Which of these is a correct representation of the hierarchy of biological organization from least to most organization?
A) organelle of an intestinal cell, digestive system, small
intestine, large intestine, intestinal tissue, organism
B)
molecule, intestinal cell organelle, intestinal cell, intestinal
tissue, digestive system, organism
C) organelle of a stomach
cell, digestive system, small intestine, large intestine, intestinal
tissue, organism
D) molecule, small intestine, large intestine,
intestinal tissue, digestive system, organization
B
Circulatory systems compensate for _____.
A) the slow rate at which diffusion occurs over large
distances
B) temperature differences between the lungs and the
active tissue
C) the need to cushion animals from trauma
D)
the problem of communication systems involving only the nervous system
D
Organisms with a circulating body fluid that is distinct from the
fluid that directly surrounds the body's cells are likely to have
A) an open circulatory system.
B) a closed circulatory
system.
C) a gastrovascular cavity.
D) branched tracheae.
B
To adjust blood pressure independently in the capillaries of the
gas-exchange surface and in the capillaries of the general body
circulation, an organism would need a(n)
A) open circulatory
system.
B) hemocoel.
C) lymphatic system.
D)
four-chambered heart.
D
Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow in
reptiles and mammals?
A) left ventricle → aorta → lungs →
systemic circulation
B) right ventricle → pulmonary vein →
pulmocutaneous circulation
C) pulmonary vein → left atrium →
left ventricle → pulmonary circuit
D) vena cava → right atrium →
right ventricle → pulmonary circuit
D
If a molecule of CO₂ released into the blood in your left toe is
exhaled from your nose, it must pass through all of the following
except
A) the pulmonary vein.
B) an alveolus.
C) the
trachea.
D) the right atrium.
A
Which of the following develops the greatest pressure on the blood in
the mammalian aorta?
A) systole of the left atrium
B)
diastole of the right ventricle
C) systole of the left ventricle
D) diastole of the right atrium
C
To become bound to hemoglobin for transport in a mammal, atmospheric
molecules of oxygen must cross
A) zero membranesoxygen binds
directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the plasma of the
blood.
B) one membranethat of the lining in the lungsand then
bind directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the plasma of the
blood.
C) two membranesin and out of the cell lining the
lungand then bind directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the
plasma of the blood.
D) five membranesin and out of the cell
lining the lung, in and out of the endothelial cell lining the
pulmonary capillary, and into the red blood cellto bind with hemoglobin.
D
Small swollen areas in the neck, groin, and axillary region are
associated with
A) increased activity of the immune system.
B) a broken limb.
C) blood sugar that is abnormally high.
D) dehydration.
A
You cut your finger, and after putting pressure on the wound for several minutes, you notice that it is still bleeding profusely. What may be the problem?
A) There are too many antigens to allow clotting.
B)
Hemoglobin levels are too high to allow clotting.
C) Mast cells
are not releasing their chemical messengers.
D) Platelets are
not functioning properly, or there are too few to be effective.
D
A normal event in the process of blood clotting is the
A)
production of erythropoietin.
B) conversion of fibrin to
fibrinogen.
C) activation of prothrombin to thrombin.
D)
increase in platelets.
C
Innate immunity
A) is activated immediately upon infection.
B) depends on a newly infected animal's previous exposure to the
same pathogen.
C) is based on recognition of antigens that are
specific to different pathogens.
D) is found only in vertebrate animals.
A
Engulfing-phagocytic cells of innate immunity include
I) neutrophils.
II) macrophages.
III) dendritic cells.
IV) natural killer cells.
A) I and III
B) II and IV
C) I, II, and III
D) I and IV
C
Acidity in human urine is an example of
A) cell-mediated immune
responses.
B) antibody activation.
C) innate immunity.
D) adaptive immunity.
C
A boy falls while riding his bike. A scrape on his hand almost immediately begins to bleed and becomes red, warm, and swollen. What response is occurring?
A) autoimmune response
B) lytic response
C) adaptive
immune response
D) inflammatory response
D
Inflammatory responses typically include
A) clotting proteins
migrating away from the site of infection.
B) increased activity
of phagocytes in an inflamed area.
C) reduced permeability of
blood vessels to conserve plasma.
D) release of substances to
decrease the blood supply to an inflamed area.
B
The cells and signaling molecules that initiate inflammatory
responses are
A) the phagocytes and the lysozymes.
B) the
phagocytes and the chemokines.
C) the dendritic cells and the
interferons.
D) the mast cells and the histamines.
D
Mammals have Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that can recognize a kind of
macromolecule that is absent from vertebrates but present in/on
certain groups of pathogens, including viral
A)
lipopolysaccharides.
B) double-stranded DNA.
C)
double-stranded RN
C
The cells involved in innate immunity, whose absence increases the
chances of developing malignant tumors, are
A) cytotoxic T
cells.
B) natural killer cells.
C) helper T cells.
D) macrophages
B
You and a friend were in line for a movie when you noticed the woman in front of you sneezing and coughing. Both of you were equally exposed to the woman's virus, but over the next few days, only your friend acquired flu-like symptoms and was ill for almost a week before recovering. Which one of the following is a logical explanation for this?
A) Your friend had antibodies to that virus.
B) You had an
adaptive immunity to that virus.
C) Your friend had an autoimmune
disorder.
D) Your friend had allergies.
B
what major advantage is conveyed by having a system of adaptive immunity?
A) It results in effector cells with specificity for a large number
of antigens.
B) It allows for the destruction of
antibodies.
C) It enables a rapid defense against an antigen that
has been previously encountered.
D) It enables an animal to
counter most pathogens almost instantly the first time they are encountered
C
Vaccination increases the number of
A) different receptors that
recognize a pathogen.
B) lymphocytes with receptors that can
bind to the pathogen.
C) epitopes that the immune system can
recognize.
D) macrophages specific for a pathogen.
B
An immunoglobulin (Ig) molecule, of whatever class, with regions
symbolized as C or V, H or L, has a light chain made up of
A)
one C region and one V region.
B) three C regions and one V
region.
C) one H region and one L region.
D) three H
regions and one L region.
A
If a patient is missing B and T cells, what would be absent from the immune response?
A) memory
B) lysozymes
C) defense against
bacteria
D) cytokines
A
Select the pathway that would lead to the activation of cytotoxic T
cells.
A) B cell contact antigen → helper T cell is activated →
clonal selection occurs
B) body cell becomes infected with a
virus → new viral proteins appear → class I MHC molecule-antigen
complex displayed on cell surface
C) self-tolerance of immune
cells → B cells contact antigen → cytokines released
D)
complement is secreted → B cell contacts antigen → helper T cell activated
B
This type of immunity is present only when a newborn infant is being
fed by actively nursing on its mother and ends when nursing ends.
A) innate immunity
B) active immunity
C) passive
immunity
D) cell-mediated immunity
C
A patient complaining of watery, itchy eyes and sneezing after being
given a flower bouquet as a birthday gift should first be treated with
A) a vaccine.
B) complement.
C) sterile pollen.
D) antihistamines.
D
Which of the following would prevent allergic attacks?
A) blocking the attachment of the IgE antibodies to the mast
cells
B) blocking the antigenic determinants of the IgM
antibodies
C) reducing the number of helper T cells in the
body
D) reducing the number of cytotoxic cells
A
Which of the following is the best definition of autoimmune
disease?
A) a condition in which B cells and T cells
respond independently to antigens and do not interact
correctly
B) a condition in which the adaptive immune system
fails to recognize the second infection by the same antigen
C) a
condition in which self molecules are treated as non-self
D) a
condition in which the immune system creates random antibodies
without being triggered by an antigen
A
Which of the following is a type of local signaling in which a cell secretes a signal molecule that affects neighboring cells?
A) hormonal signaling
B) autocrine signaling
C) paracrine signaling
D) synaptic signaling
C
A cluster of tumor cells that produces and secretes growth factors to
induce surrounding cells to grow and divide are showing which type of
cell-to-cell signaling?
A. autocrine
B. paracrine
C.
endocrine
D. neuroendocrine
B

Which of the following types of signaling is represented in the
figure?
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) hormonal
D) synaptic
D
What is the only type of chemical signal that does not alter the physiology of the animal producing the signal?
A) pheromones
B) paracrine
C) neuroendocrine
D) neural
A
What property of steroid hormones allows them to cross the phospholipid bilayer?
A) Steroid hormones act on cells close to where they were produced
and very few molecules are required to travel such a short distance to
cross the lipid bilayer.
B) Steroid hormones are lipid soluble
and easily cross the phospholipid bilayer.
C) Steroid hormones
can act in very small concentrations and very few molecules of
steroids need to cross the lipid bilayer.
D) Steroid hormones
act on the same cells in which they are produced
B
Testerone functions inside a cell by
A) coordinating a phosphorylation cascade that increase
spermatogenesis
B) binding with a receptor protein that enters
the nucleus and activates specific gene
C) acting as a steroid
signal receptor that activates ion channel proteins
D) acting as
a signal receptor that activates tyrosine kinases
B
The reason that the steroid hormone aldosterone affects only a small number of cell in the body is that _____.
A) It is unable to enter nontarget cells.
B) only its target
cells contain aldosterone receptors
C) only its target cell gets
exposed to aldosterone
D) nontarget cells destroy aldosterone
before it can produce any effect
B
Tadpoles must undergo a major metamorphosis to become frogs. This change includes reabsorption of the tail, growth of limbs, calcification of the skeleton, increase in rhodopsin in the eye, development of lungs, change in hemoglobin structure, and reformation of the gut from the long gut of an herbivore to the short gut of a carnivore. Amazingly, all of these changes are induced by thyroxine. What is the most likely explanation for such a wide array of effects of thyroxine?
A) Different tissues have thyroxine receptors that activate
different signal transduction pathways.
B) Some tissues have
membrane receptors, while other tissues have thyroxine receptors
within the nucleus
C) There are many different forms of
thyroxine, each specific to a different tissue
D) Different
releasing hormones release thyroxine to different tissues.
A
If a biochemist discovers a new molecule, which of the following pieces of data would allow her to draw the conclusion that the molecule is a steroid hormone?
I) The molecule is lipid soluble.
II) The molecule is derived
from a series of steps beginning with cholesterol.
III) The
molecule acts at a target tissue some distance from where it is
produced.
IV) The molecule uses a carrier protein when in an
aqueous solution such as blood
A) II and IV
B) I, III, IV
C) I, III
D) I, II, III, IV
D
The steroid hormone that coordinates molting in arthropods is
A) ecdysteroid
B) glucagon.
C) thyroxine.
D) oxytocin.
A
Insect hormones and their receptors
A) act independently of
each other.
B) are a focus in pest-control research.
C)
utilize cell-surface receptors only.
D) are active independently
of environmental cues.
B
During mammalian labor and delivery, the contraction of uterine
muscles is enhanced by oxytocin. This is an example of
A) a
negative feedback system.
B) a hormone that acts in an
antagonistic way with another hormone.
C) a hormone that is
involved in a positive feedback loop.
D) signal transduction
immediately changing gene expression in its target cells.
C
When a person gets dehydrated while exercising on a hot day, their
pituitary gland releases ADH, a hormone that signals the kidneys to
retain more water. This is an example of
A) emergent
properties
B) chemical cycling
C) positive feedback
regulation
D) negative feedback regulation
D
An example of antagonistic hormones controlling homeostasis is
A) thyroxine and parathyroid hormone in calcium balance.
B) insulin and glucagon in glucose metabolism.
C)
progestins and estrogens in sexual differentiation.
D)
epinephrine and norepinephrine in fight-or-flight responses.
B
Which endocrine disorder is correctly matched with the malfunctioning
gland?
A) diabetes insipidus and the posterior pituitary gland
B) giantism and the posterior pituitary gland
C) goiter
and the thyroid gland
D) diabetes mellitus and the parathyroid glands
C
Fight-or-flight reactions include activation of
A) the
parathyroid glands, leading to increased metabolic rate.
B) the
thyroid gland, leading to an increase in the blood calcium
concentration.
C) the anterior pituitary gland, leading to
cessation of gonadal function.
D) the adrenal medulla, leading
to increased secretion of epinephrine.
D
If a person loses a large amount of water in a short period of time,
he or she may die from dehydration. ADH can help reduce water loss
through its interaction with its target cells in the
A) anterior
pituitary.
B) posterior pituitary.
C) adrenal gland.
D) kidney
D
The force driving simple diffusion is _____, while the energy source for active transport is _____.
A) the concentration gradient; ADP
B) the concentration gradient; ATP
C) transmembrane pumps; electron transport
D) phosphorylated protein carriers; ATP
B
When a person drinks alcohol, the rate of urination increases. This suggests that ADH may be affected by alcohol consumption in some way. Which of the following best accounts for the increase in urination?
A)
B)
C)
D)
D
The body fluids of an osmoconformer would be ________ with its
________ environment.
A) hyperosmotic; freshwater
B)
isotonic; freshwater
C) hyperosmotic; saltwater
D)
isoosmotic; saltwater
D
The fluid with the highest osmolarity is
A) distilled water.
B) plasma in birds.
C) plasma in mammals.
D)
seawater in a tidal pool.
D
n animals, nitrogenous wastes are produced mostly from the catabolism
of
A) starch and cellulose.
B) triglycerides and steroids.
C) proteins and nucleic acids.
D) phospholipids and glycolipids.
C
The advantage of excreting nitrogenous wastes as urea rather than as
ammonia is that
A) urea can be exchanged for Na+.
B) urea
is less toxic than ammonia.
C) urea requires more water for
excretion than ammonia.
D) urea does not affect the osmolar gradient.
B
Which nitrogenous waste has the greatest number of nitrogen atoms?
A) ammonia
B) ammonium ions
C) urea
D) uric acid
D

Which of the following is synthesized by mammals, most amphibians,
sharks, and some bony fishes, and has lower toxicity than its
nitrogenous substrate?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B
Birds secrete uric acid as their nitrogenous waste because uric acid
A) is readily soluble in water.
B) is metabolically less
expensive to synthesize than other excretory products.
C)
requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, thus reducing
body mass.
D) excretion allows birds to live in desert environments.
C
Which process in the nephron is least selective?
A) filtration
B) reabsorption
C) active transport
D) secretion
A
Choose a pair that correctly associates the mechanism for osmoregulation or nitrogen removal with the appropriate animal.
A) metanephridium - flatworm
B) flame bulb - sponge
C)
exchange across the body surface - marine invertebrate
D)
malpighian tubule - clam
C
Materials are returned to the blood from the filtrate by which of the
following processes?
A) filtration
B) ultrafiltration
C) selective reabsorption
D) secretion
C
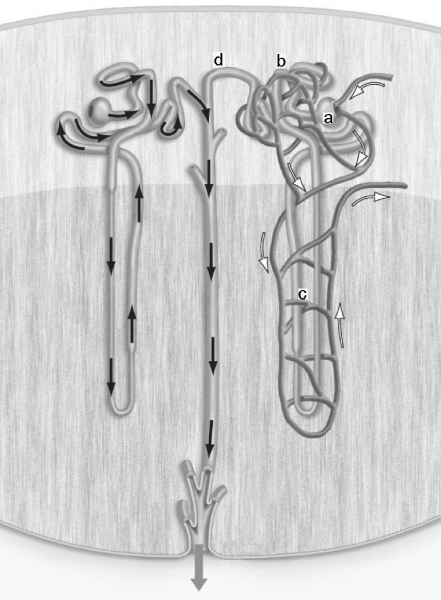
The figure above shows a nephron. Filtration takes place in the structure labeled _____.
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
A
A primary reason that the kidneys have one of the highest metabolic
rates of all body organs is that
A) it stores the body's excess
fats.
B) it has membranes of varying permeability to water.
C) it operates an extensive set of active-transport ion pumps.
D) it is the body's only means of shedding excess nutrients.
C
What is the function of the osmotic gradient found in the kidney? The osmotic gradient allows for ________.
A) the filtration of large cells at the glomerulus
B)
electrolytes to move from low to high concentration in the absence of
ATP
C) the precise control of the retention of water and
electrolytes
D) the loop of Henle to deliver water to the renal vein.
C
The loop of Henle dips into the renal cortex. This is an important feature of osmoregulation in terrestrial vertebrates because _______.
A) the loop of Henle plays an important role in
detoxification
B) differential permeabilities of ascending and
descending limbs of the loop of Henle are important in establishing an
osmotic gradients
C) additional filtration takes place along the
loop of Henle
D) absorptive processes taking place in the loop
of Henle are hormonally regulated
B
Processing of filtrate in the proximal and distal tubules
A)
achieves the sorting of plasma proteins according to size.
B)
achieves the conversion of toxic ammonia to less toxic urea.
C)
maintains homeostasis of pH in body fluids.
D) regulates the
speed of blood flow through the nephrons.
C
The high osmolarity of the renal medulla is maintained by all of the
following except
A) diffusion of salt from the thin segment of
the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
B) active transport of
salt from the upper region of the ascending limb.
C) the spatial
arrangement of juxtamedullary nephrons.
D) diffusion of salt
from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.
D
Osmoregulatory adjustment via the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
system can be triggered by
A) sleeping for one hour.
B)
severe sweating on a hot day.
C) eating a bag of potato chips.
D) eating a pizza with olives and pepperoni.
B
which of the following aspects of eukaryotic reproduction are found only among invertebrates?
A) Sexual and asexual reproduction
B) external and internal
fertilization
C) hermaphroditism and parthenogenesis
D)
fission and budding
D
In an animal that switches between sexual and asexual reproduction, when is sexual reproduction more likely to occur?
A) when males and females find each other
B) when conditions
for survival are unfavorable
C) when conditions for survival are
favorable
D) what conditions favor sexual over asexual remains a
complete mystery
B
What makes sexually reproduced offspring genetically different from their parents?
A) genetic recombination during mitosis
B) crossing over during mitosis
C) genetic recombination during meiosis
D) sexual reproduction does not produce genetically different offspring
C
which of the following is most true of sexual reproduction?
A) Sexual reproduction is completed more rapidly than asexual
reproduction.
B) Asexual reproduction is better suited to
environments with extremely varying conditions.
C) Asexual
reproduction produces offspring of greater genetic variety.
D)
Only half of the offspring from sexually reproducing females are also females.
D
On a submarine expedition to the ocean bottom, you discover a
population of fish that are only female. What type of reproduction
does this fish likely use.
A) Sexual
B) Budding
C)
Cloning
D. Parthenogenesis
D
Mature human sperm and ova are similar in that
A) they both
have the same number of chromosomes.
B) they are approximately
the same size.
C) they each have a flagellum that provides
motility.
D) they are produced from puberty until death.
A
Human sperm cells first arise in the
A) prostate gland.
B) vas deferens.
C) seminiferous tubules.
D) epididymis.
C

In the above figure, which letter points to the prostate gland?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B

In the above figure, which letter points to the urethra?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) E
D
A male's "primary" sex characteristics include
A)
deepening of the voice at puberty.
B) embryonic differentiation
of the seminal vesicles.
C) growth of skeletal muscle.
D)
elongation of the skeleton prior to puberty.
B
A physician finds that a nine-year-old male patient is entering puberty much earlier than is usual. Such a condition is most likely the result of a tumor in the _____.
A) anterior pituitary, producing elevated levels of
gonadotropin-stimulating hormone
B) testes, producing elevated
levels of estrogen
C) anterior pituitary, producing elevated
levels of testosterone
D) hypothalamus, producing elevated levels
of testerone
A

In the above figure, which letter points to the endometrium?
A)
A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E

In the above figure, which letter points to the corpus luteum?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
D
The primary difference between estrous and menstrual cycles is that
A) the endometrium shed by the uterus during the estrous cycle
is reabsorbed, whereas the shed endometrium of menstrual cycles is
excreted from the body.
B) behavioral changes during estrous
cycles are much less apparent than those of menstrual cycles.
C)
season and climate have less pronounced effects on estrous cycles than
they do on menstrual cycles.
D) copulation normally occurs
across the estrous cycle, whereas in menstrual cycles copulation only
occurs during the period surrounding ovulation.
A
In correct chronological order, the three phases of the human ovarian
cycle are
A) menstrual → ovulation → luteal.
B) follicular
→ luteal → secretory.
C) menstrual → proliferative → secretory.
D) follicular → ovulation → luteal.
D