1) In a well-fed human eating a Western diet, the richest source of
stored chemical energy in the body is
A) fat in adipose tissue.
B) glucose in the blood.
C) protein in muscle cells.
D) glycogen in muscle cells.
E) calcium phosphate in bone.
Answer: A
2) Animals that migrate great distances would obtain the greatest
energetic benefit of storing chemical energy as
A) proteins.
B) minerals.
C) carbohydrates.
D) amino acids.
E) fats.
Answer: E
3) Certain nutrients are considered "essential" in the
diets of some animals because
A) only those animals use those
nutrients.
B) the nutrients are subunits of important polymers.
C) these animals are not able to synthesize these nutrients.
D) the nutrients are necessary coenzymes.
E) only certain
foods contain them.
Answer: C
4) To maintain adequate nutrition, animals require dietary access to
certain amino acids. An amino acid that is referred to as
"nonessential" would be best described as one that
A)
can be made by the animal's body from other substances.
B) is
not used by the animal in biosynthesis.
C) must be ingested in
the diet.
D) is not readily absorbed by the gastrointestinal
tract.
E) is not found in many proteins.
Answer: A
5) Which pair correctly associates a physiological process with the
appropriate vitamin?
A) blood clotting and vitamin C
B)
normal vision and vitamin A
C) synthesis of cell membranes and
vitamin D
D) protection of skin from cancer and vitamin E
E) production of white blood cells and vitamin K
Answer: B
6) The fat-soluble vitamins include
A) vitamin A.
B)
vitamin B12.
C) vitamin C.
D) iodine.
E) calcium.
Answer: A
7) Which pair correctly associates a biochemical process with the
appropriate mineral associated with its use in animals?
A)
maintenance of bone and calcium
B) cofactor in enzymes that make
ATP and magnesium
C) thyroid hormone synthesis and iron
D)
nucleic acid synthesis and sulfur
E) glucose homeostasis and iodine
Answer: A
8) A general rule relating the capacity of a specific animal's
digestive system to provide adequate access to substrates for
biosynthesis of cellular components, as well as fuel molecules needed
for ATP production, is that the animal should have access to
A)
a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet.
B) a diet low in lipids
and high in protein.
C) a low-calorie diet with a large intake
of fluids, especially water.
D) a diet that matches the
"food pyramid" for the species.
E) a diet that
maximizes vitamins and minerals.
Answer: D
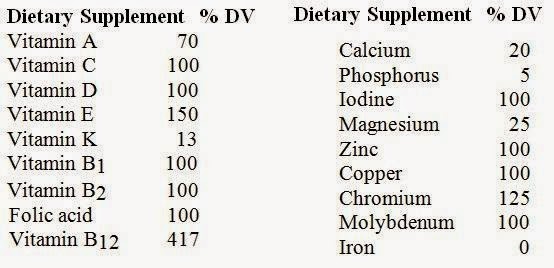
Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
9) The most likely reason that some of the vitamins and minerals
in this supplement are found at less than 100% is
A) that it
would be chemically impossible to add more.
B) these vitamins
and minerals are too large in size to reach 100%.
C) it is too
easy to overdose on minerals such as phosphorus and calcium.
D)
it is dangerous to overdose on fat-soluble vitamins such as A and K.
E) these supplements are meant for those who have been deprived
of healthy foods.
Answer: D

Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
10) A mineral that is especially important for preventing anemia
is
A) zinc.
B) iron.
C) iodine.
D) molybdenum.
E) folic acid.
Answer: B

Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
11) Folic acid supplements have become especially important for
pregnant women because
A) folic acid supplies vitamins that only
pregnant women can use.
B) the folic acid is stored in adipose
tissue by pregnant women so supplements are needed to make more
available in the circulation.
C) the fetus makes high levels of
folic acid.
D) folic acid deprivation is associated with neural
tube abnormalities in a fetus.
E) folic acid deprivation is a
cause of heart abnormalities in a newborn.
Answer: D

Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
12) Excessive iron absorption and accumulation to toxic levels
is associated with
A) excessive blood volume.
B) a liver
abnormality that results in a decreased number of red blood cells.
C) various forms of inherited or acquired anemia.
D) the
genetic disorder known as hemochromatosis.
E) menstruation and menopause.
Answer: D

Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
13) Fat digestion yields fatty acids and glycerol, whereas
protein digestion yields amino acids; both digestive processes
A) are catalyzed by the same enzyme.
B) are excludible
intracellular processes in most organisms.
C) add a water
molecule to break bonds (hydrolysis).
D) require the presence of
hydrochloric acid to lower the pH.
E) require ATP as an energy source.
Answer: C

Use the following table showing the contents of a multivitamin
supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (DV) to
answer the following questions.
14) Ingested dietary substances must cross cell membranes to be
used by the body, a process known as
A) ingestion.
B)
digestion.
C) hydrolysis.
D) absorption.
E) elimination.
Answer: D
15) In marine sponges, intracellular digestion of peptides is usually
immediately preceded by
A) hydrolysis.
B) endocytosis.
C) absorption.
D) elimination.
E) secretion.
Answer: B
16) The large surface area in the gut directly facilitates
A)
secretion.
B) absorption.
C) elimination.
D)
filtration
E) temperature regulation.
Answer: B
17) An advantage of a complete digestive system over a gastrovascular
cavity is that the complete system
A) excludes the need for
extracellular digestion.
B) allows specialized functions in
specialized regions.
C) allows digestive enzymes to be more
specific.
D) allows extensive branching.
E) facilitates
intracellular digestion.
Answer: B
18) Earthworms, grasshoppers, and birds all have a
A) gastric
cecae.
B) larynx.
C) crop.
D) pharynx.
E) epiglottis.
Answer: C
19) Because the foods eaten by animals are often composed largely of
macromolecules, this requires the animals to have mechanisms for
A) elimination.
B) dehydration synthesis.
C)
enzymatic hydrolysis.
D) regurgitation.
E) demineralization.
Answer: C
20) In the digestive system, peristalsis is
A) a process of fat
emulsification in the small intestine.
B) voluntary control of
the rectal sphincters regulating defecation.
C) the transport of
nutrients to the liver through the hepatic portal vessel.
D) a
common cause of loss of appetite, fatigue, and dehydration.
E)
smooth muscle contractions that move food along the esophagus.
Answer: E
21) After ingestion by humans, the first category of macromolecules
to be chemically digested by enzymes in the mouth is
A)
proteins.
B) carbohydrates.
C) cholesterol and other
lipids.
D) nucleic acids.
E) minerals.
Answer: B
22) Salivary amylase digests
A) protein.
B) starches.
C) monosaccharides.
D) glucose.
E) maltose.
Answer: B
23) Among mammals, it is generally true that
A) all types of
foods begin their enzymatic digestion in the mouth.
B) after
leaving the oral cavity, the bolus enters the larynx.
C) the
epiglottis prevents swallowed food from entering the trachea.
D)
the esophagus is a key source of digestive enzymes.
E) the
trachea leads to the esophagus and then to the stomach.
Answer: C
24) Digestive secretions with a pH of 2 are characteristic of the
A) small intestine.
B) stomach.
C) pancreas.
D) liver.
E) mouth.
Answer: B
25) Pepsin is a digestive enzyme that
A) is manufactured by the
pancreas.
B) helps stabilize fat-water emulsions.
C)
splits maltose into monosaccharides.
D) begins the hydrolysis of
proteins in the stomach.
E) is denatured and rendered inactive
in solutions with low pH.
Answer: D
26) Upon activation by stomach acidity, the secretions of the
parietal cells
A) initiate the digestion of protein in the
stomach.
B) initiate the mechanical digestion of lipids in the
stomach.
C) initiate the chemical digestion of lipids in the
stomach.
D) include pepsinogen.
E) delay digestion until
the food arrives in the small intestine.
Answer: A
27) The bile salts
A) are enzymes.
B) are manufactured by
the pancreas.
C) emulsify fats in the duodenum.
D)
increase the efficiency of pepsin action.
E) are normally an
ingredient of gastric juice.
Answer: C
28) Complex nutrients are digested and then absorbed into the lymph
or bloodstream as
A) disaccharides.
B) polymers.
C)
monomers.
D) enzymes.
E) peptides.
Answer: C
29) An enzyme with high activity in an acidic environment is
A)
amylase.
B) pepsin.
C) gastrin.
D) trypsin.
E) sucrose.
Answer: B
30) The absorption of fats differs from that of carbohydrates in that
the
A) processing of fats does not require any digestive
enzymes, whereas the processing of carbohydrates does.
B) fat
absorption occurs in the stomach, whereas carbohydrates are absorbed
from the small intestine.
C) carbohydrates need to be emulsified
before they can be digested, whereas fats do not.
D) most
absorbed fat first enters the lymphatic system, whereas carbohydrates
directly enter the blood.
E) fats, but not carbohydrates, are
digested by bacteria before absorption.
Answer: D
31) A nutritional monomer that can be transported in the blood after
a typical meal is
A) sucrose.
B) maltose.
C) fatty
acid.
D) dipeptide.
E) trinucleotide.
Answer: C
32) For a nondiabetic person, the glucose concentration in this part
of the vasculature varies more than in any other part.
A)
abdominal artery
B) coronary arteries
C) pulmonary veins
D) hepatic portal vessel
E) jugular vein
Answer: D
33) Glandular secretions that are released initially as inactive
precursors of digestive enzymes are the
A) protein-digesting
enzymes.
B) fat-solubilizing bile salts.
C)
acid-neutralizing bicarbonate.
D) carbohydrate-digesting
enzymes.
E) hormones such as gastrin.
Answer: A
34) Because adult lampreys attach onto the surface of large fish for
long periods of time to feed on body fluids, they can accomplish
nutritional balance without need for a
A) liver.
B)
pancreas.
C) intestine.
D) stomach.
E) gallbladder.
Answer: D
35) Constipation can result from the consumption of a substance that
A) contains plenty of fiber.
B) promotes water
reabsorption in the large intestine.
C) speeds up movement of
material in the large intestine.
D) decreases water reabsorption
in the small intestine.
E) stimulates peristalsis.
Answer: B
36) Historically inaccurate diagnosis of acid reflux disorders and
gastric ulcers has been improved by
A) pH monitoring.
B)
X-ray technology.
C) the diagnosis and treatment of H. pylori
infection.
D) colonoscopy.
E) sonography.
Answer: C
37) A hiatal hernia that disrupts the functional relationship between
the smooth muscle in the esophagus and that in the stomach would be
most likely to increase the frequency of
A) gastric reflux.
B) premature entry of food into the duodenum.
C) excess
secretion of pepsinogen.
D) increased stomach pH.
E)
retention of food in the stomach.
Answer: A
38) A significant contribution of intestinal bacteria to human
nutrition is the benefit of bacterial
A) production of vitamins
A and C.
B) generation of gases needed for elimination.
C)
absorption of organic materials.
D) production of vitamin K.
E) recovery of water from fecal matter.
Answer: D
39) The cells that secrete acidic fluid in the stomach are
A)
the chief cells of the stomach.
B) the parietal cells of the
stomach.
C) not needed for the transformation of pepsinogen to
pepsin.
D) in the lumen of the stomach.
E) adding
secretions along the esophagus.
Answer: D
40) Stomach cells are moderately well adapted to the acidity and
protein-digesting activities in the stomach by having
A) a
sufficient colony of H. pylori.
B) a thick, mucous secretion and
active mitosis of epithelial cells.
C) a high level of secretion
by chief cells.
D) a high level of secretion from parietal
cells.
E) secretions enter the stomach from the pancreas.
Answer: B
41) The molar teeth of herbivorous mammals are especially effective
at
A) cutting.
B) ripping.
C) grinding.
D)
splitting.
E) piercing.
Answer: C
42) A group of animals among which a relatively long cecum is likely
to be found is the
A) carnivores.
B) herbivores.
C)
autotrophs.
D) heterotrophs.
E) omnivores.
Answer: D
43) The adaptations suited to a carnivorous diet include
A)
broad, flat molars.
B) a rumen.
C) ingestion of feces.
D) bile salts.
E) amylase.
Answer: B
44) Cattle are able to survive on a diet consisting almost entirely
of plant material because
A) they are autotrophic.
B)
cattle, like rabbits, re-ingest their feces.
C) they manufacture
all 15 amino acids out of sugars in the liver.
D) cattle saliva
has enzymes capable of digesting cellulose.
E) they have
cellulose-digesting, symbiotic microorganisms in chambers of their stomachs.
Answer: E
45) Analysis of jawbones from the skeletal remains of a vertebrate
animal reveal its dietary patterns owing to
A) the position of
muscle attachment sites.
B) the prevalence of specific kinds of
teeth.
C) the size of the mouth opening.
D) the evidence
of food molecules still present.
E) whether the mouth is the
most anterior structure.
Answer: B
46) An enlarged cecum is typical of
A) rabbits, horses, and
herbivorous bears.
B) carnivorous animals.
C) tubeworms
that digest via symbionts.
D) humans and other primates.
E) tapeworms and other intestinal parasites.
Answer: A
47) Coprophagy, the nutrition-boosting ingestion of fecal material,
is important for the nutritional balance of
A) ruminants such as
cows.
B) insects and arthropods.
C) rabbits and their
relatives.
D) squirrels and some rodents.
E) very large
animals, such as elephants.
Answer: C
48) PKU (phenylketonuria) is a hereditary condition in which infants
and young children who ingest the amino acid phenylalanine risk
serious neurological damage. However, the risk of damage can be
substantially reduced by the severe restriction of phenylalanine in
the diet. Which of the following is the nutritional concept that forms
the basis for this preventive treatment?
A) enzymatic hydrolysis
B) essential nutrients
C) symbiosis
D) dehydration
synthesis
E) structural anatomy of the brain
Answer: B
49) When the digestion and absorption of organic molecules results in
more energy-rich molecules than are immediately required by an animal,
the excess is
A) eliminated in the feces.
B) stored as
starch in the liver.
C) stored as glycogen in the liver and
muscles.
D) oxidized and converted to ATP.
E) hydrolyzed
and converted to ADP.
Answer: C
50) Hypoglycemia, or low levels of glucose in the blood of a healthy
human, is "corrected" by a(n)
A) increase in the
secretion of insulin.
B) increase in the secretion of glucagon.
C) increase in the secretion of both insulin and glucagon.
D) decrease in the secretion of both insulin and glucagon.
E) increase in the secretion of thyroid hormones.
Answer: B
51) A fasting animal whose energy needs exceed those provided in its
diet draws on its stored resources in which order?
A) fat, then
glycogen, then protein
B) glycogen, then protein, then fat
C) liver glycogen, then muscle glycogen, then fat
D)
muscle glycogen, then fat, then liver glycogen
E) fat, then
protein, then glycogen
Answer: C
52) Obesity in humans is most clearly linked to
A) type 1
diabetes and prostate cancer.
B) type 1 diabetes and breast
cancer.
C) type 2 diabetes and muscle hypertrophy.
D) type
2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
E) type 2 diabetes and
decreased appetite.
Answer: D
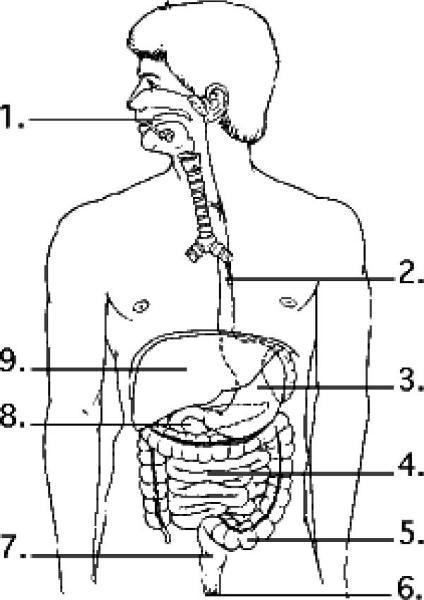
53) Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. The
agents that help emulsify fats are produced in
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 8
E) 9
Answer: E

54) Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. The
highest rate of nutrient absorption occurs at location(s)
A) 3
only.
B) 4 only.
C) 1 and 4.
D) 3 and 4.
E) 1,
3, and 4.
Answer: B

55) Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. Most
of the digestion of fats occurs in section(s)
A) 3 only.
B) 4 only.
C) 1 and 4.
D) 3 and 4.
E) 1, 3,
and 4.
Answer: B

56) Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above.
Bacteria that produce vitamins as products are residents of location
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 7.
E) 8.
Answer: C
Mouse mutations can affect an animal's appetite and eating habits.
The ob gene codes for a satiety factor, the hormone leptin. The db
gene product, the leptin receptor, is required to respond to the
satiety factor.
57) Leptin is a product of adipose cells. Therefore, a very
obese mouse would be expected to have
A) increased gene
expression of ob and decreased expression of db.
B) increased
gene expression of db and decreased expression of ob.
C)
decreased transcription of both ob and db.
D) mutation of ob or db.
Answer: D
Mouse mutations can affect an animal's appetite and eating habits.
The ob gene codes for a satiety factor, the hormone leptin. The db
gene product, the leptin receptor, is required to respond to the
satiety factor.
58) Many obese humans produce normal or increased levels of
leptin without satiety, so the search for healthy regulation of food
intake should focus on
A) providing supplementary leptin.
B) inactivation of leptin.
C) overexpression of the leptin
receptor gene.
D) eliminating carbohydrates from the diet.
E) inhibition of leptin receptors.
Answer: D
59) Which of the following animals is incorrectly paired with its
feeding mechanism?
A) lionsubstrate feeder
B) baleen
whalesuspension feeder
C) aphidfluid feeder
D)
clamsuspension feeder
E) snakebulk feeder
Answer: A
60) The mammalian trachea and esophagus both connect to the
A)
large intestine.
B) stomach.
C) pharynx.
D) rectum.
E) epiglottis.
Answer: C
61) Which of the following organs is incorrectly paired with its
function?
A) stomachprotein digestion
B) oral
cavitystarch digestion
C) large intestinebile production
D) small intestinenutrient absorption
E) pancreasenzyme production
Answer: C
62) Which of the following is not a major activity of the stomach?
A) mechanical digestion
B) HCl secretion
C) mucus
secretion
D) nutrient absorption
E) enzyme secretion
Answer: D
63) After surgical removal of an infected gallbladder, a person must
be especially careful to restrict dietary intake of
A) starch.
B) protein.
C) sugar.
D) fat.
E) water.
Answer: D
64) If you were to jog 1 km a few hours after lunch, which stored
fuel would you probably tap?
A) muscle proteins
B) muscle
and liver glycogen
C) fat stored in the liver
D) fat
stored in adipose tissue
E) blood proteins
Answer: B