Mycoplasmas are bacteria that lack cell walls. On the basis of this
structural feature, which
statement concerning mycoplasmas should
be true?
A) They are gram-negative.
B) They are subject to
lysis in hypotonic conditions.
C) They lack a cell membrane as
well.
D) They undergo ready fossilization in sedimentary
rock.
E) They possess typical prokaryotic flagella.
B
Though plants, fungi, and prokaryotes all have cell walls, we place
them in different taxa.
Which of these observations comes closest
to explaining the basis for placing these
organisms in different
taxa, well before relevant data from molecular systematics
became
available?
A) Some closely resemble animals, which
lack cell walls.
B) Their cell walls are composed of very
different biochemicals.
C) Some have cell walls only for
support.
D) Some have cell walls only for protection from
herbivores.
E) Some have cell walls only to control osmotic balance
B
Which is the bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier,
allowing nutrients to enter
the cell and wastes to leave the
cell?
A) plasma membrane
B) capsule
C) cell
wall
D) nucleoid region
E) pili
A
Which statement about bacterial cell walls is false?
A)
Bacterial cell walls differ in molecular composition from plant cell
walls.
B) Cell walls prevent cells from bursting in hypotonic
environments.
C) Cell walls prevent cells from dying in
hypertonic conditions.
D) Bacterial cell walls are similar in
function to the cell walls of many protists, fungi,
and
plants.
E) Cell walls provide the cell with a degree of
physical protection from the environment
C
Which of these is the most common compound in the cell walls of
gram-positive bacteria?
A) cellulose
B)
lipopolysaccharide
C) lignin
D) peptidoglycan
E) protein
D
Penicillin is an antibiotic that inhibits enzymes from catalyzing the
synthesis of
peptidoglycan, so which prokaryotes should be most
vulnerable to inhibition by penicillin?
A) mycoplasmas
B)
gram-positive bacteria
C) archaea
D) gram-negative
bacteria
E) endospore-bearing bacteria
B
The predatory bacterium, Bdellovibrio bacteriophorus, drills into a
prey bacterium and, once
inside, digests it. In an attack upon a
gram-negative bacterium that has a slimy cell
covering which can
inhibit phagocytosis, what is the correct sequence of
structures
penetrated by B. bacteriophorus on its way to the
preyʹs cytoplasm?
1. membrane composed mostly of
lipopolysaccharide
2. membrane composed mostly of
phospholipids
3. peptidoglycan
4. capsule
A) 2 → 4 → 3
→1
B) 1 → 3 → 4 → 2
C) 1 → 4 → 3 → 2
D) 4 → 1 → 3 →
2
E) 4 → 3 → 1 → 2
D
Jams, jellies, preserves, honey, and other foodstuffs with a high
sugar content hardly ever
become contaminated by bacteria, even
when the food containers are left open at room
temperature. This
is because bacteria that encounter such an environment
A) undergo
death by plasmolysis.
B) are unable to metabolize the glucose or
fructose, and thus starve to death.
C) undergo death by
lysis.
D) are obligate anaerobes.
E) are unable to swim
through these thick and viscous materials.
A
In a hypothetical situation, the genes for sex pilus construction and
for tetracycline
resistance are located together on the same
plasmid within a particular bacterium. If this
bacterium readily
performs conjugation involving a copy of this plasmid, then the
result
should be
A) a transformed bacterium.
B) the
rapid spread of tetracycline resistance to other bacteria in that
habitat.
C) the subsequent loss of tetracycline resistance from
this bacterium.
D) the production of endospores among the
bacteriumʹs progeny.
E) the temporary possession by this
bacterium of a completely diploid genome.
B
In a bacterium that possesses antibiotic resistance and the potential
to persist through very
adverse conditions, such as freezing,
drying, or high temperatures, DNA should be located
within, or be
part of, which structures?
1. nucleoid region
2.
flagellum
3. endospore
4. fimbriae
5. plasmids
A)
1 only
B) 1 and 4
C) 1 and 5
D) 1, 3, and 5
E) 2,
4, and 5
D
Which two structures play direct roles in permitting bacteria to
adhere to each other, or to
other surfaces?
1.
capsules
2. endospores
3. fimbriae
4. plasmids
5.
flagella
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and
4
E) 3 and 5
B
The typical prokaryotic flagellum features
A) an internal 9 + 2
pattern of microtubules.
B) an external covering provided by the
plasma membrane.
C) a complex ʺmotorʺ embedded in the cell wall
and plasma membrane.
D) a basal body that is similar in structure
to the cellʹs centrioles.
C
Prokaryotic ribosomes differ from those present in eukaryotic
cytosol. Because of this,
which of the following is
correct?
A) Some selective antibiotics can block protein
synthesis of bacteria without effects on
protein synthesis in the
eukaryotic host.
B) Eukaryotes did not evolve from
prokaryotes.
C) Translation can occur at the same time as
transcription in eukaryotes but not in
prokaryotes.
D) Some
antibiotics can block the synthesis of peptidoglycan in the walls of
bacteria.
E) Prokaryotes are able to use a much greater variety
of molecules as food sources than
can eukaryotes.
A
) Which statement about the genomes of prokaryotes is
correct?
A) Prokaryotic genomes are diploid throughout most of
the cell cycle.
B) Prokaryotic chromosomes are sometimes called
plasmids.
C) Prokaryotic cells have multiple chromosomes,
ʺpackedʺ with a relatively large
amount of protein.
D) The
prokaryotic chromosome is not contained within a nucleus but, rather,
is found at
the nucleoid region.
E) Prokaryotic genomes are
composed of linear DNA (that is, DNA existing in the form
of a
line with two ends)
D
If a bacterium regenerates from an endospore that did not possess any
of the plasmids that
were contained in its original parent cell,
the regenerated bacterium will probably
A) lack
antibiotic-resistant genes.
B) lack a cell wall.
C) lack a
chromosome.
D) lose base pairs from its chromosome.
E) be
unable to survive in its normal environment.
A
Which of the following is composed almost entirely of peptidoglycan?
A) endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D) cell wall
E) capsule
D
Which of the following requires ATP to function, and permits some
species to respond to
taxes (plural of taxis)?
A)
endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D) cell
wall
E) capsule
C
Not present in all bacteria, this cell covering enables cells that
possess it to resist the
defenses of host organisms:
A)
endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D) cell
wall
E) capsule
E
Not present in all bacteria, this structure enables those that
possess it to germinate after
exposure to harsh conditions, such
as boiling:
A) endospore
B) sex pilus
C)
flagellum
D) cell wall
E) capsule
A
Which of the following is a structure that permits conjugation to
occur?
A) endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D)
cell wall
E) capsule
B
Which of the following is an important source of endotoxin in
gram-negative species?
A) endospore
B) sex pilus
C)
flagellum
D) cell wall
E) capsule
D
) If this structure connects the cytoplasm of two bacteria, one of
these cells may gain new
genetic material:
A)
endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D) cell
wall
E) capsule
B
Which of the following contains a copy of the chromosome, along with
a small amount of
dehydrated cytoplasm, within a tough
wall?
A) endospore
B) sex pilus
C) flagellum
D)
cell wall
E) capsule
A
Regarding prokaryotic reproduction, which statement is
correct?
A) Prokaryotes form gametes by meiosis.
B)
Prokaryotes feature the union of haploid gametes, as do
eukaryotes.
C) Prokaryotes exchange some of their genes by
conjugation, the union of haploid
gametes, and
transduction.
D) Mutation is a primary source of variation in
prokaryote populations.
E) Prokaryotes skip sexual life cycles
because their life cycle is too short.
D
Which of these statements about prokaryotes is correct?
A)
Bacterial cells conjugate to mutually exchange genetic
material.
B) Their genetic material is confined within a nuclear
envelope.
C) They divide by binary fission, without mitosis or
meiosis.
D) The persistence of bacteria throughout evolutionary
time is due to their genetic
homogeneity (i.e.,
sameness).
E) Genetic variation in bacteria is not known to
occur, nor should it occur, because of
their asexual mode of reproduction.
C
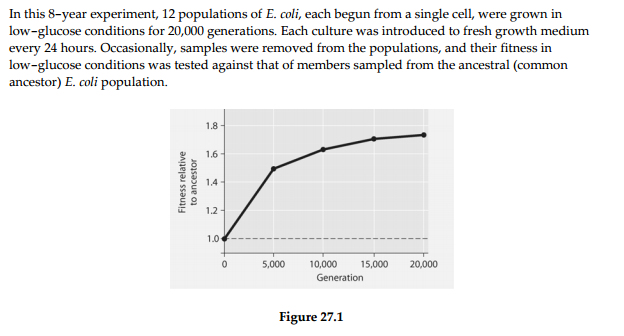
) Which term best describes what has occurred among the experimental
populations of cells
over this 8-year period?
A)
microevolution
B) speciation
C) adaptive radiation
D)
sexual selection
E) stabilizing selection
A

If it occurs in the absence of any other type of adaptation listed
here, which of these is least
reasonable in terms of promoting
bacterial survival over evolutionary time in a
low-glucose
environment?
A) increased efficiency at transporting glucose into
the cell from the environment
B) increased ability to survive on
simple sugars, other than glucose
C) increased ability to
synthesize glucose from amino acid precursors
D) increased
reliance on glycolytic enzymes
E) increased sensitivity to, and
ability to move toward, whatever glucose is present in its
habitat
D

) Which of these can be inferred from Figure 27.1?
A) Most of
the genetic change that permitted adaptation to the new,
low-glucose
environment occurred toward the conclusion of the
experiment.
B) Rates of mitosis increased over the course of the
experiment.
C) The highest rate of genetic change occurred during
the first quarter of the experiment.
D) After 5,000 generations,
the bacteria were 100% more fit than the original, ancestral
bacteria
C

) If the vertical axis of Figure 27.1 refers to ʺDarwinian fitness,ʺ
then which of these is the
most valid and accurate measure of
fitness?
A) number of daughter cells produced per mother cell per
generation
B) amount of ATP generated per cell per unit
time
C) average swimming speed of cells through the growth
medium
D) amount of glucose synthesized per unit time
E)
number of generations per unit time
E
If new genetic variation in the experimental populations arose solely
by spontaneous
mutations, then the most effective process for
subsequently increasing the prevalence of the
beneficial
mutations in the population over the course of generations is
A)
transduction.
B) binary fission.
C) conjugation.
D)
transformation.
E) meiosis
B
E. coli cells typically make most of their ATP by metabolizing
glucose. Under the conditions
of this experiment, what should be
true of E. coliʹs generation time (especially early in the
course
of the experiment, but less so later on)?
A) Generation time
should be the same as in the typical environment.
B) Generation
time should be faster than in the typical environment.
C)
Generation time should be slower than in the typical
environment.
D) It is theoretically impossible to make any
predictions about generation time, under
these conditions.
C
If the experimental population of E. coli lacks an F factor or F
plasmid, and if bacteriophage
are excluded from the bacterial
cultures, then which of these is a means by which
beneficial
mutations might be transmitted horizontally to other
E. coli cells?
A) via sex pili
B) via transduction
C)
via conjugation
D) via transformation
E) both A and C above
D
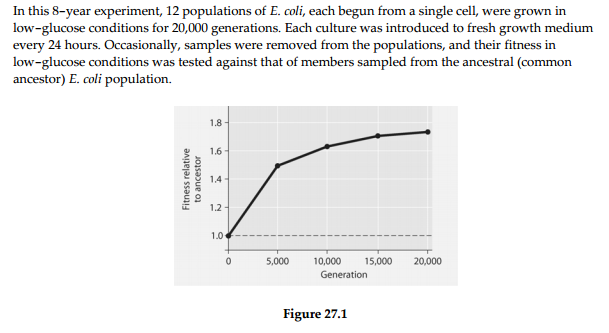
Among the six statements below, which two best account for the
results obtained by the
researchers (see Figure 27.1)?
1.
Low-glucose conditions caused mutations that made individual E. coli
cells better suited
to these conditions.
2. Daughter cells
acquired the ability to tolerate low-glucose conditions as they
received
the enzymes and membrane components that had been
modified by their mother cell.
3. The initial E. coli population
may have included some cells whose genes favored their
survival
in low-glucose conditions–OR–such genetic variants arose by chance
early in the
experiment.
4. The first few generations of E.
coli in low-glucose conditions responded to the challenge
by
increasing the use of certain enzymes and ion pumps, while decreasing
the use of others.
This behavior was recorded in their gene
sequences, which were later transmitted to
daughter
cells.
5. From generation to generation, there was an increase in
the proportion of the
experimental populations adapted to
low-glucose conditions, because such bacteria
produced relatively
more offspring than did ancestral bacteria under
low-glucose
conditions.
6. During each generation,
individual cells evolved to increase their survival
in
low-glucose conditions.
A
Which term is least closely associated with the others?
A) Hfr
cells making use of a sex pilus
B) rolling circle
replication
C) the ʺtoilet paperʺ model of replication
D)
conjugation involving an F factor
E) recombination involving a bacteriophage
E
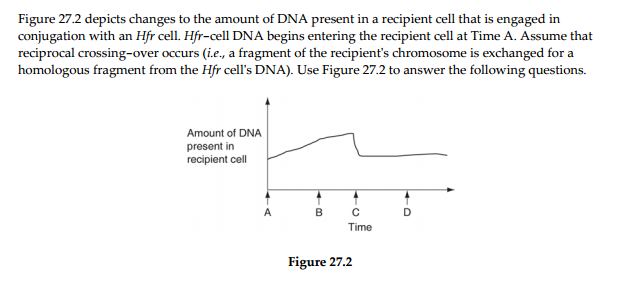
What is occurring at Time C that is decreasing the DNA
content?
A) crossing-over
B) cytokinesis
C)
meiosis
D) degradation of DNA that was not retained in the
recipientʹs chromosome
E) reversal of the direction of conjugation
D

How is the recipient cell different at Time D than it was at Time
A?
A) It has a greater number of genes.
B) It has a greater
mass of DNA.
C) It has a different sequence of base
pairs.
D) It contains bacteriophage DNA.
E) It has a greater
number of introns.
C

) Which two processes are responsible for the shape of the curve at
Time B?
1. transduction
2. entry of single-stranded Hfr
DNA
3. rolling circle replication of single-stranded Hfr
DNA
4. activation of DNA pumps in plasma membrane
5. ʺtoilet
paperʺ replication of recipient cellʹs plasmids
A) 1 and
4
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 5
D) 1 and 3
E) 4 and 5
B

During which two times can the recipient accurately be described as
ʺrecombinantʺ due to
the sequence of events portrayed in Figure
27.2?
A) during Times C and D
B) during Times A and
C
C) during Times B and C
D) during Times A and B
E)
during Times B and D
A

Which question, arising from the results depicted in Figure 27.2, is
most interesting from a
genetic perspective, and has the greatest
potential to increase our knowledge base?
A) If reciprocal
crossing-over could occur even if the piece of donated Hfr DNA
is
identical to the homologous portion of the recipientʹs
chromosome, what prevents this
from occurring?
B) Why do
geneticists refer to the same structure by at least three different
names: sex
pilus, mating bridge, and conjugation tube? Why all
the jargon?
C) What forces are generally responsible for
disrupting the mating bridge?
D) How is it that a recipient cell
does not necessarily become an Hfr cell as the result
of
conjugation with an Hfr cell?
E) What makes a cell an
ʺHfr cellʺ?
A

Among the six statements below, which two best account for the
results obtained by the
researchers (see Figure 27.1)?
3. The initial E. coli population may have included some cells
whose genes favored their
survival in low-glucose
conditions–OR–such genetic variants arose by chance early in the
experiment.
5. From generation to generation, there was an increase in the
proportion of the
experimental populations adapted to low-glucose
conditions, because such bacteria
produced relatively more
offspring than did ancestral bacteria under
low-glucose
conditions.
During each generation, individual
cells evolved to increase their survival in
low-glucose
conditions.
A) 3 and 5
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 4
D) 1
and 6
E) 1 and 3
A
) Photoautotrophs use
A) light as an energy source and CO2 as a
carbon source.
B) light as an energy source and methane as a
carbon source.
C) N2 as an energy source and CO2 as a carbon
source.
D) CO2 as both an energy source and a carbon
source.
E) H2S as an energy source and CO2 as a carbon source.
A
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Archaea and
bacteria have different membrane lipids.
B) Both archaea and
bacteria generally lack membrane-enclosed organelles.
C) The cell
walls of archaea lack peptidoglycan.
D) Only bacteria have
histones associated with DNA.
E) Only some archaea use CO2 to
oxidize H2, releasing methane.
D
Which of the following features of prokaryotic biology involves
metabolic cooperation
among cells?
A) binary fission
B)
endospore formation
C) endotoxin release
D) biofilms
E) photoautotrophy
D
Which prokaryotic group is mismatched with its members?
A)
Proteobacteriadiverse gram-negative bacteria
B) Gram-positive
bacteriasymbionts in legume root nodules
C) Spirocheteshelical
heterotrophs
D) Chlamydiasintracellular parasites
E)
Cyanobacteriasolitary and colonial photoautotrophs
B
Plant-like photosynthesis that releases O2 occurs in
A)
cyanobacteria.
B) chlamydias.
C) archaea.
D)
actinomycetes.
E) chemoautotrophic bacteria
A