Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P I - Joints
front 1 Joints (aka Articulartions) | back 1 Sites where 2 or more bones meet. |
front 2 Functions of Joints | back 2 Functions of joints: give skeleton mobility and hold skeleton together |
front 3 Classifications of Joints | back 3 2 classifications of Joints: 1. Structural: 3 types based on what material binds the joints and whether a cavity is present. Fibrous (Connective Tissue) 2. Functional classifications: 3 types based on
movement joint allows |
front 4 Fibrous Joints | back 4
|
front 5 Fibrous Joints: Sutures | back 5 Fibrous joint
|
front 6 Fibrous Joints: Syndesmoses | back 6
|
front 7 Fibrous Joints: Gomphoses | back 7
|
front 8 Cartilaginous Joints | back 8
|
front 9 Cartilaginous Joints: Synchondroses | back 9
|
front 10 Cartilaginous Joints: Symphyses | back 10
|
front 11 Synovial Joints | back 11
|
front 12 Characteristics of synovial joints | back 12
|
front 13 General Structure of Synovial Joints: | back 13 Synovial joints have 6 general features: |
front 14 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Articular Cartilage | back 14 1. Articular cartilage: consists of hyaline cartilage covering ends of bones (Prevents crushing of bone ends) |
front 15 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Joint (Synovial) Cavity | back 15 2. Joint (synovial) cavity: small, fluid-filled potential space that is unique to synovial joints |
front 16 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Articular (joint) capsule | back 16
3. Articular (joint) capsule: 2 layers thick |
front 17 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Synovial fluid | back 17 4. Synovial fluid: viscous, slippery filtrate of plasma & hyaluronic acid. Lubricates & nourishes articular cartilage. Contains phagocytic cells to remove microbes & debris. |
front 18 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Different Types of reinforcing ligaments | back 18 5. Different types of reinforcing ligaments |
front 19 General Structure of Synovial Joints: Nerves & blood vessels | back 19 6. Nerves & blood vessels: Nerves detect pain; monitor joint position & stretch. Capillary beds supply filtrate for synovial fluid. |
front 20 General Structure of Synovial Joints - other features | back 20
|
front 21 Bursae and Tendon Sheaths | back 21
|
front 22 Factors Influencing Stability of Synovial Joints | back 22 Three factors determine stability of joints to prevent dislocations:
|
front 23 Movements Allowed by Synovial Joints | back 23
|
front 24 3 General Types of Movements Allowed by Synovial Joints | back 24 Three general types of movements
|
front 25 Synovial Joints: Gliding Movements | back 25  Gliding movements: One flat bone surface glides or slips over another
similar surface. |
front 26 Synovial Joints: Angular Movements | back 26 Angular movements: Increase or decrease angle between 2 bones. Movement along sagittal plane. Angular movements include:
|
front 27 Synovial Joint - Angular Movements in Pictures | back 27  |
front 28 Synovial Joints: Rotations | back 28  Rotation: turning of bone around its own long axis, toward midline or away from it
|
front 29 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Supination and pronation | back 29  Supination and pronation: rotation of radius and ulna
|
front 30 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Inversion and Eversion | back 30 
|
front 31 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Protraction and retraction | back 31 
|
front 32 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion | back 32 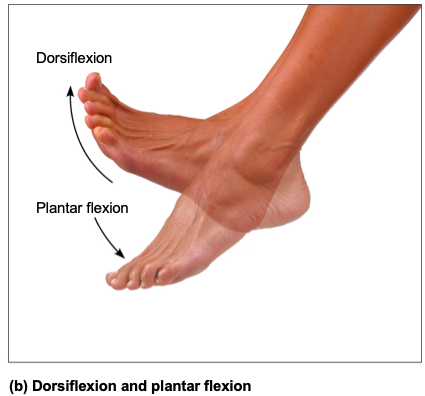 Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of foot
|
front 33 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Elevation and Depression of mandible | back 33  Elevation and depression of mandible:
Elevation: lifting body part superiorly
Depression: lowering body part |
front 34 Synovial Joints, Special movements: Opposition | back 34 
Opposition: movement of thumb |
front 35 Six different types of synovial joints | back 35 Categories are based on shape of articular surface, as well as movement joint is capable of
|
front 36 Synovial Plane Joint - diagram | back 36  |
front 37 Synovial Hinge Joint - diagram | back 37  |
front 38 Synovial Pivot Joint - diagram | back 38  |
front 39 Synovial Condylar Joint - diagram | back 39  |
front 40 Synovial Saddle Joint - diagram | back 40  |
front 41 Synovial Ball-and-socket Joint: diagram | back 41  |
front 42 Knee Joint | back 42
|
front 43 Knee Joint: Femoropatellar joint | back 43 Femoropatellar joint (femur & patella)
|
front 44 Knee Joint: Lateral & Medial Joints | back 44
|
front 45 Three ligaments that act to stabilize knee joint | back 45 Capsular, extracapsular, or intracapsular ligaments |
front 46 Intracapsular ligaments | back 46 1 of 3 ligaments that act to stabilize knee joint
Intracapsular ligaments reside within capsule, but
outside synovial cavity: |
front 47 Capsular, extracapsular ligaments | back 47 2 of 3 ligaments that act to stabilize knee joint:
|
front 48 Common Knee Injuries | back 48 Knee absorbs great amount of vertical force; however, it is
vulnerable to horizontal blows –Lateral blows to extended knee can result in tears in tibial collateral ligament, medial meniscus, & anterior cruciate ligament –Injuries affecting just ACL are common in runners who change direction, twisting ACL –Surgery usually needed for repairs |
front 49 Common Joint Injuries: Cartilage Tears | back 49 Cartilage tears:
|
front 50 Common Joint Injuries: Sprains | back 50 Sprains
|