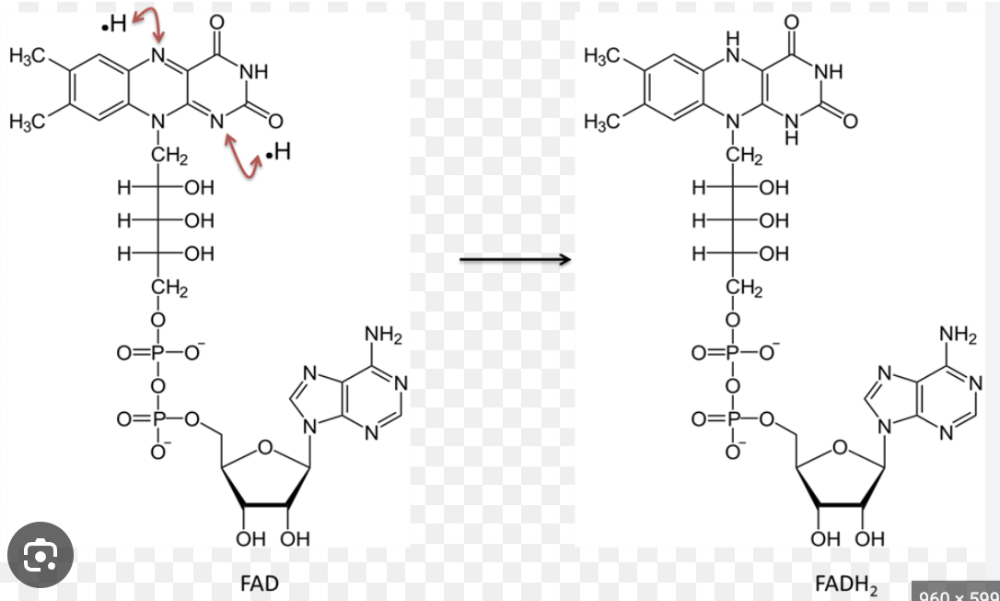 Name the structure | back 35 FAD+ vs. FADH |
front 36 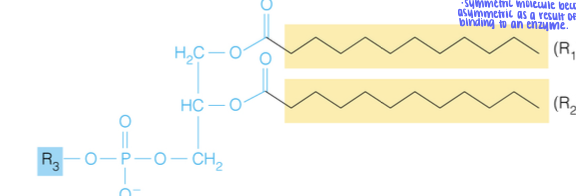 Name the structure | back 36 Glycerophospholipid - lipid with phosphate containing head group - When R3 is is H, the structure is a phosphatidic acid. - Part of membrane lipids |
front 37 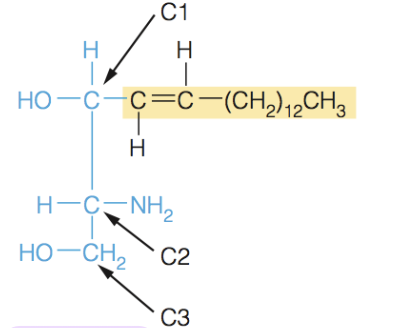 Name the structure | back 37 Spingosine - sphingolipids are built on the amino alcohol spingospine, rather than glycerol - includes long chain tail, so it requires the addition on one fatty acid tail to make a suitable membrane lipid |
front 38 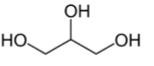 Name the structure | back 38 Glycerol - does not have any stereocenters. When it is derivatized, the symmetric molecules becomes asymmetric (pro-chiral) when bound to enzyme |
front 39 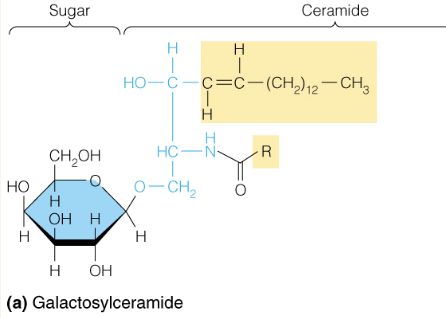 Name the structure | back 39 Glycospingolipids - includes cerebrosides, gangliosides which are common in membranes of the brain and nerve cells |
front 40 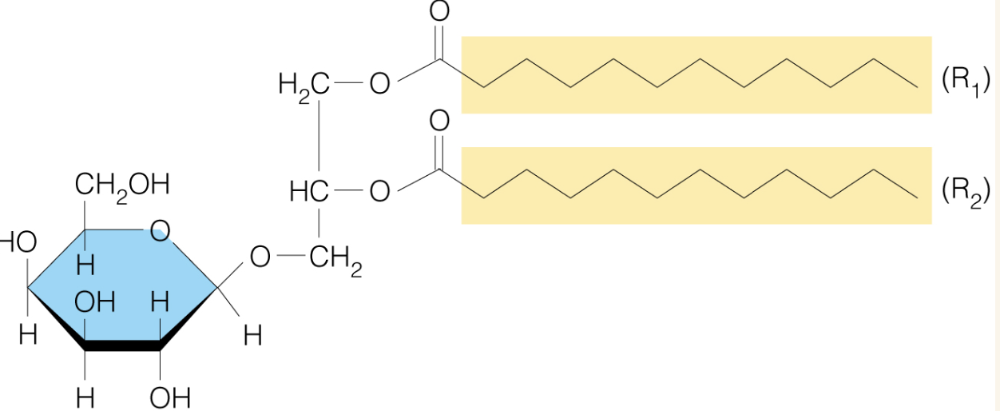 Name the structure | back 40 Glycoglycerolipids - widespread in plants and bacterial membrane |
front 41 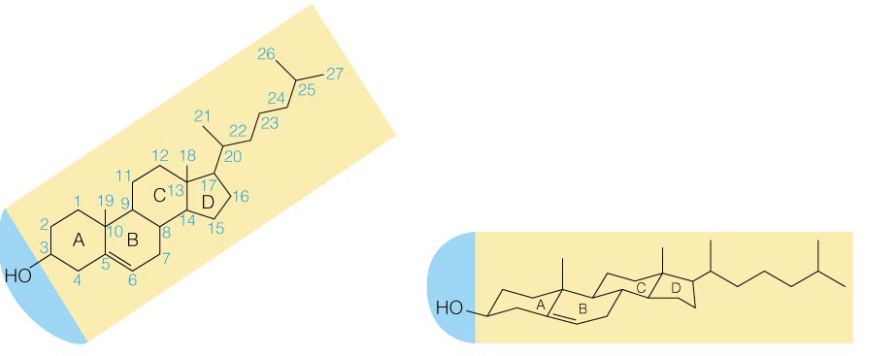 Name the structure | back 41 Cholesterol |
front 42 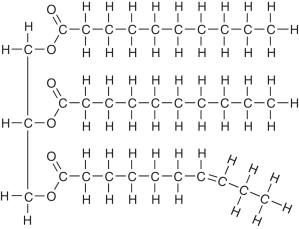 Name the structure | back 42 triaglycerol |
front 43 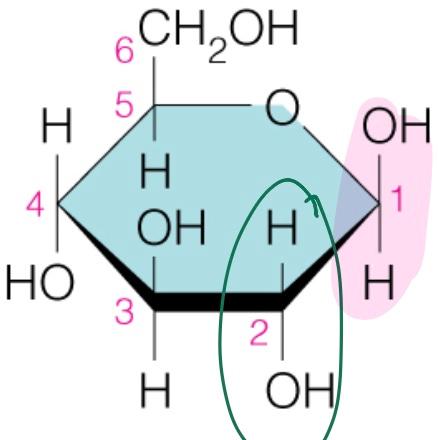 Name the sugar | back 43 Glucose |
front 44 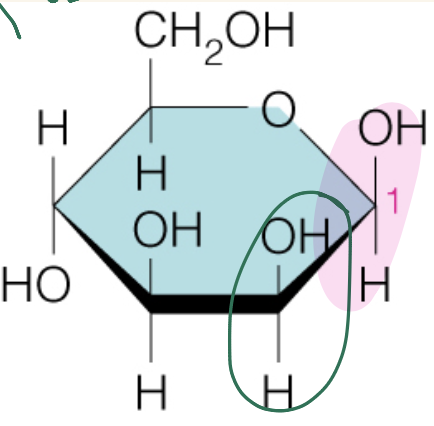 Name the sugar | back 44 Mannose |
front 45 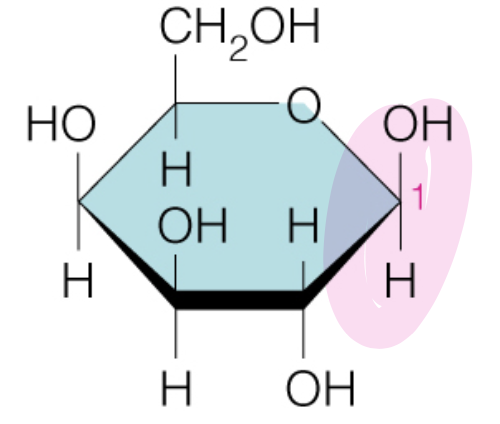 Name the sugar | back 45 Galactose |
front 46 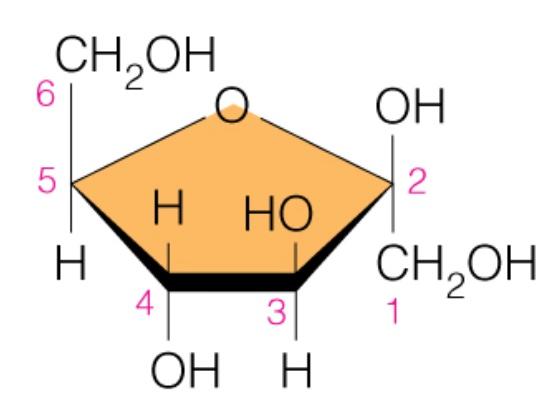 Name the sugar | back 46 Fructose |
front 47 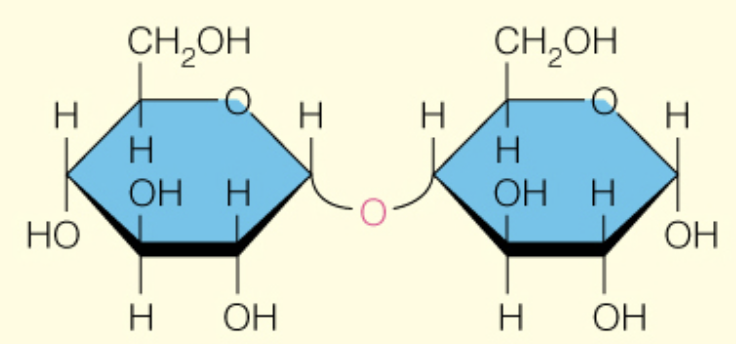 Name the disaccharide | back 47 Maltose B-d-glcp (1 to 4) B-d-glcp |
front 48 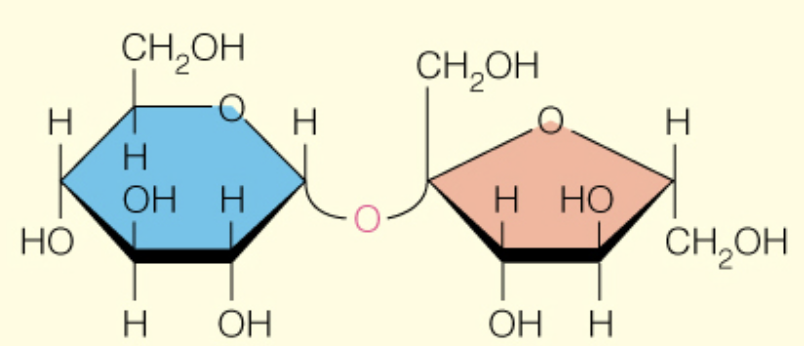 Name the disaccharide | back 48 Sucrose a - D -glcp (1 to 2) B-D-fruf |
front 49 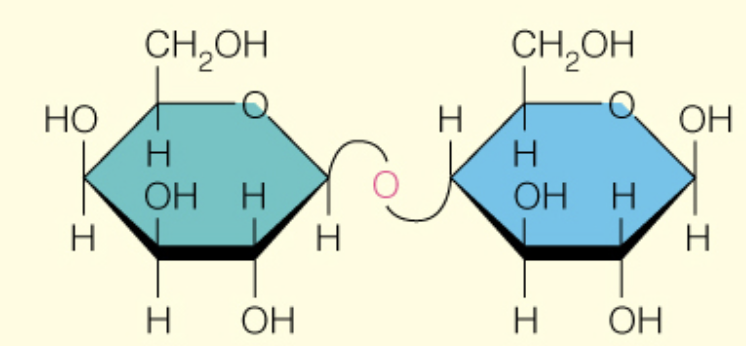 Name the disaccharide | back 49 Lactose B-d-Galp (1 to 4) B-d-Glcp |