Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 4 General Biology
front 1 Evidence that all living cells have a common origin is provided by: | back 1 basic similarities in cell structure and chemistry. |
front 2 It is advantageous for cells to be small because: | back 2 a small cell has a small volume relative to surface area, thereby increasing efficient transport. |
front 3 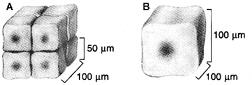 Figure 4-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). Which of the following statements about Figure 4-1 is true? | back 3 Figure B has a smaller surface area to volume ratio than Figure A. |
front 4 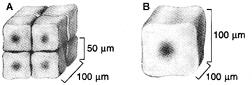 Figure 4-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). Based on your knowledge of basic geometric relationships, the actual surface area to volume ratio for Figure B in Figure 4-2 is: | back 4 0.06. |
front 5 One strategy that allows larger cells to have an effective surface area to volume ratio is: | back 5 having thin, finger-like projections. |
front 6 Which of the following descriptions or structures does NOT match the cell type? | back 6 Smallest cell are egg cells. |
front 7 Which scientist first viewed living cells? | back 7 Anton van Leeuwenhoek. |
front 8 The ratio of the size of the image seen with the microscope to the actual size of the object is called: | back 8 magnification. |
front 9 You want to determine the location of a specific protein in a cell using a colored stain. Which of the following is the best technique for this purpose? | back 9 fluorescence microscopy. |
front 10 Electron microscopes have a much higher resolution than either the human eye or any light microscope because: | back 10 of the very short (nanometer) wavelengths of electrons. |
front 11 The scanning electron microscope differs from the transmission electron microscope in that the scanning electron microscope: | back 11 gives a three dimensional image of the object being studied. |
front 12 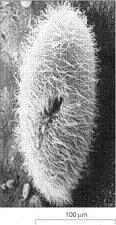 The accompanying figure is the product of a: | back 12 scanning electron microscope. |
front 13 Differential centrifugation is a process that: | back 13 separates components of the cell that have different densities. |
front 14 A eukaryotic cell: | back 14 has a variety of membranous organelles. |
front 15 Membrane-bounded organelles facilitate faster chemical reactions because: | back 15 reactants are within close proximity to each other. |
front 16 Which of the following structures or activities is NOT directly part of the endomembrane system? | back 16 Ribosomes. |
front 17 DNA is associated with proteins, forming a complex called: | back 17 chromatin. |
front 18 Nucleoli contain chromosomal regions that specialize in making: | back 18 RNA. |
front 19 A single cell in a smoker's lung has become cancerous. It doubles its DNA and divides much faster than a normal lung cell. The most likely change that would have caused this condition took place in the: | back 19 nucleus. |
front 20 The largest and most complex assembly of proteins in the eukaryotic cell, consisting of 30 different proteins, is the __. | back 20 nuclear pore. |
front 21 If a toxin, such as a bacterial toxin, destroys ribosomes, what cellular activity will be affected first? | back 21 Protein synthesis. |
front 22 The smooth endoplasmic reticulum: | back 22 Synthesizes lipids. |
front 23 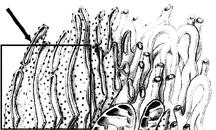 Figure 4-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 4-2. The rough endoplasmic reticulum indicated by the arrow is responsible for: | back 23 Protein synthesis. |
front 24  Figure 4-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Which of the following functions would most likely be occurring in the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum in Figure 4-2? | back 24 Molecular chaperone activity. |
front 25 Proteins made on ribosomes may be further modified within the: | back 25 Golgi complex. |
front 26 The cis face of the Golgi complex is most directly involved in which of the following? | back 26 Accepting vesicles from the ER. |
front 27 A glycoprotein destined for secretion from the cell would move through the Golgi complex in this sequence: | back 27 cis face to medial region to trans face. |
front 28 The __ can be considered a sorting, processing and packaging center. | back 28 Golgi complex. |
front 29 Some white blood cells can engulf bacteria. The engulfed bacteria are encased in a vesicle formed from the plasma membrane. This vesicle fuses with a primary lysosome. The new combined vesicle is now called a secondary lysosome. The reason for forming a secondary lysosome is: | back 29 to mix the pathogens with strong hydrolytic enzymes and destroy them. |
front 30 All of the following functions are performed by plant vacuoles EXCEPT: | back 30 storage of nucleic acids. |
front 31 One function of peroxisomes involves the process of: | back 31 Detoxification. |
front 32 The theory that chloroplasts and mitochondria had their evolutionary beginnings in eukaryotic cells as endosymbionts is supported by all of the following EXCEPT: | back 32 chloroplasts and mitochondria do NOT interact with or depend on any of the other cellular components. |
front 33 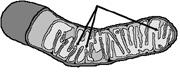 Figure 4-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The organelle featured in Figure 4-3: | back 33 plays a central role in energy metabolism. |
front 34 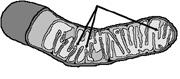 Figure 4-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The structures indicated by the arrows in Figure 4-3 are: | back 34 Cristae. |
front 35  Figure 4-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The main process that occurs at the site of the structures marked by arrows in Figure 4-3 is: | back 35 conversion of food molecules to ATP. |
front 36 Which of the following organelles plays an important role in apoptosis, or programmed cell death? | back 36 Mitochondria. |
front 37 A cellular structure found in plant but not animal cells is the: | back 37 Chloroplast. |
front 38 An individual flattened membrane within the chloroplast is called the: | back 38 Thylakoid. |
front 39 The formation of carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water occurs in the portion of the chloroplast called the: | back 39 Stroma. |
front 40 Which of the following structures would not be found in cells of a plant's roots? | back 40 Chloroplasts. |
front 41 Which of the following is a key component of the cytoskeleton? | back 41 Microtubules. |
front 42 You isolate a cellular structure and determine that it is composed of a-tubulin and b-tubulin. Based on this evidence, you correctly identify this structure as: | back 42 A microtubule. |
front 43 Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? | back 43
|
front 44 The force necessary to cause microtubules of cilia and flagella to slide alongside one another is provided through the action of __ proteins, which derive the energy to perform their work directly from __ molecules. | back 44 Dynein;ATP. |
front 45 Which of the following statements concerning centrioles is FALSE? | back 45 They have a 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules. |
front 46 As a result of testing an experimental drip on a vertebrate cell, you notice that the cell cortex becomes more fluid, and although the cell remains strong, it loses its ability to move. Based on this evidence, you correctly conclude that the drug most directly affected: | back 46 Actin filaments. |
front 47 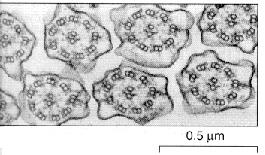 The structures in the micrograph are: | back 47 Both cilia and flagella. |
front 48 Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? | back 48 Integrins - receptors. |
front 49 Which of the following is NOT a cell covering or part of a cell covering? | back 49 Cristae. |
front 50 Which of the following is(are) composed of a gluelike polysaccharide called pectin and is located between the primary walls of adjacent plant cells? | back 50 Middle lamella. |