Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 3 General Biology
front 1 Which of the following is not a property of carbon? | back 1 Carbon-to-carbon bonds are limited to single bonds. |
front 2 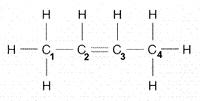 The number of electron pairs shared between carbon 2 and 3 in the accompanying figure is: | back 2 two. |
front 3 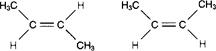 The two molecules in the following figure represent | back 3 Geometric isomers. |
front 4 The highly polarized nature of compounds containing carboxyl groups can be attributed to the presence of two: | back 4 Highly electronegative oxygen atoms. |
front 5 This functional group is weakly basic because it can accept an H+ ion: | back 5 amino. |
front 6 Hydrocarbons are hydrophobic because: | back 6 The covalent bonds between hydrogen and carbon are nonpolar. |
front 7 The chemical interactions of large organic molecules are largely determined by: | back 7 their functional groups. |
front 8 Which of these terms is most inclusive? | back 8 carbohydrate. |
front 9 Carbohydrate molecules: | back 9 are a source of energy. |
front 10 A chemical reaction in which monomers become covalently linked and thus synthesizes polymers from their building blocks is called: | back 10 Condensation. |
front 11 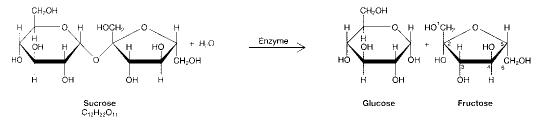 Figure 3-1 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). The process illustrated in Figure 3-1 is called: | back 11 Hydrolysis. |
front 12 In which of the following reactions must the equivalent of a water molecule be added in order to break a bond? | back 12 glycogen → glucose |
front 13 Which of the following illustrates hydrolysis? | back 13 the reaction of a fat to form glycerol and fatty acids. |
front 14 Glucose dissolves in water because: | back 14 it has polar hydroxyl groups that interact with polar water molecules. |
front 15 The difference between a hexose and a pentose is that: | back 15 a hexose always has six carbons, but a pentose always has five carbons. |
front 16 Monosaccharides are water soluble because: | back 16 they have a large number of polar hydroxyl groups. |
front 17 Which pair is mismatched? | back 17 monsaccharide - maltose. |
front 18 Which one of the following carbohydrates is the most structurally complex? | back 18 Cellulose. |
front 19 Amyloplasts are organelles that store: | back 19 Starch. |
front 20 A carbohydrate energy storage molecule found in animal liver and muscle cells is: | back 20 Glycogen. |
front 21 Which of the following is NOT true of lipids? | back 21 They have many oxygen-containing functional groups. |
front 22 The hydrolysis of triacylglycerol will yield: | back 22 Three fatty acids and one glycerol. |
front 23 Which of the following molecules is NOT grouped with the lipids. | back 23 Glycoproteins. |
front 24 A molecule of a saturated triacylglycerol contains: | back 24 The maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains. |
front 25 Which of the following statements concerning unsaturated fats is correct? | back 25 They are generally liquid at room temperature. |
front 26 An amphipathic molecule has: | back 26 A hydrophobic and a hydrophilic portion. |
front 27 If you partially hydrogenate oleic acid, the resulting molecule most likely would: | back 27 have a double bond changed from cis to trans . |
front 28 You isolate a compound that is insoluble in water, has alternating single and double bonds, and has a bright orange color. You correctly conclude that this compound is a: | back 28 carotenoid. |
front 29 Which of the following statements concerning steroids is FALSE? | back 29 They are always detrimental to living organisms. |
front 30 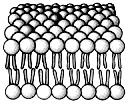 The most abundant molecules in this structure are: | back 30 Phospholipids. |
front 31 The primary difference between the amino acids commonly found in proteins is in their: | back 31 R or variable groups. |
front 32 Amino acids are important biological buffers because: | back 32 their amino and carboxyl groups can accept and release protons (H+ ). |
front 33 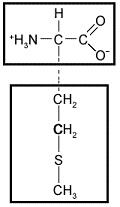 The following amino acid would be characterized as __ based on the chemical properties of its side chain. | back 33 Nonpolar. |
front 34 Which of the following is responsible for the alpha-helical structure of proteins? | back 34 Hydrogen bonds. |
front 35 Proteins with alpha-helical forms exhibit this property: | back 35 Elasticity. |
front 36 If glycine and alanine undergo condensation, the new bond that is formed is between the: | back 36 carbon of the carboxyl group and the nitrogen of the amino group. |
front 37 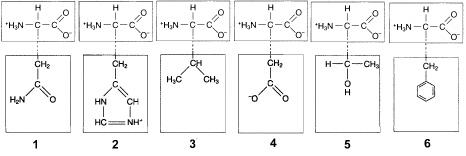 Figure 3-2 Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s). In Figure 3-2, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids? | back 37 2 and 4. |
front 38 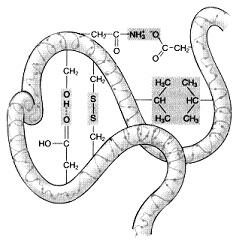 All of the following types of chemical bonds are responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of this polypeptide except: | back 38 Peptide bond. |
front 39 Molecular chaperones are proteins that mediate the folding process of: | back 39 Other proteins. |
front 40  If the differently shaded portions of this molecule represent different polypeptide chains, then this figure is representative of: | back 40 the quaternary structure of a protein. |
front 41 Which of the following statements is true of proteins? | back 41 Proteins lose some or all of their normal activity if their three-dimensional structure is disrupted. |
front 42 This molecule transmits heredity information: | back 42 Nucleic acid. |
front 43 DNA most directly determines which __ are made by a cell. | back 43 Proteins. |
front 44 Which of the following statements best summarizes the differences between RNA and DNA? | back 44 DNA comprises the genes, while RNA is a direct participant in the process of protein synthesis. |
front 45 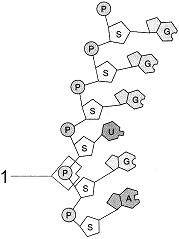 Figure 3-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The molecular fragment represented in Figure 3-3 is: | back 45 RNA. |
front 46  Figure 3-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The type of connection between the atoms at the point labeled 1 in Figure 3-3 is: | back 46 a phosphodiester linkage. |
front 47 Analysis of a certain polymer shows that it contains phosphate groups, ribose sugars, and pyrimidines. Based on this information, which of the following is the best description of this compound? | back 47 It is most likely ribonucleic acid. |
front 48 Which pair matches the correct macromolecule with the bond that joins its subunits? | back 48 nucleic acid-phosphodiester linkage. |
front 49 When a nucleic acid undergoes hydrolysis, the resulting subunits are: | back 49 Nucleotides. |
front 50 ATP is important in living organisms because: | back 50 it can transfer some of its energy to other chemicals and thus serves as the primary energy currency of all cells. |