Cleavage

The rapid mitotic division of the zygote, starting the first week of development
Blastomeres
Progressively smaller cells produced by cleavage
Morula

A solid ball of cells formed 3-4 days after fertilization
Blastocyst
- A fluid filled ball of cells that enters the uterine cavity
- Occurs a day after the morula is formed
Implantation
The attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrium 6–8 days after fertilization
Inner cell mass

- Where the blastocyst attaches to the endometrium
- Embryoblast
How does the endometrium respond to the blastocyst
- Becomes more vascularized
- Endometrial glands enlarge
Decidua
The portion of the endometrium that is modified after implantation
Week One - 12-24 hours after ovulation
Fertilization
Week One - 30 hours after fertilation
Cleavage
Week One - 3-4 Days after fertilization
Morula
Week One - 4 1/2 - 5 days after fertilization
Blastocyst enters uterine cavity
Week One - 6 days after fertilization

Implantation
Trilaminar embryonic disc
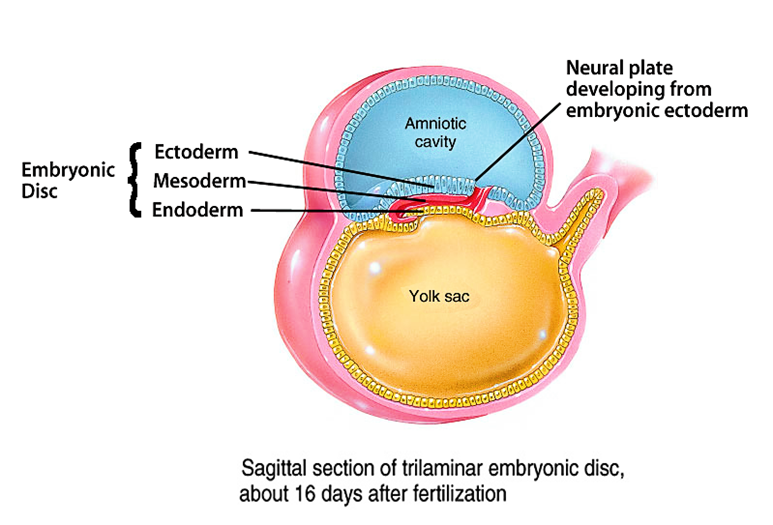
- Formed during growth of developing embryo
- Composed of cells which develop to become the fetus
- visible 3 weeks post-fertilization
Three primary germ layers of Trilaminar embryonic disc

- The ectoderm is the superficial layer
- The mesoderm is in the middle
- The endoderm forms the inner layer
Ectoderm
- The superficial layer of the Trilaminar embryonic disc
- Differentiates into the tissues of the brain and nerves, and the epidermis of the skin
Mesoderm
- The middle layer of the Trilaminar embryonic disc
- Matures to form blood, muscles, bones, and other connective tissue derivatives
Endoderm
- The inner layer of the Trilaminar embryonic disc
- Gives rise to the epithelial lining of the digestive tract, respiratory tract, and several other organs; also the endothelial lining of blood vessels
Extraembryonic membranes

Formed during growth of developing embryo
- amnion - Innermost layer
- yolk sac
- allantois
- chorion - Outermost layer
Amnion
- Innermost Extraembryonic membrane
- Forms a protecting amniotic cavity (filled with amniotic fluid) around the embryo
Yolk sac
- Layer of Extraembryonic membrane
- Provides nutrients and becomes the site of early blood formation
Allantois
- Layer of Extraembryonic membrane
- Helps form the umbilical cord, works gas exchange and waste removal
Chorion
- Outermost layer of Extraembryonic membrane
- Forms the fetal portion of the placenta and takes over production of hCG
Where does the placenta develop from

The chorionic villi of the embryo and endometrium of the mother
What is managed in the placenta
- Nutrients and wastes are managed
- Mixing of fetal and mothers blood is prevented
What hormone secretion is taken over by the placenta
Occurs as the corpus luteum in the ovary gradually atrophies.
- hCG
- estrogen
- progesterone
Organogenesis

The 4th-8th weeks of development
When does embryonic folding occurs (head, laterals, tail)
During week 4
When have all major body systems started to develop
By the end of week 8