Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Circuits Practice
front 1  Multiple Correct. Which arrangements of resistors shown above have
the same resistance between the terminals? Select two answers | back 1 A, D |
front 2  In the circuit shown above, what is the value of the potential
difference between points X and Y if the 6–volt | back 2 (A) |
front 3  How would the ammeter reading change when another lamp is connected
in parallel with the first lamp as shown by the dashed lines? | back 3 (A) |
front 4  How would the voltmeter reading change when another lamp is connected
in parallel with the first lamp as shown by the dashed lines? | back 4 (D) |
front 5  The four resistors shown below have the lengths and cross–sectional
areas indicated and are made of material (A) | back 5 (B) |
front 6  Two capacitors are connected in parallel as shown above. A voltage V
is applied to the pair. What is the ratio of charge stored on C1 to
the charge stored on C2, when C1 = 1.5C2 ? | back 6 (C) |
front 7  The five incomplete circuits below are composed of resistors R, all
of equal resistance, and capacitors C, all of Into which circuit should the battery be connected to obtain the
greatest steady power dissipation? | back 7 (D) |
front 8  The five incomplete circuits below are composed of resistors R, all
of equal resistance, and capacitors C, all of Which circuit will retain stored energy if the battery is connected to it and then disconnected? (A) A | back 8 (B) |
front 9  The circuit shown above left is made up of a variable resistor and a
battery with negligible internal resistance. A graph of the power P
dissipated in the resistor as a function of the current I supplied by
the battery is given above right. What is the emf of the
battery? | back 9 (B) |
front 10  In the circuit shown above, the value of r for which the current I is
0.5 ampere is | back 10 (D) |
front 11  In the diagrams above, resistors R1 and R2 are shown in two different
connections to the same source of emf E that has no internal
resistance. How does the power dissipated by the resistors in these
two cases compare? | back 11 (C) |
front 12  The diagram above shows part of a closed electrical circuit. When
there is a steady current in the circuit, the amount of charge passing
a point per unit of time is | back 12 (C) |
front 13  Two concentric circular loops of radii b and 2b, made of the same
type of wire, lie in the plane of the page, as shown above. The total
resistance of the wire loop of radius b is R. What is the resistance
of the wire loop of radius 2b? | back 13 (C) |
front 14 The total capacitance of several capacitors in parallel is the sum of
the individual capacitances for which of the following
reasons? | back 14 (A) |
front 15 A wire of length L and radius r has a resistance R. What is the
resistance of a second wire made from the same material that has a
length L/2 and a radius r/2? | back 15 (B) |
front 16  Which current is greater I1 or I2? | back 16 (C) |
front 17  What is the current I1? | back 17 (B) |
front 18  Which of the following changes would increase the value of
I1? | back 18 (C) |
front 19 A 60-W incandescent bulb and a 13.3-Watt compact fluorescent light
are both plugged into a 110-volt household circuit and lit. Which bulb
has the greater resistance? | back 19 (B) |
front 20  In the circuit shown above, what is the resistance R? | back 20 (B) |
front 21  In the circuit shown above, the current in each battery is 0.04
ampere. What is the potential difference between the points x and
y? | back 21 (C) |
front 22  A 12–volt storage battery, with an internal resistance of 2, is
being charged by a current of 2 amperes as shown in the diagram above.
Under these circumstances, a voltmeter connected across the terminals
of the battery will read | back 22 (D) |
front 23  The batteries in each of the circuits shown above are identical and
the wires have negligible resistance. | back 23 (A0 |
front 24  The batteries in each of the circuits shown above are identical and
the wires have negligible resistance. | back 24 (C) |
front 25  The batteries in each of the circuits shown above are identical and
the wires have negligible resistance. | back 25 (C) |
front 26 When two identical parallel–plate capacitors are connected in series,
which of the following is true of the equivalent capacitance? | back 26 (C) |
front 27 The emf of a battery is 12 volts. When the battery delivers a steady
current of 0.5 ampere to a load, the potential difference between the
terminals of the battery is 10 volts. What terminal voltage would you
expect if the battery were connected to a load with less
resistance? | back 27 (D) |
front 28  In the circuit shown above, the emf's of the batteries are given, as
well as the currents in the outside branches and the resistance in the
middle branch. What is the magnitude of the potential difference
between X and Y? | back 28 (D) |
front 29  Which graph best represents the voltage versus time across the
resistor R? | back 29 (A) |
front 30  Which graph best represents the current versus time in the
circuit? | back 30 (A) |
front 31  Which graph best represents the voltage across the capacitor versus
time? | back 31 (B) |
front 32 A wire of resistance R dissipates power P when a current I passes
through it. The wire is replaced by another wire with resistance 3R.
The power dissipated by the new wire when the same current passes
through it is | back 32 (D) |
front 33 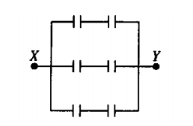 The diagram above represents a circuit of six 2–microfarad
capacitors. What potential difference must be applied between points X
and Y so that the charge on each plate of each capacitor will have
magnitude 6 | back 33 (B) |
front 34  In the circuit above, the emf's and the resistances have the values
shown (0.3 Ω, 0.2 Ω and 1,5 Ω) . The current I in | back 34 (A) |
front 35  In the circuit above, the emf's and the resistances have the values
shown (0.3 Ω, 0.2 Ω and 1,5 Ω) . The current I in | back 35 (C) |
front 36  In the circuit shown above, the battery supplies a constant voltage V
when the switch S is closed. The value of the capacitance is C, and
the value of the resistances are R1 and R2. In the time after the
switch is closed, the current supplied by the battery is | back 36 (C) |
front 37  If the ammeter in the circuit above reads zero, what is the
resistance R ? | back 37 (D) |
front 38  If the current through the ammeter is to flow toward the bottom of
the page, how must the resistance R compare to the value found in
#37? | back 38 (A) |
front 39 A resistor R and a capacitor C are connected in series to a battery
of terminal voltage V0. Which of the following equations relating the
current I in the circuit and the charge Q on the capacitor describes
this circuit? | back 39 (B) |
front 40  Which of the following combinations of 4 resistors would dissipate 24 W when connected to a 12 Volt battery? (A) | back 40 (D) |
front 41  Three identical capacitors, each of capacitance 3.0 F, are connected
in a circuit with a 12 V battery as shown above. The potential
difference between points Y and Z is | back 41 (B) |
front 42  The circuit in the figure above contains two identical lightbulbs in
series with a battery. At first both bulbs glow with equal brightness.
| back 42 (B) |
front 43  When the switch S is open in the circuit shown above, the reading on
the ammeter A is 2.0 A. When the switch is closed, the reading on the
ammeter is | back 43 (B) |
front 44 Two conducting cylindrical wires are made out of the same material.
Wire X has twice as much resistance than wire Y. Which of the
following could be true? | back 44 (C) |
front 45  The figures above show parts of two circuits, each containing a
battery of emf ε and internal resistance r. The current in each
battery is 1 A, but the direction of the current in one battery is
opposite to that in the other. If the potential differences across the
batteries' terminals are 10 V and 20 V as shown, what are the values
of ε and r? | back 45 (C) |
front 46  What is the current through the 6.0 ꭥ resistor shown in the
accompanying circuit diagram? Assume all batteries have negligible
resistance. | back 46 (A) |
front 47  Rank the current through the bulbs. | back 47 (D) |
front 48  Bulb K burns out. Which of the following statements is true? | back 48 (D) |
front 49  Bulb M burns out. Which of the following statements is true? | back 49 (D) |
front 50  The voltmeter in the accompanying circuit diagram has internal
resistance 10.0 kꭥ and the ammeter has internal resistance 25.0 ꭥ. The
ammeter reading is 1.00 mA. The voltmeter reading is most
nearly: | back 50 (C) |
front 51 When two resistors, having resistance R1 and R2, are connected in
parallel, the equivalent resistance of the combination is 5 ꭥ. Which
of the following statements about the resistances is correct? | back 51 (A) |
front 52 When a single resistor is connected to a battery, a total power P is
dissipated in the circuit. How much total power is dissipated in a
circuit if n identical resistors are connected in series using the
same battery? Assume the internal resistance of the battery is
zero. | back 52 (C) |
front 53  In the accompanying circuit diagram, the current through the 6.0–ꭥ
resistor is 1.0 A. What is the power supply voltage V? | back 53 (D) |
front 54  In the circuit diagrammed above, the 3.00–ꭥF capacitor is fully
charged at 18.0 ꭥC. What is the value of the power supply voltage
V? | back 54 (C) |
front 55  Given the simple electrical circuit above, if the current in all
three resistors is equal, which of the following statements must be
true? | back 55 (C) |
front 56  If all of the resistors in the above simple circuit have the same
resistance, which would dissipate the greatest power? | back 56 (D) |
front 57  The following diagram represents an electrical circuit containing two
uniform resistance wires connected to a single flashlight cell. Both
wires have the same length, but the thickness of wire X is twice that
of wire Y. | back 57 (D) |
front 58  Five identical light bulbs, each with a resistance of 10 ohms, are
connected in a simple electrical circuit with a switch and a 10 volt
battery as shown in the diagram below. Which bulb (or bulbs) could
burn out without causing other bulbs in the circuit to also go
out? | back 58 (A) |
front 59  With the switch open, what would be the potential difference across
the 15 ohm resistor? | back 59 (A) |
front 60  With the switch open, what must be the voltage supplied by the
battery? | back 60 (D) |
front 61  When the switch is closed, what would be the current in the
circuit? | back 61 (C) |
front 62  How would the current through the 2 ohm resistor compare to the
current through the 4 ohm resistor? | back 62 (C) |
front 63  What would be the potential at point B with respect to point C in the
above circuit? | back 63 (D) |
front 64  A circuit is connected as shown. All light bulbs are identical. When
the switch in the circuit is closed | back 64 (A) |
front 65  Through which resistor(s) would there be the greatest
current? | back 65 (C) |
front 66  Which resistor(s) have the greatest rate of energy
dissipation? | back 66 (C) |
front 67  The circuit shown has an ideal ammeter with zero resistance and four
identical resistance light bulbs which are initially illuminated. A
person removes the bulb R4 from its socket thereby permanently
breaking the electrical circuit at that point. Which statement is true
of the circuit after removing the bulb? | back 67 (A) |
front 68 A current through the thin filament wire of a light bulb causes the
filament to become white hot, while the larger wires connected to the
light bulb remain much cooler. This happens because: | back 68 (B) |
front 69  In the circuit above the voltmeter V draws negligible current and the
internal resistance of the battery is 1.0 ohm. The reading of the
voltmeter is | back 69 (C) |
front 70  For the circuit shown, a shorting wire of negligible resistance is
added to the circuit between points A and B. When this shorting wire
is added, bulb #3 goes out. Which bulbs (all identical) in the circuit
brighten? | back 70 (B) |
front 71  For the configuration of capacitors shown, both switches are closed
simultaneously. After equilibrium is established, what is | back 71 (D) |
front 72 A student wants to make a brighter light bulb. He decides to modify
the filament. How should the filament of a light bulb be modified in
order to make the light bulb produce more light at a given
voltage? | back 72 (B) |
front 73  For the circuit shown, the ammeter reading is initially I. The switch
in the circuit then is closed. Consequently: | back 73 (C) |
front 74  In the circuit shown above, the potential difference between points a
and b is zero for a value of capacitance C of | back 74 (A) |
front 75  For the circuit shown, when a shorting wire (no resistance) connects the points labeled A and B, which of the numbered light bulbs become brighter? Assume that all four bulbs are identical and have resistance R . (A) Bulb 1 only | back 75 (D) |
front 76  For the RC circuit shown, the resistance is R = 10.0 ꭥ, the
capacitance is C = 5.0 F and the battery has voltage ξ= 12 volts . The
capacitor is initially uncharged when the switch S is closed at time
t=0. At some time later, the current in the circuit is 0.50 A. What is
the magnitude of the voltage across the capacitor at that
moment? | back 76 (C) |
front 77  In the circuit shown above, a constant current device is connected to
some identical light bulbs. After the switch S in the circuit is
closed, which statement is correct about the circuit? | back 77 (D) |
front 78  Two resistors, one with resistance R and the second with resistance 4R are placed in a circuit with a voltage V. (A) 4 P | back 78 (A) |
front 79  A battery, an ammeter, three resistors, and a switch are connected to
form the simple circuit shown above. When the switch is closed what
would happen to the potential difference across the 15 ohm
resistor? | back 79 (C) |
front 80  What would be the current at point E in the circuit? | back 80 (A) |
front 81  What would be the potential at point B with respect to point
D? | back 81 (A) |
front 82  Two resistors and a capacitor are connected with a 10 volt battery, a
switch and an ideal ammeter to form the simple electrical circuit
shown. After the switch is closed and the current in the circuit
reaches a constant value, what is the reading on the ammeter in the
circuit? | back 82 (B) |
front 83  When the switch is closed, what would be the current in the circuit
shown in the diagram above if the two batteries are opposing one
another? | back 83 (D) |
front 84  The diagram above shows an electrical circuit composed of 3 resistors
and 1 capacitor. If each resistor has a resistance of 10 Ω and the
capacitor has a value of 10 μF, what would be the charge stored in the
capacitor when an EMF of 10 V is maintained in the circuit for a
sufficient time to fully charge the capacitor? | back 84 (C) |
front 85  Given 4 identical resistors of resistance R, which of the following configurations would have an equivalent resistance of 4/3 R? (A) | back 85 (A) |
front 86  What would be the total current being supplied by the battery in the
circuit shown above? | back 86 (C) |
front 87  Which of the following wiring diagrams could be used to experimentally determine R using Ohm's Law? Assume an ideal voltmeter and an ideal ammeter. (A) | back 87 (B) |
front 88 Closing which of the switches will produce the greatest power
dissipation in R2? | back 88 (C) |
front 89 Closing which of the switches will produce the greatest reading on
the ammeter? | back 89 (D) |
front 90 Closing which of the switches will produce the greatest voltage
across R3? | back 90 (A) |