Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 8 general biology
front 1 The splitting of molecules into smaller components is referred to as: | back 1 Catabolism. |
front 2 Which of the following statements concerning anabolic reactions is FALSE? | back 2 They may split complex molecules into their components. |
front 3 Aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, and fermentation: | back 3 release free energy. |
front 4 Cellular respiration is most accurately described as a(n) __________ process. | back 4 catabolic. |
front 5 Select the anaerobic pathway. | back 5 fermentation |
front 6 The overall reaction for the aerobic respiration of glucose is summarized as: | back 6 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + Energy. |
front 7 In aerobic respiration, glucose is completely: | back 7 oxidized to carbon dioxide. |
front 8 Aerobic respiration is classified as: | back 8 a redox process. |
front 9 The transfer of electrons from glucose to oxygen during aerobic respiration takes place in a stepwise fashion through a number of intermediates rather than by direct transfer. This is because: | back 9 the energy of the electrons can be used to make ATP. |
front 10 In aerobic respiration, the electrons associated with the hydrogen atoms in glucose are ultimately transferred to: | back 10 oxygen in a series of steps. |
front 11 Which of the following is not one of the four stages of the aerobic respiration of glucose? | back 11 hydrolysis |
front 12 If conditions are aerobic, pyruvate flows directly into the __________ where some of its atoms are converted next to __________. | back 12 mitochondia; acetyl coenzyme A |
front 13 Which of the following is an end product of glycolysis? | back 13 ATP |
front 14 Which process does not match the location in a typical eukaryotic cell? | back 14 glycolysis-mitochondrion |
front 15 glycolysis-mitochondrion | back 15 cytosol. |
front 16 During chemiosmosis, __________ are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to electron acceptor molecules, and the energy released is used to create a(n) __________ gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. | back 16 electrons; proton |
front 17 Which of the following statements concerning decarboxylation reactions is FALSE? | back 17 They involve the removal of two protons and two electrons. |
front 18 In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is converted to two three-carbon molecules of: | back 18 pyruvate. |
front 19 Glycolysis yields a net energy profit of __________ ATP molecules per molecule of glucose. | back 19 2 |
front 20 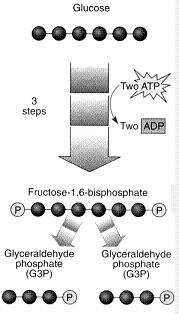 The chemical reaction illustrated in the figure is: | back 20 the energy investing phase of glycolysis. |
front 21 Considering only glycolysis and the conversion of pyruvate molecules to acetyl CoA molecules, how many NADH molecules will be produced from one glucose molecule | back 21 Four |
front 22 One product of the initial (first) reaction of the citric acid cycle is: | back 22 Citrate. |
front 23 During the citric acid cycle, each acetyl group entering the cycle yields: | back 23 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 |
front 24 In the citric acid cycle, two acetyl CoA molecules are metabolized to: | back 24 4 CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP. |
front 25 A glucose molecule that is metabolized via aerobic respiration has been completely broken down and released as CO2 by the end of: | back 25 the citric acid cycle. |
front 26 In the electron transport chain, exergonic redox processes drive the endergonic reaction in which: | back 26 ATP is produced by phosphorylation of ADP |
front 27 Coenzyme Q: | back 27 Transfers electrons. |
front 28 The role of the oxygen molecules required for aerobic respiration is | back 28 to accept the low energy electrons at the end of the electron transport chain. |
front 29 During aerobic respiration, oxygen is | back 29 Reduced |
front 30 A drowning death would be most directly due to: | back 30 The lack of oxygen to accept hydrogen |
front 31 Organismal body heat is a: | back 31 byproduct of exergonic reactions |
front 32 Peter Mitchell demonstrated ATP production by aerobic bacteria by placing the bacteria in: | back 32 an acidic environment. |
front 33 Which of the following statements about the electron transport chain is true? | back 33 The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy |
front 34 When hydrogen ions (protons) are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane, they form a proton gradient. ATP is then formed by a process known as: | back 34 Chemiosmosis |
front 35 In chemiosmosis, ATP is produced as hydrogen ions (protons) pass through: | back 35 ATP synthase. |
front 36 Select the processes that are matched with the incorrect amount of ATP produced by that process per glucose molecule. | back 36 citric acid cycle-4 ATP |
front 37 When one molecule of glucose is completely oxidized in aerobic respiration, the net amount of ATP produced is: | back 37 36 to 38 |
front 38 In the skeletal muscle cells of vertebrates, as many as __________ molecules of ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose. This is less than might be expected, because electrons from NADH produced during glycolysis must be shuttled through the ____________ membrane at a cost. | back 38 36; mitochondrial |
front 39 One important regulation point in the aerobic respiration of mammals occurs in glycolysis at the site of the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which is: | back 39 inhibited by high levels of ATP. |
front 40 Deamination of amino acids in mammals yields amino groups that are converted to __________, which is(are) excreted, and __________, which is(are) converted to one of the reactants of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. | back 40 urea; carbon chains |
front 41 One gram of __________ contains more than twice the amount of energy of a gram of glucose. | back 41 Lipids |
front 42 Which of the following molecules can provide energy through cellular respiration? | back 42 glucose, lipids and proteins |
front 43 Saturated fatty acids store more energy than unsaturated fatty acids. Based on your knowledge of aerobic respiration, you draw this conclusion because saturated fatty acids: | back 43 Are more highly reduced |
front 44 Anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration in that anaerobic respiration: | back 44 can utilize NO3 - as the terminal electron acceptor. |
front 45 The production of alcohol or lactate from pyruvate during __________ occurs as a means of regenerating __________ from __________. | back 45 fermentation; NAD+; NADH |
front 46 During fermentation, the immediate fate of the electrons in NADH is that they: | back 46 are transferred to an organic molecule. |
front 47 Select the molecule that contains the most stored chemical energy: | back 47 lactate. |
front 48 Select the molecule that contains the least stored chemical energy: | back 48 Oxygen |
front 49 The ability of some bacteria to produce lactate is exploited by humans to make: | back 49 yogurt and sauerkraut. |
front 50 Which of the following statements is not correct about lactic acid fermentation? | back 50 Oxygen is the final electron acceptor of this pathway. |