Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 1 General Biology
front 1 Which of the following is NOT a major theme of biology? | back 1 The mechanisms of disease. |
front 2 The cell theory states that all living organisms: | back 2 Are composed of basic units called cells. |
front 3 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all living organisms? | back 3 Multicellularity. |
front 4 The science of life is: | back 4 Biology. |
front 5 If an organism is eukaryotic, then by definition it will: | back 5 Possess a nucleus. |
front 6 In all organisms, hereditary information is encoded within ___ molecules. | back 6 DNA. |
front 7 A prokaryotic cell differs from a eukaryotic cell in that a prokaryotic cell: | back 7 Is exemplified by bacteria. |
front 8 Biological growth involves an increase in:
| back 8 Both the number and size of cells. |
front 9 In living organisms, chemical reactions responsible for growth, repair, and nutrition are collectively referred to as:
| back 9 Metabolism. |
front 10 Homeostasis in living organisms involves processes that: | back 10 maintain a constant internal environment. |
front 11 If a particular protein were being produced in excess of the cell's needs, then __ mechanisms intervene to stop production. | back 11 homeostatic. |
front 12 Cilia and flagella are most directly involved in: | back 12 movement. |
front 13 Organisms that are sessile as adults: | back 13 do not move from place to place. |
front 14 Which of the following stimuli most directly causes the Venus Flytrap to catch an insect? | back 14 touch. |
front 15 Which of the following is a characteristic of asexual, as opposed to sexual, reproduction? | back 15 a cell splitting in half. |
front 16 One benefit of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that: | back 16 the interaction of the genes from both parents brings about generic variation. |
front 17 Which of the following is NOT an adaptation of Burchell's zebras to their environment? | back 17 asexual reproduction. |
front 18 Reductionism refers to the method of investigating structures by: | back 18 studying the parts of the structures. |
front 19 Which of the following is the most basic level of chemical organizations? | back 19 atom. |
front 20 When tissues organize into functional structures they form: | back 20 an organ. |
front 21 All of the members of the same species occupying the same area at the same time constitute: | back 21 a population. |
front 22 Which of the following is NOT a term related to information transfer in living systems? | back 22 taxon. |
front 23 Which of the following is NOT true of proteins? | back 23 they contain the code or the "recipe" for making other molecules that are important for life processes. |
front 24 Information in living organisms can be transmitted by: | back 24 genes, hormones, & neurotransmitters. |
front 25 Which of the following is NOT true of hormones? | back 25 they are a type of gene. |
front 26 Which of the following is NOT a concept or term related to the flow of energy through living systems? | back 26 sexual reproduction. |
front 27 Autotrophs: | back 27 synthesize complex molecules from CO2, water, and energy. |
front 28 Which of the following represents the pattern of energy flow within an ecosystem? | back 28 from producers to consumers to decomposers. |
front 29 All of the following are associated with the process of evolution, but which of these statements best defines the overall process of evolution? | back 29 changing of populations over time. |
front 30 Which of the following is produced via the process of cellular respiration? | back 30 carbon dioxide. |
front 31 Using the Linnaean system of nomenclature, corn is named Zea mays. In this name, the specific epithet is: | back 31 mays. |
front 32 Which of the following terms includes the fewest species of organisms. | back 32 population. |
front 33 As you move one step higher in the hierarchical classification system, similar families of organisms are next grouped together in the same: | back 33 order. |
front 34 The domain Eukarya includes all of the following EXCEPT: | back 34 bacteria. |
front 35 You discover an organism that is eukaryotic, unicellular & photosynthetic. Based on this evidence, you organize this organism to the: | back 35 protist group. |
front 36 To what group do I belong? I am neither prokaryotic nor photosynthetic, and I obtain nutrients by secreting digestive enzymes into my environment. | back 36 fungi. |
front 37 One of the conclusions drawn from Darwin’s theory of evolution is that: | back 37 organisms living today descended with modifications from previously existing forms. |
front 38 In Darwin’s theory of evolution, adaptation involves changes in: | back 38 communities. |
front 39 The ultimate source of generic variation within a population is: | back 39 mutations in DNA. |
front 40 Which of the following is NOT a concept or term related to evolution? | back 40 cellular respiration. |
front 41 In the deductive approach to scientific thought processes, we begin with __ and make __ based on that information. | back 41 premises; conclusions. |
front 42 A hypothesis is: | back 42 a tentative explanation. |
front 43 A good hypothesis: | back 43 is falsifiable. |
front 44  The organism in the accompanying figure can be classified as: | back 44 a bird. |
front 45 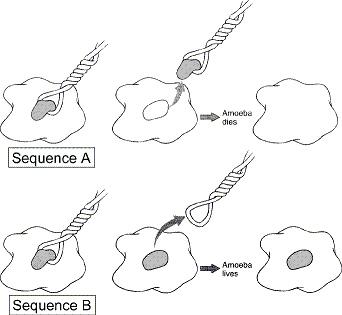 Figure 1-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Sequence A in Figure 1-1 represents: | back 45 the experimental group. |
front 46  Figure 1-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Sequence B in Figure 1-1 represents: | back 46 the control group. |
front 47 If we want to examine the effect of a fertilizer on the size of zucchini produced, we would need to establish both experimental and control groups. The experimental group has all the following: soil, fertilizer, water, sun, and zucchini seeds. The control group for this experiment would have all of the same components except: | back 47 fertilizer. |
front 48 The term sampling error refers to inaccuracies in an experiment due to: | back 48 the test being conducted on a very small population of test subjects |
front 49 Similar orders are placed in the same class. | back 49 True. |
front 50 When you use deductive reasoning you draw conclusions from specific observations. | back 50 False. |