Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 7 General biology
front 1 Most components of energy conversion systems evolved very early; thus, the most fundamental aspects of energy metabolism tend to be: | back 1 very similar in a wide range of different organisms. |
front 2 The ultimate source of energy for almost all living organisms is: | back 2 the sun. |
front 3 Kilojoules are: | back 3 units of work. |
front 4 The life and death of cells are governed by: | back 4 the laws of thermodynamics. |
front 5 An organism can exchange matter and energy with its surroundings. Thus, any change in an organism's energy content must be balanced by a corresponding change in the energy content of the surroundings. As such, an organism is referred to as: | back 5 an open system. |
front 6 Which of the following statements is contrary to the first law of thermodynamics? | back 6 When gasoline is burned, its energy is destroyed. |
front 7 Which word is defined by this statement: A measure of this disorder, or randomness? | back 7 entropy |
front 8 In order for a cell to maintain a high degree of order, it must: | back 8 constantly use energy. |
front 9 The sum of all chemical activities taking place in an organism is: | back 9 metabolism. |
front 10 Which of the following accurately represents the relationship between the terms anabolism, catabolism, and metabolism? | back 10 metabolism = catabolism + anabolism |
front 11 Catabolic reactions involve the: | back 11 breakdown of large organic molecules to simple building blocks. |
front 12 Pathways that have an overall energy requirement are referred to as: | back 12 anabolic reactions. |
front 13 Every type of chemical bond contains a certain amount of energy. The total bond energy, which is essentially equivalent to the total potential energy of the system, is a quantity known as: | back 13 enthalpy. |
front 14 An exergonic reaction is considered to be: | back 14 spontaneous. |
front 15 Which of the following statements is true of spontaneous reactions? | back 15 The amount of free energy after the reaction is less than before the reaction. |
front 16 When the free energy of the reactants is greater than the free energy of the products, such a reaction is referred to as: | back 16 an exergonic reaction. |
front 17 In a reaction in which the rate of the reverse reaction is equal to the rate of the forward reaction, a state of __________ is attained. | back 17 dynamic equilibrium |
front 18 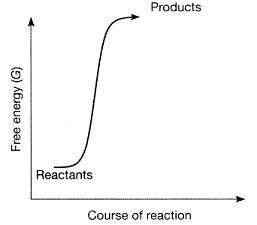 Figure 7-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Which of the following statements about Figure 7-1 is true? | back 18 The reaction is endergonic, and also the products have more free energy than the reactants. |
front 19  Figure 7-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).Which of the following conclusions can be accurately derived from the Figure 7-1? | back 19 ΔG is positive. |
front 20 Energy stored within the molecules of ATP is in the form of __________ energy. | back 20 potential |
front 21 Consider the following two chemical equations:
The free energy change difference between the chemical equations (A) and (B) above is accomplished by: | back 21 combining an endergonic and an exergonic reaction. |
front 22 Which of the following statements concerning ATP is FALSE? | back 22 It stores energy for long periods. |
front 23 The reaction ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi is classified as an: | back 23 exergonic reaction. |
front 24 Select the compound that contains the most energy: | back 24 ATP |
front 25 Select the phosphorylation reaction: | back 25 glucose + ATP → glucose-P + ADP |
front 26 The maintenance of a high ATP to ADP ratio within cells ensures that: | back 26 the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP will be strongly exergonic. |
front 27 The transfer of electrons from one compound to another is equivalent to __________ transfer. | back 27 energy |
front 28 __________ is a process where energy (as electrons) is released, whereas __________ is a process where energy (as electrons) is accepted. | back 28 Oxidation; reduction |
front 29 XH2 + NAD+ → X + NADH + H+. In the preceding equation, NAD+ is said to be in a ____________ state and NADH is in a __________ state. | back 29 oxidized; reduced |
front 30 Select the reduced molecule: | back 30 NADH |
front 31 Select the hydrogen acceptor molecule that stores electrons in the process of photosynthesis: | back 31 nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) |
front 32 FAD and cytochromes are classified as: | back 32 hydrogen or electron acceptors. |
front 33 Because enzymes affect the speed of chemical reactions without being consumed, they are referred to as: | back 33 catalysts |
front 34 Which of the following statements concerning enzymes is FALSE? | back 34 Most enzymes are RNA molecules. |
front 35 Enzymes are important biological catalysts because they: | back 35 lower the activation energy of a biochemical reaction. |
front 36 Which of the following statements concerning activation energy is FALSE? | back 36 Catalysts raise a reaction's activation energy. |
front 37 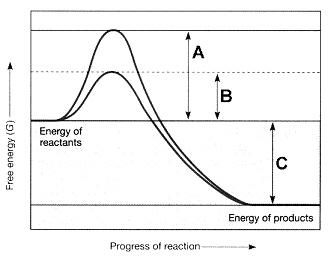 Figure 7-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 7-2. The line on the graph labeled B represents the: | back 37 activation energy with an enzyme. |
front 38  Figure 7-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 7-2. The line on the graph labeled C represents the: | back 38 change in free energy. |
front 39 Parts of the enzyme molecule that interact with a substrate are called: | back 39 active sites. |
front 40 The substance on which an enzyme acts is called the: | back 40 substrate |
front 41 What refers to the situation in which the binding of a substrate to the enzyme causes a change in the enzyme's shape, facilitating an enzyme's function? | back 41 induced fit |
front 42 Hydrolases are one important class of enzyme that function to catalyze: | back 42 splitting a molecule using water. |
front 43 Which refers to an organic, nonpolypeptide compound that binds to the apoenzyme and serves as a cofactor? | back 43 coenzyme |
front 44 Which of the following does not represent a method by which cells regulate enzyme activity? | back 44 heat denaturation of the enzyme |
front 45 Select the enzyme that does not match the reaction: | back 45 kinase-breaks peptide bonds |
front 46 If one continues to increase the temperature in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the rate of the reaction: | back 46 increases and then decreases rapidly. |
front 47 You conduct an experiment in which you add increasing amounts of substrate to an enzyme solution and then measure the resulting reaction rate. You graph your results, plotting the rate of the reaction on the Y-axis versus substrate concentration on the X-axis. What do you conclude from your graph? | back 47 The reaction rate increases with increasing substrate concentration up to a point, above which the rate remains constant. |
front 48 An allosteric enzyme: | back 48 allows a substance other than the substrate to bind to the enzyme, thereby activating or inactivating it. |
front 49 Competitive inhibitors inhibit enzymatic reactions by: | back 49 temporarily bonding into the active site. |
front 50 Penicillin is a drug that acts by: | back 50 irreversibly inhibiting transpeptidase. |