Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
biochem cell bio exam 1 10/1
front 1 difference between covalent and non covalent bonds | back 1 atoms in a covalent bond share some of their electrons, but the atoms in a non-covalent bond do not share any electrons. |
front 2 Which term describes all types of noncovalent bonds | back 2 electrostatic |
front 3 London dispersion forces are attractive forces that arise when ________ | back 3 oppositely charged dipoles, created through the random distribution of electrons around their atoms’ nuclei, interact |
front 4
Which statements are TRUE (select all)?
| back 4 The carboxylic acid (COOH) functional group could form hydrogen bond with water Hydrocarbon chains can interact through dispersion forces |
front 5 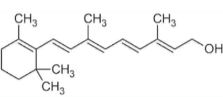 The molecule shown below is primarily ______ because ___________ | back 5 non-polar; it mostly contains atoms with similar electronegativity properties |
front 6 Which molecule below is the most hydrophilic (water loving)? Hint: This molecule will be highly polar | back 6 Urea |
front 7 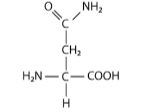 This amino acid below is in the _____ category. It’s R-group has a _____ functional group, which means it will ______ when the pH is extremely low | back 7 Polar/amide/not change |
front 8 hydroxyl | back 8 OH |
front 9 Carboxylic acid | back 9 CO2H |
front 10 Amine | back 10 NH2 |
front 11 Methyl | back 11 CH3 |
front 12 The primary structure of a protein is determined by the | back 12 the identity of the amino acids in the peptide sequence |
front 13 Which is/are a true statement(s)? Use the figure and the table below
for reference | back 13 hemoglobin is tetrameric and has quaternary structure. |
front 14 Which of the following statements is TRUE (select all)? | back 14 The primary amino acid sequence
Proline-Alanine-Glycine- |
front 15 A peptide bond is stronger than a single covalent bond because it has
a partial | back 15 The rotation of the bond is limited due to resonance |
front 16 Which statement correctly describes the bonds that form within a
protein? (select all) | back 16 None of the above |
front 17 Glycine and proline are known as “helix breakers”. Explain why | back 17 Both amino acids disrupt the regular hydrogen bonding pattern
essential for alpha |
front 18 Which of the following statements are true about PrPC and/or Prp Sc ?
(select one) | back 18 PrPc can spontaneously undergo the conformational change to become PrPsc |
front 19 Protein folding is mostly driven by | back 19 hydrophobic effect |
front 20 Molecular chaperones help the ∆F508 form of CFTR re-fold | back 20 False |
front 21 Which of the following best describes the change in entropy that occurs during protein folding A. Entropy of both the water and the protein increase. | back 21 Entropy of the water increases; entropy of the protein decreases |
front 22 The K D of Protein A for Ligand B is 300 nM. The KD of Protein C for
Ligand D is 10 | back 22 Protein A binds Ligand B with higher affinity than Protein C binds Ligand D When the concentration of Ligand B is 300nM, half the binding sites on Protein A will be filled |
front 23 Explain what characteristics of the protein and its ligand provides specificity of binding (i.e. what dictates the Kd of a protein-protein or protein-ligand interaction?) | back 23 The architecture of the bonds, as well as the number of bonds, formed between the atoms on the ligand and the atoms on the amino acids in the binding pocket of the protein |
front 24 Which types of chemical bonds typically hold the protein and ligand together? | back 24 Non-covalent bonds like hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals,
hydrogen bonds and |
front 25 A nuclear import peptide sequence can occur anywhere (inside or
outside) on a folded | back 25 FALSE; It is true that a nuclear import peptide typically has a
string of basic amino acids, but |
front 26 GEF adds a phosphate to GDP to make GTP | back 26 FALSE; GEF triggers the release of GDP from a G-protein to allow GTP to bind in its place. |
front 27 One of the ways that glycosylation is used in the ER is to mark
proteins for sorting to other | back 27 TRUE; the sugar groups that are added during glycosylation are
continually modified as the |
front 28 Post-translational modifications refer to | back 28 The formation of covalent bonds between protein subunits |
front 29 A secreted protein, once translated, will follow which of the
following pathways through | back 29 ER, vesicle, Golgi, vesicle, PM |
front 30 hydrophobic effect | back 30 tendency of nonpolar molecules to clump together in water, while being excluded by water molecules |
front 31 how to know if amino acid is polar | back 31 Side chains contain amide or hydroxyl groups |
front 32 How to know if amino acid is non polar | back 32 Side chains are mostly hydrocarbon |
front 33 how to know if amino acid is basic | back 33 Side chains contain amine functional groups |
front 34 how to know amino acid is acidic | back 34 Side chains contain carboxyl groups |
front 35 nonpolar amino acids | back 35 glycine, alanine, valine, cysteine, proline, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, trypyophan, phenylalnine |
front 36 polar amino acids | back 36 serine, threonine, tyrosine, asparagine, glutamine |
front 37 basic amino acids | back 37 lysine, arginine, histidine |
front 38 acidic amino acids | back 38 aspartic acid, glutamic acid |