About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to
life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of
living matter?
A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen
B)
carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
C) oxygen, hydrogen,
calcium, nitrogen
D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
E)
carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
Answer: D
Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute
quantities. Which of the following is a trace element that is required
by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as
bacteria or plants?
A) nitrogen
B) calcium
C) iodine
D) sodium
E) phosphorus
Answer: C
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the most abundant elements of
living matter.
B) Some trace elements are very abundant on
Earth.
C) Virtually all organisms require the same elements in
the same quantities.
D) Iron is an example of an element needed
by all organisms.
E) Other than some trace elements, animals are
mostly made up of the same elements as plants, in similar proportions.
Answer: C
What factors are most important in determining which elements are
most common in living matter?
A) the relative abundances of the
elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere
B) the emergent
properties of the simple compounds made from these elements
C)
the reactivity of the elements with water
D) the chemical
stability of the elements
E) both the relative abundances of the
elements and the emergent properties of the compounds made from these elements
Answer: E
Why is each element unique and different from other elements in
chemical properties?
A) Each element has a unique atomic mass.
B) Each element has a unique atomic weight.
C) Each
element has a unique number of protons in its nucleus.
D) Each
element has a unique number of neutrons in its nucleus.
E) Each
element has different radioactive properties.
Answer: C
Knowing just the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about
which of the following?
A) the chemical properties of the
element
B) the number of protons in the element
C) the
number of neutrons in the element
D) the number of protons plus
neutrons in the element
E) both the number of protons and the
chemical properties of the element
Answer: D
In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the
same?
A) They have the same number of protons.
B) They
have the same number of neutrons.
C) They have the same number
of electrons.
D) They have the same number of electrons in their
valence shell.
E) They have the same number of electron shells.
Answer: D
Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 and a mass number of 16. Thus, what
is the atomic mass of an oxygen atom?
A) exactly 8 grams
B) exactly 8 daltons
C) approximately 16 grams
D)
approximately 16 daltons
E) 24 amu (atomic mass units)
Answer: D
The nucleus of a nitrogen atom contains 7 neutrons and 7 protons.
Which of the following is a correct statement concerning nitrogen?
A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7
daltons and an atomic mass of 14.
B) The nitrogen atom has a
mass number of approximately 14 daltons and an atomic mass of 7.
C) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 14 and an atomic mass
of 7 grams.
D) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of 7 and an
atomic number of 14.
E) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of
14 and an atomic mass of approximately 14 daltons.
Answer: E
Molybdenum has an atomic number of 42. Several common isotopes exist,
with mass numbers of 92, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, and 100. Therefore, which
of the following can be true?
A) Molybdenum atoms can have
between 50 and 58 neutrons.
B) The isotopes of molybdenum have
different electron configurations.
C) The isotopes of molybdenum
can have between 50 and 58 protons.
D) The isotopes of
molybdenum have between 50 and 58 neutrons and have different electron
configurations.
E) The isotopes of molybdenum have between 50
and 58 protons and have different electron configurations.
Answer: A
Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon, and has an atomic
mass of 12 daltons. A mole of carbon in naturally occurring coal,
however, weighs slightly more than 12 grams. Why?
A) The atomic
mass does not include the mass of electrons.
B) Some carbon
atoms in nature have an extra proton.
C) Some carbon atoms in
nature have more neutrons.
D) Some carbon atoms in nature have a
different valence electron distribution.
E) Some carbon atoms in
nature have undergone radioactive decay.
Answer: C

Which of the following best describes the relationship between the
atoms described below? [SEE IMAGE]
A) They are isomers.
B)
They are polymers.
C) They are isotopes.
D) They contain 1
and 3 protons, respectively.
E) They each contain 1 neutron.
Answer: C
The precise weight of a mole of some pure elements like silicon (Si)
can vary slightly from the standard atomic mass, or even from sample
to sample. Why?
A) The element may undergo radioactive decay.
B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic
particles.
C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with
each other, and that changes the weight of the element.
D) The
element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic
composition may vary from sample to sample.
E) The amount of
energy absorbed by the element affects the mass of its electrons, and
thus the atomic mass can vary slightly.
Answer: D
One difference between carbon-12 (12/6 C) is that carbon-14 (14/6 C)
has
A) two more protons than carbon-12.
B) two more
electrons than carbon-12.
C) two more neutrons than carbon-12.
D) two more protons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
E) two more electrons and two more neutrons than carbon-12.
Answer: C
An atom has 6 electrons in its outer shell. How many unpaired
electrons does it have?
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 2 or 4
Answer: B
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 is heavier than
nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains how
many neutrons?
A) 6
B) 7
C) 8
D) 12
E) 14
Answer: C
Electrons exist only at fixed levels of potential energy. However, if
an atom absorbs sufficient energy, a possible result is that
A)
an electron may move to an electron shell farther away from the
nucleus.
B) an electron may move to an electron shell closer to
the nucleus.
C) the atom may become a radioactive isotope.
D) the atom would become a positively charged ion, or cation,
and become a radioactive isotope.
E) the atom would become a
negatively charged ion, or anion.
Answer: A
The atomic number of neon is 10. Therefore, which of the following is
most correct about an atom of neon?
A) It has 8 electrons in its
outer electron shell.
B) It is inert.
C) It has an atomic
mass of 10 daltons.
D) It has 8 electrons in its outer electron
shell and it is inert.
E) It has 8 electrons in its outer
electron shell, it is inert, and it has an atomic mass of 10 daltons.
Answer: D
From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the
phosphorus atom has
A) 15 neutrons.
B) 15 protons.
C) 15 electrons.
D) 8 electrons in its outermost electron
shell.
E) 15 protons and 15 electrons.
Answer: E
Atoms whose outer electron shells contain 8 electrons tend to
A) form ions in aqueous solutions.
B) form hydrogen bonds
in aqueous solutions.
C) be stable and chemically nonreactive,
or inert.
D) be gaseous at room temperature.
E) be both
chemically inert and gaseous at room temperature.
Answer: E
The atomic number of each atom is given to the left of each of the
elements below. Which of the atoms has the same valence as carbon
(12/6 C)?
A) ₇N nitrogen
B) ₉F flourine
C) ₁₀Ne neon
D) ₁₂Mg magnesium
E) ₁₄Si silicon
Answer: E
Two atoms appear to have the same mass number. These atoms
A)
must have the same atomic number.
B) must have the same number
of electrons.
C) must have the same chemical properties.
D) must have the same number of protons + neutrons.
E)
must have the same atomic number, the same number of protons +
neutrons, the same number of electrons, and the same chemical properties.
Answer: D
Fluorine has an atomic number of 9 and a mass number of 19. How many
electrons are needed to complete the valence shell of a fluorine atom?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 0
D) 7
E) 9
Answer: A
24) What is the maximum number of electrons in a single 2 p orbital
of an atom?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Answer: B
The organic molecules in living organisms have a measurably lower
ratio of carbon-13/carbon-12, two stable isotopes of carbon that
comprise approximately 1.1% and 98.9% of atmospheric carbon,
respectively. What is a reasonable explanation for this phenomenon?
A) Photosynthesis preferentially uses carbon dioxide molecules
with carbon-12, and the lower carbon-13/carbon-12 ratio propagates
through the food chain.
B) Carbon dioxide molecules with
carbon-13 stay in the upper atmosphere and are less available to
terrestrial plants and algae.
C) Carbon-13 has a different
valence electron configuration and is therefore less chemically
reactive than carbon-12.
D) Oxygen atoms preferentially react
with carbon-13, thereby enriching the atmosphere with carbon dioxide
molecules containing carbon-13 atoms.
E) Carbon dioxide
molecules containing carbon-13 are heavier and sink into the ocean
depths, making them less available to living organisms.
Answer: A
Phosphorus-32, a radioactive isotope of phosphorus-31 (atomic number
15), undergoes a form of radioactive decay whereby a neutron turns
into a proton and emits radiation in the form of an electron. What is
the product of such radioactive decay of phosphorus-32?
A)
phosphorus-31
B) a positively charged phosphorus-31 ion
C)
a negatively charged phosphorus-32 ion
D) sulfur-32 (atomic
number 16)
E) the conversion of the phosphorus-32 atom into pure energy
Answer: D
An atom with atomic number 12 would have what type of chemical
behavior in bonding with other elements?
A) It would form ions
with a +1 charge.
B) It would form ions with a +2 charge.
C) It would form ions with a -1 charge.
D) It would form
ions with a -2 charge.
E) It would form two covalent bonds with
other atoms.
Answer: B
If a salamander relied on hydrogen bonds to cling to surfaces, what
type of surface would cause the most problems for this animal?
A) a surface coated with a thin film of water
B) a surface
made with carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bonded together
C) a surface made with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
covalently bonded together
D) a surface made with carbon,
hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms covalently bonded together
E) a surface made with silicon and oxygen atoms covalently
bonded together
Answer: B
A covalent chemical bond is one in which
A) electrons are
removed from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two
atoms become oppositely charged.
B) protons and neutrons are
shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms.
C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to
satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms.
D)
outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner
electron shell of another atom.
E) an electron occupies a hybrid
orbital located between the nuclei of two atoms.
Answer: C
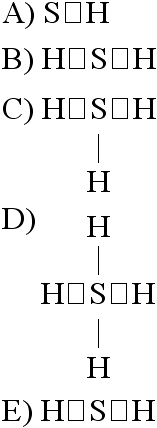
If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with
atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below
would be formed?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
Answer: B
What is the maximum number of covalent bonds an element with atomic
number 8 can make with hydrogen?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
Answer: B
Nitrogen (N) is much more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of
the following statements is correct about the atoms in ammonia (NH₃)?
A) Each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge; the
nitrogen atom has a partial negative charge.
B) The nitrogen
atom has a strong positive charge; each hydrogen atom has a strong
positive charge.
C) Each hydrogen atom has a slight negative
charge; the nitrogen atom has a strong positive charge.
D) The
nitrogen atom has a slight positive charge; each hydrogen atom has a
slight negative charge.
E) There are covalent bonds between the
hydrogen atoms and polar bonds between each hydrogen atom and the
nitrogen atom.
Answer: A
When two atoms are equally electronegative, they will interact to
form
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) van der Waals interactions.
C) polar covalent bonds.
D) nonpolar covalent bonds.
E) ionic bonds.
Answer: D
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms?
A) a nonpolar covalent bond
B) a polar covalent bond
C) an ionic bond
D) a hydrogen bond
E) a hydrophobic interaction
Answer: B
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when
A) one of the atoms
sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other atom.
B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative.
C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons.
D)
one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom.
E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements.
Answer: A
Which of the following molecules contains the most polar covalent
bond?
A) H₂
B) O₂
C) CO₂
D) H₂O
E) CH₄
Answer: D
In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following
would you expect?
A) An atom can form covalent bonds with
multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single
partner atom.
B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite
ends of a continuous spectrum, from nearly equal to completely unequal
sharing of electrons.
C) Both involve electrical attraction
between the electrons of one atom and the nucleus of the other atom.
D) Ionic interactions remain when covalent bonds are broken in
water. Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds.
Answer: B
What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
A) Covalent bonds are formed between atoms to form molecules;
ionic bonds are formed between atoms to form compounds.
B)
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between
atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between
atoms.
C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons
between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between
atoms.
D) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons
between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of protons between
atoms.
E) Covalent bonds involve the transfer of electrons
between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Answer: C
In ammonium chloride salt (NH₄Cl) the anion is a single chloride ion,
Cl. What is the cation of NH₄Cl?
A) N, with a charge of +1
B) NH, with a charge of +1
C) H₃, with a charge of +1
D) NH₄, with a charge of +1
E) NH₄, with a charge of +4
Answer: D
The atomic number of chlorine is 17. The atomic number of magnesium
is 12. What is the formula for magnesium chloride?
A) MgCl
B) MgCl₂
C) Mg₂Cl
D) Mg₂Cl₂
E) MgCl₃
Answer: B
How many electron pairs are shared between carbon atoms in a molecule
that has the formula C₂H₄?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Answer: C
Which bond or interaction would be difficult to disrupt when
compounds are put into water?
A) covalent bond
B) hydrogen
bond
C) van der Waals interaction
D) ionic bond
E)
either covalent bonds or ionic bonds
Answer: A
Which of the following explains most specifically the attraction of
water molecules to one another?
A) nonpolar covalent bond
B) polar covalent bond
C) ionic bond
D) hydrogen
bond
E) hydrophobic interaction
Answer: D
Van der Waals interactions result when
A) hybrid orbitals
overlap.
B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a
molecule.
C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water.
D) two polar covalent bonds react.
E) a hydrogen atom
loses an electron.
Answer: B
What bonding or interaction is most likely to occur among a broad
array of molecules of various types (polar, nonpolar, hydrophilic,
hydrophobic)?
A) covalent bonding
B) polar covalent
bonding
C) ionic bonding
D) hydrogen bonding
E) van
der Waals interactions
Answer: E
Which of the following is not considered to be a weak molecular
interaction?
A) a covalent bond
B) a van der Waals
interaction
C) an ionic bond in the presence of water
D) a
hydrogen bond
E) both a hydrogen bond and a covalent bond
Answer: A
Which of the following would be regarded as compounds?
A) H₂O,
O₂, and CH₄
B) H₂O and O₂
C) O₂ and CH₄
D) CH₄ and
O₂, but not H₂O
E) H₂O and CH₄, but not O₂
Answer: E
What is the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be covalently
bonded in a molecule containing two carbon atoms?
A) 2
B)
3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
Answer: D
Which of the following is true for this reaction?
3 H₂ + N₂ ↔ 2
NH₃
A) The reaction is nonreversible.
B) Hydrogen and
nitrogen are the reactants of the reverse reaction.
C) Hydrogen
and nitrogen are the products of the forward reaction.
D)
Ammonia is being formed and decomposed.
E) Hydrogen and nitrogen
are being decomposed.
Answer: D
Which of the following correctly describes chemical equilibrium?
A) Forward and reverse reactions continue with no effect on the
concentrations of the reactants and products.
B) Concentrations
of products are higher than the concentrations of the reactants.
C) Forward and reverse reactions have stopped so that the
concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the
products.
D) Reactions stop only when all reactants have been
converted to products.
E) There are equal concentrations of
reactants and products, and the reactions have stopped.
Answer: A
Which of the following correctly describes any reaction that has
reached chemical equilibrium?
A) The concentration of the
reactants equals the concentration of the products.
B) The rate
of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
C) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of
the reaction.
D) All of the products have been converted to the
reactants of the reaction.
E) Both the forward and the reverse
reactions have stopped with no net effect on the concentration of the
reactants and the products.
Answer: B
Which of these systems is least likely to be at chemical equilibrium?
A) a test tube of living cells
B) a test tube of organic
molecules, kept in the freezer
C) a test tube of dry organic
molecules, kept at room temperature
D) a test tube of organic
molecules dissolved in water, kept at room temperature
E) a test
tube of dead cells in water, kept at room temperature
Answer: A
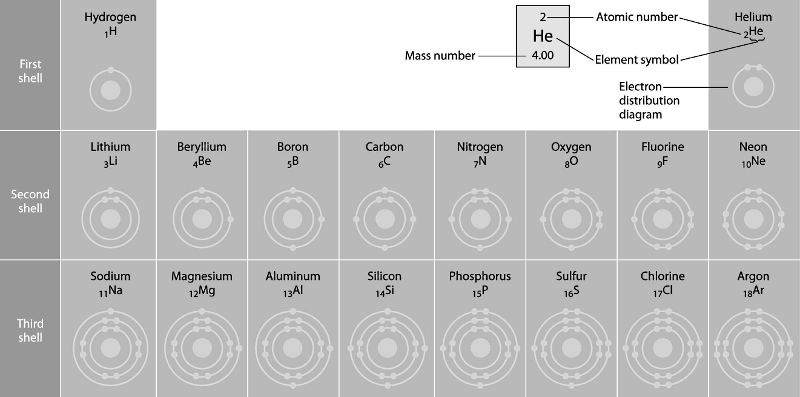
Refer to the figure above (first three rows of the periodic table).
If life arose on a planet where carbon is absent, which element might
fill the role of carbon?
A) boron
B) silicon
C)
nitrogen
D) aluminum
E) phosphorus
Answer: B
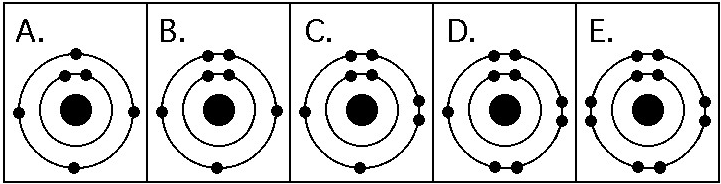
Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an element with chemical properties most similar to Helium
(₂He)?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: E

Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an atom that can form covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: C

Which drawing in the figure above depicts the electron configuration
of an atom capable of forming three covalent bonds with other atoms?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: B

Which drawing in the figure above is of the electron configuration of
a sodium ₁₁Na⁺ ion?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: E

Which drawing in the figure above depicts the most electronegative
atom?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: D

Which drawing in the figure above depicts an atom with a valence of
3?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: B

Which drawing in the figure above depicts an atom with a valence of
2?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Answer: C
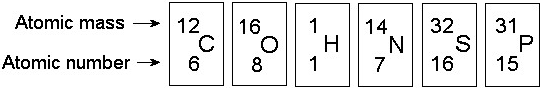
In the figure above, how many electrons does nitrogen have in its
valence shell?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 7
D) 8
E) 14
Answer: B

In the figure above, how many unpaired electrons does phosphorus have
in its valence shell?
A) 15
B) 2
C) 3
D) 7
E) 5
Answer: C

How many neutrons are present in the nucleus of a phosphorus-32 (³²P)
atom (see the figure above)?
A) 5
B) 15
C) 16
D) 17
E) 32
Answer: D

How many electrons does an atom of sulfur have in its valence shell
(see the figure above)?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 16
E) 32
Answer: B

Based on electron configuration, which of these elements in the
figure above would exhibit a chemical behavior most like that of
oxygen?
A) carbon
B) hydrogen
C) nitrogen
D)
sulfur
E) phosphorus
Answer: D

The illustration above shows a representation of formic acid. A
formic acid molecule
A) will form hydrogen bonds with water
molecules.
B) has a tetrahedral configuration of hybrid electron
orbitals for the carbon atom.
C) consists of largely nonpolar
covalent bonds.
D) is held together by hydrogen bonds.
E)
has a tetrahedral shape and will form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Answer: A

What results from the chemical reaction illustrated above?
A) a
cation with a net charge of +1
B) a cation with a net charge of
-1
C) an anion with a net charge of +1
D) an anion with a
net charge of -1
E) a cation with a net charge of +1 and an
anion with a net charge of -1
Answer: E

What is the atomic number of the cation formed in the reaction
illustrated above?
A) 1
B) 8
C) 10
D) 11
E) 16
Answer: D

What causes the shape of the molecule shown above?
A) the
configuration of the 2 p orbitals in the carbon atom
B) the
configuration of the 1 s orbital in the carbon atom
C) the
configuration of the sp hybrid orbitals of the electrons shared
between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
D) the packing of the
carbon and hydrogen atoms in a crystal lattice
E) hydrogen
bonding configurations between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
Answer: C

In the methane molecule shown in the figure above, bonds have formed
that include both the s orbital valence electrons of the hydrogen
atoms and the p orbital valence electrons of the carbon. The electron
orbitals in these bonds are said to be
A) double orbitals.
B) tetrahedral orbitals.
C) complex orbitals.
D)
hybrid orbitals.
E) polar orbitals.
Answer: D

Which one of the atoms shown would be most likely to form a cation
with a charge of +1?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
Answer: A

Which one of the atoms shown would be most likely to form an anion
with a charge of -1?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
Answer: D

Which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form a
polar covalent bond?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
Answer: A

Which of the following pairs of atoms would be most likely to form an
ionic bond?
[SEE IMAGE FOR CHOICES]
Answer: B
A group of molecular biologists is trying to synthesize a new
artificial compound to mimic the effects of a known hormone that
influences sexual behavior. They have turned to you for advice. Which
of the following compounds is most likely to mimic the effects of the
hormone?
A) a compound with the same number of carbon atoms as
the hormone
B) a compound with the same molecular mass (measured
in daltons) as the hormone
C) a compound with the same
three-dimensional shape as part of the hormone
D) a compound
with the same number of orbital electrons as the hormone
E) a
compound with the same number of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms as the hormone
Answer: C
In the term trace element, the modifier trace means that
A) the
element is required in very small amounts.
B) the element can be
used as a label to trace atoms through an organism's metabolism.
C) the element is very rare on Earth.
D) the element
enhances health but is not essential for the organism's long-term
survival.
E) the element passes rapidly through the organism.
Answer: A
Compared with ³¹P, the radioactive isotope ³²P has
A) a
different atomic number.
B) a different charge.
C) one
more proton.
D) one more electron.
E) one more neutron.
Answer: E
The reactivity of an atom arises from
A) the average distance
of the outermost electron shell from the nucleus.
B) the
existence of unpaired electrons in the valence shell.
C) the sum
of the potential energies of all the electron shells.
D) the
potential energy of the valence shell.
E) the energy difference
between the s and p orbitals.
Answer: B
Which statement is true of all atoms that are anions?
A) The
atom has more electrons than protons.
B) The atom has more
protons than electrons.
C) The atom has fewer protons than does
a neutral atom of the same element.
D) The atom has more
neutrons than protons.
E) The net charge is 1-.
Answer: A
Which of the following statements correctly describes any chemical
reaction that has reached equilibrium?
A) The concentrations of
products and reactants are equal.
B) The reaction is now
irreversible.
C) Both forward and reverse reactions have halted.
D) The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
E) No reactants remain.
Answer: D
We can represent atoms by listing the number of protons, neutrons,
and electrons: for example,
2p⁺; 2n⁰; 2e⁻ for helium. Which of
the following represents the 18O isotope of oxygen?
A) 6p⁺, 8n⁰,
6e⁻
B) 8p⁺, 10n⁰, 8e⁻
C) 9p⁺, 9n⁰, 9e⁻
D) 7p⁺, 2n⁰,
9e⁻
E) 10p⁺, 8n⁰, 9e⁻
Answer: B
The atomic number of sulfur is 16. Sulfur combines with hydrogen by
covalent bonding to form a compound, hydrogen sulfide. Based on the
number of valence electrons in a sulfur atom, predict the molecular
formula of the compound:
A) HS
B) HS₂
C) H₂S
D) H₃S₂
E) H₄S
Answer: C
What coefficients must be placed in the following blanks so that all
atoms are accounted for in the products?
C₆H₁₂O₆ → ____ C₂H₆O +
____ CO₂
A) 1; 2
B) 3; 1
C) 1; 3
D) 1; 1
E) 2; 2
Answer: E