Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ancient Greek, Roman, and Etruscan Art; AP Art History
front 1 Athenian Agora, Artist/Culture | back 1 Greek |
front 2 Anavysos Kouros, Artist/Culture | back 2 Greek |
front 3 Peplos Kore from the Acropolis, Artist/Culture | back 3 Greek |
front 4 Niobides Krater, Artist/Culture | back 4 Niobid Painter (Greek) |
front 5 Doryphoros (Spear Bearer), Artist/Culture | back 5 Polykleitos (Greek) |
front 6 Acropolis, Artist/Culture | back 6 Iktinos and Kallikrates (Greek) |
front 7 Grave Stele of Hegeso, Artist/Culture | back 7 Kallimachos (Greek) |
front 8 Winged Victory of Samothrace, Artist/Culture | back 8 Greek |
front 9 Great Alter of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon, Artist/Culture | back 9 Greek |
front 10 Seated Boxer, Artist/Culture | back 10 Greek |
front 11 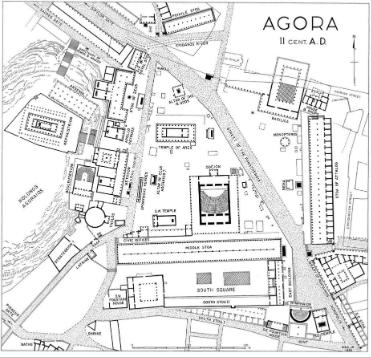 | back 11 Athenian Agora |
front 12  | back 12 Anavysos Kouros |
front 13  | back 13 Peplos Kore from the Acropolis |
front 14  | back 14 Niobides Krater |
front 15  image is of a rendition of the bronze original, not the Roman marble copy | back 15 Doryphoros (Spear Bearer) |
front 16  | back 16 Acropolis |
front 17  | back 17 Parthenon |
front 18  | back 18 Helios, Horses, and Dionysus |
front 19  | back 19 Plaque of the Ergastines |
front 20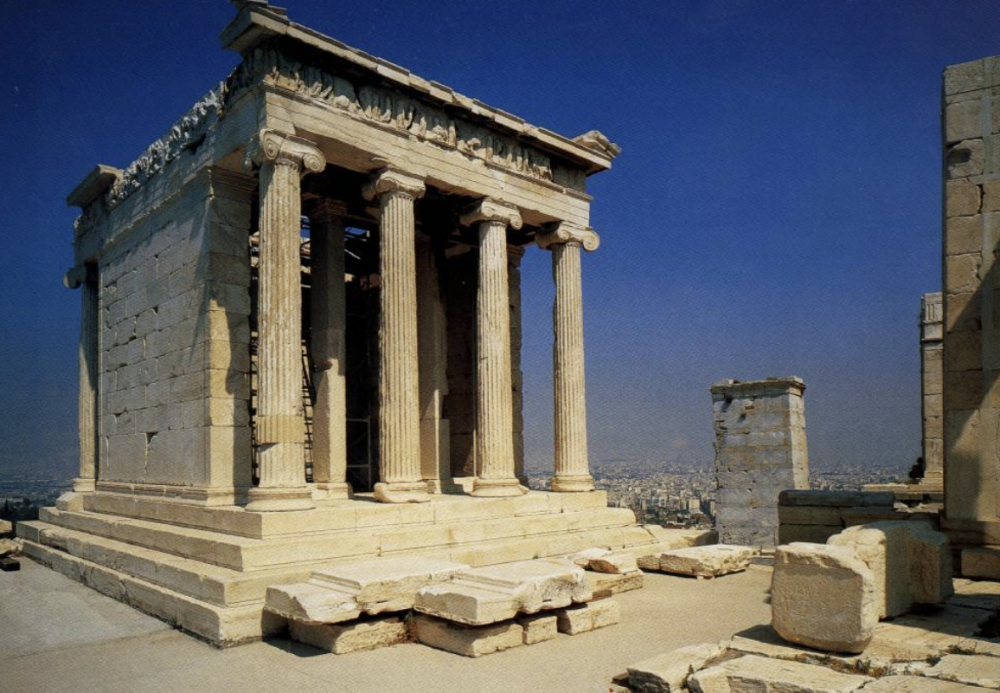  | back 20 Temple of Athena Nike |
front 21  | back 21 Victory (Nike) Adjusting Her Sandal |
front 22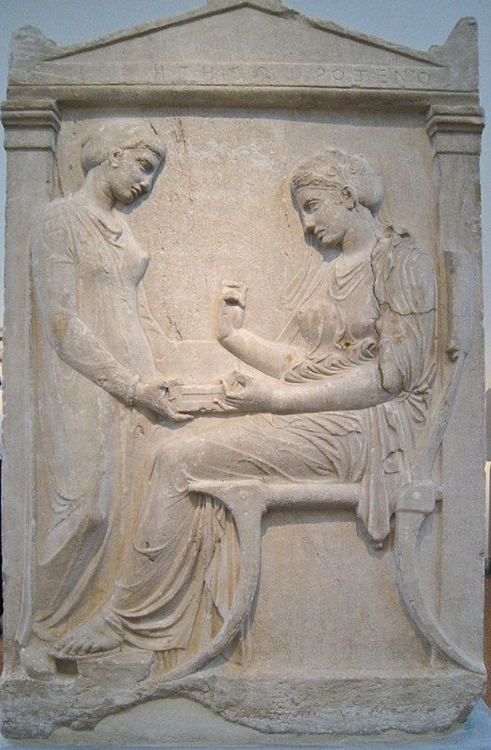  | back 22 Grave Stele of Hegeso |
front 23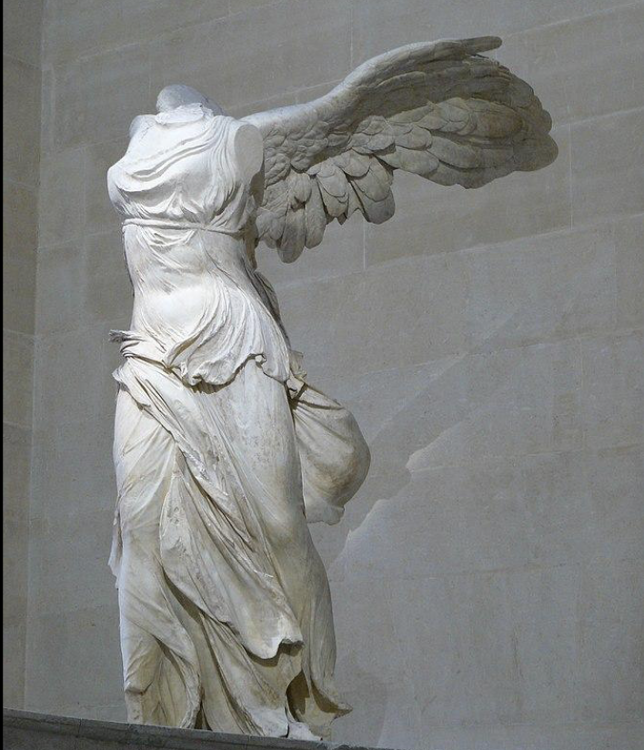  | back 23 Winged Victory of Samothrace |
front 24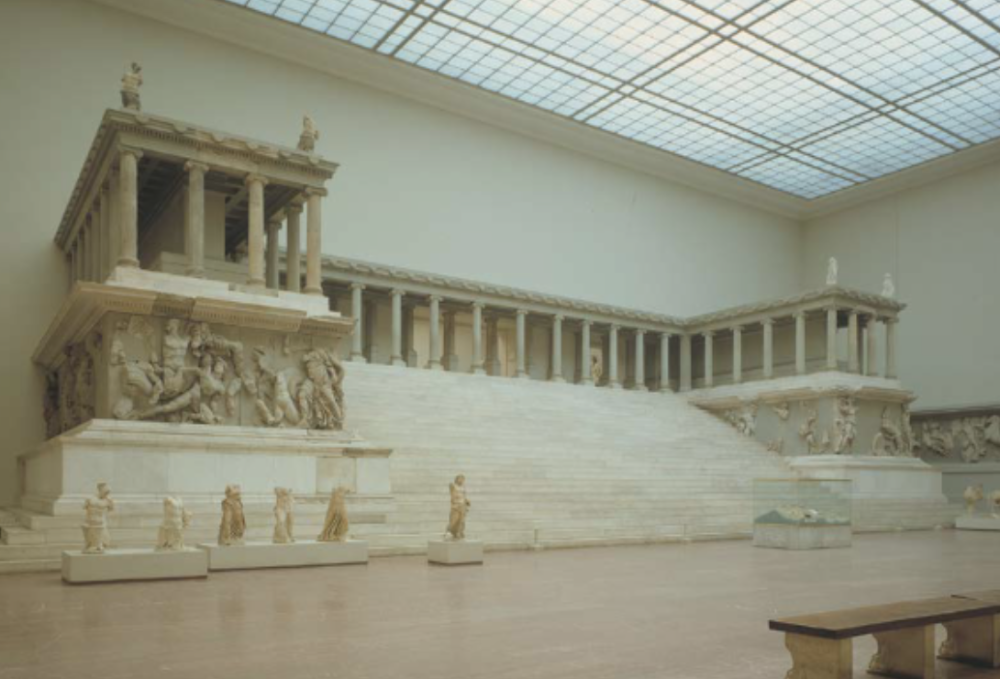  | back 24 Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon |
front 25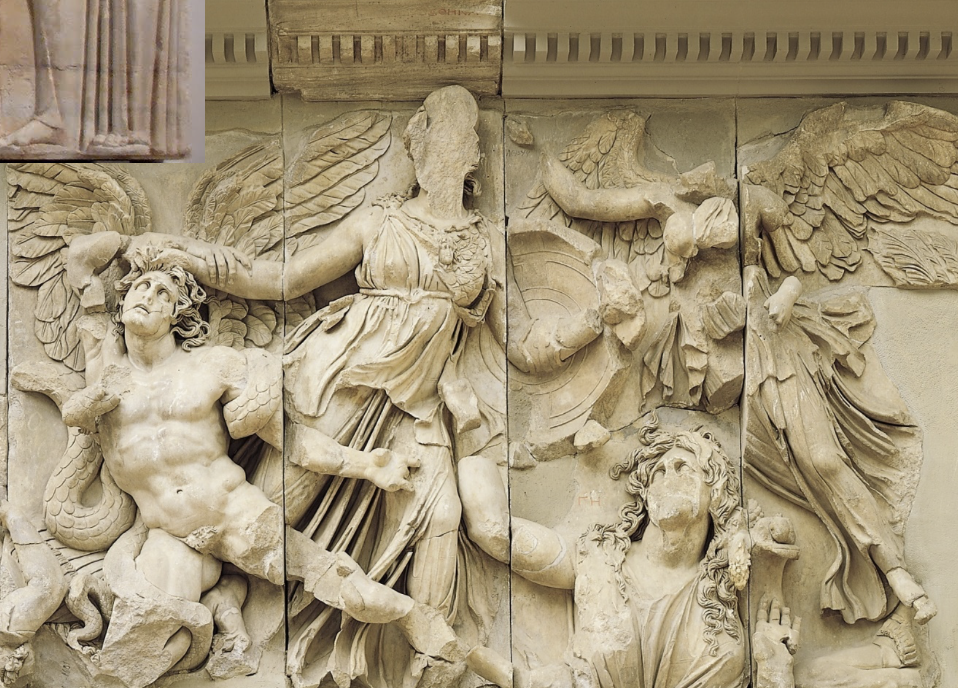  | back 25 Athena Frieze |
front 26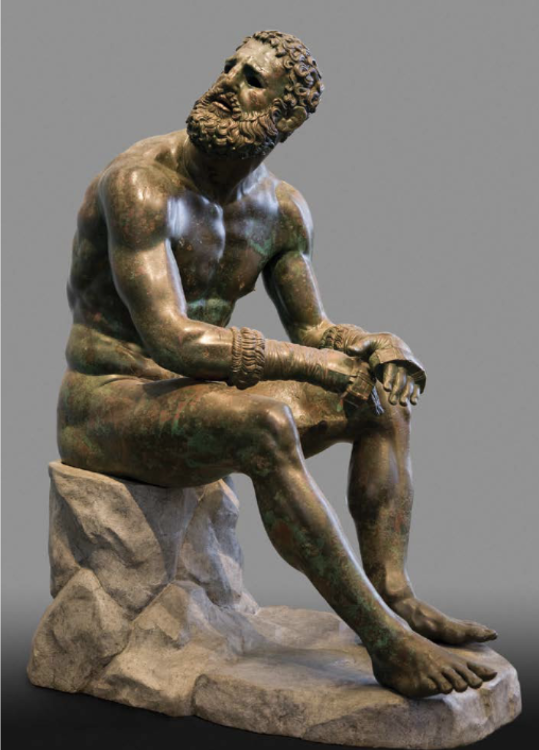  | back 26 Seated Boxer |
front 27 Athenian Agore, Style | back 27 Archaic through Hellenistic |
front 28 Anavysos Kouros, Style | back 28 Archaic |
front 29 Peplos Kore, Style | back 29 Archaic |
front 30 Niobides Krater, Style | back 30 Classical |
front 31 Doryphoros, Style | back 31 Classical |
front 32 Acropolis, Style | back 32 Classical |
front 33 Grave Stele of Hegeso, Style | back 33 Classical |
front 34 Winged Victory of Samothrace, Style | back 34 Hellenistic |
front 35 Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon, Style | back 35 Hellenistic |
front 36 Seated Boxer, Style | back 36 Hellenistic |
front 37 Athenian Agora, Medium | back 37 Plan |
front 38 Anavysos Kouros, Medium | back 38 Marble and Paint |
front 39 Peplos Kore, Medium | back 39 Marble and Paint |
front 40 Niobides Krater, Medium | back 40 Clay, red-figure technique with white highlights |
front 41 Doryphoros, Medium | back 41 Roman Marble Copy of Greek Bronze Original |
front 42 Acropolis, Medium | back 42 Marble |
front 43 Grave Stele of Hegeso, Medium | back 43 Marble and paint |
front 44 Winged Victory of Samothrace, Medium | back 44 Marble |
front 45 Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon, Medium | back 45 Marble |
front 46 Seated Boxer, Medium | back 46 Bronze |
front 47 Athenian Agora, Location | back 47 Athens, Greece |
front 48 Peplos Kore, Location | back 48 Acropolis, Athens, Greece |
front 49 Acropolis, Location | back 49 Athens, Greece |
front 50 Great Altar of Zeus and Athena, Location | back 50 Pergamon, Turkey |
front 51 Acropolis | back 51 Greek, "high city," means a rugged, raised rock; site of the city's most important temple(s) |
front 52 Acroterion | back 52 acroteria (pl); sculpture in the round placed on a roof |
front 53 Agora | back 53 an open square or space used for public meetings or business in Ancient Greece |
front 54 Amphiprostyle | back 54 having four columns both in the front and rear of a temple |
front 55 Black-figure | back 55 silhouetting of dark figures against a light background of natural, reddish clay, with linear details incised through the silhouettes |
front 56 Cella | back 56 the main shrine room of a temple where a cult statue is housed |
front 57 Contraposto | back 57 a graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips and bent knees |
front 58 encaustic | back 58 paint made of pigment mixed with wax |
front 59 entablature | back 59 lintel above the columns; contains the architrave and the frieze |
front 60 entasis | back 60 slight bulging or curve in the shaft of a column to correct the visual illusion of concavity |
front 61 fluted shaft | back 61 shallow vertical grooves running along the long, narrow cylinder that comprises the majority of the column |
front 62 frieze | back 62 a broad horizontal band of decoration and/or sculpture on architecture |
front 63 gigantomachy | back 63 battle between gods and giants in Greek mythology |
front 64 Isocephalism | back 64 tradition of depicting heads of figures on the same level; implies a single ground line |
front 65 kiln | back 65 an oven used for making pottery |
front 66 kouros (m) / kore (f) | back 66 an archaic Greek sculpture of an idealized standing youth |
front 67 krater | back 67 a large Ancient Greek bowl used for mixing water and wine |
front 68 lost-wax casting | back 68 a sculpture that is carved out of clay and dipped in wax; the sculpture is put into a clay casting and heated so that the wax will drip out of a hole at the bottom; as a result, space is left between the clay casting and the clay interior; molten metal is then poured into this space; after cooling, the case is cracked so that the now-metal sculpture can be released |
front 69 metopes | back 69 space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze; often decorated with low relief carving |
front 70 order | back 70 a style represented by a characteristic design of the columns and entablature |
front 71 panathenaic way | back 71 a ceremonial road for a procession built to honor Athena |
front 72 parapet | back 72 low protective wall or barrier |
front 73 parthenos | back 73 virgin; often used to refer to Athena as Athena Parthenosq |
front 74 pediment | back 74 the triangular top of a classical building; typically on top of an entablature and a portico |
front 75 peplos | back 75 a garment worn by women in Ancient Greece, usually full length and tied at the waist |
front 76 peristyle | back 76 colonnade around the perimeter of the building |
front 77 red-figure | back 77 in later Greek pottery, the silhouetting of red figures against a black background, with painted linear details; the reverse of black-figure painting |
front 78 stoa | back 78 covered walkway attached to a building; used as a framing device for the structure |
front 79 stylobate | back 79 the floor of a temple |
front 80 triglyph | back 80 part of a Doric entablature frieze; has three vertical grooves |
front 81 wet drapery | back 81 deeply incised drapery that is clingy and tight so that it reveals the shape of the body |
front 82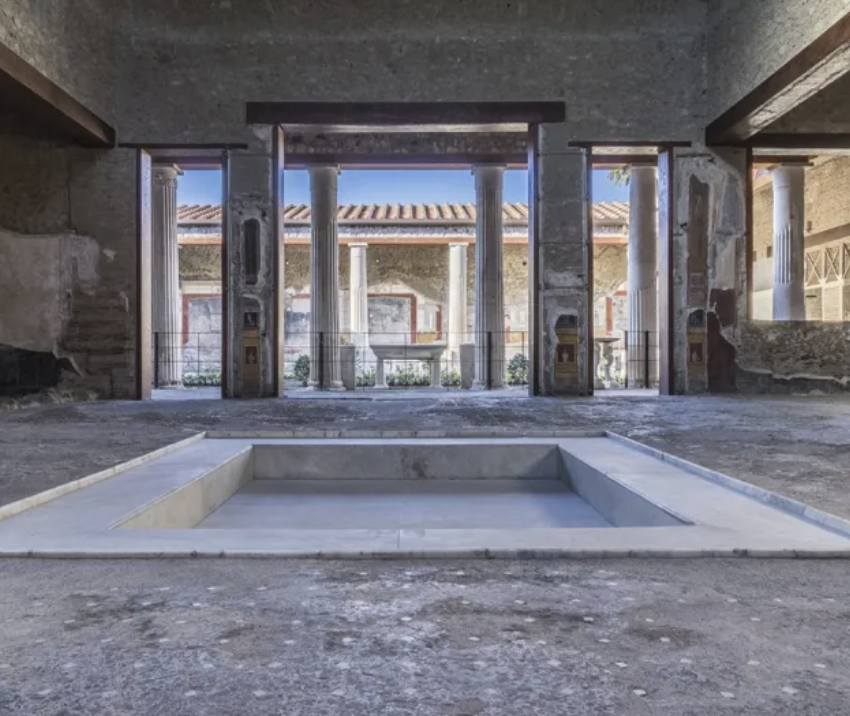  | back 82 House of the Vettii |
front 83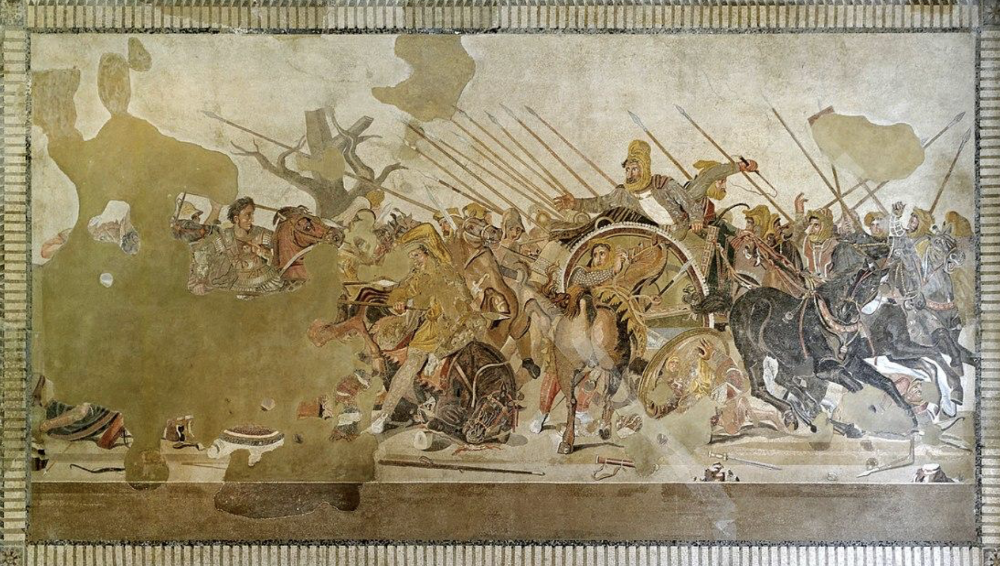  | back 83 Alexander Mosaic |
front 84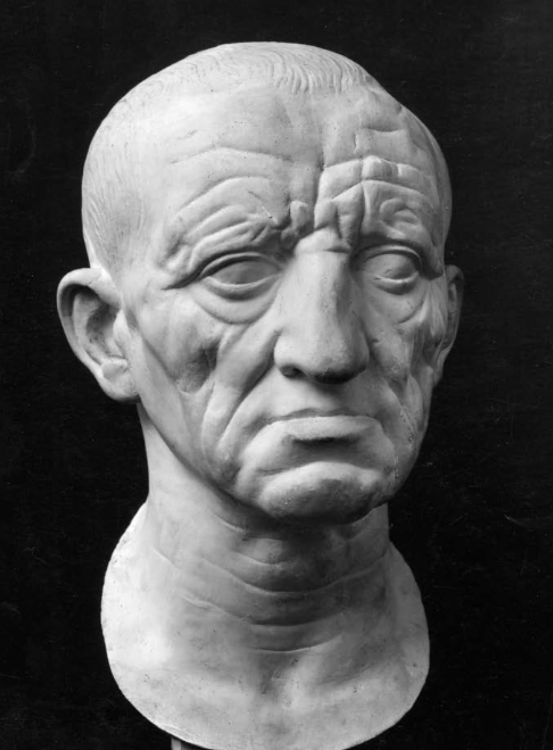  | back 84 Head of a Roman Patrician |
front 85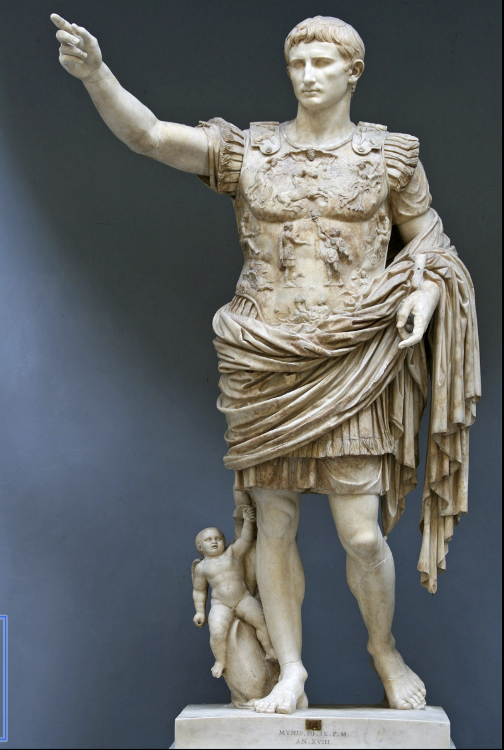  | back 85 Augustus of Prima Porta |
front 86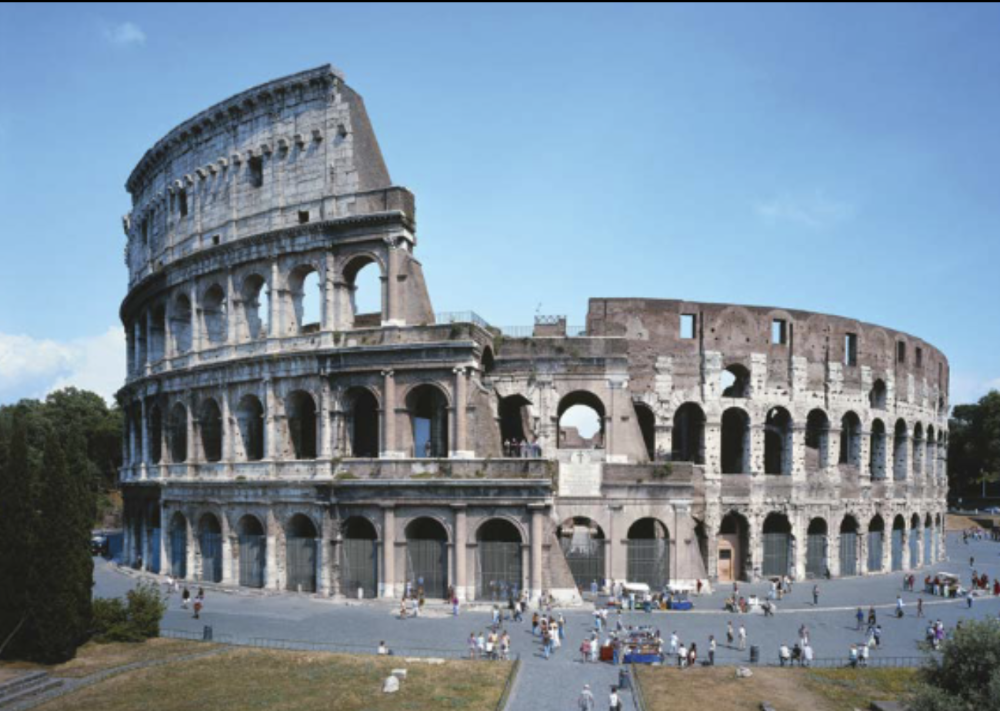  | back 86 Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater) |
front 87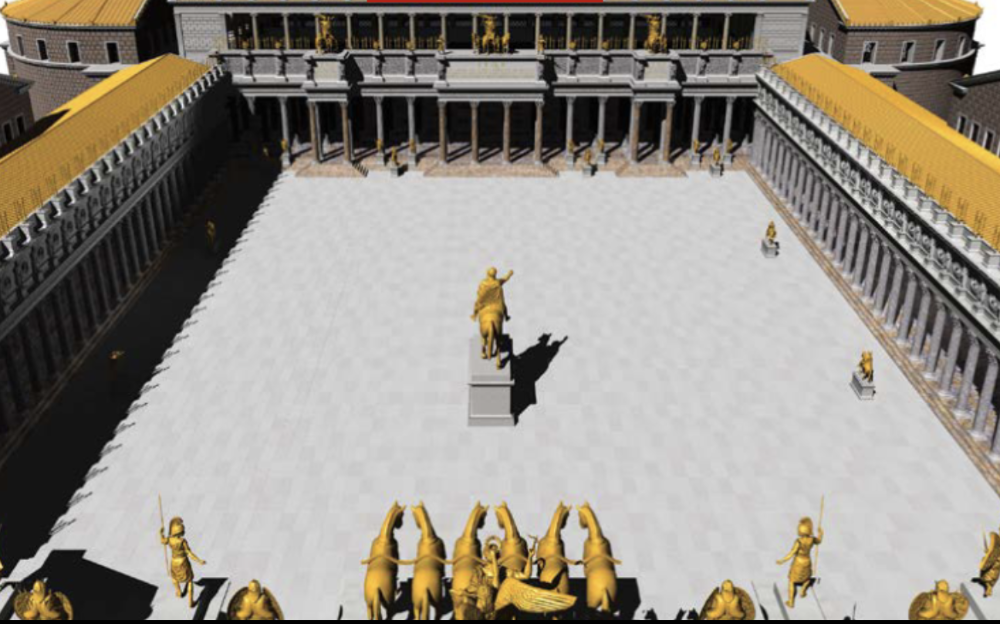  | back 87 Forum of Trajan |
front 88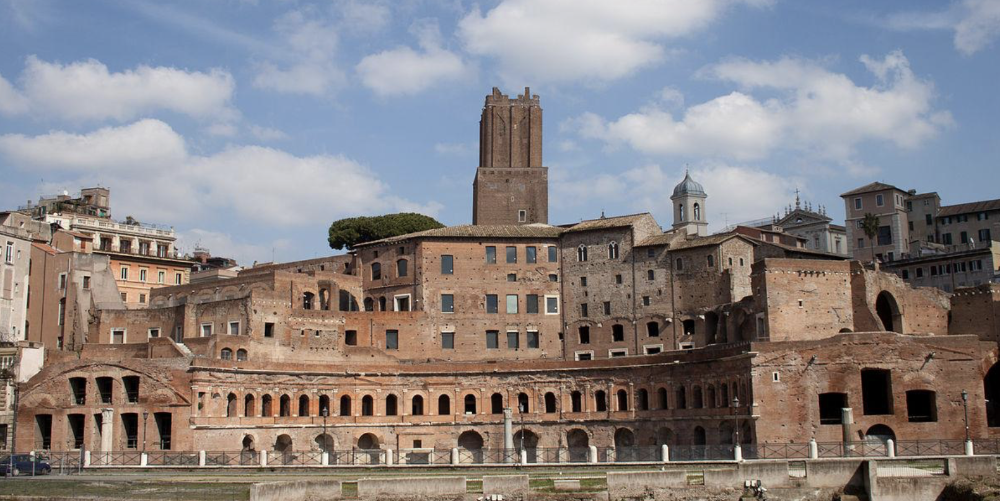  | back 88 Trajan Markets |
front 89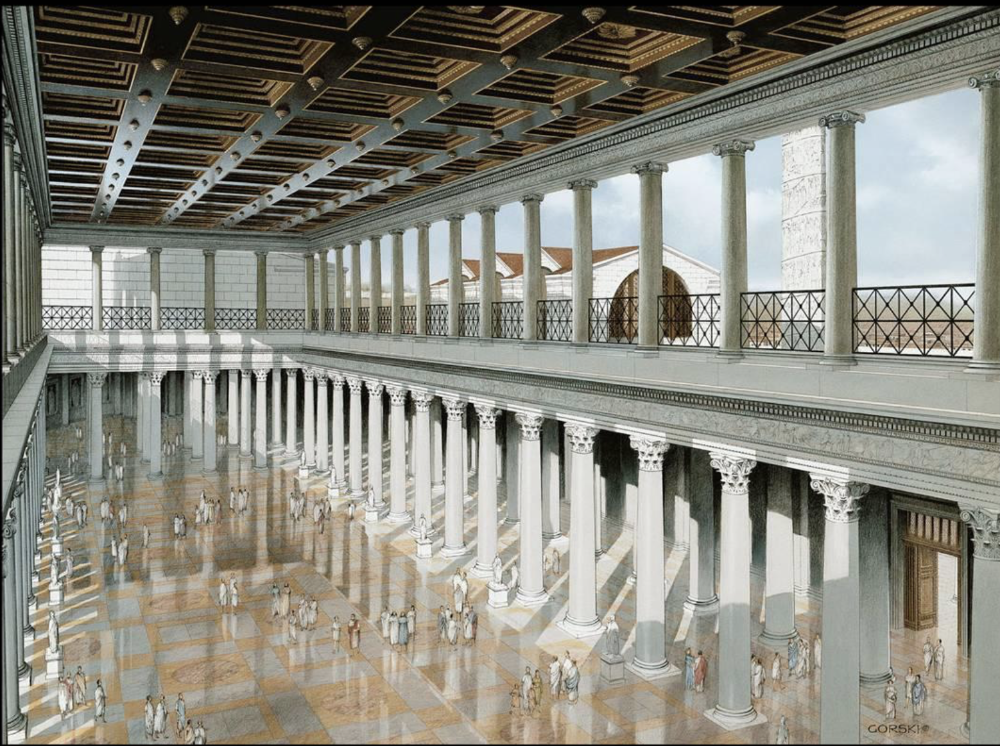  | back 89 Basilica Ulpia |
front 90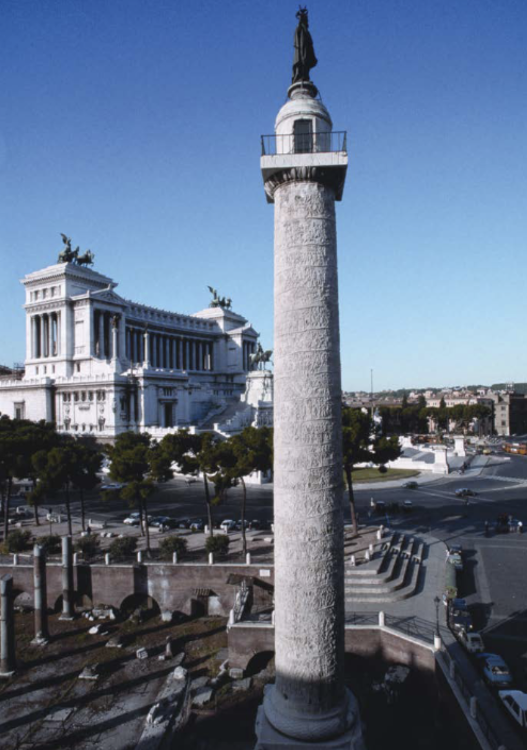  | back 90 Column of Trajan |
front 91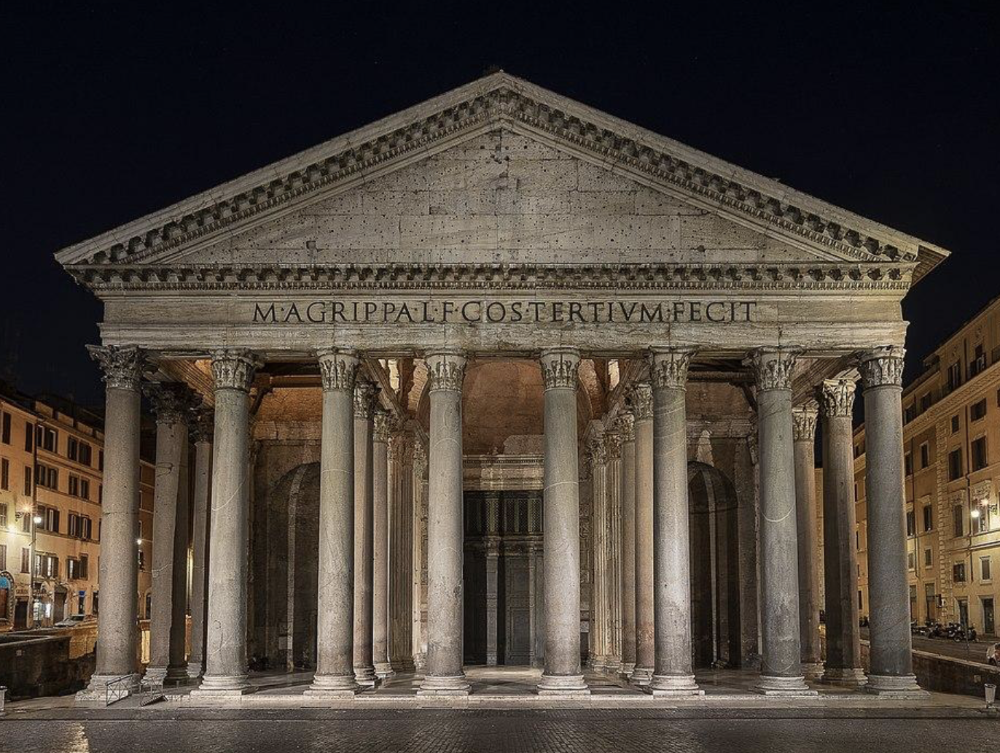  | back 91 Pantheon |
front 92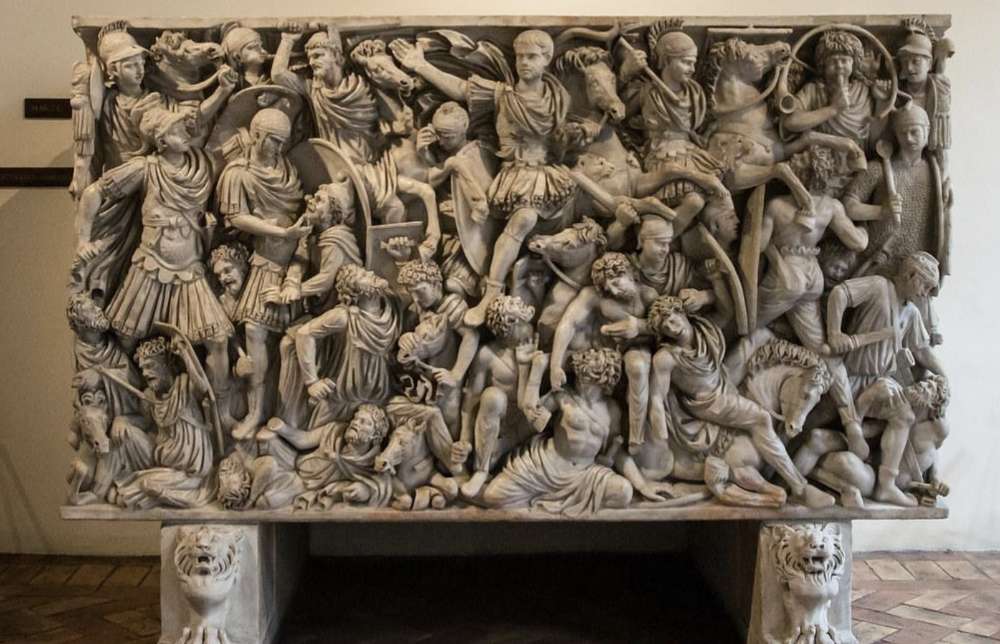  | back 92 Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus |
front 93 House of the Vettii, Artist/Culture | back 93 Roman |
front 94 Alexander Mosaic, Artist/Culture | back 94 Roman |
front 95 Head of a Roman Patrician, Artist/Culture | back 95 Roman |
front 96 Augustus of Prima Porta, Artist/Culture | back 96 Roman |
front 97 Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater), Artist/Culture | back 97 Roman |
front 98 Forum of Trajan, Artist/Culture | back 98 Apollodorus of Damascus |
front 99 Pantheon, Artist/Culture | back 99 Roman |
front 100 Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus, Artist/Culture | back 100 Roman |
front 101 House of the Vettii, Style | back 101 Early Empire |
front 102 Alexander Mosaic, Style | back 102 Republic |
front 103 Head of a Roman Patrician, Style | back 103 Republic |
front 104 Augustus of Prima Porta, Style | back 104 Early Empire |
front 105 Forum of Trajan, Style | back 105 High Empire |
front 106 Pantheon, Style | back 106 High Empire |
front 107 Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus, Style | back 107 Late Empire |
front 108 House of the Vettii, Medium | back 108 Cut stone and fresco |
front 109 Alexander Mosaic, Medium | back 109 Mosaic |
front 110 Head of a Roman Patrician, Medium | back 110 Marble |
front 111 Colosseum, Medium | back 111 Stone and Concrete |
front 112 Forum of Trajan, Medium | back 112 Brick and Concrete (architecture); marble (columns) |
front 113 Pantheon, Medium | back 113 concrete with stone facing |
front 114 Ludovisi Battle Sarchophagus, Medium | back 114 Marble |
front 115 House of the Vettii, Location | back 115 Pompeii, Italy |
front 116 Alexander Mosaic, Location | back 116 House of Faun, Pompeii |
front 117 Colosseum, Location | back 117 Rome, Italy |
front 118 Forum of Trajan, Location | back 118 Rome, Italy |
front 119 Pantheon, Location | back 119 Rome, Italy |
front 120 apse | back 120 the semicircular rounded end of a basilica OR the endpoint of a church where the altar is located |
front 121 arcade | back 121 an open-air courtyard in a Roman house or forum |
front 122 Basilica | back 122 in Roman and Christian architecture, an axially planned building with a long nave, side aisles, and apses (in Christian architecture, this is where the altar is placed) |
front 123 bust | back 123 a sculpture depicting a head, neck, and upper chest of a figure |
front 124 clerestory | back 124 the top of a church nave that is windowed and lets in light |
front 125 coffer | back 125 in architecture, a sunken panel in a ceiling to lighten the weight of the ceiling |
front 126 cubicula | back 126 small underground rooms in catacombs serving as mortuary chapels OR a roman bedroom flanking an atrium |
front 127 cupola/dome | back 127 a rounded, circular roof; achieved by rotating an arch on its axis 180 degrees |
front 128 engaged column | back 128 a column that is still attached to a wall |
front 129 foreshortening | back 129 a visual effect in which an object is shortened and turned deeper into the picture plane to give the effect of receding in space |
front 130 forum | back 130 a public square with market place in a Roman city |
front 131 fresco | back 131 a painting technique that involves applying paint onto a freshly plastered wall; the paint forms a bond with the plaster and becomes durable and long-lasting |
front 132 impluvium | back 132 a rectangular basin in a Roman house that is placed in the open-air atrium in order to collect rain water |
front 133 keystone | back 133 the center stone of an arch that holds the others in place |
front 134 mosaic | back 134 a decoration using pieces of stone, marble, or colored glass, called tesserae, that are cemented to a wall or floor |
front 135 nave | back 135 the main aisle of a church |
front 136 oculus | back 136 a round opening at the top of a dome |
front 137 peristyle | back 137 an atrium surrounded by columns in a Roman house |
front 138 perspective | back 138 depth and recession in a painting |
front 139 linear perspective | back 139 a mathematical system for creating the illusion of space and distance on a flat surface |
front 140 orthogonals | back 140 straight lines emanating from the vanishing point |
front 141 horizon line | back 141 the physical line at which sky meets land; this will be wherever the vanishing point is |
front 142 vanishing point | back 142 a point in the picture plane that is the intersection of orthogonals |
front 143 atmospheric/aerial perspective | back 143 the effect the atmosphere has on the appearance of an object as it is viewed from a distance (contrast decreases; colors become less saturated) |
front 144 portrait bust | back 144 a sculptured representation of the upper part of the human figure including the head and neck and usually part of the shoulders and breast |
front 145 taberna | back 145 single-room shops covered by a wide doorway |
front 146 tesserae | back 146 small pieces of colored stone or marble; used to create a mosaic |
front 147 vault | back 147 a ceiling constructed with arches |
front 148 barrel vault | back 148 an arch extended into space horizontally that is curved at the top |
front 149 groin vault | back 149 two intersecting barrel vaults |
front 150 veristic | back 150 sculptures from the Roman Republic characterized by extreme realism (and even exaggeration) of facial features |
front 151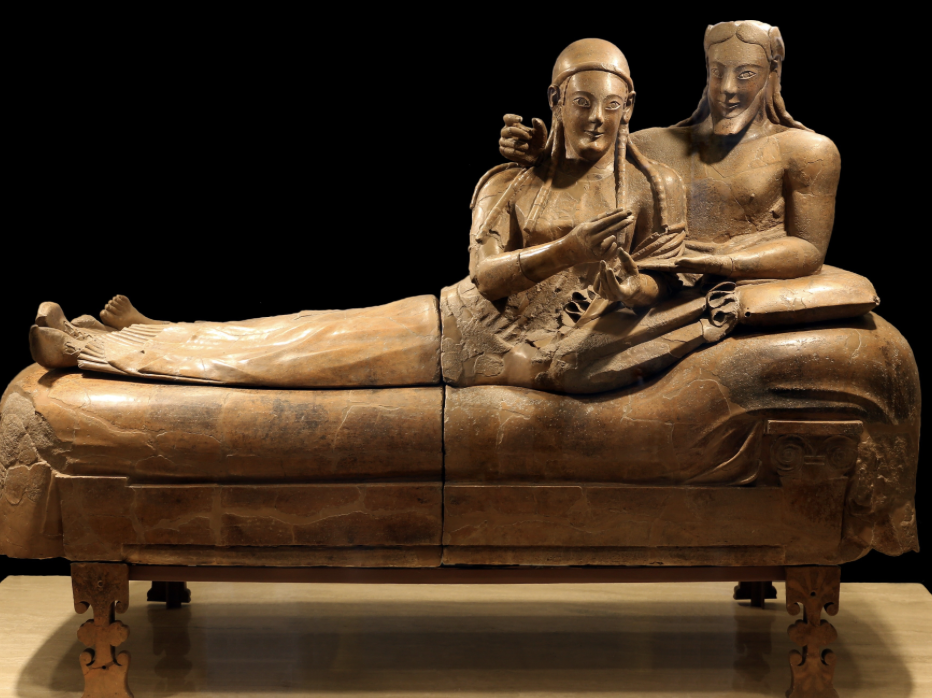  | back 151 Sarcophagus of the Spouses |
front 152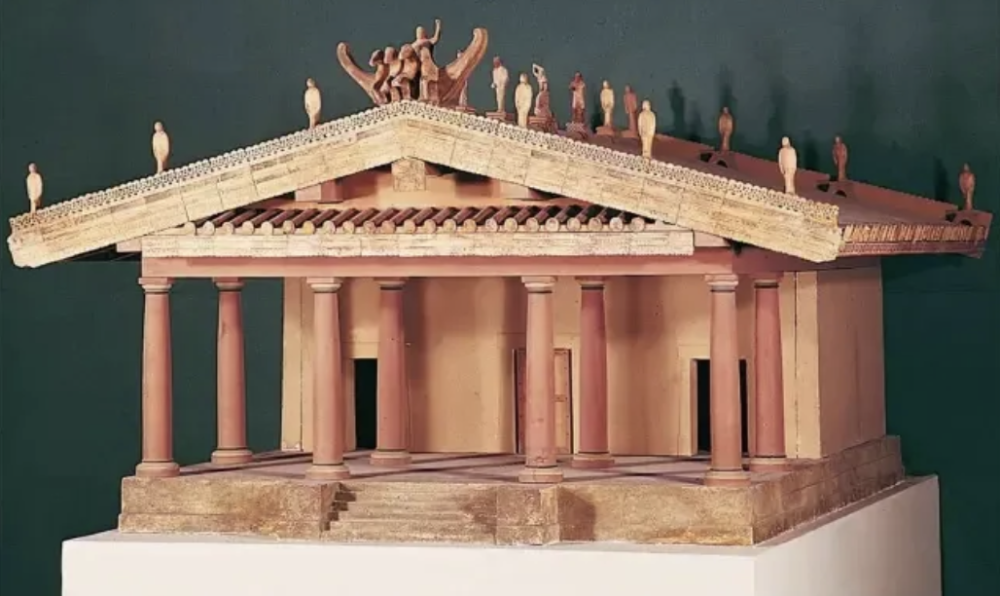  | back 152 Temple of Minerva |
front 153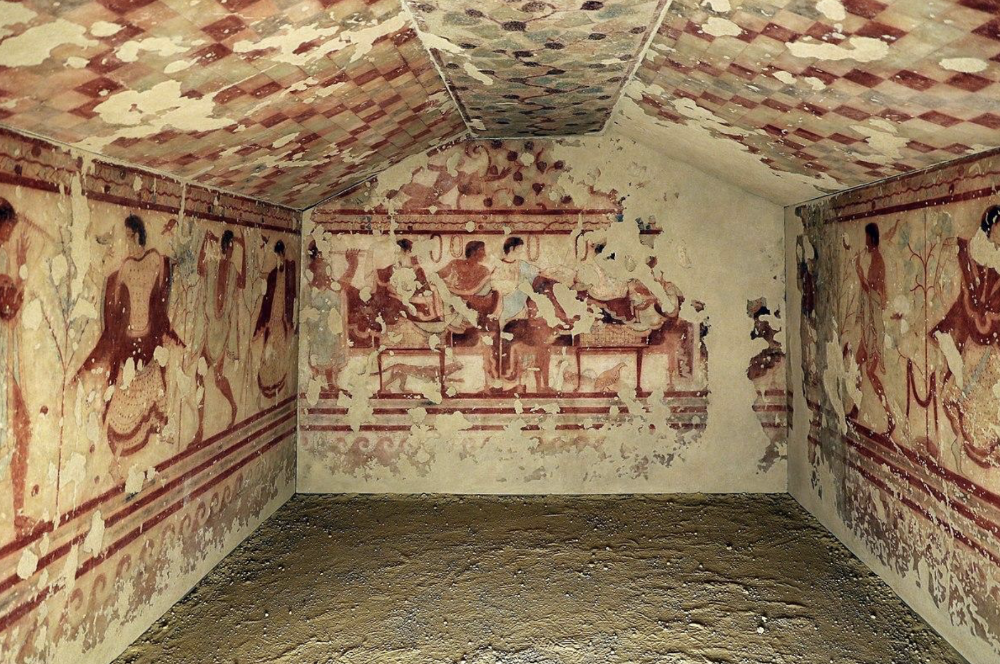  | back 153 Tomb of the Triclinium |
front 154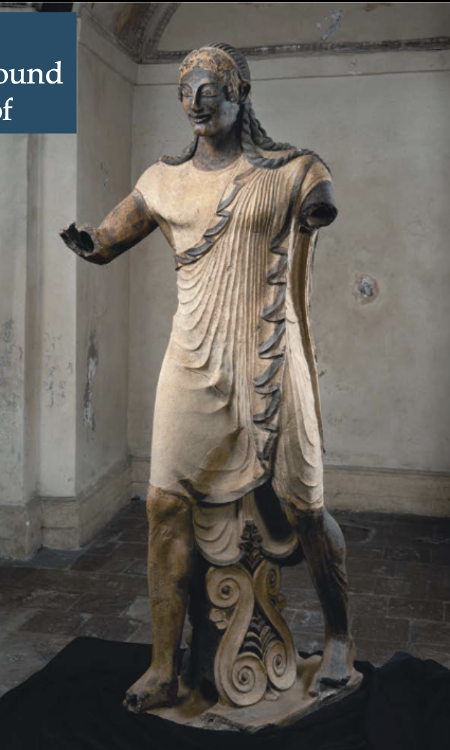  | back 154 Sculpture of Apollo |
front 155 Sarcophagus of the Spouses, Artist/Culture | back 155 Etruscan |
front 156 Temple of Minerva and Sculpture of Apollo, Artist/Culture | back 156 Master Sculptor Vulca |
front 157 Tomb of the Triclinium, Artist/Culture | back 157 Etruscan |
front 158 Sarcophagus of the Spouses, Medium | back 158 Terra Cotta |
front 159 Temple of Minerva and Sculpture of Apollo, Medium | back 159 original temple of wood, mud brick, and tufa (volcanic rock); terra cotta sculpture |
front 160 Tomb of the Triclinium, Medium | back 160 tufa and fresco |
front 161 Temple of Minerva and Sculpture of Apollo, Location | back 161 Veli, Italy |
front 162 Tomb of the Triclinium, Location | back 162 Tarquinia, Italy |
front 163 acroterion | back 163 sculptures in the round placed on the roof |
front 164 necropolis | back 164 literally a "city of the dead," large burial area |
front 165 fresco | back 165 a painting technique that involves applying paint onto a freshly plastered wall; the paint forms a bond with the plaster and becomes durable and long-lasting |
front 166 tufa | back 166 a type of limestone |
front 167 tumulus | back 167 burial mounds in Etruscan architecture, tumuli covered one or more subterranean multi-chambered tombs cut out of the local tufa |
front 168 triclinium | back 168 a dining table in ancient Italy that has a couch on three sides for reclining at meals |
front 169 tuscan | back 169 an order of ancient architecture featuring slender, smooth wooden columns that sit on simple bases; no carvings on frieze or capitals |