Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MINERAL DEPOSITS
front 1 Metallic ores | back 1 ferrous metals, base metals, precious metals, radioactive minerals |
front 2 ferrous metals | back 2 (iron, manganese, molybdenum, and |
front 3 base metals | back 3 copper, lead, zinc, and tin |
front 4 precious metals | back 4 gold, silver, the platinum group metals |
front 5 radioactive minerals | back 5 uranium, thorium, and radium |
front 6 Nonmetallic minerals | back 6 the nonfuel mineral ores that are not associated with the production of metals. These include phosphate, potash, halite, trona, sand, gravel, limestone, sulfur, and many others. |
front 7 Fossil fuels | back 7 the organic mineral substances that can be utilized as fuels, such as coal, petroleum, natural gas, coalbed methane, gilsonite, and tar sands. |
front 8 Ore Body | back 8 accumulation of a solid and fairly continuous mass of |
front 9 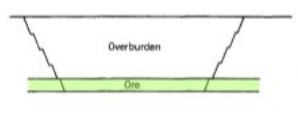 | back 9 Tabular, flat, sheets – bedding planes |
front 10 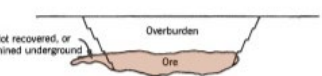 | back 10 Lenticular/lensoid, podiform |
front 11 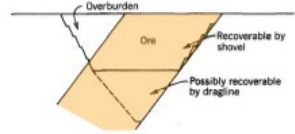 | back 11 Cylindrical/Pipes/chimneys |
front 12 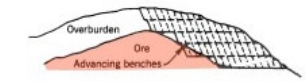 | back 12 Irregular, disseminated |
front 13 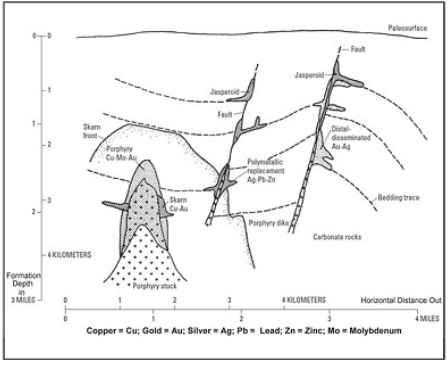 | back 13 Veins |
front 14 Syngenetic ores | back 14 Primary |
front 15 Epigenetic ores | back 15 Secondary |
front 16 Magmatic | back 16 (Chromite, Nickel-copper and PGE’s) and Diamonds |
front 17 Hydrothermal | back 17 ore constituents (e.g. Cu, Pb, Au, etc.) are dissolved in a hot aqueous solution along with other deposit constituents (e.g. Si, S, Fe) |
front 18 Most Common source for minerals in the Philippines | back 18 Hydrothermal |
front 19 Supergene enrichment | back 19 surface waters percolate downward |
front 20 Hypogene Enrichent | back 20 - a process that occurs as deep, upwelling magmatic fluids concentrate ore minerals in the crust |
front 21 Skarn | back 21 Gold |
front 22 Surficial | back 22 originate from surface or near-surface processes |
front 23 Latherite | back 23 Surficial (Mostly Ni and Fe) |
front 24 Limonite | back 24 More Fe less Ni |
front 25 Saprolite | back 25 More Ni Less Fe |