Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 2 questions
front 1 A polypeptide of unknown sequence was digested with staphylococcal protease in bicarbonate buffer (pH 10), and separately with chymotrypsin. Based on these results, what is the sequence of this polypeptide? 1. Staphylococcal protease digest (pH 10): -GNFLIME -TD -DKAYE 2. Chymotrypsin digest: -LIMETD -DKAY -EGNF | back 1 DKAYEGNFLIMETD |
front 2 In which of the following techniques is the protein denatured? | back 2 2-D Gel Electrophoresis |
front 3 What result would you expect, for the polypeptide, PRKLPR, treated with carboxypeptidase A? A)PRK + LPR B) PRKL + PR C) P+ RKLPR D) PRKLP + R E) none | back 3 E) none |
front 4 Which amino acid has a side chain that forms a covalent bond with its own α-amino group, creating a ring structure? | back 4 P, proline |
front 5 Which of these following tripeptides is most positively charged at pH 4? A)Tyr-Ser-Thr B) Asn-His-Met C)Tyr-Cys-Ala D)Gly-Glu-Gln E) Thr-Trp-Phe | back 5 B) Asn-His-Met |
front 6 How does fetal hemoglobin (Hb-F) ensure the fetus gets oxygen from the adult's hemoglobin (Hb-A)? | back 6 Hb-F has a higher affinity for oxygen due to the replacement of β with γ subunits, resulting in reduced BPG binding. |
front 7 What is the function of iodoacetate (IOAc)? | back 7 To prevent disulfide bonds from reforming |
front 8 Which of the following forces best describes stabilization of a protein's quaternary structure? | back 8 Burial of non-polar sidechains between subunits |
front 9 Which of the following best describes protein folding inside a cell? A) Protein folding is driven by primary structure and may be assisted by molecular chaperones B) Protein folding depends only on hydrogen bonding C) Protein folding depends only on side-chain interactions D) Proteins fold randomly until they reach their native structure E) Proteins remain unfolded until they form quaternary structures | back 9 A) Protein folding is driven by primary structure and may be assisted by molecular chaperones |
front 10 Which cleavage reagent could have produced the peptide INWARD as an internal fragment? Note: "Internal" means the last amino acid shown is not the C-terminal amino acid of the full-length polypeptide. | back 10 Staphylococcal Protease at pH 7 |
front 11 What key product results from using Edman's reagent? | back 11 Amino acid-PTH derivative |
front 12 All of the following describe the β-sheet, EXCEPT: A) Amino acid side chains alternate above and below the sheet. B) β sheets have a pleated, edge-on appearance. C) Strands align either in parallel or anti-parallel, within a sheet. D) No exceptions. All of these are true. E) Parallel β sheets contain as few as two strands. | back 12 E) Parallel β sheets contain as few as two strands. |
front 13 What best describes a protein's tertiary structure? | back 13 The overall three-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain |
front 14 All of the following statements describe the amino acid glycine, EXCEPT: A) Its hydrogen sidechain allows it to pack inside a collagen triple helix. B) It is not found in alpha helices or beta sheets. C) It is the only achiral amino acid. D) It has a pI of 5.5. E) Its permissive phi and si bond angles make it more flexible. | back 14 B) It is not found in alpha helices or beta sheets. |
front 15 Which of the following correctly matches a scientist with their contribution? A) Ramachandran: change in free energy accounts for the change in enthalpy and entropy, as a function of temperature. B) Anfinsen: phi-psi dihedrals of structured proteins fall into clusters of secondary structure. C) Bohr: a protein's tertiary structure is directed by its primary structure. D) Levinthal: protein folding must follow a pathway. E) Gibbs: metabolic CO2 stabilizes hemoglobin in the T-state. | back 15 D) Levinthal: protein folding must follow a pathway. |
front 16 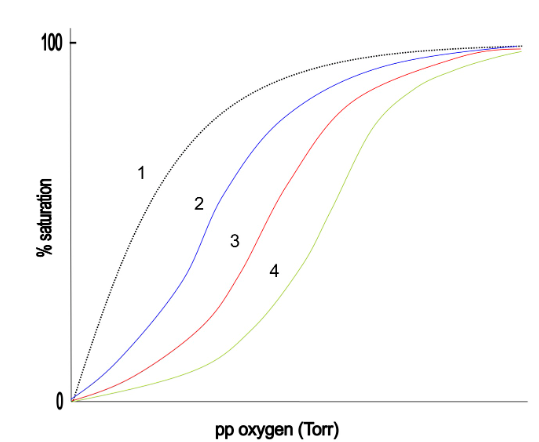 If the red curve (3) is Hb-A, which of the following indicates cooperative oxygen binding by Hb-F, the fetal hemoglobin? | back 16 2 |
front 17 What structural consequence arises from the hydrophobic patch formed by the sickle-cell (Hb-S) mutation? | back 17 Hb-S molecules aggregate into insoluble fibers under low oxygen conditions. |
front 18 How many amino acids make an α-helix 99 Å in length? | back 18 66 |
front 19 What was the key conclusion of Anfinsen’s experiment with ribonuclease A? | back 19 Protein structure is determined by its amino acid sequence |
front 20 Which of the following statements is true about the Bohr effect? A) Hemoglobin binding to oxygen is unaffected by pH B) Hemoglobin binds oxygen more tightly at lower pH C) Hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen increases at higher [H+] D) Myoglobin shows a Bohr effect similar to hemoglobin E) Hemoglobin releases oxygen more efficiently at lower pH | back 20 E) Hemoglobin releases oxygen more efficiently at lower pH |
front 21 What is the overall charge of histidine at pH 1? | back 21 +2 |
front 22 What explains cooperative binding in hemoglobin? | back 22 The binding of one oxygen molecule increases the affinity for additional oxygen molecules. |
front 23 All of the following statements can describe SDS-PAGE, EXCEPT: A) It uses an electrical current. B) It does not involve protein denaturation. C) It is following by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining to visualize the protein bands. D) It is an analytical technique. E) It does not require DTT or β-ME. | back 23 B) It does not involve protein denaturation. |
front 24 Which of the following defines the chirality of naturally occurring amino acids? A) L configuration, based on glyceraldehyde B) D configuration, based on glyceraldehyde C) S configuration, based on glyceraldehyde D) Naturally occurring amino acids are not chiral. E) R configuration, based on glyceraldehyde | back 24 A) L configuration, based on glyceraldehyde |
front 25 Which of the following amino acids can form a disulfide linkage? A) C B) S C)Y D) M E) M and C | back 25 A) C |
front 26 The oxygen-binding curve of myoglobin is | back 26 hyperbolic |
front 27 What are the amino acid side chains that are always charged at physiological pH? | back 27 Glu, Asp, Lys, and Arg |
front 28 What is the pI for the peptide, LATCH? | back 28 7.2 |
front 29 Which amino acid contains a sulfur atom in its side chain? A) Lys B) Try C) Trp D) Ser E)Met | back 29 E) Met |
front 30 Consider the schematic of the heterotrimeric protein below, where the dash, "-" indicates an intermolecular disulfide bond. BO-X What is/are the products of separation by SDS-PAGE, WITHOUT reducing agent? | back 30 B + O-X |
front 31 Which of the following amino acids contains a non-polar, aromatic side chain? A) N B) R C) S D) E E) F | back 31 F |
front 32 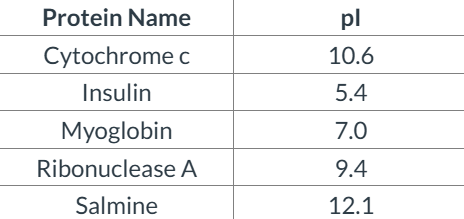 Which of the proteins in this table can be purified BEST by anion-exchange chromatography at pH 7.4? | back 32 Insulin |
front 33 Which statement about protein denaturation is true? A) Denatured proteins lose their primary structure B) Denatured proteins lose their native function C) Denaturation breaks peptide bonds D) Denaturation affects only tertiary and quaternary structures E) Denaturation is another term for hydrolysis | back 33 B) Denatured proteins lose their native function |
front 34 Can two different amino acids with the same side-chain pKa have different net charges, when the solution pH > side-chain pKa ? | back 34 Yes, because one side chain may be neutral when deprotonated, while the other has a negative charge when deprotonated. |
front 35 What type of secondary structure is most prominent in myoglobin? | back 35 α-helices |
front 36 What bond is primarily responsible for the primary structure of a protein? | back 36 peptide bonds |
front 37 The______ sidechain of arginine is______when the solution pH is above its pKa of______. | back 37 guanidino, neutral, 12.5 |
front 38 What is the primary role of myoglobin in muscle tissue? | back 38 Binding and storage of oxygen in muscle cells |
front 39 What mutation is responsible for sickle-cell anemia? | back 39 Valine instead of glutamate in the β subunit of hemoglobin |
front 40 What type of secondary structure is characterized by hydrogen bonds forming between the carbonyl oxygen of one amino acid and the amide hydrogen of another amino acid four residues away? | back 40 α-helix |
front 41 All of the following statements describe the peptide bond, EXCEPT: A) The correct order for atoms in the peptide bond plane is Cα1, CO, NH, Cα2. B) Peptide bonds are formed from a condensation reaction between two amino acids. C) The partial charges of the amide NH and carbonyl O allow for hydrogen bonds within the polypeptide backbone. D) The rigid peptide bond plane allows for no rotation of the side chains. E) The peptide bond stays in a trans configuration due to its partial double-bond character. | back 41 D) The rigid peptide bond plane allows for no rotation of the side chains. |
front 42 Which two amino acids act as helix breakers due to their ϕ and ψ angle flexibility? | back 42 Proline and Glycine |
front 43 Which molecule stabilizes the T state of hemoglobin, reducing its affinity for oxygen? | back 43 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate |
front 44 Which state of hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen? | back 44 R (relaxed) state |
front 45 Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found in a protein’s interior, away from water? A) K B) R C) V D) E E) S | back 45 C) V |
front 46 What is the main characteristic of fibrous proteins? | back 46 Serve structural roles in cells and tissues |
front 47 How does the coiled-coil structure in viral spike proteins facilitate fusion with host cells? | back 47 By undergoing a conformational change that brings viral and host membranes closer |
front 48 Which of the following sequences could be found in α-keratin? A) LMIWAFMVLFIIVILMFWAALIVALW B) GPPGPPGPPGPPGPPGPPGPP C) VSKINRSMKQFHEDVEELKNR D) YSTDQRHDYSTDQRHDYSTDQRHD E) GSGAGSGSGAGAGSGAGSGAGSGA | back 48 C) VSKINRSMKQFHEDVEELKNR |
front 49 In affinity chromatography of a mixture of 3 proteins, the protein with no affinity for the ligand elutes ____, low Kd for the ligand elutes _____, and high Kd for the ligand elutes ____. | back 49 first; last; second |
front 50 Which of the following functional groups is common to all standard amino acids? A) Phosphate B) Sulfhydryl C) Amide D) Carboxyl E) Methyl | back 50 D) Carboxyl |